Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry
Chemistry
Uploaded by
equilife.foundationOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry
Chemistry
Uploaded by
equilife.foundationCopyright:
Available Formats
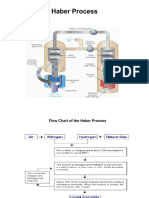
The Haber process, also known as the Haber-Bosch process, is a chemical process for
the industrial production of ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen and hydrogen. It is the most
important process for ammonia production today, and accounts for more than 99% of
world ammonia production.
The Haber process was developed in the early 1900s by Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch,
and was first used commercially in 1913. The process is reversible, and the production
of ammonia is exothermic, meaning that it releases energy. The reaction is favored at
lower temperatures and higher pressures. However, the reaction rate is very slow at low
temperatures, so a catalyst is used to accelerate the reaction.
The Haber process is typically carried out at a pressure of 150-200 atmospheres and a
temperature of 400-450 degrees Celsius. The catalyst used is typically a mixture of iron
and potassium oxide. The nitrogen and hydrogen gases are passed through a reactor
containing the catalyst, and the ammonia that is produced is condensed and removed.
The unreacted nitrogen and hydrogen are recycled back to the reactor.
The Haber process is a very energy-intensive process, and accounts for about 1% of
global energy consumption. However, it is an essential process for the production of
fertilizer, which is used to feed the world's population. Ammonia is also used in the
production of other chemicals, such as nitric acid and urea.
Here is a summary of the Haber process:
1. Nitrogen gas from the air and hydrogen gas from natural gas are compressed
and mixed together.
2. The gas mixture is passed through a reactor containing a catalyst, such as iron
and potassium oxide.
3. At high temperature and pressure, the nitrogen and hydrogen react to form
ammonia.
4. The ammonia is condensed and removed, and the unreacted nitrogen and
hydrogen are recycled back to the reactor.
The Haber process has revolutionized agriculture and has made it possible to feed the
world's growing population. It is an essential process for the production of fertilizer, and
is also used in the production of other important chemicals.
You might also like
- Stamicarbon Project PDFDocument30 pagesStamicarbon Project PDFMir Hasib Ul Latif100% (7)
- Simulation Ammonia Plant On PRO IIDocument58 pagesSimulation Ammonia Plant On PRO IIFabrizio Dugo100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- HaberDocument4 pagesHaberamber psycheNo ratings yet
- Haber-Bosch Process PaperDocument15 pagesHaber-Bosch Process Paperapi-529628802No ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument6 pagesHaber ProcessLuis Daniel Gil PachecoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2farah.syafiqah.asNo ratings yet
- Haber - Bosch ProcessDocument12 pagesHaber - Bosch Processapi-487208181No ratings yet
- Haber Bosch Process, Revision of The Revised Edition 2017, 2017Document20 pagesHaber Bosch Process, Revision of The Revised Edition 2017, 2017Mark Anthony HenryNo ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument10 pagesHaber ProcessTon5698No ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument33 pagesAmmoniaWilly ChandraNo ratings yet
- Assignment BNFDocument3 pagesAssignment BNFhassan aliNo ratings yet
- The Haber and Contact ProcessesDocument3 pagesThe Haber and Contact Processesjavison_501100% (1)
- Ammonia ConversionDocument24 pagesAmmonia ConversionKashan AslamNo ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 22Document7 pagesHSC Chemistry Lesson Plan 22Ali HaidarNo ratings yet
- 1صناعاتDocument15 pages1صناعاتroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- Ammonia Formation ProjectDocument14 pagesAmmonia Formation ProjectNebyu DanielNo ratings yet
- Haber's ProcessDocument12 pagesHaber's ProcessCripsy CrunchyNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry: The Haber Process & The Ostwald ProcessDocument16 pagesIndustrial Chemistry: The Haber Process & The Ostwald ProcessIbrahimDewaliNo ratings yet
- Haber-Bosch Ammonia ReactionDocument25 pagesHaber-Bosch Ammonia ReactionJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionsDocument49 pagesReversible ReactionsArhum KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Habers Bosch Process: Submitted byDocument10 pagesHabers Bosch Process: Submitted byHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Haber-Bosch ProcessDocument20 pagesThe Haber-Bosch ProcessEnesEmreTaşNo ratings yet
- Production of AmmoniaDocument2 pagesProduction of AmmoniaSDh KimseunghyunNo ratings yet
- Haber Process and AmmoniaDocument2 pagesHaber Process and AmmoniaAaron HongNo ratings yet
- Fritz HaberDocument5 pagesFritz HaberJake YANNo ratings yet
- Haber ProcessDocument3 pagesHaber ProcessIzzat AnuarNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia: Sunny ChawlaDocument6 pagesProduction of Ammonia: Sunny ChawlapsshnkrNo ratings yet
- AmmoniaDocument59 pagesAmmoniavcoolkrazy0% (3)
- Feasibilty For The ProjectDocument18 pagesFeasibilty For The ProjectRana UzairNo ratings yet
- Haber AmmoniaDocument22 pagesHaber AmmoniaKabilanNo ratings yet
- Draft Assignment ChemistryDocument1 pageDraft Assignment Chemistrynurirdinabk22No ratings yet
- Urea WordDocument2 pagesUrea WordpushprajNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentVishal RajNo ratings yet
- Production of Ammonia: Department of Chemical Engineering A Report OnDocument29 pagesProduction of Ammonia: Department of Chemical Engineering A Report OnDr.AhmedNo ratings yet
- CHE 431 Assignment - Group 1Document11 pagesCHE 431 Assignment - Group 1Abdulrahman OlamilekanNo ratings yet
- 2009 06 Brouwer UreaKnowHow - Com Thermodynamics of The Urea ProcessDocument15 pages2009 06 Brouwer UreaKnowHow - Com Thermodynamics of The Urea ProcessMohit BayerNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Its UsesDocument17 pagesAmmonia and Its UsesHussain HashmiNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Synthesis CatalystsDocument16 pagesAmmonia Synthesis CatalystsSaqib Ali0% (1)
- Ammonia: How Is Ammonia Manufactured?Document3 pagesAmmonia: How Is Ammonia Manufactured?Khondokar TarakkyNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper OutlineDocument2 pagesConcept Paper Outlinestardustmoonlight18No ratings yet
- Chemical Technology Production of Ammonia: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicDocument3 pagesChemical Technology Production of Ammonia: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Urea Production PDFDocument10 pagesAmmonia and Urea Production PDFئارام ناصح محمد حسێنNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Energy 1Document20 pagesHydrogen Energy 1Yash ChorariaNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Urea ProductionDocument10 pagesAmmonia and Urea Productionwaheed_bhattiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 10 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid and Nitric AcidDocument17 pagesTOPIC 10 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid and Nitric AcidKaynine KikoNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and Derivatives - Trans & Gas UsageDocument17 pagesAmmonia and Derivatives - Trans & Gas UsageragilpriyantoNo ratings yet
- TechDocument8 pagesTechNagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Ammonia ProductionDocument7 pagesAmmonia ProductionIkhtiander IkhtianderNo ratings yet
- The Process of Making Ammonium NitrateDocument11 pagesThe Process of Making Ammonium NitratelicrankyilNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen: Nitrogen Is The Most Abundant Element in Earth's AtmosphereDocument13 pagesNitrogen: Nitrogen Is The Most Abundant Element in Earth's AtmosphereAmit YadubanshiNo ratings yet
- Development and Recent Progress On Ammonia Synthesis Catalysts For Haber-Bosch ProcessDocument23 pagesDevelopment and Recent Progress On Ammonia Synthesis Catalysts For Haber-Bosch ProcessEzgi GeyikNo ratings yet
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidFrom EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNo ratings yet
- Elements of Chemistry, In a New Systematic Order, Containing all the Modern DiscoveriesFrom EverandElements of Chemistry, In a New Systematic Order, Containing all the Modern DiscoveriesNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Soap ManufactureFrom EverandThe Handbook of Soap ManufactureRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Economics - SssDocument1 pageEconomics - Sssequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- Economics - SssDocument1 pageEconomics - Sssequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- Year 10 and 11 - PhysicsDocument15 pagesYear 10 and 11 - Physicsequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- Year 10 and 11 - PhysicsDocument15 pagesYear 10 and 11 - Physicsequilife.foundationNo ratings yet
- Year 10 and 11 - PhysicsDocument15 pagesYear 10 and 11 - Physicsequilife.foundationNo ratings yet