Professional Documents
Culture Documents
262 - Embryology Physiology) Ectoderm
262 - Embryology Physiology) Ectoderm
Uploaded by
arya409090Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
262 - Embryology Physiology) Ectoderm
262 - Embryology Physiology) Ectoderm
Uploaded by
arya409090Copyright:
Available Formats
Last edited: 8/8/2021
ECTODERM
Ectoderm Medical Editor: Jan Camille M. Santico
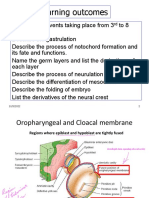
OUTLINE II) NEURULATION
I) GASTRULATION ● The cells from the primitive node continue to migrate
II) NEURULATION cranially, forming a tube/cord underneath the ectoderm
and in between the mesoderm. This tube is the
III) ECTODERMAL DERIVATIVES notochord.
IV) APPENDIX ● The notochord secretes growth factors and proteins
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS which induces the overlying ectoderm cells to proliferate
and thicken, forming the neural plate
VI) REFERENCES ● The neural plate proliferates and invaginates along its
central axis, forming the neural groove and neural folds
● The neural folds move closer and fuse, forming the
I) GASTRULATION neural tube
o The lateral parts of the neural fold differentiate into
● The inner cell mass of a blastocyst differentiates into a neural crest cells
bilaminar disc, which is made up of: o The neural crest cells detach once the folds fuse
o Epiblast
o Hypoblast ● See Figure 4. Neurulation [Moore et al, 2016]
● Gastrulation is the process wherein the three germ III) ECTODERMAL DERIVATIVES
layers and the axial orientation are established in the
embryo [Moore et al, 2016] (A) NEURAL TUBE DERIVATIVES
o The bilaminar disc is converted into a trilaminar disc ● Anterior neuropore
● Prechordal plate o Cranial end of the neural tube
o thickened portion of the endodermal layer located o Closes around day 24/25 (with sufficient folate
towards the cranial end of the embryo supplementation)
● Primitive Streak ● Posterior neuropore
o A thickened linear band of epiblast located caudally in o Caudal end of the neural tube
the median plane of the dorsal aspect of the o Closes around day 26-28
embryonic disc [Moore et al, 2016] ● Failure of these neuropores to close will result in spina
o See Figure 3. Gastrulation [Moore et al, 2016] bifida, anencephaly, myelomeningocele, etc
● Primitive node ● The neural tube undergoes vesiculation to form the
o An enlarged group of cells located in the anterior central nervous system
portion of the primitive streak o Neurons
● At the primitive node, some epiblast cells invaginate and o Glial cells (astrocytes, oligodendrocytes)
migrate downwards and towards the cranial end, forming o Posterior pituitary
a third layer in between the epiblast and hypoblast. o Pineal gland
● The migrating epiblast cells in between the epiblast and o Retina
hypoblast form the mesoderm (B) NEURAL CREST CELL DERIVATIVES
● The migrating epiblast cells invade the hypoblast layer
below, converting it into endoderm ● Mnemonic: CREST CELL
● The epiblast layer on top differentiates into ectoderm o Chromaffin cells (adrenal medulla)
o Rostral tissues (connective tissue, bones, and
muscles of the head and neck)
o Enteric nervous system
o Satellite cells and Schwann cells (glial cells of PNS)
o The PNS (spinal nerves, ganglia)
o Carotid bodies (measure concentrations of oxygen
and CO2)
o Endocardial cushions (forming the septum and valves
of the heart)
o Light skin/dark skin – melanocytes
o Leptomeninges of the brain (pia mater, arachnoid
mater)
Figure 1. Gastrulation
ECTODERM EMBRYOLOGY: Note #1. 1 of 4
(C) PLACODES (D) SURFACE ECTODERM
● All the remaining parts of the embryonic surface not
covered by the placode and the neural plate are
considered surface ectoderm
● Surface ectoderm differentiates into epithelial tissue
o Epidermis
o Nails
o Hair
o Sweat glands
o Lining of nasal cavity (except roof, comes rom
olfactory placode)
o Lining of oral cavity
o External ear canal
o Lining of inferior anus (below pectinate line)
Figure 2. Placodes ● Rathke’s pouch
o Invagination/budding of epithelial tissue along the
● Ectodermal placodes are thickened areas of the cranial nasal pharynx
ectoderm which differentiate into various structures o Differentiates into the anterior pituitary gland
o Fuses with the posterior pituitary gland precursor
(1) Olfactory placode (from the hypothalamus) to form the pituitary gland
● Differentiates into olfactory epithelium
o Tissue at the roof of the nasal cavity Remember
o Includes the receptor cells and supporting cells Mnemonic for Ectodermal Derivatives: ECTODERM
o Function: smell Epithelial tissue (inside and outside the body)
Central nervous system
(2) Lens placode The lens placode
Otic and Olfactory placode
● Differentiates into the lens Dang neural crest cells
o Function: far/near vision; allows the eye to focus on Eyes (retina)
objects at varying distances Rathke’s pouch anterior pituitary gland
o Ciliary muscles control the lens, turning it globular or Melatonin (from pineal gland)
flat to adjust the focusing power
(3) Otic placode
● Differentiates into the inner ear, which is made up of:
o Cochlea – hearing, sound waves
o Vestibule – static equilibrium
o Semicircular canals – dynamic equilibrium
(4) Precursors of Cranial Nerve Ganglia
● Nodose placode nodose ganglia
● Trigeminal placode trigeminal ganglia
● Geniculate placode geniculate ganglia
2 of 4 EMBRYOLOGY: Note #1. ECTODERM
IV) APPENDIX
Figure 3. Gastrulation [Moore et al, 2016]
Figure 4. Neurulation [Moore et al, 2016]
ECTODERM EMBRYOLOGY: Note #1. 3 of 4
V) REVIEW QUESTIONS
What is the thickened linear band of epiblast cells
which is vital to gastrulation?
a. Prechordal plate
b. Primitive node
c. Primitive groove
d. Primitive streak
Which structure induces the formation of the neural
plate?
a. Primitive streak
b. Prechordal plate
c. Notochord
d. Rathke’s pouch
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the
neural tube?
a. Retina
b. Posterior pituitary gland
c. Lens
d. Pineal gland
Which of the following is NOT a neural crest cell
derivative?
a. Chromaffin cells
b. Nodose ganglion
c. Spinal nerves
d. Melanocytes
Which of the following is NOT a derivative of the
surface ectoderm?
a. Hair
b. Sweat glands
c. Lining of the oral cavity
d. Lining of the duodenum
CHECK YOUR ANSWERS
VI) REFERENCES
● Moore, K.; Persaud, T.V.N. & Torchia, M. (2016). The
Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology. 10th Ed.
Elsevier
4 of 4 EMBRYOLOGY: Note #1. ECTODERM
You might also like
- Biological Science NotesDocument35 pagesBiological Science NotesPianomanSuperman100% (2)
- Veterinary Embryology (Class Notes) PDFDocument77 pagesVeterinary Embryology (Class Notes) PDFluis feo0% (3)
- Embryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainDocument100 pagesEmbryology Made Ridiculously Simple Presentation (1) Updated (1) AgainAya Sobhi100% (4)
- Neurulation, Vesiculation, Neural Crest Cell Migration (2) AtfDocument5 pagesNeurulation, Vesiculation, Neural Crest Cell Migration (2) Atfaizaeyeet22No ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument38 pagesImportant Questionsas3941asNo ratings yet
- 04 - Develpment Week 3Document12 pages04 - Develpment Week 3hiba jasimNo ratings yet
- Development of CNSDocument84 pagesDevelopment of CNSSamuel frankNo ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous System: Matt Velkey 454A Davison, Green Zone, Duke SouthDocument45 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous System: Matt Velkey 454A Davison, Green Zone, Duke SouthAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- Neuro Embryology Useful NotesDocument8 pagesNeuro Embryology Useful NotesredderdatNo ratings yet
- 3rd WeekDocument55 pages3rd WeekMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Embryo If Embryonic Period PDFDocument12 pagesEmbryo If Embryonic Period PDFRyna Miguel MasaNo ratings yet
- Development of CNS and Spinal CordDocument41 pagesDevelopment of CNS and Spinal CordAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- The Differentiation of Nervous System-2018Document36 pagesThe Differentiation of Nervous System-2018NadhillaHauraWahyudianaNo ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous System and Special Senses: NeurulationDocument56 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous System and Special Senses: NeurulationTeodora GeorgescuNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 TransesDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 8 TransesJaysa Faye PeconadaNo ratings yet
- ANAT3411Document51 pagesANAT3411Kai Dong ChoongNo ratings yet
- BMS301, L33, Histology, Cerebral CortexDocument24 pagesBMS301, L33, Histology, Cerebral Cortexkareemosama9916No ratings yet
- Trans 5 - Frog OrganogenesisDocument32 pagesTrans 5 - Frog Organogenesisangelica sherinnNo ratings yet
- A&P - 1a. Development & Organisation of The Nervous System (10p)Document10 pagesA&P - 1a. Development & Organisation of The Nervous System (10p)Gabriel StratulatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: NeuroembryologyDocument13 pagesLecture 1: NeuroembryologyRaul Docto100% (1)
- 3rd WeekDocument54 pages3rd WeekJeniNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue Part 1Document25 pagesNervous Tissue Part 1nhcsmlmolNo ratings yet
- Development of The Eye: Michael PownerDocument45 pagesDevelopment of The Eye: Michael PownerAishah SiddiqahNo ratings yet
- Embryo IDocument28 pagesEmbryo IggNo ratings yet
- General Principle & Eye Development EZRADocument28 pagesGeneral Principle & Eye Development EZRAezradamanikNo ratings yet
- Ns1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDocument4 pagesNs1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyMark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- CNS DevelopmentDocument158 pagesCNS DevelopmentMubashir SiyalNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week of Development 2022Document36 pages3rd Week of Development 2022aameena nadaNo ratings yet
- 06 NeurulationDocument5 pages06 NeurulationcarlgangcaNo ratings yet
- NERVOUSDocument37 pagesNERVOUScolombres.andreiNo ratings yet
- 01 - Embryology and Introduction To The Nervous System - AMDDocument10 pages01 - Embryology and Introduction To The Nervous System - AMDLiza Elaine Ulep CawasNo ratings yet
- Gas Tru LationDocument53 pagesGas Tru LationSam MumoNo ratings yet
- 3.development of Brain StemDocument41 pages3.development of Brain Stemhamza_shoaib99No ratings yet
- PNS 4 Optic NerveDocument48 pagesPNS 4 Optic NerveRaghad AbbadyNo ratings yet
- 2-Histology of Nerve Tissue The Nervous System Part 2Document29 pages2-Histology of Nerve Tissue The Nervous System Part 2Ahmad MsalmahNo ratings yet
- Tufts ABO 2013 Study Guide PDFDocument150 pagesTufts ABO 2013 Study Guide PDFPopoNo ratings yet
- Slides - 02-04 - Ectoderm Derivatives and NeurulationDocument14 pagesSlides - 02-04 - Ectoderm Derivatives and NeurulationSebastian RuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Overview 1Document44 pagesLecture 10 Overview 1mariam tarek100% (1)
- CNS Histology 1Document60 pagesCNS Histology 1naderipourkianaNo ratings yet
- Lab 20 - Nervous System Histology Pre-LabDocument6 pagesLab 20 - Nervous System Histology Pre-LabshouldbsleepnNo ratings yet
- Development of The NSDocument7 pagesDevelopment of The NSJean Pierre Chastre LuzaNo ratings yet
- Embryology: Embryo - Fertilization To 8th WeekDocument5 pagesEmbryology: Embryo - Fertilization To 8th WeekCygrusNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument9 pagesNeurulationaesha890% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument296 pagesNervous SystemDr. Serin KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Acrisologobsbio2 ADocument3 pagesAcrisologobsbio2 ACrisologo AllenNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDocument48 pagesChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Development of The Brain 2014 Clinical NeuroscienceDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Development of The Brain 2014 Clinical NeuroscienceMarta Casals CollNo ratings yet
- Cns EmbryoDocument90 pagesCns EmbryoMonesa Christy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument7 pagesNeurulationFranTeodosioNo ratings yet
- 3RD To 8TH Week (I)Document31 pages3RD To 8TH Week (I)RaoulSusanto SusantoNo ratings yet
- Isolated Ocular Motor Nerve PalsiesDocument9 pagesIsolated Ocular Motor Nerve PalsiesGian Carlo Giusto BurboaNo ratings yet
- BMS301, L45, Histology, MedullaDocument34 pagesBMS301, L45, Histology, Medullakareemosama9916No ratings yet
- Gastrulation Somites and Folding TSRDocument27 pagesGastrulation Somites and Folding TSRAsia SattiNo ratings yet
- Transient Structures, Subsequently Developing Into The Diverse Components of The Face and NeckDocument15 pagesTransient Structures, Subsequently Developing Into The Diverse Components of The Face and NecknohacksNo ratings yet
- Development of Muscular System AtfDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Muscular System AtfKim Sa-buNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument40 pagesMedulla Oblongata Anatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd Gradetuhin100% (1)
- L2 - Basic Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument24 pagesL2 - Basic Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeConger CongerNo ratings yet
- (OS 202A) Neuroembryology.2Document4 pages(OS 202A) Neuroembryology.2mark_mondiaNo ratings yet
- MBBS I Assignment Sanjay SirDocument2 pagesMBBS I Assignment Sanjay SirAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- PDF - Curs 9-10 An 1 Sem 1 ENGDocument33 pagesPDF - Curs 9-10 An 1 Sem 1 ENGachraf rabadiNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 Flatworms NoblanksDocument27 pagesLecture6 Flatworms NoblanksRen StudyNo ratings yet
- ANAT0001 Formation of The Body PlanDocument7 pagesANAT0001 Formation of The Body PlanOmed ZarifiNo ratings yet
- Basic Embryology Series PDFDocument252 pagesBasic Embryology Series PDFGrace Nduta0% (1)
- Avagliano2018 DefectosTuboNeuralDocument13 pagesAvagliano2018 DefectosTuboNeuraliloveshopee9No ratings yet
- Development of Embryo ChickDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Embryo ChickSafira Dwi OktavianiNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument6 pagesNeurulationnumannazir3276No ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument45 pagesHuman BrainNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Textbook of Clinical Neuroanatomy 3Rd Edition Vishram Singh Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pages(Download PDF) Textbook of Clinical Neuroanatomy 3Rd Edition Vishram Singh Full Chapter PDFengleslamoth100% (7)
- Embryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MADocument34 pagesEmbryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MAIbrahim Foondun100% (1)
- HAMILDocument82 pagesHAMILNandya CarolineNo ratings yet
- Embryology ObgDocument36 pagesEmbryology ObgsamrusangaliNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology of Frog: SpermDocument21 pagesDevelopmental Biology of Frog: SpermRavindra MadurNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15 Serial Transverse Section of A 24 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument5 pagesExercise 15 Serial Transverse Section of A 24 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- Claire Bolalin - Quiz (Neurulation)Document1 pageClaire Bolalin - Quiz (Neurulation)Claire BolalinNo ratings yet
- Trans 5 - Frog OrganogenesisDocument32 pagesTrans 5 - Frog Organogenesisangelica sherinnNo ratings yet
- NeuroembryologyDocument7 pagesNeuroembryologykidNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Nervous Sytem PresentationDocument157 pagesGroup 6 - Nervous Sytem PresentationNgirlNo ratings yet
- Bio 109 Module 4Document18 pagesBio 109 Module 4Marites Maylanon0% (1)
- Basic Embryology Series-1-1Document229 pagesBasic Embryology Series-1-1davidbenedict870No ratings yet
- Study QuestionDocument24 pagesStudy QuestionEbookslatinosEbookslatinosNo ratings yet
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDocument3 pages24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Stiles-Jernigan - The Basics of Brain DevelopmentDocument22 pagesStiles-Jernigan - The Basics of Brain DevelopmentBrunela SperanzaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology of Frog: SpermDocument21 pagesDevelopmental Biology of Frog: SpermRavindra MadurNo ratings yet
- Labexercises3 4Document11 pagesLabexercises3 4Sittie Rainnie BaudNo ratings yet
- Neurulation, OrganogenesisDocument2 pagesNeurulation, OrganogenesisClaire BolalinNo ratings yet
- General Embryology PDFDocument9 pagesGeneral Embryology PDFmedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Embryology 1&2Document39 pagesAnatomy Embryology 1&2Nadeen ShahwanNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology QuestionsDocument10 pagesDevelopmental Biology QuestionsSurajit Bhattacharjee100% (1)
- Neurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes TheDocument6 pagesNeurulation Refers To The Folding Process in Vertebrate Embryos, Which Includes Theaaliya saaheenNo ratings yet