Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PRELIM LECTURE IT 215 MODULE 3 and 4
PRELIM LECTURE IT 215 MODULE 3 and 4
Uploaded by
krisneltancingco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesWe define a population as all measurements of interest, while a sample is a subset of a population. Since we cannot survey the entire population, we use sampling to make inferences about populations. There are probabilistic sampling techniques where every member has an equal chance of selection, like random sampling, and non-probabilistic techniques where the chance of selection is not equal, such as convenience sampling. This section also discusses measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode, which are averages used to find the most representative score in a sample or data set.
Original Description:
Original Title
PRELIM-LECTURE-IT-215-MODULE-3-and-4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWe define a population as all measurements of interest, while a sample is a subset of a population. Since we cannot survey the entire population, we use sampling to make inferences about populations. There are probabilistic sampling techniques where every member has an equal chance of selection, like random sampling, and non-probabilistic techniques where the chance of selection is not equal, such as convenience sampling. This section also discusses measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode, which are averages used to find the most representative score in a sample or data set.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views15 pagesPRELIM LECTURE IT 215 MODULE 3 and 4
PRELIM LECTURE IT 215 MODULE 3 and 4
Uploaded by
krisneltancingcoWe define a population as all measurements of interest, while a sample is a subset of a population. Since we cannot survey the entire population, we use sampling to make inferences about populations. There are probabilistic sampling techniques where every member has an equal chance of selection, like random sampling, and non-probabilistic techniques where the chance of selection is not equal, such as convenience sampling. This section also discusses measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode, which are averages used to find the most representative score in a sample or data set.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 15
We define a population as the collection
of all responses, measurements, or counts
that are of interest while sample is a just
a subset of a population. Since we cannot
get the whole population to respond, we
are using samples to get a statement
about a population.
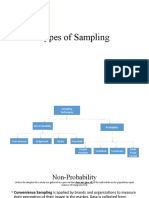
Probabilistic Sampling
Techniques
• Any method of selecting a
sample that utilizes a random
sample.
•Each member of the population
has an equal chance of being
selected.
•USES: allows researchers to use
statistical methods to analyze
sample results.
•Example: Draw lots, Raffle draw.
Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling
• The sample size of each stratum in this technique is proportionate to the
population size of the stratum when viewed against the entire
population.
• USES: when the researcher wants to highlight a specific subgroup in
the population.
ICS
Population 400 Students
BSAIT BSAIS
Stratum 200 200
Sample 100 100
➢ Cluster Sampling
• Researchers select groups or
clusters, and then from each cluster,
the researcher selects the individual
subjects by either simple random or
systematic random sampling.
• Example: Strategy in Census
Nonprobability Sampling
Techniques
•A sampling technique
in which the members
of the population are
not given an equal
chance in the selection
of the sample.
Purposive Sampling
Choosing a sample based on the
previous knowledge of the population
and the specific purpose of the study
or investigation.
Example: Your research is about the
Life and Experiences of people living
in Poverty. To whom do you think you
can get the data? You can get data
from the people who are experiencing
poverty.
Convenience Sampling
• It is the process of selecting a sample based
on the convenience of the investigator.
• The sample is selected based on its availability.
• Example: Your research is all about senior
high school students and you are currently
teaching in SHS so who are your respondents
for the research? Why did you choose it? I
will choose my students because it’s already
available.
Measure of
Central
Tendency
This section discusses three
central tendency statistics: the mean,
the median, and the mode. The three
are different kinds of ‘averages’ used
in different situations. Their general
purpose is the same, namely, to find
the single most representative score
in the sample. Measure of central
tendency can be used for ungrouped
and grouped data.
You might also like
- Kareeen ResearchDocument92 pagesKareeen ResearchLeu Gim Habana Panugan0% (1)
- Survey Results On Question, Do You Plan To Take A Vacation Abroad?Document2 pagesSurvey Results On Question, Do You Plan To Take A Vacation Abroad?Kharen Padlan100% (2)
- Sampling Methods LectureDocument2 pagesSampling Methods LectureBaste BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Sampling 2023Document63 pagesSampling 2023Titanium TssNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 SamplingDocument25 pagesChapter 7 Samplingdjyo2002.doNo ratings yet
- Ba1 7Document37 pagesBa1 7shrayan189No ratings yet
- Lecture 05Document29 pagesLecture 05Yashodara WijekoonNo ratings yet
- Topic 7Document46 pagesTopic 7honathapyarNo ratings yet
- Sampling PowerpointDocument21 pagesSampling PowerpointMuhammad Furqan Aslam AwanNo ratings yet
- Sampling: ResearchDocument87 pagesSampling: ResearchSMK MaruvsNo ratings yet
- Applied Social Science Research MethodsDocument18 pagesApplied Social Science Research MethodsAggreyDuduNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Selecting Certain Number of Study Units From A Defined PopulationDocument19 pagesSampling: Selecting Certain Number of Study Units From A Defined PopulationbkdfiesefllNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument22 pagesSamplingkumarianuradha125.akNo ratings yet
- Selecting SampleDocument22 pagesSelecting SampleYohanes M Restu Dian RNo ratings yet
- RM Unit 2Document52 pagesRM Unit 2mayankjain08248No ratings yet
- Sampling PPTDocument46 pagesSampling PPTvijendrameena044No ratings yet
- By Okite MosesDocument33 pagesBy Okite MosesBanolka NobNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques & Samples TypesDocument55 pagesSampling Techniques & Samples TypesRajan SahNo ratings yet
- PR-2Document13 pagesPR-2Macarasig IcoNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument64 pagesSampling and Sampling DistributionNIKHIL PATTNAIK100% (1)
- Research Methodology: Chapter 11-SamplingDocument28 pagesResearch Methodology: Chapter 11-SamplingSerah JavaidNo ratings yet
- 2006 - Philosophy, Methodology and Action ResearchDocument43 pages2006 - Philosophy, Methodology and Action ResearchnurleennaNo ratings yet
- Sampling: Dr. Ghazala KausarDocument32 pagesSampling: Dr. Ghazala KausarMohammad HarisNo ratings yet
- 3 Unit: SamplingDocument25 pages3 Unit: SamplingVirupaksha GoudNo ratings yet
- SAMPLINGDocument19 pagesSAMPLINGseenubarman12No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Statistical Methods and Sampling TechniquesDocument2 pagesLecture 2 - Statistical Methods and Sampling TechniquesRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Sampling & Sampling DistributionsDocument34 pagesSampling & Sampling DistributionsBhagwat BalotNo ratings yet
- PSYC 334 Session 9 SlidesDocument56 pagesPSYC 334 Session 9 SlidesFELIX ADDONo ratings yet
- Chapter8 Sampling IoxODocument24 pagesChapter8 Sampling IoxOantonio montemayorNo ratings yet
- Sample and Sampling TechniqueDocument39 pagesSample and Sampling TechniqueJayshree VasavaNo ratings yet
- Research Population, Sample Size & Sampling Methods - Quantitative ResearchDocument22 pagesResearch Population, Sample Size & Sampling Methods - Quantitative ResearchJanelle DuranNo ratings yet
- Probability SamplingDocument22 pagesProbability Samplingbasaallen566No ratings yet
- Research Methods & MaterialsDocument78 pagesResearch Methods & MaterialsSintayehuNo ratings yet
- Research Design, Sampling and Data Collection ToolsDocument40 pagesResearch Design, Sampling and Data Collection ToolsMoud KhalfaniNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Sample Size Determination - UnlockedDocument47 pagesSampling and Sample Size Determination - Unlockeddhanusat20001828No ratings yet
- Unit 7.2 LectureDocument14 pagesUnit 7.2 LectureSAIRA QAMARNo ratings yet
- 2.sampling & TypesDocument20 pages2.sampling & Typesdangerous saifNo ratings yet
- Identifying The Different Random Sampling Techniques AutosavedDocument18 pagesIdentifying The Different Random Sampling Techniques AutosavedTatsuya KirigayaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Scales and Selecting Sampling 21102022 095103amDocument21 pagesMeasurement and Scales and Selecting Sampling 21102022 095103amMuhammad ZubairNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 Sampling DesignDocument18 pagesLecture8 Sampling DesignagharizwanaliNo ratings yet
- Sampling DesignDocument57 pagesSampling DesignGetachew DemissieNo ratings yet
- Sampling 8.3.16Document40 pagesSampling 8.3.16Arham SheikhNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Research StatisticsDocument10 pagesConcepts in Research StatisticsKristina PabloNo ratings yet
- Types of SamplingDocument13 pagesTypes of SamplingCAELUM ONLINENo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument59 pagesSamplingpooja100% (1)
- Notes - Sampling Design - Mac 2023Document41 pagesNotes - Sampling Design - Mac 2023wan nur adnin wan ghazaliNo ratings yet
- 6) BIOSTATISTICsDocument99 pages6) BIOSTATISTICsMadhulikaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Sampling: Unit-IiiDocument41 pagesTheory of Sampling: Unit-IiiRachna MGMTNo ratings yet
- Sampling 2Document9 pagesSampling 2halayehiahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Sampling Techniques LectureDocument30 pagesLecture 9 Sampling Techniques Lectureephraimsmart11No ratings yet
- Sampling (Method)Document31 pagesSampling (Method)kia.reshuNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Sampling TechniquesDocument31 pagesTopic 4 - Sampling TechniquesELDA MAUNDINo ratings yet
- Umehabiba - 2340 - 4448 - 3 - Lec 1,2Document41 pagesUmehabiba - 2340 - 4448 - 3 - Lec 1,2alinagarbn.no2No ratings yet
- SamplingDocument16 pagesSamplingkurfunkle kurtzNo ratings yet
- BIOMETRYDocument37 pagesBIOMETRYAddisu GedamuNo ratings yet
- NCM 111a Notes - 2Document3 pagesNCM 111a Notes - 2Kimberly BucoyNo ratings yet
- Course 5 - Research Design - Sampling DesignDocument46 pagesCourse 5 - Research Design - Sampling Designteuku ismaldyNo ratings yet
- Population - RESEARCHDocument21 pagesPopulation - RESEARCHvrvasukiNo ratings yet
- LR 2 SamplingDocument27 pagesLR 2 Samplinggiovannie alvarezNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document37 pagesPresentation 1Afia TawiahNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Decentralization and Service DeliveryDocument11 pagesChallenges in Decentralization and Service Deliverynfavor47No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Comm 215 ConcordiaDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Comm 215 Concordiahenry gNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research ProposalDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Research ProposalRiajul IslamNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document11 pagesHomework 1Dridi FyrasNo ratings yet
- Ashwin ProjectDocument35 pagesAshwin ProjectShraddha WagheNo ratings yet
- Com390 - The Effects of Instagram Use On Relationship Satisfaction 1Document15 pagesCom390 - The Effects of Instagram Use On Relationship Satisfaction 1api-377601353No ratings yet
- Group 1 Research No. 1 I. Title: Learning Syles of Sophomore Students of PupDocument4 pagesGroup 1 Research No. 1 I. Title: Learning Syles of Sophomore Students of PupAe RaNo ratings yet
- Wacholder IIIDocument9 pagesWacholder IIIHANS BENNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception Towards HDFC BankDocument55 pagesConsumer Perception Towards HDFC BankMohammad KhadeerNo ratings yet
- Research Methods - SamplingDocument34 pagesResearch Methods - SamplingMohsin Raza100% (1)
- Frequency Distribution SamplesDocument11 pagesFrequency Distribution SamplesEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Surveys: Summer 2021Document39 pagesDesign and Analysis of Surveys: Summer 2021larrry666No ratings yet
- Isaac Banda-MPH 2012 DissertationDocument60 pagesIsaac Banda-MPH 2012 DissertationmalikmanNo ratings yet
- MB0050 - Research Methodology (Book ID: B1206) Assignment - Set-1Document12 pagesMB0050 - Research Methodology (Book ID: B1206) Assignment - Set-1fcanitinjainNo ratings yet
- Tata SkyDocument99 pagesTata SkyRehman Sadiq67% (3)
- Nutrition Survey Guidelines For Somalia - Revised March 2006Document62 pagesNutrition Survey Guidelines For Somalia - Revised March 2006mustikaarumNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study On Establishing A Food Kiosk in Sacred Heart School. Group 2 3Document44 pagesA Feasibility Study On Establishing A Food Kiosk in Sacred Heart School. Group 2 3Gabz luiz TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Pune Uni M.B.A. (2016 Pattern)Document118 pagesPune Uni M.B.A. (2016 Pattern)yogeshNo ratings yet
- CDF - Project ProposalDocument14 pagesCDF - Project ProposalTatenda KaneNo ratings yet
- Ii Bba Production and Materials Management - 416BDocument21 pagesIi Bba Production and Materials Management - 416BponnasaikumarNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards Tata Nano Car With Special Reference To Coimbatore City August 2013 1598968308 05Document2 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards Tata Nano Car With Special Reference To Coimbatore City August 2013 1598968308 05Tussharr SinghNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Preferences For Mtr-RteDocument18 pagesA Study On Consumer Preferences For Mtr-RteMonalisa Barik0% (1)
- Practical Research 1 Fire SurvivorsDocument81 pagesPractical Research 1 Fire SurvivorsYammNo ratings yet
- Medical Lab L3-L4Document147 pagesMedical Lab L3-L4Morgan HeritageNo ratings yet
- Association of Screen Time With Academic Performance and Behaviour Among Primary School Children of Kandy District Sri LankaDocument6 pagesAssociation of Screen Time With Academic Performance and Behaviour Among Primary School Children of Kandy District Sri LankaAira RamosaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument27 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyAlvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- Ffects of Pornography Addiction On Grade 11 StudentsDocument60 pagesFfects of Pornography Addiction On Grade 11 StudentsRia TabuacNo ratings yet
- Project On Distribution Channel of PepsiDocument60 pagesProject On Distribution Channel of Pepsiruchikunal69% (13)