Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math Gr10 Q2-Module-1 (32pages)
Math Gr10 Q2-Module-1 (32pages)
Uploaded by
Hazel LuzwellCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Question 1 (1 Point)Document44 pagesQuestion 1 (1 Point)milanchabhadiya288No ratings yet
- Analysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsJuan Carlos Álvarez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1 Math 10 Graphs of Polynomial Functions FinalDocument29 pagesModule 2 1 Math 10 Graphs of Polynomial Functions FinalJacob Sanchez100% (1)
- Math10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionDocument32 pagesMath10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionChaz grant borromeo89% (9)
- US Army Identification of Ammunition CourseDocument90 pagesUS Army Identification of Ammunition Courselygore100% (2)
- Contractor Safety Stand Down 2016Document25 pagesContractor Safety Stand Down 2016ekoimampNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Module-1 - Illustrating-Polynomial-FunctionDocument16 pagesQuarter 2-Module-1 - Illustrating-Polynomial-FunctionDianne Dynah Bilaro DyNo ratings yet
- G10 Math Q2 Module-1Document24 pagesG10 Math Q2 Module-1L. RikaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 q2 Week 1 Module 1 Polynomial Functions For Reproduction 1Document32 pagesMath 10 q2 Week 1 Module 1 Polynomial Functions For Reproduction 1Jowinmay NudaloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Guided Learning Activity KitDocument40 pagesMathematics: Guided Learning Activity KitAnony MousNo ratings yet
- Activities 1 4Document7 pagesActivities 1 4Marlyn GuiangNo ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 10 - Module 1Document16 pagesQ2 Mathematics 10 - Module 1Mari100% (1)
- Q2 - Mathematics 10 - Mod17 - Graphs and Polynomials Dunctions - v2Document28 pagesQ2 - Mathematics 10 - Mod17 - Graphs and Polynomials Dunctions - v2Ruby Rose B. Panganod-Araba100% (1)
- Degree Leading Coefficient and Constant Term of A Polynomial FunctionDocument5 pagesDegree Leading Coefficient and Constant Term of A Polynomial Functionsusan aralarNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q2 Module 1Document14 pagesMath10 Q2 Module 1Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsDocument25 pagesMathematics: Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- DIRECTION: Write All Answers and Required Solutions in The Test Booklet. Determine Whether Each Statement Is TRUE or FALSE. (1 Point Each)Document3 pagesDIRECTION: Write All Answers and Required Solutions in The Test Booklet. Determine Whether Each Statement Is TRUE or FALSE. (1 Point Each)MariaRebeccaObafialFloresNo ratings yet
- Q2 1st Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ2 1st Summative TestIsrael BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based EducationDocument25 pagesMathematics: Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based EducationRachel Yam 3nidadNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module - Q2, WK 1 - 2Document4 pagesMath 10 Module - Q2, WK 1 - 2Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q2 Module 1Document16 pagesMath10 Q2 Module 1Ella OrizaNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q2 Module 1Document16 pagesMath10 Q2 Module 1Joan Layos MoncaweNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Polynomial FunctionsDocument21 pagesWeek 1 Polynomial FunctionspotatersNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Solving Logarithmic Equations and InequalitiesDocument28 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Solving Logarithmic Equations and InequalitiesBenjamin JamesNo ratings yet
- TG Grade-10Document137 pagesTG Grade-10irene.buysonNo ratings yet
- General Math Quarter 1 Week 3: CompetenciesDocument10 pagesGeneral Math Quarter 1 Week 3: CompetenciesVic KinnzNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 4: Algebraic ExpressionsDocument23 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 4: Algebraic ExpressionsMa.Cristine Joy Inocentes50% (2)
- Q2 1st Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ2 1st Summative TestIsrael BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Real-Life of Exponential Functions and Their Transformations Are, Population GrowthDocument3 pagesReal-Life of Exponential Functions and Their Transformations Are, Population GrowthSecret LungsNo ratings yet
- Math 114 Activity 1Document4 pagesMath 114 Activity 1DanielNo ratings yet
- Math 2ND Quarter Module 1Document20 pagesMath 2ND Quarter Module 1Fatima UliNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDocument22 pagesQuarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDianne Dynah Bilaro DyNo ratings yet
- Math11 BC Q3 M5 PDFDocument12 pagesMath11 BC Q3 M5 PDFsevynNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Document54 pages2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Urduja Kyle OdiacerNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 18: Solving Exponential Equations and InequalitiesDocument19 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 18: Solving Exponential Equations and InequalitiesDaphneeNo ratings yet
- Mtap G10S2 Polynomial FunctionsDocument2 pagesMtap G10S2 Polynomial FunctionsLedesma, Elijah O.No ratings yet
- General-Mathematics Q1 W8Document13 pagesGeneral-Mathematics Q1 W8jenayadaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math-2 PDFDocument32 pagesGen Math-2 PDFshamera binayonNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Summative Test 1Document15 pagesGen Math Summative Test 1encarNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Learning Materials For Senior High School: Tagum City College of Science and Technology Foundation IncDocument17 pagesSupplementary Learning Materials For Senior High School: Tagum City College of Science and Technology Foundation Incjaylyn carasNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Summative Test 2Document32 pagesGen Math Summative Test 2encarNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Quarter2 Week1to2 Melc01to03 Module1 Macadangdang Magdalena Et AlDocument45 pagesMath 10 Quarter2 Week1to2 Melc01to03 Module1 Macadangdang Magdalena Et AlDheztinee GabrielNo ratings yet
- Math 10 q1 WK 6 Module 6 Division of PolynomialsDocument30 pagesMath 10 q1 WK 6 Module 6 Division of PolynomialsClarissa FanilagNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics First Quarter Exam 1Document6 pagesGeneral Mathematics First Quarter Exam 1eliana tm31No ratings yet
- Gen Math11 - Q1 - Mod12 - Inverse of One To One Functions - 08082020Document16 pagesGen Math11 - Q1 - Mod12 - Inverse of One To One Functions - 08082020Leo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Week 4 KURT CLARENCE REPALDADocument15 pagesMath 7 Week 4 KURT CLARENCE REPALDAJubs codesNo ratings yet
- Math Gr9 Qtr1 Module 8 Final 22 PagesDocument22 pagesMath Gr9 Qtr1 Module 8 Final 22 Pagesapple chanNo ratings yet
- G10 Math Q2 Module-2Document12 pagesG10 Math Q2 Module-2lc camposoNo ratings yet
- G10 Math Q2 Module-2Document12 pagesG10 Math Q2 Module-2Joseph Cristopher Oporto AumanNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4Jervin BolisayNo ratings yet
- Pinamuk-An Integrated School: Senior High School DepartmentDocument2 pagesPinamuk-An Integrated School: Senior High School DepartmentHyu Ed GallardoNo ratings yet
- FinalQ2 Math10.ExamDocument4 pagesFinalQ2 Math10.ExamHope NudaloNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 MathematicsDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 MathematicsBaby Dm100% (3)
- MODULE MATH 10 q2 w1Document4 pagesMODULE MATH 10 q2 w1Jamie DulayNo ratings yet
- GenMath11 Q1 Mod9 Intercepts Zeroes and Asymptotes of Functions 08082020Document32 pagesGenMath11 Q1 Mod9 Intercepts Zeroes and Asymptotes of Functions 08082020Leo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Math G8 Modules Q1 - Q4Document296 pagesMath G8 Modules Q1 - Q4Cielo LanzaderasNo ratings yet
- Genmath PT q1Document5 pagesGenmath PT q1Irene Cayupan - CabañeroNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics 11 Module 2 2021Document17 pagesGeneral Mathematics 11 Module 2 2021Mica Ella OlivarNo ratings yet
- Gen-Math11 Q1 Mod7 Presentions-Of-functions 08082020Document16 pagesGen-Math11 Q1 Mod7 Presentions-Of-functions 08082020Ralph MapacpacNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 General MathematicsDocument18 pagesGrade 11 General MathematicsTop Ten AwardsNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice (Nx1)Document4 pagesI. Multiple Choice (Nx1)Rhea M. VillartaNo ratings yet
- Math 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-2Document15 pagesMath 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-2kenrick090% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quiz 2Document3 pagesQuiz 2Andres Palacios GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Order ProcessDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Order ProcessfilipNo ratings yet
- The 7 Levels of Wealth ManualDocument215 pagesThe 7 Levels of Wealth Manualawakejoy89% (18)
- PDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhDocument7 pagesPDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhvrsNo ratings yet
- Purusa Sukta and Big Bang Theory (A Comparative Analysis)Document1 pagePurusa Sukta and Big Bang Theory (A Comparative Analysis)ShubhamShekharNo ratings yet
- En 300 330-1 V1.8.1Document68 pagesEn 300 330-1 V1.8.1SosialNo ratings yet
- Specifications For Lime Slurry Injection For Ground ImprovementDocument5 pagesSpecifications For Lime Slurry Injection For Ground ImprovementSrini BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Metro Manila Skyway Stage 3 - Toll Regulatory BoardDocument2 pagesMetro Manila Skyway Stage 3 - Toll Regulatory BoardKenneth Paul DalusongNo ratings yet
- Math 3FM3 Fall 2012 Course OutlineDocument2 pagesMath 3FM3 Fall 2012 Course OutlineAngela DaqustNo ratings yet
- Carole King - Hard Rock CafeDocument1 pageCarole King - Hard Rock CafeauresmikeNo ratings yet
- Compressed Gas Cylinder Safety GuideDocument1 pageCompressed Gas Cylinder Safety GuideNguyenLinh27No ratings yet
- Gebremichael Te-Ame ThesisDocument146 pagesGebremichael Te-Ame ThesisMichael AbrahaNo ratings yet
- RDGFGDocument4 pagesRDGFGRobin SinghNo ratings yet
- Ai Viva QuestionsDocument13 pagesAi Viva QuestionsNew BornNo ratings yet
- Added by Guest, Last Edited by Guest On Jun 12, 2007 Show CommentDocument5 pagesAdded by Guest, Last Edited by Guest On Jun 12, 2007 Show CommentNarendrareddy RamireddyNo ratings yet
- Ingenieria Basica y Detalle ISADocument50 pagesIngenieria Basica y Detalle ISAdalver17100% (1)
- Computing Discounts Informal AssessmentDocument5 pagesComputing Discounts Informal Assessmentsayer_nicoleNo ratings yet
- Pricerfileinterfacespecification Pfi4Document34 pagesPricerfileinterfacespecification Pfi4nthgrNo ratings yet
- Senior 2 Topic Revision - MCQ Question (Series 2) AnswerDocument10 pagesSenior 2 Topic Revision - MCQ Question (Series 2) AnswerLi Xin FooNo ratings yet
- G006 Sinexcel BESS Micro Grid Solution - MalawiDocument2 pagesG006 Sinexcel BESS Micro Grid Solution - MalawiSyed Furqan RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Checklists & Tips For Energy Efficiency in Thermal UtilitiesDocument3 pagesChecklists & Tips For Energy Efficiency in Thermal UtilitiesEjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Scale NewDocument18 pagesScale NewASDFNo ratings yet
- Widiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pDocument10 pagesWidiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pnayla nadrahNo ratings yet
- VIT Wow - CFD - AssignementDocument4 pagesVIT Wow - CFD - AssignementShashank AminNo ratings yet
- Icda RulesDocument9 pagesIcda RulesRichard ZhuNo ratings yet
Math Gr10 Q2-Module-1 (32pages)
Math Gr10 Q2-Module-1 (32pages)
Uploaded by
Hazel LuzwellOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math Gr10 Q2-Module-1 (32pages)
Math Gr10 Q2-Module-1 (32pages)
Uploaded by
Hazel LuzwellCopyright:
Available Formats
10
Department of Education
National Capital Region
S CHOOLS DIVIS ION OFFICE
MARIK INA CITY
MATHEMATICS
Quarter 2: Module 1
Graphs of Polynomial Functions
Writers: Christlie Rose R. Nicolas
Cover Illustrator: Joel J. Estudillo
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
What I Need to Know
Hello Grade 10 learners! In this module, you will learn how to:
a) Illustrate polynomial functions (M10AL-IIa-1)
b) Understand, describe and interpret the graphs of polynomial
functions.
You can say that you have understood the lesson in this module if you
can already:
1. illustrate polynomial functions
2. determine the x- and y-intercepts of the graph of a polynomial function;
3. describe and interpret the end behavior of the graph of polynomial
function.
What I Know
Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer.
1. Which of the following could be the value of n in f(x) = xn if f(x) is a
polynomial function?
1
A. √−8 B. -7 C. 0 D. 2
2. Which of the following is not a polynomial function?
A. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝜋 C. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 3 + √7𝑥
1 1
B. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = − 2 𝑥 3 − 𝑥 + 1 D. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 4 − 2𝑥 5
3. What is the leading coefficient of 𝑔(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 2 − 3𝑥 4 ?
A. -5 B. -3 C. 1 D. 4
4. How should the polynomial function 𝑓(𝑥 ) = 2𝑥 + 𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 5 + 4 be
written in standard form?
A. f x x 3 2 x 3x 5 4 C. f x 4 2 x x 3 3x 5
B. f x 4 3x 5 2 x x 3 D. f x 3x 5 x 3 2 x 4
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
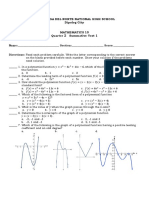
5. Which of the following are the x-intercepts
Figure 1
in the given graph (Figure 1)?
A. x = -2, 1
B. x = 2, 1
C. x = 2, -1
D. x = -2, -1
6. In Figure 1, which of the following is the y-
intercept?
A. -2 C. 1
B. 0 D. 2
7. Which of the following could be the graph of 𝑔(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 3 + 2𝑥 2 + 1?
A. B. C. D.
8. Using leading coefficient test, what could be the behavior of the graph
of 𝑓(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 4 + 8𝑥 2 − 12𝑥?
A. Rising on both left and right end of the graph.
B. Falling on both left and right end of the graph.
C. Rising on the left and falling on the right end of the graph.
D. Falling on the left and rising on the right end of the graph.
9. The demographer in Marikina predicts that the population, P, will
increase t years from now in Barangay San Roque which can be
modeled by the function 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 9𝑡 4 + 530𝑡 2 + 15 800. What will be the
population two (2) years from now?
A. 18 064 C. 20 764
B. 20 692 D. 21 647
10. A sales manager of a shoe factory determines that its profit, P, in
thousands of pesos, can be modeled by the function 𝑃 (𝑥 ) = 0.4𝑥 3 +
𝑥 2 − 7, where x represents the number of pair of shoes sold. What is
the profit when there are 120 pairs of shoes sold?
A. ₱ 425 625 C. ₱ 705 593
B. ₱ 691 200 D. ₱ 750 333
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
What’s In
Before we discuss further about polynomial function, let us recall first
the concept of polynomials.
Determine whether the following algebraic expression is polynomial or
not by putting a check mark ( ). If polynomial, identify its kind according to
number of terms and its degree. The first one is done for you.
Kind of Polynomial According to… Not
Algebraic Expression Polynomial
No. of Terms Degree Polynomial
25x2 monomial quadratic
2
1. 𝑥 + 3𝑥 − 1
2. 2𝜋
3. 4𝑥 √2 − √3𝑥 + 9
1
4. 𝑥 3 − 7𝑥 −1
5. 10 − 7𝑥
How was the activity? Have you remembered how to
determine polynomials? We will further discuss it.
What’s New
The above activity is very much related to our topic for today. A big help
if you got most of the items correctly. It only means that you have a good
foundation of it. If not, it’s ok. Let us deal with it.
Now, may I request you to be a keen observer. Through examples and
non-examples, examine and determine whether the following is a polynomial
function or not.
Polynomial Function Not Polynomial Function
𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 3𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 3 − 𝑥 − 12 𝑗(𝑥 ) = 3𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 −3 − 𝑥 − 12
7
𝑔(𝑥 ) = 32 − 7𝑥 2 𝑘 (𝑥 ) = 32 − 2
𝑥
ℎ(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 4 + √2𝑥 2 − 5 𝑚(𝑥 ) = √2𝑥 5 − 𝑥 3 − 5
Can you see the difference between the examples and
non-examples of polynomial functions? Kindly write
down your ideas how to determine a polynomial function
and when does it does not become.
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
What is It
Polynomial functions are not just algebraic expressions. It varies
depending on its degree of the polynomial which pertains to the highest
exponent or power among the terms in the function.
Lesson 1. Polynomial Functions and its kinds
Definition: POLYNOMIAL FUNCTION
A polynomial function in one variable x, is defined by an equation
of the form P(x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + an-2xn-2 + …+ a1x + a0, where:
a. the coefficients a0, a1, a2,…,an, represent real numbers
b. an ≠ 0
c. n represents a non-negative integer
Let us use the previous examples and non-examples.
Polynomial Function Not Polynomial Function
2 3
𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 3𝑥 + 4𝑥 − 𝑥 − 12 𝑗(𝑥 ) = 3𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 −3 − 𝑥 − 12
7
𝑔(𝑥 ) = 32 − 7𝑥 2 𝑘 (𝑥 ) = 32 − 2
𝑥
4 2
ℎ(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 + √2𝑥 − 5 𝑚(𝑥 ) = √2𝑥 5 − 𝑥 3 − 5
Explanation:
1. f(x), g(x) and h(x) are all polynomial functions because it satisfies the
three conditions.
2. j(x) is not a polynomial function because the second term ( 4𝑥 −3 ) has a
negative integer exponent which violates the third condition.
3. k(x) is not a polynomial function because its second term (𝑥72) also
violates the third condition where the exponents should be non-
7
negative integer. It seems to be positive on the first look, but once 𝑥2 is
simplified, it will become 7𝑥 −2.
4. m(x) is not a polynomial function because the exponent on its first term,
5
√2𝑥 5 = (2𝑥 )2 , violates the third condition that the exponents should be
5
non-negative integer; the exponent 2 is not an integer.
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
Try this! 😊
Which of the following is a polynomial function?
a. 𝑝(𝑥 ) = 5𝑥 4 − 𝑥 3 + 7𝑥 2 + 2
b. 𝑝(𝑥 ) = − 𝑥 5 + 7√𝑥 3 − 4
For polynomial functions, we can determine the parts of a polynomial
function. It can also be written in standard form if and only if the terms are
written in decreasing powers of x.
Based on its definition:
A polynomial function is a function of the form
Px a n x n a n1 x n1 a n2 x n2 ... a1 x a0 , a n 0 , where:
a) a 0 , a1 ,..., a n are real numbers called coefficients
n
b) an x is the leading term
c) a n is the leading coefficient
d) a 0 is the constant term
Example:
WRITTEN IN LEADING CONSTANT
DEGREE
POLYNOMIAL STANDARD FORM COEFFICIENT TERM
Exponent in Numerical a0
FUNCTION Terms are written in decreasing powers of x the leading coefficient in the number without
term leading term literal coefficient
𝑓(𝑥) = 3𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 3 − 𝑥 − 12 f(x) = 4x3 + 3x2 – x – 12 3 4 -12
𝑔(𝑥) = 32 − 7𝑥 2 g(x) = -7x2 + 32 3 -7 32
ℎ(𝑥) = −𝑥 4 2
+ √2𝑥 − 5 h(x) = – x3 + √𝟐x2 – 5 4 -1 -5
Polynomial functions can also be written in factored form such as:
a) p(x) = x3 – 4x + 2 can be written into m(x) = (x – 1)2 (x + 2)
b) n(x) = 2x4 + 7x3 – 4x2 can be written into n(x) = x2 (2x – 1)(x + 4)
c) t(x) = -2x4 – 14x3 + 2x2 + 14x can be written into t(x) = -2x (x + 7) (x2 – 1)
There is a need to recall and master factoring techniques and related
theorems to easily factor out these polynomial functions. It is a pre-requisite in
graphing.
Lastly, polynomial functions can be classified according to its degree.
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
KIND OF
DESCRIPTION GRAPH
POLYNOMIAL
Linear Function Degree: 1
Form:
𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏
where m is the slope and b is
the y-intercept
Graph: Linear
Example: 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 2𝑥 + 1
Quadratic Degree: 2
Function Form:
𝑔(𝑥 ) = 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐
where a, b, c are real numbers;
and a ≠ 0
Graph: Parabola
Example: 𝑔(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 + 1
Cubic Function Degree: 3
Form:
ℎ(𝑥 ) = 𝑎𝑥 3 + 𝑏𝑥 2 + 𝑐𝑥 + 𝑑
where a, b, c, d are real
numbers; and a ≠ 0
Graph: Curve passing through
y-axis with turning points.
Example: ℎ(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 3
What’s More
A. Identify whether the following is a polynomial function. If so, fill in the table
below. The first one is done for you. 😊 (1 pt. each)
POLYNOMIAL
POLYNOMIAL
COEFFICIENT
STANDARD
CONSTANT
FUNCTION
FUCNTION
LEADING
DEGREE
FORM
TERM
NOT
GIVEN
f(x) = 3x4 + 2x5 – x + 1 √ f(x) = 2x5 + 3x4 – x + 1 5 2 1
g(x) = -8x + 4x2 + 7x3
h(x) = x6 + 8x – 3x2 – 6
p(x) = 5x-3 + 2x – 9
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
B. Answer the following problems with complete solution (if necessary).
Mathlusog at Home:
Mrs. Nicolas converted
her idle backyard into an urban
gardening where she planted
commonly used vegetables and
crops in cooking.
Use the lay-out of her
backyard and your knowledge
of polynomials in solving the
following:
1) Write and simplify a polynomial function that represents the perimeter of (a)
kalamansi; (b) onion and garlic.
2) Write and simplify a polynomial function that represents the land area for (a)
petchay; (b) talong and okra
3) If each kangkong reached a height of (x + 8) inches, what is the volume of
kangkong in the backyard?
4) Differentiate the polynomial functions formed in perimeter, area, and
volume.
5) If you will have a chance to change your backyard into urban gardening,
what kind of plants will you have and why?
What I Have Learned
Write “Fact” if the statement is correct, otherwise, write “BLUFF”.
1) An algebraic expression is a polynomial function if the coefficients are
real numbers, a0 ≠ 0 and the exponents are integers.
2) The polynomial function 𝑗(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 3 + 5𝑥 2 − 3𝑥 is in standard form.
3) The leading coefficient in ℎ(𝑥 ) = −7𝑥 4 + 𝑥 5 − 3𝑥 + 1 is -7.
4) The graph of 𝑗(𝑥 ) = 2𝑥 2 + 𝑥 − 4 is a parabola.
5) The degree of the polynomial ℎ(𝑥 ) = −7𝑥 4 + 𝑥 5 − 3𝑥 + 1 is 5.
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
What I Can Do
“PERFORMANCE TASK: BIRTHDAY CAKE”
Goal: Make a birthday cake design for your loved one.
Role: You will be a cake designer.
Audience: Classmates, teacher and your chosen loved one.
Situation: Your loved one’s birthday is upcoming. You want to surprise him/her
with a cake that you personally designed.
Product: The expected output must be the following:
1) Identify your loved one whom you will surprise with a birthday cake.
2) Create a sketch of your cake with complete label of its dimensions. Your
cake may have several layers and not limited to a circular shape.
3) In your sketch, write expressions in terms of x to represent each
dimension of the cake.
4) Write the polynomial function that represents its volume.
5) Interview a baker to show your design and ask for its cost. You may do
the interview online (for safety purposes).
Standard for Success: Be guided with the scoring rubrics.
CRITERIA 3 2 1 0
Completed all the Lacks 1. Lacks 2-3. Lacks 4 or more.
Details
tasks indicated in the
×2
‘product’.
All representations Committed 1 error. Committed 2-3 Committed 4 or
on each dimension errors. more errors.
Construction
and volume of the
×5
cake are correct and
accurate.
Work is Artwork is generally Artwork is somewhat Artwork is not unique
Creativity
exceptionally unique unique and unique and nor interesting.
×3
and interesting. interesting. interesting.
Assessment
Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer.
2𝑥 𝑛
1. Which of the following could be the value of n in 𝑔(𝑥 ) = if g(x) is a
5
polynomial function?
2
A. -5 B. √2 C. D. 2
5
2. Which of the following is a polynomial function?
A. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 3𝑥 2 − 8𝑥 3 + 𝑥 4 C. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 3 + √7𝑥
1 1
B. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = − 2 𝑥 3 − 𝑥 −1 + 1 D. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 4 − 2𝑥 5
8
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
3. What is the leading coefficient of ℎ(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 − 5𝑥 9 + 15𝑥 4 ?
A. -5 B. -1 C. 9 D. 15
4. Which of the following polynomial functions is written in standard form?
A. 𝑘 (𝑥 ) = 𝑘 3 + 4𝑘 + 3𝑘 5 − 7 C. 𝑝(𝑥 ) = 9𝑥 5 − 𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 2
B. 𝑚(𝑥 ) = 2𝑥 5 + 3𝑥 + 4𝑥 3 D. 𝑞(𝑥 ) = 4 − 𝑥 3 + 2𝑥 + 𝑥 0
5. If the transportation fare in tricycle is represented by 𝑡(𝑥 ) = 2𝑥 + 15,
where x means the distance travelled, how much is the fare when you
acquired 7 kilometers?
A. ₱ 20 C. ₱ 44
B. ₱ 29 D. ₱ 105
Additional Activities
A. Write “YES” if the given is a polynomial function. Otherwise, write “NO”.
1) 𝑏(𝑥 ) = 4 − 𝑥 3 + 2𝑥 2 + 𝑥 0
1
2) ℎ(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 5 − 6𝑥 3 +
2
−7
3) 𝑤(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 + √𝑥 2 +1
B. Rewrite the following polynomial functions on its standard form. Then,
identify its degree, leading coefficient and constant.
1) 𝑗(𝑥 ) = 19 − 7𝑥 3 + 𝑥 9 − 𝑥 5
2) 𝑑 (𝑥 ) = −6𝑥 4 + 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 3 − 𝑥
Lesson 2. INTERCEPTS OF THE GRAPH
What’s In
Keep in mind the definition of polynomial functions so that we will always
be on the right track. With this, let us examine how much you remembered.
Identify which of the following given is a polynomial function. Then,
rewrite it in standard form; and identify the degree, leading coefficient and
constant term. If not polynomial function, put a check on its corresponding
column. Let us complete the table below:
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
POLYNOMIAL
POLYNOMIAL
COEFFICIENT
STANDARD
CONSTANT
FUNCTION
FUCNTION
LEADING
DEGREE
FORM
TERM
NOT
GIVEN
𝑓(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 7 − 𝑥 + 2𝑥 3 − 1
𝑔(𝑥) = 5𝑥 8 − 4𝑥 + 2𝑥 7
ℎ(𝑥) = √𝑥 4 − 𝑥 + 2𝑥 −1 − 1
What’s New
Before we begin graphing the polynomial functions, let us recall the
concept of x- and y-intercepts.
ACTIVITY: PLOT TO THINK
1. Plot the following points in the Cartesian
Plane. Use a RED pen for SET A and use
a BLUE pen for SET B.
SET A SET B
A (2, 0) F (0, 2)
B (-3, 0) G (0, -3)
C (5,0) H (0, 5)
D (-4, 0) I (0, -4)
E (-6, 0) J (0, -6)
2. Answer the following questions using the previous activity:
a. On what axis do points in SET A lie? ______________________
b. On what axis do points in SET B lie? ______________________
c. Which among the two sets of points represent x-intercept? Y-intercept?
___________________________________________________
d. What is the difference between x- and y-intercepts in terms of:
d.1 ordered pairs? ________________________________________
d.2 exact location in the Cartesian plane? _____________________
10
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
What is It
It is important for us to know how do these polynomial functions look like
in our life. Graphing polynomial functions is our target skill for this section.
With our previous activity, we explored the difference between the x- and
y-intercepts.
x-intercept: If y=0, then (x,0) passes through the x-axis.
y- intercept: If x=0, then (0,y) passes through the y-axis.
Through the intercepts, the polynomial functions can easily be graphed.
However, knowledge and skills in factoring must be also be mastered.
Example 1: Graph the polynomial function f(x) = x3 + 3x2 – x - 3 .
Solution:
Step 1: Get the factors of the given polynomial function.
Using the theorems and synthetic division, the factors of f(x) are as
follows:
f(x) = (x – 1) (x +1) (x + 3)
Step 2: Solve for the x-intercept and its ordered pairs.
According to the definition of x-intercept, substitute y = 0. However, there
is no y in the given function. Always remember that the representation of a
function f(x) can be replaced by y because they are equal.
f(x) = (x – 1) (x +1) (x + 3)
y = (x – 1) (x +1) (x + 3)
0 = (x – 1) (x +1) (x + 3)
Then, apply the zero-product property.
0 = (x – 1) (x +1) (x + 3)
x–1=0 x+1=0 x+3=0
x=1 x = -1 x = -3
(1, 0) (-1, 0) (-3, 0)
With this, we can easily say that the x-intercepts of a function is
commonly known as the zeros of the function (all possible values of x).
11
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
Step 3: Solve for the y-intercept and its ordered pairs.
According to the definition of y-intercept, substitute x = 0. It can be
substituted in either of the given polynomial function in standard form or on its
factored form.
Standard Form Factored Form
f(x) = x3 + 3x2 – x – 3 f(x) = (x – 1) (x +1) (x + 3)
f(0) = (0) + 3(0) – (0) – 3
3 2 f(0) = (0 – 1) (0 +1) (0 + 3)
f(0) = -3 f(0) = (-1) (1) (3)
f(0) = -3
So, the ordered pair is (0, -3). It will end up to the same answer. And
observing it carefully, we can easily say that the y-intercept of polynomial
function pertains to the constant of a function.
Step 4: Identify its companions.
As quoted, “No man is an island”. Even in polynomial functions, it can be
easily graphed if we know the companions of the intercepts. In other words, we
need to identify the values of x beside the intercepts.
(-3,0) (1,0)
(-1,0)
Again, x – intercepts are -3, -1, 1 which gives us the ordered pairs: (-
3,0), (-1,0) and (1,0). Plot these points in a Cartesian plane to easily identify the
companions.
Based on the figure on the right side, choose value(s) of x on the left, in
between and right side of the x-intercepts. Those are the companions to easily
graph whether it will go up or down.
12
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
As you can notice in the figure
on the left, there is no circle on the
origin. It is because it is already known
which is for the y-intercept. So, the
companions are -4, -2, and 2. With
these values of x, substitute it on the
given function to get the value of y.
If x = -4 If x = -2 If x = 2
f(x) = x3 + 3x2 – x – 3 f(x) = x3 + 3x2 – x – 3 f(x) = x3 + 3x2 – x – 3
f(-4) = (-4)3 + 3(-4)2 – (-4) – 3 f(-2) = (-2)3 + 3(-2)2 – (-2) – 3 f(2) = (2)3 + 3(2)2 –(2)– 3
f(-4) = -15 f(-2) = 3 f(2) = 15
(-4, -15) (-2, 3) (2, 15)
Step 5: Plot the ordered pairs
found in the intercepts and
companions. Then, connect the
points following the x-values from
left to right.
Guide Points
x – intercepts:(-3,0), (-1,0), (1,0)
y – intercept: (0, -3)
Companions: (-4, -15), (-2, 3), (2, 15)
See the graph on the right.
Example 2: Graph the polynomial function g(x) = x3 – x2 – 2x.
Solution:
Step 1: Get the factors of the given polynomial function.
Given: g(x) = x3 – x2 – 2x
Factors of g(x) : x (x + 1) (x – 2)
Step 2: Solve for the x-intercept and its ordered pairs. Let y = 0.
g(x) = x (x + 1) (x – 2)
y = x (x + 1) (x – 2)
0 = x (x + 1) (x – 2)
Then, apply the zero-product property.
13
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
0 = x (x + 1) (x – 2)
x-intercepts: x+1=0 x–2=0
0, -1, 2 x=0 x = -1 x=2
Ordered Pairs:
(0,0) (-1,0) (2,0)
(0, 0) (-1, 0) (2, 0)
Step 3: Solve for the y-intercept and its ordered pairs. Let x = 0.
Using the factored form:
g(x) = x (x + 1) (x – 2)
Let x = 0 g(0) = 0 (0 + 1) (0 – 2)
Simplify g(0) = 0 (0) (0)
So, the y-intercept is 0. If you will also observe the given polynomial function,
it does not have any constant. That is the implication when y-intercept is 0.
Step 4: Identify its companions.
To know the companions, examine
the points near the x-intercepts.
With these x -intercepts, we could
get the values of the companions if:
(2,0)
x = -2
(0,0)
x = -0.5
x=1
x=3
(-1,0)
Solve the values of y corresponding
to x values to form ordered pairs:
x -2 -0.5 1 3
g(x) -8 0.625 -2 12
Given: g(x) = x (x + 1) (x – 2)
x = -2 x = -0.5 x=1 x=3
g(x) = x (x + 1) (x – 2) g(x) = x (x + 1) (x – 2) g(x) = x (x + 1) (x – 2) g(x) = x (x + 1) (x – 2)
g(-2)=(-2) (-2 + 1) (-2 – 2) g(-0.5)=(-0.5) (-0.5 + 1) (-0.5 – 2) g(1)=(1) (1 + 1) (1 – 2) g(3)=(3) (3 + 1) (3 – 2)
g(-2)=(-2) (-1) (-4) g(-0.5)=(-0.5) (0.5) (-2.5) g(1)=(1) (2) (-1) g(3)=(3) (4) (1)
g(-2)= -8 g(-0.5)= 0.625 g(1)= -2 g(3)= 12
14
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
Step 5: Plot the ordered pairs found in the intercepts and companions.
Then, connect the points following the x-values from left to right.
(3,12)
(-0.5,0.625)
(-1,0) (0,0) (2,0)
(1,-2)
(-2,-8)
What’s More
A. Given the graphs of a polynomial function, identify the x- and y-intercepts.
Graph 1 Graph 2 Graph 3
1) x-intercept(s): _________________; y-intercept: ___
2) x-intercept(s): _________________; y-intercept: ___
3) x-intercept(s): _________________; y-intercept: ___
B. Graph the polynomial function g(x) = x 3 + x2 – 12x through identifying the
missing parts.
Given: g(x) = x3 + x2 – 12x
Factored form: g(x) = x(x+4)(x – 3)
15
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
1) Factors: ___, ___, ___
2) x – intercept(s): ___, ___, ___
Ordered Pairs: ___, ___, ___
3) y – intercept: ___
Ordered Pair: ___
4) Solve for the companions with complete solution.
x -5 -2 1 4
g(x)
5) Graph (Use a graphing paper.)
What I Have Learned
Arrange the following steps in graphing polynomial functions using the
intercepts and its companions.
____ Identify its companions.
____ Get the factors of the given polynomial function.
____ Plot the ordered pairs found in the intercepts and companions. Then,
connect the points following the x-values from left to right.
____ Solve for the y-intercept and its ordered pairs. Let x = 0.
____ Solve for the x-intercept and its ordered pairs. Let y = 0.
What I Can Do
“POLYNOMIAL RIDE!”
Situation:
Chris, and her friends enjoy roller
coasters. Whenever a new roller coaster opens
near their community, they try to be among the
first to ride.
One Saturday, they decide to ride a new
coaster built in Marikina Riverbanks. While
waiting in line, Chris notices that part of this
coaster resembles the graph of a polynomial
Image Source: Enchanted Kingdom @ek_philippines; photo credit to
function that they have been studying in their
@tomxur(IG)
Math 10 class.
16
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
1. The brochure for the coaster says that, for the first 10 seconds of the ride,
the height of the coaster can be determined by h(t ) 0.3t 3 5t 2 21t , where
t is the time in seconds and h is the height in feet. Classify this polynomial
by degree and by number of terms. (3 pts.)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
2. Graph the polynomial function where the height (h(t)) of the roller coaster
is located on the y-axis and t is on the x-axis. Label your graph correctly.
Use a graphing paper. (20 pts.)
Table of Values: h(t ) 0.3t 3 5t 2 21t
t 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
h(t) 24.4 17.5 4.9 1.6 10
3. Find the height of the coaster at t = 0 seconds. Explain why this answer
makes sense. (3 pts.)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
4. Evaluate h(60). Does this answer make sense? Is there a roller coaster
ride at this height? CLEARLY EXPLAIN your reasoning.
(Hint.: Mt. Everest is 29,028 feet tall.) (5 pts.)
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(Activity Source: lindblomeagles.org/.../GIFT%202%20Roller%20Coaster%20Polynomials...)
Assessment
Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer.
1. Where do x-intercepts located in the cartesian plane?
A. origin C. x-axis
B. quadrant D. y-axis
2. All of the following statements are true about intercepts, EXCEPT…
A. In x- and y-intercept, the points are (0, x) and (y,0).
B. In x- and y-intercept, the points are (x,0) and (0,y).
C. In x-intercept, the point intersects at x-axis.
D. In y-intercept, the point intersects at y-axis.
3. Given the factored form of a polynomial function, 𝑏(𝑥 ) = 𝑥(𝑥 − 7)(𝑥 + 1),
which of the following the y-intercept?
A. -7 B. -1 C. 0 D. 7
17
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
For numbers 4 to 5, refer to Figure 1.
4. What are the x-intercepts? Figure 1
A. x = -2, 1
B. x = 2, 1
C. x = 2, -1
D. x = -2, -1
5. Which of the following is the y-intercept?
A. -2
B. 0
C. 1
D. 2
Additional Activities
THINK DEEPER!
Do all polynomial functions have y-intercepts? If yes, how many? What
is the easiest way to spot the y-intercept(s) in the equation?
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
Lesson 3. END-BEHAVIORS OF THE GRAPH
(LEADING COEFFICIENT TEST)
What’s In
Let us have a quick recap of what we did last time!
Given the graph of a polynomial function, determine the x- and y-intercepts.
a) x-intercepts: ________________
Ordered Pairs: ________________
b) y-intercept: ________________
Ordered Pair: ________________
18
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
What’s New
Graphing polynomial functions using the intercepts and its companions
is quite laborious. However, there are theorems or concepts that can give us a
hint on how a polynomial function behaves in a graph without solving. One of
which is using the leading coefficient test.
But before we proceed, let us recall first how to identify leading
coefficient and degree of a polynomial function.
ACTIVITY 1: REMEMBER ME?
Complete the table below by identifying the leading coefficient and degree of a
polynomial function.
LEADING
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTION DEGREE
COEFFICIENT
1. y x 3 2 x 2 11x 12
2. y 2 x 5 x 2 x 1
3. y 2 x 2 x 6
4. y x3 2 x 4 1
5. y 14 x
2
Did you find it easy or difficult? This will be of great help to discover how
to apply the concept of leading coefficient test.
End-behaviors in a graph of a polynomial function gives us the direction
where x increases or decreases without bound. In a most convenient way, let
us explore how it works by doing the next activity.
Since we are in a digital world, we may download graphing apps which
is applicable in our gadgets. The following applications is easy to use. Once the
polynomial function is entered, the graph will be seen and explored right away.
Search… Download…
Ready… Explore!
NOTE: If the gadget you are using cannot accommodate these graphing apps, the teacher
will provide illustrations for exploration on Activity 2.
19
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
ACTIVITY 2: FOLLOW MY PATH
Complete the details on the table. Then, answer the following guide
questions as conclusion.
BEHAVIOR OF
LEADING DEGREE OF THE
THE GRAPH:
COEFFICIENT POLYNOMIAL
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Rising or Falling
n > 0 or Positive or Right-
Even or Odd Left-end
n<0 Negative end
𝑦 = 2𝑥 3 − 7𝑥 2 − 7𝑥 + 12
𝑦 = −𝑥 5 + 3𝑥 4 − 7𝑥 2 + 4
𝑦 = 𝑥 4 − 7𝑥 2 + 6𝑥
𝑦 = −𝑥 4 + 2𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 2 − 𝑥 − 4
𝑦 = −2𝑥 4 + 𝑥 3 − 𝑥
𝑦 = −2𝑥 3 + 4𝑥 2 − 𝑥 + 5
𝑦 = 𝑥 4 + 4𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 − 2
𝑦 = 𝑥 5 − 𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 1
CONCLUSION:
What do you observe on the end-behaviors of the graph of a polynomial
function if:
1. The degree of the polynomial is odd and the leading coefficient is positive?
If the degree of the polynomial is ________ and the leading coefficient is
________, then the graph ________ to the left and ________ to the right.
2. The degree of the polynomial is odd and the leading coefficient is negative?
If the degree of the polynomial is ________ and the leading coefficient is
________, then the graph ________ to the left and ________ to the right.
3. The degree of the polynomial is even and the leading coefficient is positive?
If the degree of the polynomial is ________ and the leading coefficient is
________, then the graph ________ to the left and ________ to the right.
4. The degree of the polynomial is even and the leading coefficient is negative?
If the degree of the polynomial is ________ and the leading coefficient is
________, then the graph ________ to the left and ________ to the right
20
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
What is It
Leading Coefficient Test helps to determine the end behaviors of a
graph of a polynomial function as x increases or decreases without bound.
Degree of the End-Behavior of the Graph
Leading Coefficient
Polynomial Left-end Right-end
Positive Odd Falling Rising
Negative Odd Rising Falling
Positive Even Rising Rising
Negative Even Falling Falling
Example 1: 𝒇(𝒙) = 𝟐𝒙𝟑 − 𝟕𝒙𝟐 − 𝟕𝒙 + 𝟏𝟐
Leading Coefficient: 2 Positive
Degree of the Polynomial: 3 Odd
Given these conditions, it is expected the left-end
behavior is continuously falling and the right-end is
continuously rising.
Example 2: 𝒈(𝒙) = −𝒙𝟓 + 𝟑𝒙𝟒 − 𝟕𝒙𝟐 + 𝟒
Leading Coefficient: -1 Negative
Degree of the Polynomial: 5 Odd
The end-behaviors of the graph is rising to the left-
end and falling to the right-end.
Example 3: 𝒉(𝒙) = 𝒙𝟒 + 𝟒𝒙𝟐 + 𝟕𝒙 − 𝟐
Leading Coefficient: 1 Positive
Degree of the Polynomial: 4 Even
The end-behaviors of the graph is both rising.
21
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
Example 4: 𝒌(𝒙) = −𝟐𝒙𝟒 + 𝒙𝟑 − 𝒙
Leading Coefficient: -2 Negative
Degree of the Polynomial: 4 Even
The end-behaviors of the graph is both falling.
What’s More
Without graphing the given polynomial functions, identify whether the following
will rise and/or falls on left and right-hand of the graph.
LEFT-END RIGHT-END
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTION
BEHAVIOR BEHAVIOR
1. y x 5
2. y x 4 16
3. y x 4 2 x 2 15
4. y x 3 x 2 12 x
5. y x 3 2 x 2 11x 12
What I Have Learned
Complete the table below.
Degree of the End-Behavior of the Graph
Leading Coefficient
Polynomial Left-end Right-end
Positive Odd
Positive Even
Negative Even
Negative Odd
22
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
What I Can Do
“PERFORMANCE TASK: MATH ART”
Goal: Make an abstract or artwork using the graphs of polynomial functions.
Role: You will be graphic artist.
Audience: Classmates and teacher.
Situation: You will post your artwork in an exhibit for a cause.
Product:
1) Merge at least three polynomial functions with labels.
2) Make an artwork that can be visualized and created through those graphs.
3) You may use graphing apps if applicable.
Standard for Success: Be guided with the scoring rubrics.
CRITERIA 3 2 1 0
Details Completed all the tasks indicated in Lacks 1. Lacks 2-3. Lacks 4 or more.
×2 the ‘product’.
All polynomial functions were Committed 1 Committed 2-3 Committed 4 or
Construction
graphed correctly and accurately error. errors. more errors.
×5
with complete labels. Neatly done.
Artwork is exceptionally unique and Artwork is Artwork is Artwork is not
Creativity interesting. generally unique somewhat unique nor
×3 and interesting. unique and interesting.
interesting.
Assessment
Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer.
1. What does leading coefficient test implies in the graph?
A. end-behaviors C. movement
B. intercepts D. multiplicity
2. Which of the following is TRUE in 𝑝(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 3 + 6𝑥 2 + 2𝑥 − 12?
A. There is no y-intercept.
B. The highest degree is 12.
C. The leading coefficient is 1.
D. The polynomial function is quadratic.
3. Which of the following polynomial functions has a graph that falls to the
left-end and rises to the right-end?
A. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 + 5
B. 𝑔(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 4 + 3𝑥 2 + 𝑥 + 2
C. ℎ(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 + 5𝑥 4 + 9
D. 𝑘 (𝑥 ) = 𝑥 4 + 𝑥 5 − 3𝑥 + 2
23
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
4. Using the leading coefficient test, what could be the behavior of the
graph of 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 + 5?
A. Falling on both left and right-end of the graph.
B. Rising on both left and right-end of the graph.
C. Falling to the left and rising to the right.
D. Rising to the left and falling to the right.
5. Which of the following could be the graph of 𝑔(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 4 + 3𝑥 2 + 𝑥 + 2?
A. B. C. D.
Additional Activities
HOW DO I LOOK?: Write the letter that corresponds to the correct graph of
the given polynomial functions.
____ 1) 𝑦 = 𝑥 5 − 𝑥 3 + 5
____ 2) 𝑦 = −𝑥 3 − 5𝑥 2 + 2
____ 3) 𝑦 = −4𝑥 4 + 2𝑥 2 + 3
____ 4) 𝑦 = 𝑥 4 − 𝑥 + 1
____ 5) 𝑦 = (𝑥 − 1)2 (𝑥 + 1)
24
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
Multiple Choice. Choose the letter of the best answer.
1. What should be the value of n in f(x) = xn if f(x) is a polynomial
function?
A. an integer C. any number except 0
B. a non-negative integer D. any rational number
2. Which of the following is not a polynomial function?
A. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = √7𝑥 C. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 4𝑥 3 + 𝑥
B. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 3 − 𝑥 + 1 D. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 4𝑥 − 2𝑥 −5
3. What is the leading coefficient of 𝑔(𝑥 ) = 8𝑥 − 5𝑥 7 + 𝑥 4 ?
A. -5 B. -3 C. 4 D. 8
4. How should the polynomial function 𝑓(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 + 2𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 5 − 6 be
written in standard form?
A. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = 2𝑥 3 − 𝑥 + 3𝑥 5 − 6 C. 𝑓(𝑥 ) = 3𝑥 5 + 2𝑥 3 − 𝑥 − 6
B. 𝑓 (𝑥 ) = −𝑥 + 2𝑥 3 + 3𝑥 5 − 6 D. 𝑓(𝑥 ) = 3𝑥 5 + 2𝑥 3 + 𝑥 − 6
5. What are the x-intercepts in the given graph Figure 1
(Figure 1)?
A. x = -1, 1
B. x = -1, -1
C. x = 1
D. x = -1
6. In Figure 1, which of the following is the y-
intercept?
A. -2 C. 1
B. 0 D. 2
7. Which of the following could be the graph of 𝑔(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 3 + 2𝑥 2 + 1?
A. B. C. D.
25
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
8. Using leading coefficient test, what could be the behavior of the graph
of 𝑓(𝑥 ) = −𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 − 19?
A. Rising on both left and right end of the graph.
B. Falling on both left and right end of the graph.
C. Rising on the left and falling on the right end of the graph.
D. Falling on the left and rising on the right end of the graph.
9. A company’s profit in thousands of pesos is determined by the number
of branches x it operates: 𝑃(𝑥 ) = 𝑥 (𝑥 − 15)(𝑥 − 20). What is the profit
if x = 5?
A. 750 C. 1 875
B. 1 500 D. 750 000
10. A sales manager of a shoe factory determines that its profit, P, in
thousands of pesos, can be modeled by the function 𝑃 (𝑥 ) = 0.7𝑥 3 +
𝑥 2 − 10, where x represents the number of pair of shoes sold. What is
the profit when there are 100 pairs of shoes sold?
A. ₱ 400 C. ₱ 790 593
B. ₱ 709 990 D. ₱ 850 390
26
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
References
Banaag, GDG, et.al. (2013). Global Mathematics 10. Quezon City: The
Library Publishing House, Inc. pp.139-156
Coronel, Sr. IC, et.al. (2015). Growing Up with Math 10. Quezon City: FNB
Educational, Inc. pp. 146-164.
Nivera, GC., et.al. (2015) Grade 10 Mathematics Patterns and Practicalities.
Makati City: Salesiana BOOKS by Don Bosco Press, Inc. pp.116-163
Rosario, J. et.al. (2018). Our World of Math Grade 10. Quezon City: VIBAL
Group, Inc. pp. 77-86
27
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
Answer Key
28
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
29
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
30
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
Development Team of the Module
Writer: Christlie Rose R. Nicolas (PHS)
Editors: Imelda B. Olvida, Principal (MHHS)
John Anthony P. Santos (SNNHS)
Melody F. Grimaldo (NHS)
Rosemarie P. Ortega (PHS)
Dona G. Aquino (KNHS)
Tiburcio A. Aplacador (FHS)
Wilfredo M. Junio (MNHS)
Internal Reviewer: Dominador J. Villafria (Education Program Supervisor-Mathematics)
External Reviewer: PNU Validators
Cover Illustrator & Layout Artist: Joel J. Estudillo (SNNHS)
Management Team:
Sheryll T. Gayola
Assistant Schools Division Superintendent
OIC, Office of the Schools Division Superintendent
Elisa O. Cerveza
Chief, CID
OIC, Office of the Assistant Schools Division Superintendent
Dominador J. Villafria
Education Program Supervisor-Mathematics
Ivy Coney A. Gamatero
Education Program Supervisor– LRMS
For inquiries or feedback, please write or call:
Schools Division Office- Marikina City
Email Address: sdo.marikina@deped.gov.ph
191 Shoe Ave., Sta. Elena, Marikina City, 1800, Philippines
Telefax: (02) 682-2472 / 682-3989
DISCIPLINE • GOOD TASTE • EXCELLENCE
You might also like
- Question 1 (1 Point)Document44 pagesQuestion 1 (1 Point)milanchabhadiya288No ratings yet
- Analysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsDocument6 pagesAnalysis and Comparison of Different MicroprocessorsJuan Carlos Álvarez SalazarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1 Math 10 Graphs of Polynomial Functions FinalDocument29 pagesModule 2 1 Math 10 Graphs of Polynomial Functions FinalJacob Sanchez100% (1)
- Math10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionDocument32 pagesMath10 q2 Week1 Module1 Polynomial-Functions For-ReproductionChaz grant borromeo89% (9)
- US Army Identification of Ammunition CourseDocument90 pagesUS Army Identification of Ammunition Courselygore100% (2)
- Contractor Safety Stand Down 2016Document25 pagesContractor Safety Stand Down 2016ekoimampNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Module-1 - Illustrating-Polynomial-FunctionDocument16 pagesQuarter 2-Module-1 - Illustrating-Polynomial-FunctionDianne Dynah Bilaro DyNo ratings yet
- G10 Math Q2 Module-1Document24 pagesG10 Math Q2 Module-1L. RikaNo ratings yet
- Math 10 q2 Week 1 Module 1 Polynomial Functions For Reproduction 1Document32 pagesMath 10 q2 Week 1 Module 1 Polynomial Functions For Reproduction 1Jowinmay NudaloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Guided Learning Activity KitDocument40 pagesMathematics: Guided Learning Activity KitAnony MousNo ratings yet
- Activities 1 4Document7 pagesActivities 1 4Marlyn GuiangNo ratings yet
- Q2 Mathematics 10 - Module 1Document16 pagesQ2 Mathematics 10 - Module 1Mari100% (1)
- Q2 - Mathematics 10 - Mod17 - Graphs and Polynomials Dunctions - v2Document28 pagesQ2 - Mathematics 10 - Mod17 - Graphs and Polynomials Dunctions - v2Ruby Rose B. Panganod-Araba100% (1)
- Degree Leading Coefficient and Constant Term of A Polynomial FunctionDocument5 pagesDegree Leading Coefficient and Constant Term of A Polynomial Functionsusan aralarNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q2 Module 1Document14 pagesMath10 Q2 Module 1Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsDocument25 pagesMathematics: Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- DIRECTION: Write All Answers and Required Solutions in The Test Booklet. Determine Whether Each Statement Is TRUE or FALSE. (1 Point Each)Document3 pagesDIRECTION: Write All Answers and Required Solutions in The Test Booklet. Determine Whether Each Statement Is TRUE or FALSE. (1 Point Each)MariaRebeccaObafialFloresNo ratings yet
- Q2 1st Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ2 1st Summative TestIsrael BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based EducationDocument25 pagesMathematics: Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based EducationRachel Yam 3nidadNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Module - Q2, WK 1 - 2Document4 pagesMath 10 Module - Q2, WK 1 - 2Reygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q2 Module 1Document16 pagesMath10 Q2 Module 1Ella OrizaNo ratings yet
- Math10 Q2 Module 1Document16 pagesMath10 Q2 Module 1Joan Layos MoncaweNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Polynomial FunctionsDocument21 pagesWeek 1 Polynomial FunctionspotatersNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Solving Logarithmic Equations and InequalitiesDocument28 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Solving Logarithmic Equations and InequalitiesBenjamin JamesNo ratings yet
- TG Grade-10Document137 pagesTG Grade-10irene.buysonNo ratings yet
- General Math Quarter 1 Week 3: CompetenciesDocument10 pagesGeneral Math Quarter 1 Week 3: CompetenciesVic KinnzNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 4: Algebraic ExpressionsDocument23 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 4: Algebraic ExpressionsMa.Cristine Joy Inocentes50% (2)
- Q2 1st Summative TestDocument3 pagesQ2 1st Summative TestIsrael BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Real-Life of Exponential Functions and Their Transformations Are, Population GrowthDocument3 pagesReal-Life of Exponential Functions and Their Transformations Are, Population GrowthSecret LungsNo ratings yet
- Math 114 Activity 1Document4 pagesMath 114 Activity 1DanielNo ratings yet
- Math 2ND Quarter Module 1Document20 pagesMath 2ND Quarter Module 1Fatima UliNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDocument22 pagesQuarter 2-Module-2-Graph-of-Polynomial-FunctionDianne Dynah Bilaro DyNo ratings yet
- Math11 BC Q3 M5 PDFDocument12 pagesMath11 BC Q3 M5 PDFsevynNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Document54 pages2nd Grading LAA Grade 10Urduja Kyle OdiacerNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 18: Solving Exponential Equations and InequalitiesDocument19 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 18: Solving Exponential Equations and InequalitiesDaphneeNo ratings yet
- Mtap G10S2 Polynomial FunctionsDocument2 pagesMtap G10S2 Polynomial FunctionsLedesma, Elijah O.No ratings yet
- General-Mathematics Q1 W8Document13 pagesGeneral-Mathematics Q1 W8jenayadaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math-2 PDFDocument32 pagesGen Math-2 PDFshamera binayonNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Summative Test 1Document15 pagesGen Math Summative Test 1encarNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Learning Materials For Senior High School: Tagum City College of Science and Technology Foundation IncDocument17 pagesSupplementary Learning Materials For Senior High School: Tagum City College of Science and Technology Foundation Incjaylyn carasNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Summative Test 2Document32 pagesGen Math Summative Test 2encarNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Quarter2 Week1to2 Melc01to03 Module1 Macadangdang Magdalena Et AlDocument45 pagesMath 10 Quarter2 Week1to2 Melc01to03 Module1 Macadangdang Magdalena Et AlDheztinee GabrielNo ratings yet
- Math 10 q1 WK 6 Module 6 Division of PolynomialsDocument30 pagesMath 10 q1 WK 6 Module 6 Division of PolynomialsClarissa FanilagNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics First Quarter Exam 1Document6 pagesGeneral Mathematics First Quarter Exam 1eliana tm31No ratings yet
- Gen Math11 - Q1 - Mod12 - Inverse of One To One Functions - 08082020Document16 pagesGen Math11 - Q1 - Mod12 - Inverse of One To One Functions - 08082020Leo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Week 4 KURT CLARENCE REPALDADocument15 pagesMath 7 Week 4 KURT CLARENCE REPALDAJubs codesNo ratings yet
- Math Gr9 Qtr1 Module 8 Final 22 PagesDocument22 pagesMath Gr9 Qtr1 Module 8 Final 22 Pagesapple chanNo ratings yet
- G10 Math Q2 Module-2Document12 pagesG10 Math Q2 Module-2lc camposoNo ratings yet
- G10 Math Q2 Module-2Document12 pagesG10 Math Q2 Module-2Joseph Cristopher Oporto AumanNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document16 pagesModule 4Jervin BolisayNo ratings yet
- Pinamuk-An Integrated School: Senior High School DepartmentDocument2 pagesPinamuk-An Integrated School: Senior High School DepartmentHyu Ed GallardoNo ratings yet
- FinalQ2 Math10.ExamDocument4 pagesFinalQ2 Math10.ExamHope NudaloNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 MathematicsDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education: Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 MathematicsBaby Dm100% (3)
- MODULE MATH 10 q2 w1Document4 pagesMODULE MATH 10 q2 w1Jamie DulayNo ratings yet
- GenMath11 Q1 Mod9 Intercepts Zeroes and Asymptotes of Functions 08082020Document32 pagesGenMath11 Q1 Mod9 Intercepts Zeroes and Asymptotes of Functions 08082020Leo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Math G8 Modules Q1 - Q4Document296 pagesMath G8 Modules Q1 - Q4Cielo LanzaderasNo ratings yet
- Genmath PT q1Document5 pagesGenmath PT q1Irene Cayupan - CabañeroNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics 11 Module 2 2021Document17 pagesGeneral Mathematics 11 Module 2 2021Mica Ella OlivarNo ratings yet
- Gen-Math11 Q1 Mod7 Presentions-Of-functions 08082020Document16 pagesGen-Math11 Q1 Mod7 Presentions-Of-functions 08082020Ralph MapacpacNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 General MathematicsDocument18 pagesGrade 11 General MathematicsTop Ten AwardsNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice (Nx1)Document4 pagesI. Multiple Choice (Nx1)Rhea M. VillartaNo ratings yet
- Math 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-2Document15 pagesMath 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-2kenrick090% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quiz 2Document3 pagesQuiz 2Andres Palacios GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Order ProcessDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Order ProcessfilipNo ratings yet
- The 7 Levels of Wealth ManualDocument215 pagesThe 7 Levels of Wealth Manualawakejoy89% (18)
- PDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhDocument7 pagesPDF File Rites of The Lock-Picking With Surgat Lapaca by AftahhvrsNo ratings yet
- Purusa Sukta and Big Bang Theory (A Comparative Analysis)Document1 pagePurusa Sukta and Big Bang Theory (A Comparative Analysis)ShubhamShekharNo ratings yet
- En 300 330-1 V1.8.1Document68 pagesEn 300 330-1 V1.8.1SosialNo ratings yet
- Specifications For Lime Slurry Injection For Ground ImprovementDocument5 pagesSpecifications For Lime Slurry Injection For Ground ImprovementSrini BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Metro Manila Skyway Stage 3 - Toll Regulatory BoardDocument2 pagesMetro Manila Skyway Stage 3 - Toll Regulatory BoardKenneth Paul DalusongNo ratings yet
- Math 3FM3 Fall 2012 Course OutlineDocument2 pagesMath 3FM3 Fall 2012 Course OutlineAngela DaqustNo ratings yet
- Carole King - Hard Rock CafeDocument1 pageCarole King - Hard Rock CafeauresmikeNo ratings yet
- Compressed Gas Cylinder Safety GuideDocument1 pageCompressed Gas Cylinder Safety GuideNguyenLinh27No ratings yet
- Gebremichael Te-Ame ThesisDocument146 pagesGebremichael Te-Ame ThesisMichael AbrahaNo ratings yet
- RDGFGDocument4 pagesRDGFGRobin SinghNo ratings yet
- Ai Viva QuestionsDocument13 pagesAi Viva QuestionsNew BornNo ratings yet
- Added by Guest, Last Edited by Guest On Jun 12, 2007 Show CommentDocument5 pagesAdded by Guest, Last Edited by Guest On Jun 12, 2007 Show CommentNarendrareddy RamireddyNo ratings yet
- Ingenieria Basica y Detalle ISADocument50 pagesIngenieria Basica y Detalle ISAdalver17100% (1)
- Computing Discounts Informal AssessmentDocument5 pagesComputing Discounts Informal Assessmentsayer_nicoleNo ratings yet
- Pricerfileinterfacespecification Pfi4Document34 pagesPricerfileinterfacespecification Pfi4nthgrNo ratings yet
- Senior 2 Topic Revision - MCQ Question (Series 2) AnswerDocument10 pagesSenior 2 Topic Revision - MCQ Question (Series 2) AnswerLi Xin FooNo ratings yet
- G006 Sinexcel BESS Micro Grid Solution - MalawiDocument2 pagesG006 Sinexcel BESS Micro Grid Solution - MalawiSyed Furqan RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Checklists & Tips For Energy Efficiency in Thermal UtilitiesDocument3 pagesChecklists & Tips For Energy Efficiency in Thermal UtilitiesEjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Scale NewDocument18 pagesScale NewASDFNo ratings yet
- Widiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pDocument10 pagesWidiastini, P.M.F and Et Al. (2023) - Prima Wiyata Health. 4 (2) : 47-56pnayla nadrahNo ratings yet
- VIT Wow - CFD - AssignementDocument4 pagesVIT Wow - CFD - AssignementShashank AminNo ratings yet
- Icda RulesDocument9 pagesIcda RulesRichard ZhuNo ratings yet