Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jntuh Chemistry Ece Me Ce Chem
Jntuh Chemistry Ece Me Ce Chem
Uploaded by
varshithrajbalnackCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grade 7 Science FinalDocument52 pagesGrade 7 Science FinalZara Rejuso86% (7)
- Biology Lab Report (Respiration of Yeast)Document1 pageBiology Lab Report (Respiration of Yeast)Matthew Chu67% (6)
- Jntuh Chemistry Cse, ItDocument8 pagesJntuh Chemistry Cse, ItvarshithrajbalnackNo ratings yet
- MWEDocument13 pagesMWEsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument10 pagesAnalog CommunicationsmayaNo ratings yet
- JNTUH Applied Physics Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesJNTUH Applied Physics Important QuestionsRaparthi JaychandraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question BankDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bankbhanuc3No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFsravanti kanuguNo ratings yet
- Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Reg. NoDocument2 pagesSalem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Reg. NoAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Question BankDocument10 pagesVLSI Design Question Bankbooks babuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology Question Bank PDFDocument6 pagesEngineering Geology Question Bank PDFSasala Raju100% (1)
- OOP Through Java Question BankDocument6 pagesOOP Through Java Question BankRocky AdityaNo ratings yet
- Course Outcome Eds PDFDocument12 pagesCourse Outcome Eds PDFDileep VarmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question BankDocument8 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question BankdhruvNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesStrength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFpavanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements & InstrumentationSumanth NaniNo ratings yet
- Iare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0Document20 pagesIare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0projects allNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design QB PDFDocument11 pagesCompiler Design QB PDFvinod3457No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2022 AKTUDocument2 pagesChemistry 2022 AKTUVicky SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: 1. Group - A (Short Answer Questions)Document10 pagesObjectives: 1. Group - A (Short Answer Questions)Jinger KartikNo ratings yet
- Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Mahendra College of EngineeringDocument2 pagesSalem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Mahendra College of EngineeringAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Fem - Definitions and Terminology PDFDocument11 pagesFem - Definitions and Terminology PDFSudhakar UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- JNTUH BEE Important QuestionsDocument10 pagesJNTUH BEE Important QuestionsPalle Shivajee GoudNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends Think Ib SlidfesDocument10 pagesPeriodic Trends Think Ib Slidfesamaya chopraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF JntuDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF Jntudivya sakhamuriNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - IIDocument11 pagesStrength of Materials - IIPalle Shivajee GoudNo ratings yet
- RCSDD QBDocument12 pagesRCSDD QBanwesh qNo ratings yet
- CS QBDocument14 pagesCS QBSanjana RoyyapallyNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering QBDocument11 pagesGeotechnical Engineering QBT Rajesh Asst. Prof. - CENo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics - Ii Questionbank: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)Document8 pagesAerodynamics - Ii Questionbank: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)maniNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsDocument12 pagesObjectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsTahseen AnjumNo ratings yet
- CE1006 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesCE1006 Lesson PlanRaja RamachandranNo ratings yet
- B. Tech.: Mechanical Engineering Iv Year, Vii Sem Turbulent Flows BME7001-TEDocument4 pagesB. Tech.: Mechanical Engineering Iv Year, Vii Sem Turbulent Flows BME7001-TESunil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-BTL-QB-with Solutions-2021Document153 pagesChemistry-BTL-QB-with Solutions-2021Mvk MvkNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: (Microwave Engineering)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: (Microwave Engineering)d narsaiahNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBSridhar Koneru VenkkatNo ratings yet
- Group - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDocument15 pagesGroup - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeIshani JhaNo ratings yet
- Subject Unit: Course MaterialDocument20 pagesSubject Unit: Course Materialpathan the creatorNo ratings yet
- TOS SCIENCE 10 1st-4th Quarter 2018-19Document24 pagesTOS SCIENCE 10 1st-4th Quarter 2018-19Marvin ObraNo ratings yet
- CSP Assignment-1Document2 pagesCSP Assignment-1m.revathiNo ratings yet
- Tutorialquestion Bank: Course Title Operations Research Course Code AME021 Class Semester Year Team of InstructorsDocument17 pagesTutorialquestion Bank: Course Title Operations Research Course Code AME021 Class Semester Year Team of Instructors17951A0354 PALIKA SAHITHNo ratings yet
- First Year Syllabus - 2022-23Document25 pagesFirst Year Syllabus - 2022-23Art SplashNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design FundamentalsDocument7 pagesTutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design Fundamentalsvictor kNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Question BankDocument9 pagesComputer Graphics Question BankDr-Samson ChepuriNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer Questionsmighty statusNo ratings yet
- M 403Document10 pagesM 403Dilleswararao ChintalaNo ratings yet
- VEB2113 CourseOutlineDocument2 pagesVEB2113 CourseOutlineHISHAMNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFDocument15 pagesDigital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Part BDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank Part BPradeev BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Works Add SC f5Document7 pagesScheme of Works Add SC f5lelady77No ratings yet
- Ow Power VLSI Circuits and Systems: Course Plan ofDocument9 pagesOw Power VLSI Circuits and Systems: Course Plan ofContent for all CreatorNo ratings yet
- JNTU World: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)Document6 pagesJNTU World: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)Naresh JonnaNo ratings yet
- MP10 1Document12 pagesMP10 1Kartika Sari SubagioNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Tutorial Question BankDocument26 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Tutorial Question Bankdurga sharmaNo ratings yet
- BSc.I - AssignmentDocument7 pagesBSc.I - AssignmentRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering SyllabusDocument11 pagesTransportation Engineering SyllabusGokul KannanNo ratings yet
- Precision Engineering QBDocument8 pagesPrecision Engineering QBNavaneethasanthakumar SNo ratings yet
- Structure and Reactivity of Organic MoleculeDocument36 pagesStructure and Reactivity of Organic MoleculeAppleNo ratings yet
- IARE - CT 2019-2020 CE Question BankDocument9 pagesIARE - CT 2019-2020 CE Question BankT Chaitanya Srikrishna Asst. ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Diatonic Theory: A Mathematically Based Approach to Music FundamentalsFrom EverandFoundations of Diatonic Theory: A Mathematically Based Approach to Music FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. Ii the Chemistry of Initiation of Non-Ringed Monomers/CompoundsFrom EverandNew Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. Ii the Chemistry of Initiation of Non-Ringed Monomers/CompoundsNo ratings yet
- A Selective Strategy For Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based On MolecularDocument6 pagesA Selective Strategy For Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based On MolecularSonyanurizkiNo ratings yet
- TSR 131Document14 pagesTSR 131Prad1979No ratings yet
- Plant-Pathogens-Principles-of-Plant-Pathology (1) - 310-336Document27 pagesPlant-Pathogens-Principles-of-Plant-Pathology (1) - 310-336Pranali SonkusareNo ratings yet
- Compressed Gas Cylinder OJTDocument5 pagesCompressed Gas Cylinder OJTMr SinghNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Data Obat 1 SatuanDocument1,499 pages4.1 Data Obat 1 SatuanCrank ZakaNo ratings yet
- Steel Slag Silo: EL (+) 0.000M FFLDocument4 pagesSteel Slag Silo: EL (+) 0.000M FFLElectrical ShahNo ratings yet
- Comparison On Efficiency of Various Techniques in Biological Treatment of Effluent Water - Final 2Document8 pagesComparison On Efficiency of Various Techniques in Biological Treatment of Effluent Water - Final 2desai sanketNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity of Coarse Aggregate Aashto T 85Document1 pageSpecific Gravity of Coarse Aggregate Aashto T 85HighwayNo ratings yet
- 20180817185410MSDS Cera Expan 250Document3 pages20180817185410MSDS Cera Expan 250Karthi TkNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Olympiad MCQDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRY Olympiad MCQjahangirNo ratings yet
- 23007-Article Text-84279-2-10-20200213-1Document12 pages23007-Article Text-84279-2-10-20200213-1AnuNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical EnergyDocument4 pagesElectrochemical EnergyVia Mae CastillanoNo ratings yet
- 3096-Article Text-9046-1-10-20190712Document3 pages3096-Article Text-9046-1-10-20190712manusia relaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Different Inducers On Ligninolytic Enzyme ActivitiesDocument7 pagesInfluence of Different Inducers On Ligninolytic Enzyme ActivitiesAlina CoralinaNo ratings yet
- SC7620 Mini Sputter Coater Operating Manual: For Technical and Applications Advice Plus Our On-Line Shop For Spares andDocument33 pagesSC7620 Mini Sputter Coater Operating Manual: For Technical and Applications Advice Plus Our On-Line Shop For Spares andatul nalavadeNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals Products ListDocument51 pagesPharmaceuticals Products Listsks65No ratings yet
- Safety Data SheetDocument11 pagesSafety Data SheetLauraNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping NC Ii: Dr. Santiago Dakudao Sr. National High SchoolDocument2 pagesHousekeeping NC Ii: Dr. Santiago Dakudao Sr. National High SchoolLyn V. Estrellado100% (2)
- 2018333049,21 Thesis ProposalDocument15 pages2018333049,21 Thesis ProposalAnonymous aE0YYlCOKNo ratings yet
- OSHA 10+ GuideDocument56 pagesOSHA 10+ GuideAnsarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of NanomaterialsDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of Nanomaterialssandhiya padmanabanNo ratings yet
- Plastic Design GuidelinesDocument241 pagesPlastic Design Guidelines2023ht30006No ratings yet
- TDS 539 Glucamate DOE 120Document1 pageTDS 539 Glucamate DOE 120asesorias9educacionaNo ratings yet
- Furnizori Consumabile - 2018Document4 pagesFurnizori Consumabile - 2018Gina LazaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For General Chemistry 10th Edition Darrell D Ebbing Steven D GammonDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For General Chemistry 10th Edition Darrell D Ebbing Steven D Gammonvisearborist.af0eg100% (50)
- 15-Ktp PRR PipesDocument46 pages15-Ktp PRR PipesmohammedNo ratings yet
- Biocharasconstructionmaterial ReviewDocument15 pagesBiocharasconstructionmaterial ReviewAnura BandaraNo ratings yet
- Chemex DegreaserDocument6 pagesChemex DegreasersidsailNo ratings yet
Jntuh Chemistry Ece Me Ce Chem
Jntuh Chemistry Ece Me Ce Chem
Uploaded by
varshithrajbalnackOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jntuh Chemistry Ece Me Ce Chem
Jntuh Chemistry Ece Me Ce Chem
Uploaded by
varshithrajbalnackCopyright:
Available Formats
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.
in
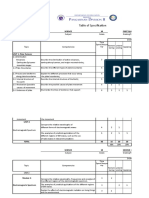
DESCRIPTIVE QUESTIONS: (WITH BLOOMS PHRASES)
UNIT I
S.no Short Answer Questions Blooms
te s
Course
1 What are atomic and molecular orbital?
taxonomy
Level
d
Remembera out come
1
2
3
4
5
Calculate the bond order in molecules of O2, O2-, O22-
Define bond order. Explain the factors affecting it
Write notes on Linear combination of atomic orbitals
U p
What is meant by doping, and how it affects on conduction?
Apply
Remember
Remember
Understand
1
1
1
1
y
+ -
6 Calculate the bond order in molecules of N2 , N2 Apply 1
7
8
i t
What is the reason for crystal field splitting Apply
What are the factors effecting the magnitude of crystal field Understand
splitting
s
1
1
9
10
e r
Explain the effect of doping on conductance Apply
What are the differences between atomic and molecular orbitals Remember
1
1
S.
No
n i v
Long Answer Question Blooms
taxonomy
Level
Course
out
come
1
2
U
Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagrams of N2, O2
factors affecting crystal field splitting?
3 Explain the important postulates of Molecular orbital theory
Explain the CFT splitting in octahedral and tetrahedral geometries?
understand
What is the reason for crystal field splitting and what are the Apply
Understand
1
1
5 Write salient features of CFT? Remember 1
6 Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagrams of F2 and explain Remember 1
its bond order
7 Write a note on LCAO Remember 1
8 Write an account on molecular orbital theory Understand 1
9 Explain about crystal field theory Understand 1
10 Mention the different between bonding orbitals and anti bonding Remember 1
orbitals
UNIT – II
S. Short Answer Questions Blooms Course
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
No taxonomy out come
Level
1 Why are NH4Cl and NH4OH buffer added during the determination Apply 2
of hardness?
2 What is the indicator used in EDTA method? Remember 2
3 A sample of hard water contains 14.6 g of Mg(HCO3)2 and 9.5 g of Apply 2
MgCl2 and 13.6 g of CaSO4. What is the temporary, permanent and
total hardness of the water sample?
4 Explain the role of anion exchange resin. Understand 2
5 How is caustic embrittlement avoided? Understand 2
6 What is carbonate hardness? How can you remove carbonate Remember 2
hardness?
7 Explain why hard water consumes a lot of soap? Apply 2
8 What is the advantage of break-point chlorination?
9 What is the phosphate conditioning?
10 Give the specifications of potable water.
Remember
Understand
Remember
te
2
2
2
s
d a
S.
no
Long Answer Questions
U p Blooms
taxonomy
Level
Course
out
come
y
1 Distinguish between temporary and permanent hardness of water. Understand 2
hardness of water by EDTA method
3 Why is hard water harmful to boilers?
s i t
2 Write a note on complexometric titrations used for estimation of Understand
Understand
2
4
r
Discuss the causes and harmful effects of scale formation.
e
What are the factors that lead to caustic embrittlement in boilers? How Remember 2
5
6
can it be prevented?
n i v
Explain the softening of water by Ion exchange process. Remember
Define Potable water and give an account of disinfection of water by Apply
chlorination and ozonisation.
2
2
water. U
Define Desalination and explain the methods of desalination.
9 Explain the difference between scale and sludge
10 Write note on specification of potable water and its treatment
Understand
8 Write a brief account on internal conditional methods of treatment of Apply
Understand
Apply
2
2
2
2
UNIT – III
S. Short answer type questions Blooms Cour
No taxonomy se out
Level come
1 Write the Nernst equation in terms of reduction potential. Understand 3
2 What is reference electrode? Remember 3
3 What do you mean by a salt bridge? Why is it used? Understand 3
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
4 What is a secondary reference electrode? Apply 3
5 Why is coating of zinc on iron called sacrificial anode Analyse 3
6 What is the difference between primary and secondary cell Understand 3
7 Lead acid battery is not completely sealed – Explain Analyse 3
8 What is an anode material in a lithium ion battery Understand 3
9 Why non aqueous solvent is used in a Lithium ion battery Understand 3
10 What is Dry corrosion? Remember 3
S.No Long Answer Questions Blooms Course
taxonomy out
Level come
1 What do you mean by sacrificial anodic protection explain with Understand 3
2
3
suitable example
Explain the construction and working of Lead acid battery.
How can you determine the PH of an unknown solution by using
Apply
Remember
te
3
3s
4
5
Quinone-Hydrone electrode
Explain Calomel electrode. Mention its advantages.
Design a cell to determine the PH of an aqueous acid unknown
d a
Remember 3
Understand 3
7
solution by using a Calomel electrode
PH of an unknown solution by using glass electrode
U p
What is a Glass electrode? Explain how can you determine the
Explain the mechanism involved in Electro chemical corrosion
Understand 3
Apply 3
8
with reactions
i t y
Write an account of lithium ion battery Understand 3
s
9 Explain the chemical reaction involved in electrochemical Remember 3
r
corrosion
e
10 Iron corrodes faster than aluminium? explain Apply 3
UNIT – IV
S.No
n i v
Short answer questions Blooms
taxonomy
Course
out
3
U What are stereoisomers?
What do you mean by specific rotation?
Differentiate between diasteromers and enantiomers
Level
Understand
Remember
Remember
come
4
4 What is Markownikoff rule Understand 4
5 Allenes do not contain any chiral centre but still exhibit optical Understand 4
activity. Explain
6 Why proxide effect is only confined to addition of only HBr Apply 4
7 State and explain Saytzeff rule? Remember 4
8 Why Markownikoff’s rule fails in the addition of HBr to Apply 4
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
propene in presence of H2O2.
9 Why is rate of SN1 reaction much faster in polar solvents than Apply 4
in a non-polar solvent.
10 How can it be decided whether the following reactions Apply 4
proceeds by SN1and SN2 mechanism
S.No Long answer questions Blooms Course
taxonomy out
Level come
1 What are SN1 and SN2 reactions. Write the mechanism with Understand 4
suitable examples and their stereochemistry.
s
2 Explain different conformations of butane with the potential Understand 4
te
energy diagram
3 What are elimination reactions? Explain Apply 4
4
dehydrohalogenations of alkyl halide with suitable examples.
What is isomerism? How it is classified? Explain with Remember
d a 4
5
suitable examples?
U p
Explain β elimination reaction with a suitable example? Understand 4
ti y
6 State and explain Markownikoff rule with a suitable example? Remember 4
7 What are addition reactions? Explain the possible mechanism Apply 4
e r s
for addition reactions with an example each.
Write synthesis and uses of paracetamol Apply 4
10
n i v
Write synthesis and uses of Aspirin.
Explain how competing E2 and SN2 reactions are affected by Apply
the following factors a) structure of substrate b) reagentc)
Apply 4
U
UNIT – V
solvent
S.No Short answer questions Blooms Course
taxonomy out
Level come
1 With the help of IR how will you distinguish between o-nitro Understand 5
phenol and p- nitrophenol
2 Define the term Red shift and blue shift. Increased conjugation Remember 5
will cause which shift?
3 Find the number of fundamental modes of vibration/ Understand 5
vibrational degrees of freedom in linear and non linear
molecules such as C6H6, CO2, H2O, SO2, N2O, HCN
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
4 What is meant by the term chemical shift explain Understand 5
5 Why C12,O16, O18 and S32 do not exhibit NMR Spectrum Remember 5
6 What is the necessary condition for a molecule to absorb IR Understand 5
radiation?
7 What is selection rule Remember 5
8 How will you distinguish between propanaldehyde and Understand 5
propanone
9 Explain the effect of polar solvents on both n to π* and π to Apply 5
π*
10 CO2 is IR active. Explain Apply 5
S.No Long answer questions Blooms
taxonomy
Level
te s
Course
out
come
a
1 Describe briefly the theory of NMR spectroscopy? What Apply 5
information can be obtained from NMR absorption peaks?
2
examples. Write any 5 applications of UV spectroscopy.
p
Explain the terms chromophore and auxochrome with suitable
d
Understand 5
3 Write any 5 applications of IR spectroscopy
U Understand 5
ti y
4 Write any 5 applications of NMR spectroscopy Remember 5
5 Write the basic principles of IR spectroscopy. Describe Understand 5
6 Schematically
e r s
various molecular vibrations in the technique.
represent and discuss various types of Understand 5
v
*
electronic transitions and hence show that n to π transition is
7 i
the lowest energy demanding among all of them
n
How would you analyze a sample by spectrophotometer Apply 5
9
U method?
What is Beer-Lambert law? Show the absorption is linearly Remember
proportional to concentration of the solution.
Describe various absorption laws involved in UV-Visible Understand
5
5
spectral method. Derive Lambert-Beer’s law.
10 Explain briefly about MRI imaging technique. Apply 5
XI. OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS: JNTUH
UNIT: I
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
1. The bond order of N2 molecule is _______.
a) 2.0 b) 3.0 c) 2.5 d) 1.0
2. The bond order of a molecule can be calculated using MOT as______
3. The electron density of Pi Molecular Orbital along internuclear axis is______.
4. The magnetic nature of O2 molecule is______.
5. The bond energy of N2 is ________than that of O2.
6. Ligands remove the degeneracy of ____________of the metal ion.
7. The most stable amongst the following: O2, O2+, O2–, O2–2 is______.
8. The bond order of F2 molecule is________.
9. Bond order = _______________.
10. What is the bond order of O2 molecule_______.
te s
11. The bond order is ______ proportional to its bond length.
a) directly b) Inversely c) no relation
d a
p
12. Which of the following molecular orbitals have lowest energy?
a) σ2pz b) σ *2pz c) π2px d) π*2px
13. In O2 molecule, the empty molecular orbital is_____
a) σ2S b) σ*2S
14. Which of the following is paramagnetic_____
a) O2– b) CN–
y U
c) σ*2Pz
c) CO
d) σ2Pz
d) NO+
a) O2
a) 1
+
b) O2+
b) 2
s
16. The bond order of O2 molecule is__
t
15. Which among the following will have the highest bond length?
i c) O2–
c) 2.5
d) O2–2
d) 3
a) O2
e r
17. Which of the following is diamagnetic
b) O2+
18. Molecular orbitals are classified as
c) O2– d) O2–2
a) σ
n i v b) π
19. Any p-orbital can accommodate upto
a) 4 electrons b) 6 electrons
c) n
c) 2 electrons
20. In an octahedral crystal field, eg., orbitals are
a) raised the energy by 0.4 ∆0
d) bonding & anti-bonding
d) 8 electrons
b) lowered the energy by 0.6 ∆0
U
UNIT-II
c) lowered the energy by 0.4 ∆0 d) raised the energy by 0.6 ∆0
1. Cation exchange resin contains ___________ mobile ions.
2. Hardness of water is expressed in terms of ____________.
3. The amount of chlorine required to kill bacteria and to remove organic matter is
called________________.
4. CaSO4 causes _____________hardness to water.
5. Addition of chlorine to water produces_________acid which acts as powerful germicide.
6. Hardness that can be easily removed by boiling and filtration is known as_________
hardness.
7. __________is used calgon conditioning.
8. Process of removing salts from water is called as__________.
9. Exhausted anion exchangers are regenerated by using___________.
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
10. Agar-Agar is used in ____________water conditioning.
11. The indicator used for the estimation of total hardness of a given water sample by EDTA
method is.
a) Starch b) EBT c) Ferroin d) Methyl orange
12. Temporary hardness of water is caused due to the presence of.
a) Calcium carbonate b) Calcium chloride c) Magnesium bicarbonate d) None
13. The method used for desalination of water is.
a) zeolite process b) Lime soda process c) Ion exchange process d) Distillation
14. The soft, loose and slimy precipitate formed within the boiler is called.
a) Scale b) Sludge c) embrittlement d) Coagulation
15. Permanent hardness of water is caused due to the presence of.
a) Calcium carbonate b) Calcium chloride c) Magnesium bicarbonate d) None
16. Tannin, Lignin are used for
a) Phosphate conditioning
c) Colloidal conditioning
b) Carbonate conditioning
d) Calgon conditioning
te s
17. Caustic embrittlement is caused due to presence of
a) NaCl b) NaOH c) MgCO3 d) KNO3
d a
p
18. Hard water after passing through cation exchanger is
a) alkaline b) acidic c) neutral d) slightly alkaline
U
19. Hard water + buffer (pH 10) + indicator (EBT) develops_____colour
a) orange b) blue c) pink d) wine-red
a) 10 mg/L CaSO4
i y
20. Which of the following water sample has maximum hardness containing?
t
b) 10 mg/L MgCl2 c) 10 mg/L MgSO4 d) 10 mg/L CaCl2
UNIT – III
e r s
v
1. _________electrode is the one which produces stable and reproducible potential.
i
2. In Daniel cell_____________is used as an anode, ________is used as a cathode.
n
3. Tinning is _______________coating.
4. Lead acid battery is a _______________type of battery.
U
5. ____________batteries cannot be recharged and reused.
6. In lead acid battery, _____________is used a cathode.
7. The emf of the cell Zn/Zn+2 (1 M) // Cu+2/Cu is _________volts.
8. Oxidation corrosion in absence of moisture is ____________corrosion.
9. Galvanizing is a process of coating __________on iron.
10. ___________coating is a most preferable than the cathodic coating.
11. Which of the following cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
a) Galvanic cell b) Daniel cell c) Dry cell d) all
12. In the anodic chamber which reaction takes place.
a) Oxidation b) Reduction c) Addition d) Substitution
13. In the cathodic chamber which reaction takes place.
a) Oxidation b) Reduction c) Addition d) Substitution
14. Origin of electrode potential is explained in __.
a) Nernst theory b) Helmholtz double layer theory
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
c) Galvanic theory d) Electrochemical theory
15. In two half cells, the one which is having high negative value acts as ___.
a) anode b) Cathode c) Dry cell d) None
16. Rusting of iron is an example for _____.
a) Dry corrosion b) electrochemical corrosion c) acid corrosion d) None
17. Coating used for the iron container used for food package coated with _______.
a) Zn b) Sn c) Pb d) Al
18. The potentials of the two electrodes used in a cell are 0.24 V and 0.6 V. The emf of the
cell formed by the two electrodes are
a) 0.36 V b) -0.36 V c) 0.84 V d) -0.84 V
19. One of the common sacrificial anodic metal is
a) Zinc b) Magnesium c) Copper d) Titanium
20. During discharging operation in lead-acid cell, the concentration of H2SO4__
a) decreases b) not affected
UNIT - IV
c) increased d) H2SO4 is not used
te s
d a
1. A molecule that can’t be superimposed on its mirror image is called _________
p
2. The ___________confirmation of n-butane is its most stable confirmation.
3. ___________states that in dehydrohalogenation, the more stable alkene, faster is formed.
U
4. A compound is said to be ______________, when it rotates the plan polarised light.
5. Polar protic solvents favour _______reaction mechanism.
y
6. HBr addition to propene in presence of peroxides gives ___________as a major product.
t
7. In SN2 mechanism, the stereochemistry of the compound ___________.
i
8. Write the structure of aspirin_____________.
s
9. Write the structure of paracetamol ____________.
r
10. Electrophilic reagents are ________charged and electron _________compounds.
e
11. The number of stereo isomers present in tartaric acid
a) 1
i v
b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
12. The correct reactivity order of A) 10 alkyl halide, B) 20 alkyl halide C) 30 alkyl halide
n
toward SN1 reaction
a) A>B>C b) B>C>A c) C>A>B d) C>B>A
U
13. The number of optically active isomers in glucose
a) 4 b) 8
a) A >B >C
c) 16
b) B > C >A
d) 2
14. The correct reactivity order of A) 10 alkyl halide, B) 20 alkyl halide C) 30 alkyl halide
towards SN2 reaction
c) C > A >B d) C > B >A
15. The major product in the addition of HBr to propene in presence of benzoyl peroxide
a) 1-bromopropane b) 2- bromopropane c) 1,2 ibromopropane d) n-propane
16. The major product in the addition of HBr to propene
b) 1-bromopropane b) 2- bromopropane c) 1,2 ibromopropane d) n-propane
17. Which among the following will show highest reactivity in nucleophilic substitution
reaction
a) CH3F b) CH3Br c) CH3Cl d) CH3I
1
18. SN mechanism for the hydrolysis of an alkyl halide involves the formation of
intermediate
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
www.android.universityupdates.in | www.universityupdates.in | www.ios.universityupdates.in
a) carbocation b) carbanion c) free radical d) carbene
19. Which of the following is an electrophile
a) NH3 b) H2O c) SO3 d) ROH
20. Which of the following will undergo homolytic fission.
a) Br2 b) HBr c) H2O d) HCl
UNIT - V
1. Number of vibrational degrees of freedom in HCN _______________
2. A molecule can absorb IR radiation only when its absorption cause a change in
_______________.
3. A set of protons with same chemical environment are called as ______________ protons.
4. The finger print region is between _______________ and _______________.
_______________.
te s
5. The splitting of NMR signal lines in the spectrum into two or more components is called
6. _______________ is used as reference standard for measurement of chemical shifts in
NMR spectroscopy.
d a
7. In UV-Visible spectroscopy, shift of absorption maxima (λmax) to shorter wavelength is
p
called _______________
8. The functional group responsible for absorption in UV-visible region is called _________
U
9. In NMR spectroscopy, the radiation used for nuclear excitation is called ____________
10. In IR spectroscopy, no. of fundamental modes of vibrations for H2O is __________.
a) CH3I b) CH3Br
i t y
11. Which of the following compounds have most deshielded protons
c) CH3Cl
1
d) CH4
12. How many signals would the following molecule show in its H NMR spectrum? of
benzene
a) 5 b)1
r
c) 6 d) 8
e s
13. In NMR spectroscopy, the radiation used for nuclear excitation is
n i v
a) microwaves
a) 1:3:2:1 b)1:2:3:1
b) IR c) Radio wave
14. A quartet has intensity ratio
c)1:3:3:1
15. Increasing order of wavelength is
d) UV
d)1:1:2:3
U a) x-ray, UV, IR, microwave b) microwave, x-ray, UV, IR, c) x-ray,IR, microwave,
UV d) UV, IR, microwave, x-ray
16. Number of vibrational degrees of freedom for CO2 is
a) 2 b)3 c)4 d)1
17. The value of TMS protons in δ scale is
a) 10 b)0 c)not predictable d)-10
18. Radiation source for UV-Visible spectrophotometer is
a) Tungsten filament lamp b) Nernst glower
c) xenon discharge tube d) Heated nichrome wire
19. When there are n-protons adjacent to a given proton, the multiplying of its NMR peak is
given by
a) 2n+1 b)n+1 c) 2n-1 d) n2
20. Which of the following molecules will not give rotational spectra?
a) CO b) HCl c) HBr d) N2
www.android.previousquestionpapers.com | www.previousquestionpapers.com | www.ios.previousquestionpapers.com
You might also like
- Grade 7 Science FinalDocument52 pagesGrade 7 Science FinalZara Rejuso86% (7)
- Biology Lab Report (Respiration of Yeast)Document1 pageBiology Lab Report (Respiration of Yeast)Matthew Chu67% (6)
- Jntuh Chemistry Cse, ItDocument8 pagesJntuh Chemistry Cse, ItvarshithrajbalnackNo ratings yet
- MWEDocument13 pagesMWEsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument10 pagesAnalog CommunicationsmayaNo ratings yet
- JNTUH Applied Physics Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesJNTUH Applied Physics Important QuestionsRaparthi JaychandraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question BankDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bankbhanuc3No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFsravanti kanuguNo ratings yet
- Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Reg. NoDocument2 pagesSalem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Reg. NoAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Question BankDocument10 pagesVLSI Design Question Bankbooks babuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology Question Bank PDFDocument6 pagesEngineering Geology Question Bank PDFSasala Raju100% (1)
- OOP Through Java Question BankDocument6 pagesOOP Through Java Question BankRocky AdityaNo ratings yet
- Course Outcome Eds PDFDocument12 pagesCourse Outcome Eds PDFDileep VarmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question BankDocument8 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question BankdhruvNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesStrength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFpavanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements & InstrumentationSumanth NaniNo ratings yet
- Iare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0Document20 pagesIare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0projects allNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design QB PDFDocument11 pagesCompiler Design QB PDFvinod3457No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2022 AKTUDocument2 pagesChemistry 2022 AKTUVicky SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: 1. Group - A (Short Answer Questions)Document10 pagesObjectives: 1. Group - A (Short Answer Questions)Jinger KartikNo ratings yet
- Salem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Mahendra College of EngineeringDocument2 pagesSalem-Campus, Attur Main Road, Minnampalli, Salem - 636 106.: Mahendra College of EngineeringAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Fem - Definitions and Terminology PDFDocument11 pagesFem - Definitions and Terminology PDFSudhakar UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- JNTUH BEE Important QuestionsDocument10 pagesJNTUH BEE Important QuestionsPalle Shivajee GoudNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends Think Ib SlidfesDocument10 pagesPeriodic Trends Think Ib Slidfesamaya chopraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF JntuDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF Jntudivya sakhamuriNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - IIDocument11 pagesStrength of Materials - IIPalle Shivajee GoudNo ratings yet
- RCSDD QBDocument12 pagesRCSDD QBanwesh qNo ratings yet
- CS QBDocument14 pagesCS QBSanjana RoyyapallyNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering QBDocument11 pagesGeotechnical Engineering QBT Rajesh Asst. Prof. - CENo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics - Ii Questionbank: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)Document8 pagesAerodynamics - Ii Questionbank: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)maniNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsDocument12 pagesObjectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsTahseen AnjumNo ratings yet
- CE1006 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesCE1006 Lesson PlanRaja RamachandranNo ratings yet
- B. Tech.: Mechanical Engineering Iv Year, Vii Sem Turbulent Flows BME7001-TEDocument4 pagesB. Tech.: Mechanical Engineering Iv Year, Vii Sem Turbulent Flows BME7001-TESunil Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-BTL-QB-with Solutions-2021Document153 pagesChemistry-BTL-QB-with Solutions-2021Mvk MvkNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: (Microwave Engineering)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: (Microwave Engineering)d narsaiahNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBSridhar Koneru VenkkatNo ratings yet
- Group - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDocument15 pagesGroup - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeIshani JhaNo ratings yet
- Subject Unit: Course MaterialDocument20 pagesSubject Unit: Course Materialpathan the creatorNo ratings yet
- TOS SCIENCE 10 1st-4th Quarter 2018-19Document24 pagesTOS SCIENCE 10 1st-4th Quarter 2018-19Marvin ObraNo ratings yet
- CSP Assignment-1Document2 pagesCSP Assignment-1m.revathiNo ratings yet
- Tutorialquestion Bank: Course Title Operations Research Course Code AME021 Class Semester Year Team of InstructorsDocument17 pagesTutorialquestion Bank: Course Title Operations Research Course Code AME021 Class Semester Year Team of Instructors17951A0354 PALIKA SAHITHNo ratings yet
- First Year Syllabus - 2022-23Document25 pagesFirst Year Syllabus - 2022-23Art SplashNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design FundamentalsDocument7 pagesTutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design Fundamentalsvictor kNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Question BankDocument9 pagesComputer Graphics Question BankDr-Samson ChepuriNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer Questionsmighty statusNo ratings yet
- M 403Document10 pagesM 403Dilleswararao ChintalaNo ratings yet
- VEB2113 CourseOutlineDocument2 pagesVEB2113 CourseOutlineHISHAMNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFDocument15 pagesDigital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Part BDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank Part BPradeev BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Works Add SC f5Document7 pagesScheme of Works Add SC f5lelady77No ratings yet
- Ow Power VLSI Circuits and Systems: Course Plan ofDocument9 pagesOw Power VLSI Circuits and Systems: Course Plan ofContent for all CreatorNo ratings yet
- JNTU World: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)Document6 pagesJNTU World: Part - A (Short Answer Questions)Naresh JonnaNo ratings yet
- MP10 1Document12 pagesMP10 1Kartika Sari SubagioNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Tutorial Question BankDocument26 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Tutorial Question Bankdurga sharmaNo ratings yet
- BSc.I - AssignmentDocument7 pagesBSc.I - AssignmentRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engineering SyllabusDocument11 pagesTransportation Engineering SyllabusGokul KannanNo ratings yet
- Precision Engineering QBDocument8 pagesPrecision Engineering QBNavaneethasanthakumar SNo ratings yet
- Structure and Reactivity of Organic MoleculeDocument36 pagesStructure and Reactivity of Organic MoleculeAppleNo ratings yet
- IARE - CT 2019-2020 CE Question BankDocument9 pagesIARE - CT 2019-2020 CE Question BankT Chaitanya Srikrishna Asst. ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Diatonic Theory: A Mathematically Based Approach to Music FundamentalsFrom EverandFoundations of Diatonic Theory: A Mathematically Based Approach to Music FundamentalsNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. Ii the Chemistry of Initiation of Non-Ringed Monomers/CompoundsFrom EverandNew Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. Ii the Chemistry of Initiation of Non-Ringed Monomers/CompoundsNo ratings yet
- A Selective Strategy For Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based On MolecularDocument6 pagesA Selective Strategy For Determination of Ascorbic Acid Based On MolecularSonyanurizkiNo ratings yet
- TSR 131Document14 pagesTSR 131Prad1979No ratings yet
- Plant-Pathogens-Principles-of-Plant-Pathology (1) - 310-336Document27 pagesPlant-Pathogens-Principles-of-Plant-Pathology (1) - 310-336Pranali SonkusareNo ratings yet
- Compressed Gas Cylinder OJTDocument5 pagesCompressed Gas Cylinder OJTMr SinghNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Data Obat 1 SatuanDocument1,499 pages4.1 Data Obat 1 SatuanCrank ZakaNo ratings yet
- Steel Slag Silo: EL (+) 0.000M FFLDocument4 pagesSteel Slag Silo: EL (+) 0.000M FFLElectrical ShahNo ratings yet
- Comparison On Efficiency of Various Techniques in Biological Treatment of Effluent Water - Final 2Document8 pagesComparison On Efficiency of Various Techniques in Biological Treatment of Effluent Water - Final 2desai sanketNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity of Coarse Aggregate Aashto T 85Document1 pageSpecific Gravity of Coarse Aggregate Aashto T 85HighwayNo ratings yet
- 20180817185410MSDS Cera Expan 250Document3 pages20180817185410MSDS Cera Expan 250Karthi TkNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Olympiad MCQDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRY Olympiad MCQjahangirNo ratings yet
- 23007-Article Text-84279-2-10-20200213-1Document12 pages23007-Article Text-84279-2-10-20200213-1AnuNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical EnergyDocument4 pagesElectrochemical EnergyVia Mae CastillanoNo ratings yet
- 3096-Article Text-9046-1-10-20190712Document3 pages3096-Article Text-9046-1-10-20190712manusia relaNo ratings yet
- Influence of Different Inducers On Ligninolytic Enzyme ActivitiesDocument7 pagesInfluence of Different Inducers On Ligninolytic Enzyme ActivitiesAlina CoralinaNo ratings yet
- SC7620 Mini Sputter Coater Operating Manual: For Technical and Applications Advice Plus Our On-Line Shop For Spares andDocument33 pagesSC7620 Mini Sputter Coater Operating Manual: For Technical and Applications Advice Plus Our On-Line Shop For Spares andatul nalavadeNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals Products ListDocument51 pagesPharmaceuticals Products Listsks65No ratings yet
- Safety Data SheetDocument11 pagesSafety Data SheetLauraNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping NC Ii: Dr. Santiago Dakudao Sr. National High SchoolDocument2 pagesHousekeeping NC Ii: Dr. Santiago Dakudao Sr. National High SchoolLyn V. Estrellado100% (2)
- 2018333049,21 Thesis ProposalDocument15 pages2018333049,21 Thesis ProposalAnonymous aE0YYlCOKNo ratings yet
- OSHA 10+ GuideDocument56 pagesOSHA 10+ GuideAnsarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of NanomaterialsDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of Nanomaterialssandhiya padmanabanNo ratings yet
- Plastic Design GuidelinesDocument241 pagesPlastic Design Guidelines2023ht30006No ratings yet
- TDS 539 Glucamate DOE 120Document1 pageTDS 539 Glucamate DOE 120asesorias9educacionaNo ratings yet
- Furnizori Consumabile - 2018Document4 pagesFurnizori Consumabile - 2018Gina LazaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For General Chemistry 10th Edition Darrell D Ebbing Steven D GammonDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For General Chemistry 10th Edition Darrell D Ebbing Steven D Gammonvisearborist.af0eg100% (50)
- 15-Ktp PRR PipesDocument46 pages15-Ktp PRR PipesmohammedNo ratings yet
- Biocharasconstructionmaterial ReviewDocument15 pagesBiocharasconstructionmaterial ReviewAnura BandaraNo ratings yet
- Chemex DegreaserDocument6 pagesChemex DegreasersidsailNo ratings yet