Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ELEC4612 - Per Unit System Topic Summary
ELEC4612 - Per Unit System Topic Summary
Uploaded by
Rizanda LeihituOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ELEC4612 - Per Unit System Topic Summary
ELEC4612 - Per Unit System Topic Summary
Uploaded by
Rizanda LeihituCopyright:
Available Formats
ELEC4612 Topic Summary
Chapter 3: Per Unit System
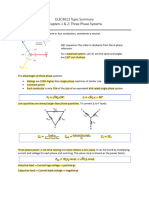
Single Line Diagrams
One-line diagrams are a graphical single-phase representation of a balanced three phase power
system. Adding equivalent circuits of network elements gives a reactance / impedance diagram.
Single Line Diagram Reactance Diagram
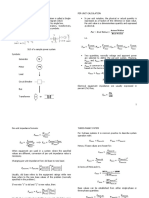
The Per-Unit System
Simplifies analysis of a power system by representing everything in terms of base parameters.
Normally base parameters of |V| and |S| are chosen initially.
𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑘𝑉 2
𝑏 𝑆𝑏
𝑝𝑢 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 = 𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑍𝑏 = 𝑀𝑉𝐴 𝐼𝑏 = 3𝑉
𝑏 √ 𝑏
In both ∆ and Y connected circuits |𝐼𝑝,𝑝𝑢 = 𝐼𝑙,𝑝𝑢 | and |𝑉𝑝,𝑝𝑢 = 𝑉𝑙,𝑝𝑢 |. In the per unit system, three
phase power becomes equivalent to single phase → 𝑆𝑝𝑢 = 𝑉𝑝𝑢 𝐼 ∗ 𝑝𝑢
To convert pu quantities to a different base quantity use:
𝑆𝑛𝑒𝑤 𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑑 2
𝑍𝑝𝑢 = 𝑍𝑝𝑢,𝑜𝑙𝑑 (
𝑆𝑜𝑙𝑑 𝑉𝑛𝑒𝑤
)
Synchronous Machines
The generator ratings are typically chosen as the base quantities for the power system.
In the equivalent impedance circuit 𝑅𝑎 is considered negligible.
Transformers
Transformers have one VA base throughout the circuit. The voltage base changes across sides based
on the turns ratio of the transformer.
𝑁2
𝑉2,𝑏 = 𝑉 𝑆𝑏 = Constant
𝑁1 1,𝑏
This means that 𝑉1,𝑝𝑢 = 𝑉2,𝑝𝑢 , 𝐼1,𝑝𝑢 = 𝐼2,𝑝𝑢 , 𝑆1,𝑝𝑢 = 𝑆2,𝑝𝑢 and 𝑍1,𝑝𝑢 = 𝑍2,𝑝𝑢 . A transformer is
represented by a single impedance in pu analysis.
Three phase transformers have 4 possible arrangements based on combinations of ∆ and Y
connections. Base impedance transfers are the same as in single phase transformers. ∆-Y and Y-∆
transformers have an inherent phase shift of 30°, with Y side voltages and currents leading the ∆
side. If 3 single-phase transformers are connected to make a 3-phase transformer, add power rating
ratings together to get the base value of |𝑆𝑏 |
Transmission Lines
In equivalent circuits, all lines are short unless given a half-line charging susceptance. In this case
assume that specific line to be a medium line represented by the pi-model.
Reactance Diagrams
Created by replacing network components in an SLD by their equivalent circuit. It is assumed that
the system is balanced (𝐼𝑁 = 0) and that resistances are negligible. To construct:
1. Choose an appropriate common MVA base for the system.
2. Consider the system to be divided into a number of sections by transformers. Choose an
appropriate kV base in one of the sections. Calculate kV bases of other sections based on
transformer turns ratios.
3. Calculate per unit values of voltages and impedances in each section and connect them up
as per the topology of the OLD. The result is a single-phase per unit impedance diagram.
You might also like
- 04-HW 04 Soln Face PDFDocument12 pages04-HW 04 Soln Face PDFBryan DavisNo ratings yet
- F120 - F160 Peco ManualDocument44 pagesF120 - F160 Peco ManualBernie WireNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Power System II-Lec01Document26 pagesAnalysis of Power System II-Lec01سعدالدين مالك الرفاعي عبدالرحمن100% (1)
- Make An Iron Man Arc Reactor PDFDocument15 pagesMake An Iron Man Arc Reactor PDFAltemir Manzanete38% (8)
- Lec 1Document14 pagesLec 1Chamod DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis-Unit-I-Q-ADocument3 pagesPower System Analysis-Unit-I-Q-Asulthan_81No ratings yet
- Chapter SixDocument30 pagesChapter Sixmelkamuab16No ratings yet
- Syllabus:: Electrical Dept. Electrical Power III Dr. Omar AlazzawiDocument97 pagesSyllabus:: Electrical Dept. Electrical Power III Dr. Omar AlazzawiAkram KhasheaNo ratings yet
- DET50083 Topic 3 Fault Current CalculationDocument19 pagesDET50083 Topic 3 Fault Current Calculation25det20f1062No ratings yet
- BEE Star Delta ConnectionDocument9 pagesBEE Star Delta ConnectiondikshaNo ratings yet
- EEE305 Part01Document43 pagesEEE305 Part01qwertNo ratings yet
- Preview Per Unit Systems Rev 4Document18 pagesPreview Per Unit Systems Rev 4moau2013No ratings yet
- Lecture No. 3 - Per-Unit System and Impedance DiagramDocument4 pagesLecture No. 3 - Per-Unit System and Impedance DiagramSteven John De VeraNo ratings yet
- chpt12 2Document15 pageschpt12 2mksayshiNo ratings yet
- EE423 Fault Analysis NotesDocument26 pagesEE423 Fault Analysis NotesadnanNo ratings yet
- A.... Wattmeters & Measurement of PowerDocument22 pagesA.... Wattmeters & Measurement of PowerTajammul HussainNo ratings yet
- Per Unit CalculationsDocument3 pagesPer Unit CalculationssupernaenergyNo ratings yet
- Tsaadiquu PDFDocument31 pagesTsaadiquu PDFtadepeace23No ratings yet
- Lec 3 and 4 (Week2)Document21 pagesLec 3 and 4 (Week2)knowledge engineeringNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument40 pagesPower System AnalysisAkhtarNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Lec1Document22 pagesPower System Analysis Lec1Adel El-NahasNo ratings yet
- LFSCDocument79 pagesLFSCIppo MakunouchiNo ratings yet
- L3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 2 PDFDocument9 pagesL3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 2 PDFVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- 5.power System RepresentationDocument34 pages5.power System RepresentationTakawiraNo ratings yet
- Per Unit SystemDocument11 pagesPer Unit SystemKyla BelgadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument23 pagesChapter TwoMagarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- Polyphase Systems: 1. Higher RatingDocument7 pagesPolyphase Systems: 1. Higher RatingTirso MontehermosoNo ratings yet
- PE351 Lect4 2020Document31 pagesPE351 Lect4 2020Abdul RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Ee 308Document19 pagesEe 308catdogsunmoon12No ratings yet
- Grob Basic Electronics: Alternating Current CircuitsDocument11 pagesGrob Basic Electronics: Alternating Current CircuitsRebecca ElliottNo ratings yet
- Power System Representation - (Upto 09-02-16)Document16 pagesPower System Representation - (Upto 09-02-16)Shahab SaqibNo ratings yet
- Ü9 Basics On Electrical Power Grids - SolutionsDocument18 pagesÜ9 Basics On Electrical Power Grids - SolutionshaxanNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document18 pagesWeek 4Syed Faras HaiderNo ratings yet
- Per-Unit System2009-3Document26 pagesPer-Unit System2009-3Akinbode Sunday Oluwagbenga100% (1)
- ECEN 2633 Chapter 11Document6 pagesECEN 2633 Chapter 11Akira ZamudioNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Voltage Stability StudiesDocument13 pagesUnit 4 Voltage Stability StudiesAditya AdityaNo ratings yet
- Power System EngineeringDocument13 pagesPower System EngineeringNazmul IslamNo ratings yet
- Power System QADocument10 pagesPower System QARohit KhajuriaNo ratings yet
- Module5 Polyphase Unbalanced X Wattmeter X PerUnit X Symmetrical ComponetsDocument6 pagesModule5 Polyphase Unbalanced X Wattmeter X PerUnit X Symmetrical Componetsaesma21ur1459No ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components & Faults CalculationsDocument26 pagesSymmetrical Components & Faults CalculationsRTNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Part 1) Improved Teaching-Learning Delivery MethodsDocument12 pagesUnit 1 (Part 1) Improved Teaching-Learning Delivery Methods1NT20EE021 AKANKSHNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2023 10319526Document13 pagesMUCLecture 2023 10319526Mustafa AlhumayreNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis - I (17ee62) : Availaible At: VTU HUB (Android App)Document20 pagesPower System Analysis - I (17ee62) : Availaible At: VTU HUB (Android App)ShashankaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power TransmissionDocument508 pagesElectrical Power TransmissiontabishcloudNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Transmission (EE-352) : Presenter: Dr. Umbrin Sultana Assistantprofessor Eed, NeduetDocument81 pagesElectrical Power Transmission (EE-352) : Presenter: Dr. Umbrin Sultana Assistantprofessor Eed, NeduetWarishaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence ImpedanceDocument8 pagesElectrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence ImpedanceMehrdad Nirui100% (1)
- Module4 CompleteDocument46 pagesModule4 CompletePrathamNo ratings yet
- 7EN52-0464-00 - Power Measurement White Paper v5 PDFDocument8 pages7EN52-0464-00 - Power Measurement White Paper v5 PDFmemo2912No ratings yet
- Experiment # 01Document46 pagesExperiment # 01Adeel Ahmad WattooNo ratings yet
- Ee 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesEe 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersSandhosh RajaNo ratings yet
- General Safety Measures of Electromechanical System LabDocument7 pagesGeneral Safety Measures of Electromechanical System LabAbdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram: Simplified Single-Phase Balanced Three-Phase Single Line Apparatus SymbolsDocument25 pagesOne-Line Diagram: Simplified Single-Phase Balanced Three-Phase Single Line Apparatus SymbolsSafina SygNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document30 pagesUnit 6Utkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Asymmetrical Waveform Generation For Fault Testing of Grid Connected Solar InvertersDocument7 pagesAsymmetrical Waveform Generation For Fault Testing of Grid Connected Solar InvertersDean MillareNo ratings yet
- Ee 1351 Power System AnalysisDocument31 pagesEe 1351 Power System AnalysisStephen Kenth La GuerreNo ratings yet
- 2.single Line Diagram L2Document12 pages2.single Line Diagram L2Rajat Rai100% (1)
- Power Measurements Under Nonsinusoidal Conditions : A Thesis in Electrical EngineeringFrom EverandPower Measurements Under Nonsinusoidal Conditions : A Thesis in Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Nerc Bal-003-1Document12 pagesNerc Bal-003-1Rizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- ELEC4612 - 3 Phase Systems Topic SummaryDocument1 pageELEC4612 - 3 Phase Systems Topic SummaryRizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- z5492803 - ELEC9712 Mid Term Exercise - Ver02Document5 pagesz5492803 - ELEC9712 Mid Term Exercise - Ver02Rizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exercise 4Document8 pagesMid Term Exercise 4Rizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Iec 62053-22 Tahun 2003Document6 pagesIec 62053-22 Tahun 2003Rizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic ION8650 User GuideDocument228 pagesPowerLogic ION8650 User GuideRizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Mu - JSP Unit 2Document33 pagesMu - JSP Unit 2Rizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Iec62053-22 (Ed1.0) en DDocument6 pagesIec62053-22 (Ed1.0) en DRizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- 8650 CatalogueDocument8 pages8650 CatalogueRizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Power Quality ReportDocument10 pagesPower Quality ReportRizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Me Energy Systems Engineering: (Two Years Full Time)Document2 pagesMe Energy Systems Engineering: (Two Years Full Time)Rizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Cvojzp - 18 Jul 2019Document1 pageCvojzp - 18 Jul 2019Rizanda LeihituNo ratings yet
- Investigation To Improve The Control andDocument248 pagesInvestigation To Improve The Control andUday KumarNo ratings yet
- Study On The Effects of ElectromagnetsDocument6 pagesStudy On The Effects of ElectromagnetsDrake Athenaeus CaminongNo ratings yet
- Section 16E Fire Alarm and Interactive Detection SystemDocument25 pagesSection 16E Fire Alarm and Interactive Detection SystemMark Roger II HuberitNo ratings yet
- Audio StandardsDocument8 pagesAudio Standardsyomama3100% (1)
- ZCP 515-33KV Twin FDRDocument21 pagesZCP 515-33KV Twin FDRVeera ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Z80-Playground V 1 2Document4 pagesSchematic Z80-Playground V 1 2Matias Nicolas Romero Romero100% (1)
- Unitronic® Liyy (TP) : Product InformationDocument3 pagesUnitronic® Liyy (TP) : Product InformationSimen EllingsenNo ratings yet
- Hfx150 HF Long WireDocument2 pagesHfx150 HF Long WireShaunVermaakNo ratings yet
- Anit-Reverse: Current SolutionsDocument6 pagesAnit-Reverse: Current SolutionsDan DepNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Magnetism - Practice TestDocument5 pagesElectric Fields and Magnetism - Practice Testharkeerat singhNo ratings yet
- 61246904-80 - Plus Remotely Mounted IO Box - R03Document26 pages61246904-80 - Plus Remotely Mounted IO Box - R03juanNo ratings yet
- AUTOPULSE 4XTM Transmitter ModuleDocument1 pageAUTOPULSE 4XTM Transmitter Moduleordonez66No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesAbaid UllahNo ratings yet
- Ignition Coil Tester: Operating ManualDocument28 pagesIgnition Coil Tester: Operating ManualDJORJENo ratings yet
- Power Your Signal: Antenna SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPower Your Signal: Antenna SpecificationsДмитрийNo ratings yet
- X300 Series Transmitter Product Sheet Overview 27 Apr 2017Document2 pagesX300 Series Transmitter Product Sheet Overview 27 Apr 2017S.SasiNo ratings yet
- Lab12 Design of A Combinational Circuit (BCD To 7-Segment Decoder) ND Voting Machine DesignDocument5 pagesLab12 Design of A Combinational Circuit (BCD To 7-Segment Decoder) ND Voting Machine DesignAisha SheikhNo ratings yet
- JNTUA R20 B.Tech CSE Course Structure 2020 21.Document52 pagesJNTUA R20 B.Tech CSE Course Structure 2020 21.Srinath MNo ratings yet
- b9. Vibration Transmitter (Dual Channel) - Rokade - vms800Document2 pagesb9. Vibration Transmitter (Dual Channel) - Rokade - vms800Harshvardhan ShahNo ratings yet
- Different Types of LightsDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of LightsAnusha SawhneyNo ratings yet
- Directional Spool Valves, Direct Operated, With Solenoid ActuationDocument20 pagesDirectional Spool Valves, Direct Operated, With Solenoid ActuationSaber LeffiNo ratings yet
- Low Frequency TransientsDocument26 pagesLow Frequency TransientsJosNo ratings yet
- Advanced Switching Solutions: FeaturesDocument4 pagesAdvanced Switching Solutions: Featuresraza239No ratings yet
- DF13 4S 1.25C - CL0536 0003 0 00 - Catalog - D31687 - enDocument12 pagesDF13 4S 1.25C - CL0536 0003 0 00 - Catalog - D31687 - enkillianNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument25 pagesTransformersweda walata heduwaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ExmplesDocument8 pagesModule 2 Exmplesexplainer02222No ratings yet
- PULSE SOLO INTERACTIVE Instructions Colour 2c0bc9d65fDocument2 pagesPULSE SOLO INTERACTIVE Instructions Colour 2c0bc9d65fthundert9324No ratings yet
- MEI633 Maintenance & Trouble Shooting Hand BookDocument32 pagesMEI633 Maintenance & Trouble Shooting Hand BookRanjeet Singh100% (1)