Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsEconomic Growth
Economic Growth
Uploaded by
Ahmed BahaaThe document discusses economic growth and key economic concepts related to measuring and understanding economic growth. It covers definitions of economic growth, how it is measured using real GDP, factors that influence long-term economic growth such as higher standards of living, calculations of economic growth rates using real GDP data from different countries, the rule of 70 for estimating growth rate doubling times, aggregate production functions, labor productivity, and factors that influence labor supply and demand in markets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionFrom EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Celsozeca2011No ratings yet
- LRA CITIZEN CHARTER HANDBOOK (Form) - FINAL 03122020 PDFDocument349 pagesLRA CITIZEN CHARTER HANDBOOK (Form) - FINAL 03122020 PDFCharmaine Coleta100% (2)
- Ey Ifrs 10 Consolidation For Fund Managers PDFDocument32 pagesEy Ifrs 10 Consolidation For Fund Managers PDFCindy Yin100% (2)
- Midterm 1 Mock Exam With AnswersDocument9 pagesMidterm 1 Mock Exam With AnswersSally ZhuNo ratings yet
- WKSHT Macro Unit3 Lesson3 Act23 KeyDocument10 pagesWKSHT Macro Unit3 Lesson3 Act23 KeyCarl WeinfieldNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 QuestionsDocument8 pagesTutorial 8 QuestionsJudah SaliniNo ratings yet
- Topik Economic GrowthDocument11 pagesTopik Economic GrowthmbevenNo ratings yet
- QUIZ CH 23 Topik Economic Growth (Tanpa Jawaban)Document12 pagesQUIZ CH 23 Topik Economic Growth (Tanpa Jawaban)mbevenNo ratings yet
- CH13Document12 pagesCH13nbrxf9mg2mNo ratings yet
- Macro Quiz 5 PDFDocument4 pagesMacro Quiz 5 PDFcvofoxNo ratings yet
- MCQs Inflation Business Cycle - EditedDocument5 pagesMCQs Inflation Business Cycle - EditedSadia IlyasNo ratings yet
- Macro PracticeDocument32 pagesMacro PracticecholoNo ratings yet
- 1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Document6 pages1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Haifa Al-humayydNo ratings yet
- Macro - InteDocument7 pagesMacro - InteHilary ChoiNo ratings yet
- Baims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFDocument5 pagesBaims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFShahadNo ratings yet
- Study Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Document8 pagesStudy Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Kiran KachhawahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 MCBDocument6 pagesChapter 8 MCBHunter KellettNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Document31 pagesIntermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Ceren Gökçe KeskinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank 2Document6 pagesTest Bank 2Nouran BakerNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Sample MCQ (4-8)Document13 pagesTest 2 Sample MCQ (4-8)gg ggNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 ECON 343Document7 pagesAssignment 5 ECON 343Jack BNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Chapter 8 Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesMacroeconomics Chapter 8 Multiple ChoiceGene'sNo ratings yet
- ECON 1010 FinalDocument30 pagesECON 1010 FinalMaliha Rubaba FarhadNo ratings yet
- University of Cape Coast College of Humanities and Legal Studies School of Economics Department of Economic Studies Tutorial Set Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cape Coast College of Humanities and Legal Studies School of Economics Department of Economic Studies Tutorial Set Multiple Choice QuestionsHislord BrakohNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm1Document6 pagesPractice Midterm1Bahar SamiNo ratings yet
- ECON 102 Midterm1 SampleDocument5 pagesECON 102 Midterm1 SampleexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Chap 05 - 10ce - Macro-1-5Document5 pagesChap 05 - 10ce - Macro-1-5shienalycabiles98No ratings yet
- Untitled14 PDFDocument22 pagesUntitled14 PDFErsin TukenmezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Exam ReviewoakashlerNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1Document36 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1marychaveznpfesgkmwx100% (38)
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkevin.reider416100% (11)
- 203 Sample Midterm2Document16 pages203 Sample Midterm2Annas GhafoorNo ratings yet
- ddddDocument16 pagesddddmarco111222999No ratings yet
- MCQs With Solution For ECONS (Macro)Document38 pagesMCQs With Solution For ECONS (Macro)DzifahManteau100% (1)
- Macro QuizDocument11 pagesMacro QuizRyan BekinfieldNo ratings yet
- 303 Sample 1Document8 pages303 Sample 1ايهاب غزالةNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 SolutionsれなNo ratings yet
- Fall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFDocument7 pagesFall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFctyre34No ratings yet
- Final Exam Sample QuestionsDocument11 pagesFinal Exam Sample Questionsecobalas7100% (1)
- Self Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113Document161 pagesSelf Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113markNo ratings yet
- MT 2016Document9 pagesMT 2016Ismail Zahid OzaslanNo ratings yet
- ECO121 Quiz01 Fall2022Document7 pagesECO121 Quiz01 Fall2022Đông ĐôngNo ratings yet
- Surprise Quiz IDocument5 pagesSurprise Quiz I23pgp011No ratings yet
- Study Questions 2 (Unemployment and Inflation) PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Questions 2 (Unemployment and Inflation) PDFcvofoxNo ratings yet
- Coremacroeconomics 3rd Edition Chiang Test BankDocument50 pagesCoremacroeconomics 3rd Edition Chiang Test Banktwintervoodooaq2t9100% (35)
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1Thi van DamNo ratings yet
- Unemployment (Multiple Choice Questions)Document16 pagesUnemployment (Multiple Choice Questions)NickNo ratings yet
- Practise MCDocument6 pagesPractise MCNick Chow100% (1)
- Microeconomics 9Th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument66 pagesMicroeconomics 9Th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdanielxavia55fok100% (10)
- Microeconomics 9th Edition Parkin Test BankDocument38 pagesMicroeconomics 9th Edition Parkin Test Banknbilojanoy100% (17)
- Macroeconomics Final SONBAHAR 23Document4 pagesMacroeconomics Final SONBAHAR 23MariaNo ratings yet
- F22 Macro TermTest TF MCDocument8 pagesF22 Macro TermTest TF MCjefferyliu791No ratings yet
- Tugas Bab 27 (15 Maret 2021)Document7 pagesTugas Bab 27 (15 Maret 2021)MutiaraMorentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Hi HiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 10 Questionsmarykara1915No ratings yet
- Econ 3010 Final Exam Multiple Choice (100 Points)Document9 pagesEcon 3010 Final Exam Multiple Choice (100 Points)westsiderNo ratings yet
- 3Document43 pages3Kevin HaoNo ratings yet
- Practice MCQ Set 1Document3 pagesPractice MCQ Set 1coffeedance100% (1)
- CH 26 Ad & AsDocument25 pagesCH 26 Ad & AsAli HussinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Macroeconomics 7Th Edition Blanchard 0133780589 978013378058 Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Macroeconomics 7Th Edition Blanchard 0133780589 978013378058 Full Chapter PDFdonovan.breisch589100% (20)
- Triệu Khánh Duy HE153098 MKT1610Document5 pagesTriệu Khánh Duy HE153098 MKT1610Duy KhánhNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test On Unit 6 - Attempt ReviewDocument6 pagesMCQ Test On Unit 6 - Attempt ReviewDemo Account 1No ratings yet
- Assignment in Binomial Distribution PINEDA PLM (ATTEMPT 2)Document2 pagesAssignment in Binomial Distribution PINEDA PLM (ATTEMPT 2)Patrick PinedaNo ratings yet
- The Lean Canvas: Problem Solution Unique Value Prop. Unfair Advantage Customer SegmentsDocument7 pagesThe Lean Canvas: Problem Solution Unique Value Prop. Unfair Advantage Customer SegmentsMercury17No ratings yet
- Wood and Bamboo For Rural Water SupplyDocument90 pagesWood and Bamboo For Rural Water SupplyJose Fermin SantiagoNo ratings yet
- MGT-9 2023Document10 pagesMGT-9 2023Srishti 2k22No ratings yet
- Pre Registration bsuYWvMn8IHVtDocument1 pagePre Registration bsuYWvMn8IHVtHendrix VillameroNo ratings yet
- BUZIL ROSSARI PVT LTD Franchise Opportunity - Franchise IndiaDocument6 pagesBUZIL ROSSARI PVT LTD Franchise Opportunity - Franchise IndiaMayank JainNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chapter 2Document1 pageSummary of Chapter 2AkiNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Manual Food GrinderDocument10 pagesDesign and Construction of A Manual Food GrinderAlvin S Soriano Jr.No ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument10 pagesDepreciationApril Patrizia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Stopag WrappingDocument1 pageStopag Wrappingrammer.pakpahanNo ratings yet
- BTMM Patterns and Setups1Document12 pagesBTMM Patterns and Setups1Tafara Michael100% (1)
- Handouts Sept 2021Document213 pagesHandouts Sept 2021Marta CrescenziNo ratings yet
- IndicatorsDocument3 pagesIndicators'Izzad AfifNo ratings yet
- What Is Industrial Design?Document2 pagesWhat Is Industrial Design?Carlos BaudelaireNo ratings yet
- 46SV2N075T, 200gpm@120ftDocument4 pages46SV2N075T, 200gpm@120ftSajidNo ratings yet
- Hammer Union CatalogDocument34 pagesHammer Union CatalogReyna NavaNo ratings yet
- MECH REC69 Magnetic Particle Dye Penetrant ReportDocument1 pageMECH REC69 Magnetic Particle Dye Penetrant ReporttinzarmoeNo ratings yet
- Universal Business SolutionsDocument6 pagesUniversal Business SolutionsAbraham AchuNo ratings yet
- Proposal Form - Householders Insurance PolicyDocument4 pagesProposal Form - Householders Insurance PolicyscribdNo ratings yet
- DCF Model - Blank: Strictly ConfidentialDocument5 pagesDCF Model - Blank: Strictly ConfidentialaeqlehczeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Frank - Chapter03 - Rational Consumer ChoiceDocument40 pages3 - Frank - Chapter03 - Rational Consumer ChoiceNOPPHANUT NGAMVITROJENo ratings yet
- HR/ Management GamesDocument39 pagesHR/ Management Gameskamdica100% (6)
- Reference No: 863191: American International University - BangladeshDocument1 pageReference No: 863191: American International University - BangladeshTanvir PrantoNo ratings yet
- CAPACITY PLANNING ReadingsDocument4 pagesCAPACITY PLANNING Readingsasmelash gideyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER III: Linear Programming ApplicationsDocument24 pagesCHAPTER III: Linear Programming ApplicationsLouisRemNo ratings yet
Economic Growth
Economic Growth
Uploaded by
Ahmed Bahaa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesThe document discusses economic growth and key economic concepts related to measuring and understanding economic growth. It covers definitions of economic growth, how it is measured using real GDP, factors that influence long-term economic growth such as higher standards of living, calculations of economic growth rates using real GDP data from different countries, the rule of 70 for estimating growth rate doubling times, aggregate production functions, labor productivity, and factors that influence labor supply and demand in markets.
Original Description:
Original Title
economic_growth[1]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses economic growth and key economic concepts related to measuring and understanding economic growth. It covers definitions of economic growth, how it is measured using real GDP, factors that influence long-term economic growth such as higher standards of living, calculations of economic growth rates using real GDP data from different countries, the rule of 70 for estimating growth rate doubling times, aggregate production functions, labor productivity, and factors that influence labor supply and demand in markets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesEconomic Growth
Economic Growth
Uploaded by
Ahmed BahaaThe document discusses economic growth and key economic concepts related to measuring and understanding economic growth. It covers definitions of economic growth, how it is measured using real GDP, factors that influence long-term economic growth such as higher standards of living, calculations of economic growth rates using real GDP data from different countries, the rule of 70 for estimating growth rate doubling times, aggregate production functions, labor productivity, and factors that influence labor supply and demand in markets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Economic growth
1. The best definition for economic growth is
A) a sustained expansion of production possibilities measured as the increase in real GDP over a
given period.
B) a sustained expansion of production possibilities measured as the increase in nominal GDP over
a given period.
C) a sustained expansion of consumption goods over a given period.
D) a sustained expansion of production goods over a given period.
2. Economic growth is measured by
A) changes in real GDP.
B) changes in nominal GDP.
C) changes in the employment rate.
D) All of the above are used to measure economic growth.
3. We are interested in long-term growth primarily because it brings
A) higher price levels.
B) lower price levels.
C) higher standards of living.
D) trade wars with our trading partners.
4. In 2011, Armenia had a real GDP of $4.21 billion and a population of 2.98 million. In 2012, real
GDP was $4.59 billion and population was 2.97 million. What was Armenia's economic growth
rate from 2011 to 2012?
A) 0.38 percent
B) 9.0 percent
C) 3.8 percent
D) 8.3 percent
5. During 2014, the country of Economia had a real GDP of $115 billion and the population was
0.9 billion. In 2013, real GDP was 105 billion and the population was 0.85 billion. In 2013, real
GDP per person was
A) $128
B) $124
C) $135
D) $117
6. Suppose a nation's population grows by 2 percent and, at the same time, its GDP grows by 5
percent. Approximately how fast will real GDP per person increase?
A) 3 percent per year
B) 2 percent per year
C) 5 percent per year
D) 10 percent per year
7. Which of the following is used to calculate the standard of living?
A) Real GDP/population
B) ((real GDP in the current year - real GDP in previous year)/real GDP in previous year) × 100
C) The one-third rule
D) Real GDP/aggregate hours
8. According to the Economic Times (09/2012), Standard & Poor's forecast for India's GDP growth
rate was cut by 1 percentage point to 5.5 percent as the entire Asia Pacific region feels the
pressure of ongoing economic uncertainty. India has averaged 7 percent growth in GDP since
1997. Which of the following is true?
A) India's PPF has been shifting rightward since 1997.
B) India's PPF has been shifting leftward since 1997.
C) India has been moving from a point within its PPF to points beyond its PPF.
D) India's PPF has not shifted since 1997.
9. The Rule of 70 is used to
A) Estimate how much of an economy's growth rate is due to increases in capital per hour of labor
B) Calculate the standard of living
C) Calculate the economy's growth rate
D) Estimate how long it will take the level of any variable to double
10. Using the Rule of 70, if China's current growth rate of real GDP per person was 7 percent a
year, how long would it take the country's real GDP per person to double?
A) 35 years
B) 14 years
C) 10 years
D) 49 years
11. If real GDP per person is growing at 4 percent per year, approximately how many years will it
take to double?
A) 17.5
B) 25
C) 4
D) 8
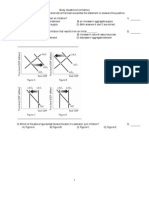
12. The aggregate production function shows how ________ varies with ________.
A) leisure time; labor
B) labor; leisure time
C) real GDP; labor
D) labor; capital
13. An aggregate production function shows the relationship between
A) real GDP and leisure.
B) real GDP and the quantity of labor employed.
C) leisure and unemployment.
D) real GDP and unemployment.
14. A movement along the aggregate production function is the result of a change in
A) the quantity of labor
B) technology
C) capital
D) interest rates
15. The aggregate production function shows that an economy increases its real GDP in the short
run by
A) developing new technologies.
B) increasing its physical capital stock.
C) using more labor.
D) exploring for new deposits of natural resources.
16. Moving along the aggregate production function, all of the following are held constant EXCEPT
A) labor
B) capital
C) human capital
D) technology
17. The aggregate production function is graphed as
A) a downward sloping curve.
B) an upward sloping straight line.
C) an upward sloping line that becomes flatter as the quantity of labor increases.
D) an upward sloping line that becomes steeper as the quantity of labor increases.
18. The decreasing slope of a production function reflects
A) diminishing returns.
B) rising unemployment.
C) decreasing costs.
D) increasing aggregate demand.
19. The real wage rate equals
A) (money wage rate)/(price level).
B) (price level)/(money wage rate).
C) (money wage rate) × (price level).
D) (money wage) + (number of hours worked)/(price level).
20. The relationship between the labor employed by a firm and the real wage rate is shown by the
A) supply of labor curve.
B) supply of jobs curve.
C) demand for jobs curve.
D) demand for labor curve.
21. The quantity of labor demanded depends on the
A) Money wage rate not the real wage rate.
B) Real wage rate not the money wage rate.
C) Price of output not the money wage rate nor the real wage rate.
D) Money wage rate AND the real wage rate.
22. 26) Which of the following is TRUE regarding the labor market?
I. The labor supply curve slopes upward because firms maximize profits as they hire more
workers.
II. If the real wage rate falls, the quantity of labor firms demand increases.
III. The demand for labor curve slopes downward because as the real wage rate falls, workers
demand to work fewer hours.
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II only
D) I, II and III
23. If the price level falls by 5 percent and workers' money wage rates remain constant, firms'
A) Quantity of labor demanded will decrease.
B) Quantity of labor demanded will increase.
C) Supply of jobs will increase.
D) None of the above answers are correct.
24. The demand for labor curve is
A) upward sloping at potential GDP and downward sloping elsewhere.
B) vertical at potential GDP.
C) downward sloping.
D) upward sloping because firms demand labor.
25. The labor demand curve slopes downward because
A) the firm maximizes profits by hiring more labor when the real wage rate rises.
B) workers supply more hours of work when the real wage rate rises.
C) the firm maximizes profits by hiring more labor when the real wage rate falls.
D) workers supply fewer hours of work when the real wage rate rises.
26. The quantity of labor supplied depends on the
A) money wage rate not the real wage rate.
B) real wage rate not the money wage rate.
C) price of output not the money wage rate nor the real wage rate.
D) level of profits.
27. People base their labor supply on the ________ because they care about ________.
A) Real wage; what their earnings will buy
B) Real wage; the equality of money wages and the price level
C) Money wage; a surplus of labor
D) Money wage; the amount of labor firms demand
28. If the price level rises by 2 percent and workers' money wages increase by 2 percent, then the
A) quantity of labor supply decreases.
B) quantity of labor supply increases.
C) quantity of labor supplied does not change because there is no change in the real wage rate.
D) More information about the dollar change in the price level and money wage rate are needed to
answer the question.
29. If the real wage rate is such that the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity of labor
demanded,
A) a full-employment equilibrium occurs.
B) actual GDP equals potential GDP.
C) the supply curve of labor is vertical.
D) Both answers A and B are correct.
30. Equilibrium in the labor market
A) cannot occur if the production function is shifting upward.
B) can happen only when actual GDP exceeds potential GDP.
C) means that resources are allocated inefficiently
D) occurs when actual GDP is equal to potential GDP
31. When the quantity of labor demanded exceeds the quantity of labor supplied, the real wage
rate
A) Rises to eliminate the labor-market shortage.
B) Falls to eliminate the labor-market surplus.
C) Rises to eliminate the labor-market surplus.
D) Falls to eliminate the labor-market shortage.
32. In the labor market, an increase in labor productivity ________ the real wage rate and
________ the level of employment.
A) raises; increases
B) raises; decreases
C) lowers; increases
D) lowers; decreases
33. Labor productivity is
A) real GDP per hour of labor times the hours of work.
B) real GDP per hour of labor times the number of people.
C) real GDP per hour of labor.
D) the rate of change in real GDP per hour of labor.
34. Dividing the value of real GDP by aggregate labor hours gives
A) the net domestic product.
B) labor productivity.
C) the size of the labor force.
D) the rate of capital accumulation.
35. Labor productivity is defined as
A) total output attributable to labor.
B) total real GDP.
C) the growth rate of the labor force.
D) real GDP per hour of labor.
36. When labor productivity increases, the demand for labor curve ________ and the supply of
labor curve ________.
A) shifts rightward; shifts rightward
B) shifts rightward; does not shift
C) shifts leftward; shifts rightward
D) shift s leftward; does not shift
37. Technological change
A) lowers the real wage rate.
B) decreases labor productivity.
C) has no effect on employment.
D) increases potential GDP.
38. Factors that influence labor productivity include ________.
A) the inflation rate, the real wage rate, and the exchange rate
B) the labor demand curve
C) physical capital, the real wage rate, and technology
D) physical capital, human capital, and technology
39. An increase in education and training
A) Increases labor productivity.
B) increases aggregate hours.
C) Decreases real GDP growth.
D) Increases the employment-to-population ratio.
40. ________ is the knowledge and skill that people have obtained from education and on-the-job
training.
A) Labor productivity
B) Human capital
C) Capital
D) Technology
41. On-the-job-training is an example of
A) Increasing labor force participation.
B) Investment in human capital.
C) Investment in physical capital.
D) Technological change.
42. The more education that workers have, the ________ is their human capital and the ________
is their productivity.
A) Larger; higher
B) Larger; smaller
C) Smaller; higher
D) Smaller; smaller
43. Which of the following is associated with classical growth theory?
I. Growth in real GDP can continue indefinitely.
II. Technological growth increases as the population grows.
III. Population explosions bring real GDP per person back to subsistence levels.
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and III
44. Classical growth theory states that
A) Growth is maximized when everyone is fully employed.
B) Growth is followed by increases in the population, eventually leaving real GDP per person
unchanged.
C) Growth in real GDP per person is difficult in the beginning but easier in the later stages.
D) Advances in technology will always insure a permanent increase in real GDP per person.
45. According to the classical growth theory of Thomas Malthus,
A) labor productivity increases continuously.
B) the population growth rate is fixed.
C) technological advances lead to permanent increases in real GDP per person.
D) increases in real GDP per person are only temporary.
46. Neoclassical growth theory predicts that
A) population growth rates slow as employment opportunities for women increase.
B) Population explosions decrease real GDP per person.
C) Economic growth leads to technological change.
D) The pursuit of profit creates perpetual growth.
47. Which of the following ideas apply to the neoclassical growth theory?
I. The rate of technological change influences the rate of economic growth.
II. Technological change promotes saving and investment.
III. Convergence of economic growth rates across countries.
A) I only
B) III only
C) I and II
D) I, II and III
48. According to new growth theory, technological change is driven by
A) random chance.
B) government policies.
C) foreign firms' attempts to increase their sales in the domestic market.
D) firms' attempts to increase their profit.
49. New growth theory assumes that
A) all inputs experience diminishing returns.
B) only random technological advances produce growth.
C) knowledge does not experience diminishing returns.
D) None of the above answers is correct.
50. Which theory emphasizes the significance of new discoveries that can be used by many people
at the same time?
A) Neoclassical growth theory
B) New growth theory
C) Classical growth theory
D) None of the above answers are correct.
51. New growth theory
A) Dates from the 18th century.
B) Concludes that economic growth is temporary.
C) States that economic growth arises from people's choices.
D) Asserts that population growth is the source of economic growth.
You might also like
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionFrom EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Celsozeca2011No ratings yet
- LRA CITIZEN CHARTER HANDBOOK (Form) - FINAL 03122020 PDFDocument349 pagesLRA CITIZEN CHARTER HANDBOOK (Form) - FINAL 03122020 PDFCharmaine Coleta100% (2)
- Ey Ifrs 10 Consolidation For Fund Managers PDFDocument32 pagesEy Ifrs 10 Consolidation For Fund Managers PDFCindy Yin100% (2)
- Midterm 1 Mock Exam With AnswersDocument9 pagesMidterm 1 Mock Exam With AnswersSally ZhuNo ratings yet
- WKSHT Macro Unit3 Lesson3 Act23 KeyDocument10 pagesWKSHT Macro Unit3 Lesson3 Act23 KeyCarl WeinfieldNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 QuestionsDocument8 pagesTutorial 8 QuestionsJudah SaliniNo ratings yet
- Topik Economic GrowthDocument11 pagesTopik Economic GrowthmbevenNo ratings yet
- QUIZ CH 23 Topik Economic Growth (Tanpa Jawaban)Document12 pagesQUIZ CH 23 Topik Economic Growth (Tanpa Jawaban)mbevenNo ratings yet
- CH13Document12 pagesCH13nbrxf9mg2mNo ratings yet
- Macro Quiz 5 PDFDocument4 pagesMacro Quiz 5 PDFcvofoxNo ratings yet
- MCQs Inflation Business Cycle - EditedDocument5 pagesMCQs Inflation Business Cycle - EditedSadia IlyasNo ratings yet
- Macro PracticeDocument32 pagesMacro PracticecholoNo ratings yet
- 1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Document6 pages1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Haifa Al-humayydNo ratings yet
- Macro - InteDocument7 pagesMacro - InteHilary ChoiNo ratings yet
- Baims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFDocument5 pagesBaims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFShahadNo ratings yet
- Study Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Document8 pagesStudy Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Kiran KachhawahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 MCBDocument6 pagesChapter 8 MCBHunter KellettNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Document31 pagesIntermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Ceren Gökçe KeskinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank 2Document6 pagesTest Bank 2Nouran BakerNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Sample MCQ (4-8)Document13 pagesTest 2 Sample MCQ (4-8)gg ggNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 ECON 343Document7 pagesAssignment 5 ECON 343Jack BNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Chapter 8 Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesMacroeconomics Chapter 8 Multiple ChoiceGene'sNo ratings yet
- ECON 1010 FinalDocument30 pagesECON 1010 FinalMaliha Rubaba FarhadNo ratings yet
- University of Cape Coast College of Humanities and Legal Studies School of Economics Department of Economic Studies Tutorial Set Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cape Coast College of Humanities and Legal Studies School of Economics Department of Economic Studies Tutorial Set Multiple Choice QuestionsHislord BrakohNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm1Document6 pagesPractice Midterm1Bahar SamiNo ratings yet
- ECON 102 Midterm1 SampleDocument5 pagesECON 102 Midterm1 SampleexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Chap 05 - 10ce - Macro-1-5Document5 pagesChap 05 - 10ce - Macro-1-5shienalycabiles98No ratings yet
- Untitled14 PDFDocument22 pagesUntitled14 PDFErsin TukenmezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Exam ReviewoakashlerNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1Document36 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1marychaveznpfesgkmwx100% (38)
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkevin.reider416100% (11)
- 203 Sample Midterm2Document16 pages203 Sample Midterm2Annas GhafoorNo ratings yet
- ddddDocument16 pagesddddmarco111222999No ratings yet
- MCQs With Solution For ECONS (Macro)Document38 pagesMCQs With Solution For ECONS (Macro)DzifahManteau100% (1)
- Macro QuizDocument11 pagesMacro QuizRyan BekinfieldNo ratings yet
- 303 Sample 1Document8 pages303 Sample 1ايهاب غزالةNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 SolutionsれなNo ratings yet
- Fall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFDocument7 pagesFall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFctyre34No ratings yet
- Final Exam Sample QuestionsDocument11 pagesFinal Exam Sample Questionsecobalas7100% (1)
- Self Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113Document161 pagesSelf Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113markNo ratings yet
- MT 2016Document9 pagesMT 2016Ismail Zahid OzaslanNo ratings yet
- ECO121 Quiz01 Fall2022Document7 pagesECO121 Quiz01 Fall2022Đông ĐôngNo ratings yet
- Surprise Quiz IDocument5 pagesSurprise Quiz I23pgp011No ratings yet
- Study Questions 2 (Unemployment and Inflation) PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Questions 2 (Unemployment and Inflation) PDFcvofoxNo ratings yet
- Coremacroeconomics 3rd Edition Chiang Test BankDocument50 pagesCoremacroeconomics 3rd Edition Chiang Test Banktwintervoodooaq2t9100% (35)
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1Thi van DamNo ratings yet
- Unemployment (Multiple Choice Questions)Document16 pagesUnemployment (Multiple Choice Questions)NickNo ratings yet
- Practise MCDocument6 pagesPractise MCNick Chow100% (1)
- Microeconomics 9Th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument66 pagesMicroeconomics 9Th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdanielxavia55fok100% (10)
- Microeconomics 9th Edition Parkin Test BankDocument38 pagesMicroeconomics 9th Edition Parkin Test Banknbilojanoy100% (17)
- Macroeconomics Final SONBAHAR 23Document4 pagesMacroeconomics Final SONBAHAR 23MariaNo ratings yet
- F22 Macro TermTest TF MCDocument8 pagesF22 Macro TermTest TF MCjefferyliu791No ratings yet
- Tugas Bab 27 (15 Maret 2021)Document7 pagesTugas Bab 27 (15 Maret 2021)MutiaraMorentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Hi HiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial 10 Questionsmarykara1915No ratings yet
- Econ 3010 Final Exam Multiple Choice (100 Points)Document9 pagesEcon 3010 Final Exam Multiple Choice (100 Points)westsiderNo ratings yet
- 3Document43 pages3Kevin HaoNo ratings yet
- Practice MCQ Set 1Document3 pagesPractice MCQ Set 1coffeedance100% (1)
- CH 26 Ad & AsDocument25 pagesCH 26 Ad & AsAli HussinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Macroeconomics 7Th Edition Blanchard 0133780589 978013378058 Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Macroeconomics 7Th Edition Blanchard 0133780589 978013378058 Full Chapter PDFdonovan.breisch589100% (20)
- Triệu Khánh Duy HE153098 MKT1610Document5 pagesTriệu Khánh Duy HE153098 MKT1610Duy KhánhNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test On Unit 6 - Attempt ReviewDocument6 pagesMCQ Test On Unit 6 - Attempt ReviewDemo Account 1No ratings yet
- Assignment in Binomial Distribution PINEDA PLM (ATTEMPT 2)Document2 pagesAssignment in Binomial Distribution PINEDA PLM (ATTEMPT 2)Patrick PinedaNo ratings yet
- The Lean Canvas: Problem Solution Unique Value Prop. Unfair Advantage Customer SegmentsDocument7 pagesThe Lean Canvas: Problem Solution Unique Value Prop. Unfair Advantage Customer SegmentsMercury17No ratings yet
- Wood and Bamboo For Rural Water SupplyDocument90 pagesWood and Bamboo For Rural Water SupplyJose Fermin SantiagoNo ratings yet
- MGT-9 2023Document10 pagesMGT-9 2023Srishti 2k22No ratings yet
- Pre Registration bsuYWvMn8IHVtDocument1 pagePre Registration bsuYWvMn8IHVtHendrix VillameroNo ratings yet
- BUZIL ROSSARI PVT LTD Franchise Opportunity - Franchise IndiaDocument6 pagesBUZIL ROSSARI PVT LTD Franchise Opportunity - Franchise IndiaMayank JainNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chapter 2Document1 pageSummary of Chapter 2AkiNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of A Manual Food GrinderDocument10 pagesDesign and Construction of A Manual Food GrinderAlvin S Soriano Jr.No ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument10 pagesDepreciationApril Patrizia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Stopag WrappingDocument1 pageStopag Wrappingrammer.pakpahanNo ratings yet
- BTMM Patterns and Setups1Document12 pagesBTMM Patterns and Setups1Tafara Michael100% (1)
- Handouts Sept 2021Document213 pagesHandouts Sept 2021Marta CrescenziNo ratings yet
- IndicatorsDocument3 pagesIndicators'Izzad AfifNo ratings yet
- What Is Industrial Design?Document2 pagesWhat Is Industrial Design?Carlos BaudelaireNo ratings yet
- 46SV2N075T, 200gpm@120ftDocument4 pages46SV2N075T, 200gpm@120ftSajidNo ratings yet
- Hammer Union CatalogDocument34 pagesHammer Union CatalogReyna NavaNo ratings yet
- MECH REC69 Magnetic Particle Dye Penetrant ReportDocument1 pageMECH REC69 Magnetic Particle Dye Penetrant ReporttinzarmoeNo ratings yet
- Universal Business SolutionsDocument6 pagesUniversal Business SolutionsAbraham AchuNo ratings yet
- Proposal Form - Householders Insurance PolicyDocument4 pagesProposal Form - Householders Insurance PolicyscribdNo ratings yet
- DCF Model - Blank: Strictly ConfidentialDocument5 pagesDCF Model - Blank: Strictly ConfidentialaeqlehczeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Frank - Chapter03 - Rational Consumer ChoiceDocument40 pages3 - Frank - Chapter03 - Rational Consumer ChoiceNOPPHANUT NGAMVITROJENo ratings yet
- HR/ Management GamesDocument39 pagesHR/ Management Gameskamdica100% (6)
- Reference No: 863191: American International University - BangladeshDocument1 pageReference No: 863191: American International University - BangladeshTanvir PrantoNo ratings yet
- CAPACITY PLANNING ReadingsDocument4 pagesCAPACITY PLANNING Readingsasmelash gideyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER III: Linear Programming ApplicationsDocument24 pagesCHAPTER III: Linear Programming ApplicationsLouisRemNo ratings yet