Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exam Leak
Exam Leak
Uploaded by
Venz Lei Collyn Atis Esin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views7 pagesThis document contains exam questions covering various topics related to plant physiology including photosynthesis, respiration, transpiration, and the differences between C3, C4, and CAM pathways. There are over 100 multiple choice or fill-in-the-blank questions testing understanding of plant anatomy, biochemical processes, and environmental influences on plant functions.
Original Description:
Original Title
EXAM LEAK
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains exam questions covering various topics related to plant physiology including photosynthesis, respiration, transpiration, and the differences between C3, C4, and CAM pathways. There are over 100 multiple choice or fill-in-the-blank questions testing understanding of plant anatomy, biochemical processes, and environmental influences on plant functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views7 pagesExam Leak
Exam Leak
Uploaded by
Venz Lei Collyn Atis EsinThis document contains exam questions covering various topics related to plant physiology including photosynthesis, respiration, transpiration, and the differences between C3, C4, and CAM pathways. There are over 100 multiple choice or fill-in-the-blank questions testing understanding of plant anatomy, biochemical processes, and environmental influences on plant functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
EXAM LEAK
1. Illustrate the applications of Respiration, Transpiration, Photosynthesis
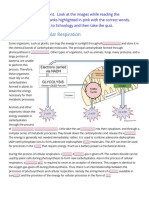
2. It is the light-induced reduction of photosynthetic activity
3. It determines productivity and net yield.
4. What are the 6 physiological processes in the plant?
5. It study of parts and functions in organisms.
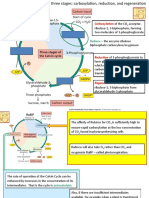
6. Physiology defines the interaction between __________ and __________, and
influencing _________, _________, _________.
7. Major Reproductive Parts of a Plant
8. Major Vegetative Parts of a Plant
9. These organisms produce their own food through photosynthesis
10. Chemical Formula for Photosynthesis
11. Photosynthesis is a _____________ process that uses light/_______ energy and
water to produce ___________.
12. Photosynthesis happens in _____________.
13. Chloroplasts are ______________ in mesophyll cells, while thylakoid membrane
are ______________ in mesophyll cells.
14. Thylakoid membrane contains the ______________ molecule, which acts as a
light ___________.
15. _____________ are the non-green pigments which are also venues for
photosynthesis.
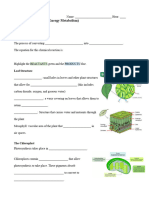
16. Draw the Leaf Cross Section. Complete all the parts, as well as that of the
mesophyll cell.
17. __________ is a specialized epidermal cell that is present in the lower epidermis.
18. Stomata allows the entry of gaseous elements like _________, _________,
__________.
19. Plant cells, compared against animal cells, have ___________, ___________,
___________.
20. Thylakoid membrane is stacked with ___________ and __________.
21. ___________ is the space around grana.
22. The venue for LDR.
23. The venue for LIR.
24. It is the breakdown of water molecules.
25. LDR only happen in the presence of ________, because the venue is __________,
which contains light antenna in the form of ____________.
26. LDR requires energy in the form of _________ and _________.
27. ___________ are arrays of protein and chlorophyll molecules embedded in
thylakoid membrane.
28. Two types of LHCs.
29. Meaning of NADPH
30. Meaning of RUBISCO
31. Deficiency of _________ causes yellowing of leaves.
32. Requirements for photosynthesis.
33. Light has a spectrum of varying wavelengths; PS is most efficient in the
_________ (425-____ nm) and in the _________ (________ - ________ nm)
34. Blue Light regulates ____________; Highest in ___________ and ___________.
35. Stomata is most open in __________.
36. Light energy from _________ is transferred from one __________ to another.
37. One chlorophyll serves as ____________, while another acts as _____________.
38. It is the downward movement of electrons, from ____________ to ____________.
39. ______________ produces energy and reducing power to be used in Calvin
Cycle.
40. Three Major Reactions in Calvin Cycle.
41. First stage yields __________.
42. Second stage yields __________.
43. The second stage is the __________ of NADPH from NADP.
44.Third stage is the use of energy to ___________ RUBP.
45. Third stage yields __________.
46. PGA means ____________, also called ____________.
47. G3P means _____________.
48. For every 1 molecule of ___________ fixed, that is, to make ___________, ____ ATP
and _____ NADPH are used.
49. ________ is the most abundant protein/enzyme in the world.
50. The above enzyme has a dual function, ___________ (when ______ consent >
_________ concent), and this is conducive to _____________.
51. The same enzyme has a dual function, ___________ (when ______ consent >
_________ concent), and this is conducive to _____________.
52. Plants have recommended ____________ because when they grow too close
together, their _________ will be too close as well, blocking the ______________,
thus leading to more tendency for ___________ and less ________________.
53. It is the biggest contributor of greenhouse gases.
54. Photorespiration leads to ___________, ______________, ____________ if Rubisco
acts as ____________.
55. Rubisco as __________ maximizes _______________.
56. Rate of photorespiration is induced by ___________, ____________, _____________,
____________.
57. Photorespiration occurs when ___________ acts as ___________.
58. Photorespiration is common in __________ conditions where high
temperatures increase ____________ in ___________.
59. Photorespiration has the ff concentrations of: oxygen _____________; Carbon
Dioxide __________.
60. Oxidation of _________ yields 1 molecule of __________ and 1 molecule of
___________.
61. In photorespiration, plants lose ___________ of the carbon it takes from Calvin
Cycle.
62. Photorespiration is a _______________ reaction which uses up to ___ ATP and ___
NADPH for every oxygenation of RuBP, which is _____ more than carboxylation
energy expenditure.
63. Photorespiration results in lower rate of _________ because of lower
photosynthetic efficiency.
64. Photorespiration is exhibited by ____ plants.
65. C3 Plants enter Calvin Cycle _______, and its first stable intermediate has __
carbons.
66. C4 Plants first incorporate Carbon Dioxide into __ carbon compound before it
enters Calvin Cycle.
67. C4 Pathway is ______ because it allows _________ in otherwise
__________-conducive environments (i.e., _____________)
68. C4 pathway is also called as _____________.
69. In there, photosynthesis occurs in both __________ and _________.
70. Mesophyll cells in C4 plants have additional enzyme, ____________.
71. Illustrate C4 pathway steps.
72. All plants have both ____ and ____.
73. ________ is the utilization of __________ in the presence of _______ to break down
the former into _________, ________, and produce cellular energy in the form of
______ and _______.
74. The above is also called ____________.
75. The chemical formula for no. 73.
76. PS: ___ energy to ___ energy :: ___: ___ energy to ____ energy
77. __________ Respiration involves _________, while ________ Respiration ________
oxygen.
78. Main product of DR is ______, and it occurs in _____ cells.
79. Stages of DR.
80. First Stage of DR occurs in ________. Its reactants are _______ and products are
__________ + _________ thru ________.
81. Kreb’s Cycle’s reactant is _______ and the products are __________ + _____ thru
________.
82. Electron Transport Chain is the ____ stage of DR, and its reactants are
__________ and the product is ____ thru ______.
83. _______ is the enzyme involved in ATP ________.
84. ________ is the production of ATP without light.
85. _________ is the production of ATP using one ____________ to synthesize ATP
from ______.
86. Plant growth leads to development of __________ and enhanced ________.
87. Two components of respiration in formula forms.
88. Provide meaning to the components of the above formulas.
89. Growth respiration is the ________ of respiration. Its representation is
___________.
90. Growth respiration produces energy for converting glucose into ___________.
91. The constant of growth respiration is either _____ or _____, based on ________
and ________.
92. Maintenance respiration is for _______________. Its representation is _______.
93. Energy in MR comes from _______ breakdown & _________ processes to produce
Carbon Dioxide.
94. The constant of maintenance respiration varies based on ________ and ________
factors.
95. Factors affecting MR also affect __________.
96. C3, C4, and CAM plants all have ____ pathway and _____ enzyme.
97. Illustrate why no photorespiration in C4.
98. First organic product in C4.
99. C3 plants involve ____ as the sole enzyme and houses it in ________.
100. C4 plants involve _________ and _________ as enzymes in Carboxylation, and
the latter is housed in ________.
101.In CAM plants, the ff. happens at nights: ___________ and ______ assimilation.
During the day, ________ happens.
102. There is no respiration in CAM plants because the _______ enables _________
which prevents photorespiration in otherwise high oxygen concentration due
to high __________.
103. __________ tells the stomata to open/close, and it is a _______ hormone as
well as a PGR, which means ________. Its messenger is ____ ion.
104. Only plants are capable of ____ synthesis.
105. Is there photosynthesis at night for C3, C4, and CAM? Why?
106. Anatomical modifications in C4 plants
107. Anatomical modification in CAM
108. _______ is the direct source of energy for all plants, while ______ and ________
are indirect sources of energy.
109. Photosynthesis is a _______ reaction. Provide therefore its components.
110.First product in Citric Acid Cycle is ____-.
111. Two phases of glycolysis.
112. The second phase of glycolysis yields ____ ATP and _____ NADPH.
113. ______________ is the most important enzyme in glycolysis. It decides the _____
of respiration based on plant factors. It has only 1 function unlike _________.
114.Theoretical Yield of ATP in respiration is _________, while Realistic Yield is
___________.
115. Explain why ETC is more efficient than glycolysis and kreb’s cycle in producing
ATP.
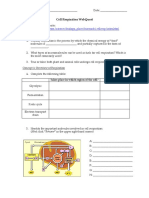
Categories C3 C4 CAM
Crop Examples
Biomass
Production
Leaf Anatomy
First Stable
Product
CO2 fixation
Glycolate
synthesis
WUE
Light Saturation
CO2
Compensation
Point
Stomatal Opening
You might also like
- MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesMacromoleculesSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane & Tonicity WorksheetDocument4 pagesCell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheetkeith tambaNo ratings yet
- Millet Booklet PDFDocument21 pagesMillet Booklet PDFViswanatha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 Photosynthesis Physiological and Ecological ConsiderationsDocument35 pagesChapter9 Photosynthesis Physiological and Ecological ConsiderationsLandau2016100% (1)
- HANDOUT - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review Sheet 2017Document3 pagesHANDOUT - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review Sheet 2017ezraburrosNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4 Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument4 pages2.2.4 Photosynthesis WorksheetHo Thi Phuong Oanh0% (1)
- Botany - BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesBotany - BiomoleculesP JagadeeswariNo ratings yet
- Latihan Chap 7 f4Document3 pagesLatihan Chap 7 f4Faizal PejerNo ratings yet
- Tuto PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesTuto PhotosynthesisFatin FatonahNo ratings yet
- hssb0400s StudygdbDocument12 pageshssb0400s StudygdbMohamed HassaneinNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B Guided Notes 2022Document6 pagesUnit 2B Guided Notes 2022Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis GR 2017Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis GR 2017api-440268289No ratings yet
- Biomolecules CornellDocument4 pagesBiomolecules CornellDivineDoctorNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetSherisa100% (1)
- K G K SCH a2VudG9uLmphbnplbkBteXBsYWNlLndjcy5lZHU Copy of 2023 Biology Fall Exam Review ParDocument8 pagesK G K SCH a2VudG9uLmphbnplbkBteXBsYWNlLndjcy5lZHU Copy of 2023 Biology Fall Exam Review Parbrittendaniel13No ratings yet
- Botany - PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesBotany - Photosynthesiskmonishasai7No ratings yet
- Cell Respiration WebQuest 2015Document3 pagesCell Respiration WebQuest 2015Haley HaunNo ratings yet
- Ds62-Into To Phsyn RespDocument4 pagesDs62-Into To Phsyn Respapi-110789702100% (1)
- Cell Energy SEDocument7 pagesCell Energy SEFakunle TimileyinNo ratings yet
- Biology EOCT - Answer KeyDocument21 pagesBiology EOCT - Answer KeyjamesNo ratings yet
- Populations in Ecosystems Summer Holiday Homework QsDocument11 pagesPopulations in Ecosystems Summer Holiday Homework QsSohail AliNo ratings yet
- LE Bare Essentials Word BankDocument51 pagesLE Bare Essentials Word BankhiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2.1-2.2Document5 pagesWorksheet 2.1-2.2Polka SalsaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Lecture Notes 1Document6 pagesPhotosynthesis Lecture Notes 1api-480153144No ratings yet
- An Overview of Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesAn Overview of Cellular RespirationpedropedroNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Guided NotesDocument4 pagesCellular Respiration Guided NotesRangerbackNo ratings yet
- SOL Review Answer SheetDocument15 pagesSOL Review Answer Sheetbrandonaniah7No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellDocument14 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellEma Fatimah100% (1)
- Study Guide For QuestDocument4 pagesStudy Guide For Questapi-352384491No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Review WorksheetDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Review Worksheetneeti100% (1)
- Cellular EnergyDocument3 pagesCellular Energyapi-224364720No ratings yet
- Science Quiz Test For Sophomore YearsDocument3 pagesScience Quiz Test For Sophomore YearsKoemiNo ratings yet
- CH 8+9 Notes Student VersionDocument32 pagesCH 8+9 Notes Student VersiontwintapesNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ReadingDocument5 pagesCellular Respiration ReadingJ15No ratings yet
- C. ATP and Respiration Practice QsDocument1 pageC. ATP and Respiration Practice Qsabdel.z.427No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Packet 2011Document6 pagesBiomolecules Packet 2011Nidhi Sisodia100% (1)
- photosynthesis-worksheetAMIDocument5 pagesphotosynthesis-worksheetAMITitus StevensonNo ratings yet
- Describing Chemical Reactions Fill inDocument6 pagesDescribing Chemical Reactions Fill inMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Review WorksheetDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis Review Worksheetbrianjay.codillaNo ratings yet
- The Light Reactions: of The Following Pairs of TermsDocument4 pagesThe Light Reactions: of The Following Pairs of TermsShare TahaNo ratings yet
- f2 Worksheet 4.4Document6 pagesf2 Worksheet 4.4nnirashiie100% (1)
- hssb0400s StudygdaDocument18 pageshssb0400s StudygdaMohamed HassaneinNo ratings yet
- Zoology EcosystemDocument5 pagesZoology EcosystemHadiya FatimaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Worksheet Energy Metabolism and Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesLecture Worksheet Energy Metabolism and Cellular RespirationJONALYN REGACHONo ratings yet
- Plant Adaptations Video QuizDocument2 pagesPlant Adaptations Video Quiz27keenkNo ratings yet
- Name: - Chapter 7 RespirationDocument3 pagesName: - Chapter 7 RespirationGhanapathi RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell Energy CycleDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Energy Cyclevaleli123No ratings yet
- Cell Energy SEDocument6 pagesCell Energy SEArt LoversNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes-Teacher LectureDocument8 pagesGuided Notes-Teacher Lectureapi-417232384No ratings yet
- Cell Resp Only ReadingDocument2 pagesCell Resp Only Readingapi-264004571100% (1)
- The Functional Groups: Can You See Me?Document4 pagesThe Functional Groups: Can You See Me?coalie galaxyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis N Respiration Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis N Respiration Review WorksheetRosty Ann Grabillo100% (1)
- Carbo and Lipid Activity 2Document2 pagesCarbo and Lipid Activity 2Perry BearNo ratings yet
- TEST I. Refer To Google Forms. TEST II. Fill in The Blanks. Write Your Answer Before Each NumberDocument3 pagesTEST I. Refer To Google Forms. TEST II. Fill in The Blanks. Write Your Answer Before Each NumberDacks WangNo ratings yet
- Photo OverviewDocument4 pagesPhoto Overviewvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- MGS M07 2011 Na CHT A 02Document4 pagesMGS M07 2011 Na CHT A 02rofi modiNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION - Classwork On Anaerobic and AerobicDocument2 pagesRESPIRATION - Classwork On Anaerobic and AerobicMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Fungi and Lignocellulosic BiomassFrom EverandFungi and Lignocellulosic BiomassChristian P KubicekNo ratings yet
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Document19 pagesChapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisSokuntheary SrunNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument14 pagesCalvin CycleWahyu ArifNo ratings yet
- Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditDocument75 pagesSijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditDiana Ana0% (2)
- Functional Biology NOTESDocument113 pagesFunctional Biology NOTESRebecca Amy JennerNo ratings yet
- Biological Sciences Research3Document21 pagesBiological Sciences Research3Neeta M UdariNo ratings yet
- C4 Plants Past Paper Question CIEDocument3 pagesC4 Plants Past Paper Question CIESevilay CaferogluNo ratings yet
- Eddie M. Raguindin: Biology TeacherDocument23 pagesEddie M. Raguindin: Biology TeacherMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Sodium: John GorhamDocument5 pagesSodium: John GorhamsergiochepoNo ratings yet
- AmaranthDocument38 pagesAmaranthRoberto MarchesiniNo ratings yet
- Solutions - AIATS Medical-2020 (XI Studying) - Test-5 (Code-C & D) - (27!01!2019)Document28 pagesSolutions - AIATS Medical-2020 (XI Studying) - Test-5 (Code-C & D) - (27!01!2019)Ûdây RäjpütNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse Biology PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesEdexcel Igcse Biology PhotosynthesisKamrul Alam MasumNo ratings yet
- Std. XII Biology Question BankDocument67 pagesStd. XII Biology Question BankShashank RautNo ratings yet
- A Molecular Phylogeny of The Grass Subfamily Panicoideae Show Multiple Origins of C4 PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesA Molecular Phylogeny of The Grass Subfamily Panicoideae Show Multiple Origins of C4 PhotosynthesisFernanda QueirozNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument37 pagesPhotosynthesisKambaska BeheraNo ratings yet
- Android-Based Image Processing Application For Rice Nitrogen ManagementDocument44 pagesAndroid-Based Image Processing Application For Rice Nitrogen ManagementJessica Yang100% (1)
- Activity10answers PDFDocument6 pagesActivity10answers PDFMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- NABARD Grade-A Exam: Notes On Agriculture & Rural Development (With Focus On Rural India)Document23 pagesNABARD Grade-A Exam: Notes On Agriculture & Rural Development (With Focus On Rural India)ritesh_singh90No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis Is A Process Used by Plants andDocument28 pagesPhotosynthesis: Photosynthesis Is A Process Used by Plants andKarl GustavNo ratings yet
- © Ocr 2021. You May Photocopy This Page. 1 of 240 Created in ExambuilderDocument240 pages© Ocr 2021. You May Photocopy This Page. 1 of 240 Created in ExambuildertzNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic NutritionDocument22 pagesAutotrophic NutritionBWAMBALE HARISONNo ratings yet
- Franco 2014Document20 pagesFranco 2014Ariadne Cristina De AntonioNo ratings yet
- 13 Photosynthesis-NotesDocument6 pages13 Photosynthesis-NotesDe DasNo ratings yet
- 11th Botany em Reduced Syllabus GuideDocument30 pages11th Botany em Reduced Syllabus GuideHari MNo ratings yet
- Biology The Dynamic Science 4th Edition Russell Solutions Manual 1Document10 pagesBiology The Dynamic Science 4th Edition Russell Solutions Manual 1matthew100% (38)
- Revision QuestionsDocument29 pagesRevision QuestionsBabasChong100% (1)
- PG BOTANY Plant Physiology Question Bank CompleteDocument10 pagesPG BOTANY Plant Physiology Question Bank CompleteAbid ShowketNo ratings yet
- Nejib Bio Item gr-11 ch-5 Sec. B, C,& I AssignmentDocument8 pagesNejib Bio Item gr-11 ch-5 Sec. B, C,& I AssignmentDaniel GtsadkanNo ratings yet