Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 6 DDSS
Assignment 6 DDSS
Uploaded by
safsafa asfsaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 6 DDSS
Assignment 6 DDSS
Uploaded by
safsafa asfsaCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
Matching Terms
1–C 5-G
2- I 6–F
3–B 7– D
4–H 8- E
II. True/ False
A. False. Every entity is an object in the real world that is different from others, but there can be
multiple entities of the same type.
B. False. Each entity can have one or more attributes that describe it.
C. False. A weak entity is represented by a double rectangle in an ERD.
D. True. Nouns are typically used to name entities, while verbs are used to name relationships.
E. False. A diamond is used to represent a relationship in an ERD.
F. False. Relationships can be created between two or more entities.
G. True. Relationships can have attributes that describe them.
III. Example
Entity : A car is an object in the real world that is different from others, and it has various properties
or details that describe it, such as its make, model, color, year, and mileage.
Entity set : A library is a collection of similar entities, which in this case are books. Each book has
various properties or details that describe it, such as its title, author, publisher, and publication date.
Volatile attribute: A volatile attribute is one that is not retained when the power to a system is
turned off. An example of a volatile attribute is RAM (Random Access Memory), which stores data
temporarily and loses it when the power is turned off.
Non-volatile attribute: A non-volatile attribute is one that is retained even when the power to a
system is turned off. An example of a non-volatile attribute is ROM (Read-Only Memory), which stores
data permanently and does not lose it when the power is turned off.
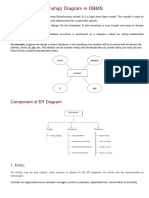
IV. Draw ERD
a.
b.
You might also like
- Database Design 5-1: Relationship Transferability Practice ActivitiesDocument4 pagesDatabase Design 5-1: Relationship Transferability Practice ActivitiesMinul MirdhaNo ratings yet
- ER (Entity Relationship) DiagramDocument13 pagesER (Entity Relationship) DiagramRutuja KadamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 ExcerciseDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 ExcerciseThảo BùiNo ratings yet
- Database Design 5-1: Relationship Transferability Practice ActivitiesDocument4 pagesDatabase Design 5-1: Relationship Transferability Practice ActivitiesMinul MirdhaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document10 pagesAssignment 3Alaa MohamedNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Tutorial 2 Practice Exercise 1. Match The Following Terms and Definitions. TermDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Tutorial 2 Practice Exercise 1. Match The Following Terms and Definitions. TermThành Long Lữ50% (2)
- Assignment 2dbmsDocument13 pagesAssignment 2dbmsTXACORPNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 ExcerciseDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 ExcerciseTủ LạnhNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument5 pagesER ModelHarpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ErDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Erkalik goyalNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramDocument10 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramSwati HansNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Model: IS 2511 - Fundamentals of Database SystemsDocument56 pagesEntity Relationship Model: IS 2511 - Fundamentals of Database Systemsjake dossryNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram: Lecturer: Rana SalahDocument25 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram: Lecturer: Rana Salahmohamed refayNo ratings yet
- 5.1 (B) ER ModelDocument10 pages5.1 (B) ER Model2002746.it.cecNo ratings yet
- dbms_unit3Document18 pagesdbms_unit3Esha Thaniya MallaNo ratings yet
- Database Design 3-3: Practice Activities: Speaking Erdish and Drawing RelationshipsDocument3 pagesDatabase Design 3-3: Practice Activities: Speaking Erdish and Drawing RelationshipsMinul MirdhaNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram in DBMSDocument12 pagesER Diagram in DBMSPankaj Prajapati PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument12 pagesER Modelwaleed.khaldNo ratings yet
- 3DBMS ER Model Concept - Javatpoint PDFDocument6 pages3DBMS ER Model Concept - Javatpoint PDFriddhi chavanNo ratings yet
- ER Model Chapter 4Document21 pagesER Model Chapter 4vibhav thakurNo ratings yet
- SyntaxDocument11 pagesSyntaxHari WishnawaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document27 pagesLecture 7Ahmad Hussain Shafi SE-3rdNo ratings yet
- Name: Vaishnavi Kailas Raut Seat No.: S190088621 Group B Assignment No: 1Document42 pagesName: Vaishnavi Kailas Raut Seat No.: S190088621 Group B Assignment No: 1VaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Data ModelsDocument92 pagesUnit-2 Data ModelsShiv PatelNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship ModelDocument5 pagesEntity Relationship Modelnayan moni dasNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument6 pagesPronounsMely FebriansariNo ratings yet
- Co1 Session3Document18 pagesCo1 Session3Jayavarapu Karthik JNo ratings yet
- DD 5 1 PracticeDocument2 pagesDD 5 1 PracticeTania SukmaNo ratings yet
- Designing ERDsDocument23 pagesDesigning ERDsmotihama12No ratings yet
- Data Modeling ER Model Concept: Component of ER DiagramDocument21 pagesData Modeling ER Model Concept: Component of ER DiagramAnick KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 DBMS NotesDocument51 pagesUnit-2 DBMS NotesAmrith MadhiraNo ratings yet
- ERDDocument20 pagesERDapi-26344848100% (2)
- Entity Relationship ModelDocument4 pagesEntity Relationship ModeluttranisinghNo ratings yet
- Section 3Document2 pagesSection 3IULIA GYONGYI LUTARUNo ratings yet
- DBMS ER Model Concept Unit2Document6 pagesDBMS ER Model Concept Unit2Surya PalNo ratings yet
- Lexical Relations: Dian Nuswantoro University SemarangDocument41 pagesLexical Relations: Dian Nuswantoro University SemarangAmm ÃrNo ratings yet
- DB AssignmentDocument2 pagesDB Assignmentزین العابدینNo ratings yet
- IBE 1 and 2Document84 pagesIBE 1 and 2Alina TeranNo ratings yet
- Database I: Methodology Entity-Relationship Data ModellingDocument61 pagesDatabase I: Methodology Entity-Relationship Data ModellingMuhammad Asghar KhanNo ratings yet
- English10 Q1 M8Document12 pagesEnglish10 Q1 M8sydleorNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship ModelDocument8 pagesEntity Relationship ModeltanujaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Entity-Relationship ModelDocument86 pagesUnit 1: Entity-Relationship ModelJua IgnNo ratings yet
- ERD PresentationDocument21 pagesERD PresentationChaudhary ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Part-2)Document15 pagesUnit-1 (Part-2)Avinash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Universes and The Identity of IndiscerniblesDocument15 pagesSymmetrical Universes and The Identity of IndiscerniblessupervenienceNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab 3 ER DIagramDocument5 pagesDBMS Lab 3 ER DIagramSYED MUHAMMAD WAQASNo ratings yet
- PDF‑документDocument2 pagesPDF‑документValter ValterNo ratings yet
- Dbms EntityDocument40 pagesDbms Entityvu4f2223087No ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramDocument6 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramMayank GoswamiNo ratings yet
- EntityDocument2 pagesEntityhotel epicsNo ratings yet
- QB C9 (L1-Introduction To OOP Concepts)Document3 pagesQB C9 (L1-Introduction To OOP Concepts)Naman PahujaNo ratings yet
- AIM - Identify Real Word Problem and Develop The Problem StatementDocument4 pagesAIM - Identify Real Word Problem and Develop The Problem StatementKUNAL SALUNKHENo ratings yet
- Er Digaram Symbols PDFDocument7 pagesEr Digaram Symbols PDFSoumitri DashNo ratings yet
- E-R ModelDocument14 pagesE-R Modelkiller HackingNo ratings yet
- Make GK EasyDocument12 pagesMake GK EasyRahul Kumar KNo ratings yet
- GRAMARRRRRRRDocument6 pagesGRAMARRRRRRRAna AnaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 & 4 Entity Relationship Modelling: Er. Pradip KharbujaDocument68 pagesTopic 3 & 4 Entity Relationship Modelling: Er. Pradip Kharbujaniravthegreate999No ratings yet
- Cb3401 Unit 2Document30 pagesCb3401 Unit 2varshavarsha3690No ratings yet
- Database System Concepts 03Document48 pagesDatabase System Concepts 03yusufahmadi792No ratings yet