Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views20231030213440IPS I
20231030213440IPS I
Uploaded by
tashuaneesThis document summarizes key concepts about atomic structure from Thomson's and Rutherford's models of the atom. It discusses the three subatomic particles (proton, electron, neutron), their properties, and who discovered them. It describes Thomson's model where electrons are embedded in a positively charged sphere and its failure. It outlines Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiment, the conclusions drawn, and the nuclear model of the atom with electrons orbiting the nucleus. However, Rutherford's model could not explain the stability of atoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Full Download Ebook PDF Introductory Chemistry by Kevin Revell PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Introductory Chemistry by Kevin Revell PDFtimothy.mees274100% (39)
- CHPT 26 PacketDocument8 pagesCHPT 26 Packethongling240% (2)
- Selina Concise Chemistry Class 9 Solutions Chapter 4Document40 pagesSelina Concise Chemistry Class 9 Solutions Chapter 4NischalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Work: Submitted To:-Miss. M.DolareDocument24 pagesChemistry Project Work: Submitted To:-Miss. M.DolareJahnvi DongreNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2nd Secondary 2018 With URLDocument72 pagesChemistry 2nd Secondary 2018 With URLMustafa HassanNo ratings yet
- Ix CH - 4 Cw.Document2 pagesIx CH - 4 Cw.Sharan Raj GuhanNo ratings yet
- Reference: Rutherford's Model of An AtomDocument4 pagesReference: Rutherford's Model of An AtomAchuliba kwotuaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Structure of AtomDocument8 pages9 Science Structure of AtomAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ix: Chapter 4: Structure of The AtomDocument6 pagesChemistry-Ix: Chapter 4: Structure of The AtomShreyashkar JhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter OneDocument16 pagesChemistry Chapter Onedemro channelNo ratings yet
- مذكرة كيمياء لغات تانية ثانوى 2020Document91 pagesمذكرة كيمياء لغات تانية ثانوى 2020Mohamed SaadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Structure of An Atom: AtomsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To The Structure of An Atom: Atomsshowmytv12No ratings yet
- YT Structure of The AtomDocument72 pagesYT Structure of The AtomAbhishek Kumar100% (1)
- Structure of An AtomDocument4 pagesStructure of An Atomsompriya007No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: ObservationDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: ObservationFerris antonyNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Structure of The Atom 1Document35 pagesCH 4 Structure of The Atom 1Shreyash Mitra Educational PurposeNo ratings yet
- CHEM CLASS 9 NCERT Structure of The Atom Neha V1.3Document10 pagesCHEM CLASS 9 NCERT Structure of The Atom Neha V1.3Gaurav ThakareNo ratings yet
- Electrons Protons Neutrons: Ernest Rutherford'S Model of An AtomDocument3 pagesElectrons Protons Neutrons: Ernest Rutherford'S Model of An AtomMadhavNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument14 pagesStructure of AtomRanjanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms: Chapter-9 1Document9 pagesStructure of Atoms: Chapter-9 1Willis ChekovNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument10 pagesStructure of Atomالمونتاج الاخيرNo ratings yet
- Acfrogdxygmpbeb0em56muyn3 N 3y9bhl1 Djt5tfeskv0jk1lv n2gltz Omwfh2jrsv7cm1dawvhkuf7focn0het8001ftzvrvxrnxqtjgtmsxdg9c18nstxv45bvjz0cos 7wrcqn4spucjqDocument10 pagesAcfrogdxygmpbeb0em56muyn3 N 3y9bhl1 Djt5tfeskv0jk1lv n2gltz Omwfh2jrsv7cm1dawvhkuf7focn0het8001ftzvrvxrnxqtjgtmsxdg9c18nstxv45bvjz0cos 7wrcqn4spucjqحسين عمار محسن سالمNo ratings yet
- Chem NoteDocument3 pagesChem Notekamruzaman shuvoNo ratings yet
- Homework 2.1: Early Models of The AtomDocument9 pagesHomework 2.1: Early Models of The AtomSneha JalanNo ratings yet
- CL-9, Chemistry-CH-4 NOTESDocument3 pagesCL-9, Chemistry-CH-4 NOTESsoniadhingra1805No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 "Structure of Atom" Concept Details Key ConceptsDocument11 pagesChapter - 4 "Structure of Atom" Concept Details Key ConceptsKishlay AnandNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument9 pagesStructure of AtomSharma RichaNo ratings yet
- L-4 Structure of The Atom NotesDocument58 pagesL-4 Structure of The Atom NotesIshita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument16 pagesAtomic ModelMA Masum HossainNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom - IXDocument11 pagesStructure of Atom - IXDINESH BISWALNo ratings yet
- ChemoDocument16 pagesChemoSoftware Lab MISKERNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics (4-5)Document38 pagesModern Physics (4-5)Vincee SamsonNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom g11Document4 pagesStructure of The Atom g11Ahmed NasrNo ratings yet
- Foundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructureDocument34 pagesFoundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructurePiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Physis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Document38 pagesPhysis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Dada RasheedNo ratings yet
- L2 Atomic ModelsDocument11 pagesL2 Atomic ModelsMusa Ahammed MahinNo ratings yet
- Document of Chapter 2Document17 pagesDocument of Chapter 2EstheruNo ratings yet
- ATOMSSDocument15 pagesATOMSSAPARAJITHA N CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Structure of Atoms: Chemistry 9Th Prepared By: Engr - Muhammad NaeemDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Atoms: Chemistry 9Th Prepared By: Engr - Muhammad NaeemMohammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Chapter Notes - Notes - ICSEDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure - Chapter Notes - Notes - ICSEItu DeyNo ratings yet
- Ernest Rutherford and The Gold Foil Experiment: Image CC BY 4.0Document25 pagesErnest Rutherford and The Gold Foil Experiment: Image CC BY 4.0sohaib389892No ratings yet
- Physics Project FileDocument8 pagesPhysics Project Filesavi guptaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure (1-35)Document35 pagesAtomic Structure (1-35)deepakkr08075% (4)
- Welcome To My PPT Name-Muskan Gope Class-9'C' Roll No. - 17 Subject - Science (Chemistry) Topic - Structure of The AtomsDocument15 pagesWelcome To My PPT Name-Muskan Gope Class-9'C' Roll No. - 17 Subject - Science (Chemistry) Topic - Structure of The AtomsMuskan GopeNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 - Assessment Tasks. Parro, IsabelDocument6 pagesMod 3 - Assessment Tasks. Parro, IsabelISABEL PARRONo ratings yet
- Iit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1Document48 pagesIit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1MD IMRAN100% (1)
- PrincesDeGuia - Nuclear ChemistryDocument10 pagesPrincesDeGuia - Nuclear ChemistryRosana BercadesNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 4. Week 6Document20 pages(CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 4. Week 6Trishia Mae Gregorio BelenNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFDocument11 pages9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFSeenu SNo ratings yet
- Atomsnotes 69472Document8 pagesAtomsnotes 69472ammonish08No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure JEE Main and Advanced (Theory)Document19 pagesAtomic Structure JEE Main and Advanced (Theory)Er. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)No ratings yet
- Chem 9th Unit 2 Org ApsDocument5 pagesChem 9th Unit 2 Org ApsMohammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Class Xi CH 2 NotesDocument14 pagesClass Xi CH 2 NotesPrabhjot SinghNo ratings yet
- AIDSDocument15 pagesAIDSMohit PathakNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument9 pagesNuclear Physics NotesNashae Hall-Pass AllenNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamental ParticlesDocument7 pages1.1 Fundamental ParticlesAman ImranNo ratings yet
- Revised Atomic StructureDocument43 pagesRevised Atomic StructureUdy MaudyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NewDocument6 pagesChapter 2 NewMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-PaperDocument7 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-PaperHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity-Notes-Dr. KK-Physics-BMSCEDocument15 pagesSuperconductivity-Notes-Dr. KK-Physics-BMSCEamritanshu.is22No ratings yet
- ARCO SAT Subject Chemistry Practice TestDocument25 pagesARCO SAT Subject Chemistry Practice TesthamdardiNo ratings yet
- 22 Scehme - Cse-Vtu-Question PapersDocument10 pages22 Scehme - Cse-Vtu-Question Papersjayanthibalasubramani2No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument56 pagesChemistryJaxon Isack90% (10)
- DP William Ruto's ManifestoDocument59 pagesDP William Ruto's ManifestoThe Star Kenya100% (1)
- Vibrational Sound Therapy ManualDocument12 pagesVibrational Sound Therapy ManualScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary SurfactantDocument7 pagesPulmonary SurfactantRohan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Biology 11th Edition StarrDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Human Biology 11th Edition StarrTabithaWatsonwbrc100% (50)
- Experiment Design in PhysicsDocument11 pagesExperiment Design in Physicsmedha0% (1)
- ET2008Document16 pagesET2008Soban Maan100% (1)
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Characteristics Properties of PhotonDocument18 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter Characteristics Properties of PhotonDevansh UppalNo ratings yet
- Full Thesis 1Document113 pagesFull Thesis 1Murtaza SieamNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Sci 502 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Sci 502 Physics For TeachersDocument4 pagesFinal Exam in Sci 502 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Sci 502 Physics For TeachersKenneth Roy MatuguinaNo ratings yet
- OCNA Sept 2009 Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy For Benign Skull Base TumorsDocument140 pagesOCNA Sept 2009 Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy For Benign Skull Base TumorsNeeraj MathurNo ratings yet
- Light As WaveDocument39 pagesLight As WaveJhon Vincent C. PerezNo ratings yet
- Fire Detection and Alarm System BasicsDocument115 pagesFire Detection and Alarm System Basicsscribd8421100% (8)
- Date Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet - 3 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level - 1 Exact DurationDocument2 pagesDate Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet - 3 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level - 1 Exact Durationmuhammad AYAANNo ratings yet
- 12P 25 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity PDFDocument78 pages12P 25 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity PDFadimegha100% (1)
- Quiz: Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds: Answers KeyDocument9 pagesQuiz: Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds: Answers KeyMegan CabahugNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewDocument15 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewPhirun ChengNo ratings yet
- Neet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Document27 pagesNeet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Deev SoniNo ratings yet
- Role of The Cesium Antimonide Layer in The Na 2 Ksb/Cs 3 SB PhotocathodeDocument7 pagesRole of The Cesium Antimonide Layer in The Na 2 Ksb/Cs 3 SB PhotocathodeDayti JuniorNo ratings yet
- June 2017 MS - Component 2 WJEC Physics AS-levelDocument12 pagesJune 2017 MS - Component 2 WJEC Physics AS-levelfadi baqainNo ratings yet
- The Early History of Quantum Tunneling - Merzbacher - Phys Today 2002-08Document6 pagesThe Early History of Quantum Tunneling - Merzbacher - Phys Today 2002-08Carlos AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom Solution PaperDocument3 pagesStructure of Atom Solution Paperlustmord688No ratings yet
- DPP-2 Moving ChargeDocument7 pagesDPP-2 Moving ChargeCharles DownsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-DongPanDocument28 pagesChapter 2-DongPanSri JunkNo ratings yet
20231030213440IPS I
20231030213440IPS I
Uploaded by
tashuanees0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThis document summarizes key concepts about atomic structure from Thomson's and Rutherford's models of the atom. It discusses the three subatomic particles (proton, electron, neutron), their properties, and who discovered them. It describes Thomson's model where electrons are embedded in a positively charged sphere and its failure. It outlines Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiment, the conclusions drawn, and the nuclear model of the atom with electrons orbiting the nucleus. However, Rutherford's model could not explain the stability of atoms.
Original Description:
Original Title
20231030213440IPS_i_4bc4d861-c875-4893-89fb-947fa79f61fb
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key concepts about atomic structure from Thomson's and Rutherford's models of the atom. It discusses the three subatomic particles (proton, electron, neutron), their properties, and who discovered them. It describes Thomson's model where electrons are embedded in a positively charged sphere and its failure. It outlines Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiment, the conclusions drawn, and the nuclear model of the atom with electrons orbiting the nucleus. However, Rutherford's model could not explain the stability of atoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pages20231030213440IPS I
20231030213440IPS I
Uploaded by
tashuaneesThis document summarizes key concepts about atomic structure from Thomson's and Rutherford's models of the atom. It discusses the three subatomic particles (proton, electron, neutron), their properties, and who discovered them. It describes Thomson's model where electrons are embedded in a positively charged sphere and its failure. It outlines Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiment, the conclusions drawn, and the nuclear model of the atom with electrons orbiting the nucleus. However, Rutherford's model could not explain the stability of atoms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
CH-4 STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
Q1. Define atom.
Ans: An atom is the smallest particle of the element that may or may not exist
independently and retain all its chemical properties.
Q2. Name the three sub-atomic particles of an atom.
Ans: (i)Electron (ii)Proton (iii)Neutron
Q3. Compare the mass and charge of sub-atomic particles in tabular form. Also
name the scientist who discovered these particles.
Ans:
SUB-ATOMIC CHARGE MASS DISCOVERED BY
PARTICLES
Proton +1 1u E. Goldstein
Electron -1 Negligible J.J. Thomson
Neutron Neutral 1u James Chadwick
Q4.List the features of Thomson’s model of atom.
Ans. 1) An atom consists of a positively charged sphere and the electrons are
embedded in it.
2)The negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude .So the atom as a
whole is electrically neutral.
Q5Write the success and failure of Thomson’s model of atom.
Ans: Success -Thomson’s model explained that atoms are electrically neutral.
Failure -The results of experiments carried out by other scientists couldn’t be
explained by this model.
Q6What are alpha particles?
Ans: Alpha particles are doubly charged helium ions (He2+).They are fast moving
particles having a considerable amount of energy.
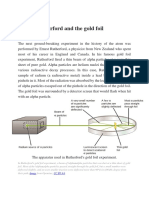
Q7Why did Rutherford select a gold foil for his experiment?
Ans: Rutherford selected a gold foil for his experiment because he wanted a thin
layer of metal and gold is the most malleable metal.
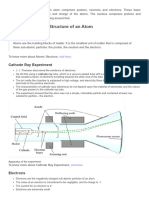
Q8 Explain Rutherford’s alpha(α) particle scattering experiment.
Ans: In his experiment ,fast moving alpha (α)particles were made to fall on a thin
gold foil
Draw fig 4.2 given in page 48
His observations and conclusions are as follows.
No OBSERVATIONS CONCLUSIONS
1 Most of the fast moving This indicates that most of the space
α- particles passed straight inside the atom is empty.
through gold foil
2 Some of the α-particles This indicates that the positive charge of the
were deflected by the foil by atom occupies very little space.
small angles
3 One out of every 12000 This indicates that all the positive charge
particles appeared to and mass of the gold atom were
rebound. concentrated in a very small volume within
the atom.
Q9 State the features of Rutherford’s nuclear model of atom.
Ans: 1.There is a positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus. Nearly
all the mass of an atom resides in the nucleus.
2.The electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths.
3.The size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom.
Q10 Write the drawbacks of Rutherford’s model of the atom.
Ans: Rutherford’s model couldn’t explain the stability of an atom. Any particle in a
circular orbit would undergo acceleration . During acceleration, charged particles
would radiate energy. Thus, the revolving electron would lose energy and finally
fall into the nucleus. If this were so, the atom should be highly unstable and
hence matter would not exist in the form that we know. But atoms are quite
stable.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You might also like
- Full Download Ebook PDF Introductory Chemistry by Kevin Revell PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Introductory Chemistry by Kevin Revell PDFtimothy.mees274100% (39)
- CHPT 26 PacketDocument8 pagesCHPT 26 Packethongling240% (2)
- Selina Concise Chemistry Class 9 Solutions Chapter 4Document40 pagesSelina Concise Chemistry Class 9 Solutions Chapter 4NischalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Work: Submitted To:-Miss. M.DolareDocument24 pagesChemistry Project Work: Submitted To:-Miss. M.DolareJahnvi DongreNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2nd Secondary 2018 With URLDocument72 pagesChemistry 2nd Secondary 2018 With URLMustafa HassanNo ratings yet
- Ix CH - 4 Cw.Document2 pagesIx CH - 4 Cw.Sharan Raj GuhanNo ratings yet
- Reference: Rutherford's Model of An AtomDocument4 pagesReference: Rutherford's Model of An AtomAchuliba kwotuaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Structure of AtomDocument8 pages9 Science Structure of AtomAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ix: Chapter 4: Structure of The AtomDocument6 pagesChemistry-Ix: Chapter 4: Structure of The AtomShreyashkar JhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter OneDocument16 pagesChemistry Chapter Onedemro channelNo ratings yet
- مذكرة كيمياء لغات تانية ثانوى 2020Document91 pagesمذكرة كيمياء لغات تانية ثانوى 2020Mohamed SaadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Structure of An Atom: AtomsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To The Structure of An Atom: Atomsshowmytv12No ratings yet
- YT Structure of The AtomDocument72 pagesYT Structure of The AtomAbhishek Kumar100% (1)
- Structure of An AtomDocument4 pagesStructure of An Atomsompriya007No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: ObservationDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: ObservationFerris antonyNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Structure of The Atom 1Document35 pagesCH 4 Structure of The Atom 1Shreyash Mitra Educational PurposeNo ratings yet
- CHEM CLASS 9 NCERT Structure of The Atom Neha V1.3Document10 pagesCHEM CLASS 9 NCERT Structure of The Atom Neha V1.3Gaurav ThakareNo ratings yet
- Electrons Protons Neutrons: Ernest Rutherford'S Model of An AtomDocument3 pagesElectrons Protons Neutrons: Ernest Rutherford'S Model of An AtomMadhavNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument14 pagesStructure of AtomRanjanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms: Chapter-9 1Document9 pagesStructure of Atoms: Chapter-9 1Willis ChekovNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument10 pagesStructure of Atomالمونتاج الاخيرNo ratings yet
- Acfrogdxygmpbeb0em56muyn3 N 3y9bhl1 Djt5tfeskv0jk1lv n2gltz Omwfh2jrsv7cm1dawvhkuf7focn0het8001ftzvrvxrnxqtjgtmsxdg9c18nstxv45bvjz0cos 7wrcqn4spucjqDocument10 pagesAcfrogdxygmpbeb0em56muyn3 N 3y9bhl1 Djt5tfeskv0jk1lv n2gltz Omwfh2jrsv7cm1dawvhkuf7focn0het8001ftzvrvxrnxqtjgtmsxdg9c18nstxv45bvjz0cos 7wrcqn4spucjqحسين عمار محسن سالمNo ratings yet
- Chem NoteDocument3 pagesChem Notekamruzaman shuvoNo ratings yet
- Homework 2.1: Early Models of The AtomDocument9 pagesHomework 2.1: Early Models of The AtomSneha JalanNo ratings yet
- CL-9, Chemistry-CH-4 NOTESDocument3 pagesCL-9, Chemistry-CH-4 NOTESsoniadhingra1805No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 "Structure of Atom" Concept Details Key ConceptsDocument11 pagesChapter - 4 "Structure of Atom" Concept Details Key ConceptsKishlay AnandNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument9 pagesStructure of AtomSharma RichaNo ratings yet
- L-4 Structure of The Atom NotesDocument58 pagesL-4 Structure of The Atom NotesIshita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument16 pagesAtomic ModelMA Masum HossainNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom - IXDocument11 pagesStructure of Atom - IXDINESH BISWALNo ratings yet
- ChemoDocument16 pagesChemoSoftware Lab MISKERNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 4 Structure of AtomShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics (4-5)Document38 pagesModern Physics (4-5)Vincee SamsonNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom g11Document4 pagesStructure of The Atom g11Ahmed NasrNo ratings yet
- Foundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructureDocument34 pagesFoundation &fundamentals of Chemistry Unit: 3 Atomic StructurePiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Physis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Document38 pagesPhysis 2nd and 3rd Term ss3Dada RasheedNo ratings yet
- L2 Atomic ModelsDocument11 pagesL2 Atomic ModelsMusa Ahammed MahinNo ratings yet
- Document of Chapter 2Document17 pagesDocument of Chapter 2EstheruNo ratings yet
- ATOMSSDocument15 pagesATOMSSAPARAJITHA N CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Structure of Atoms: Chemistry 9Th Prepared By: Engr - Muhammad NaeemDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Atoms: Chemistry 9Th Prepared By: Engr - Muhammad NaeemMohammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Chapter Notes - Notes - ICSEDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure - Chapter Notes - Notes - ICSEItu DeyNo ratings yet
- Ernest Rutherford and The Gold Foil Experiment: Image CC BY 4.0Document25 pagesErnest Rutherford and The Gold Foil Experiment: Image CC BY 4.0sohaib389892No ratings yet
- Physics Project FileDocument8 pagesPhysics Project Filesavi guptaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure (1-35)Document35 pagesAtomic Structure (1-35)deepakkr08075% (4)
- Welcome To My PPT Name-Muskan Gope Class-9'C' Roll No. - 17 Subject - Science (Chemistry) Topic - Structure of The AtomsDocument15 pagesWelcome To My PPT Name-Muskan Gope Class-9'C' Roll No. - 17 Subject - Science (Chemistry) Topic - Structure of The AtomsMuskan GopeNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 - Assessment Tasks. Parro, IsabelDocument6 pagesMod 3 - Assessment Tasks. Parro, IsabelISABEL PARRONo ratings yet
- Iit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1Document48 pagesIit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1MD IMRAN100% (1)
- PrincesDeGuia - Nuclear ChemistryDocument10 pagesPrincesDeGuia - Nuclear ChemistryRosana BercadesNo ratings yet
- (CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 4. Week 6Document20 pages(CHEM) UNIT 1. Lesson 4. Week 6Trishia Mae Gregorio BelenNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFDocument11 pages9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFSeenu SNo ratings yet
- Atomsnotes 69472Document8 pagesAtomsnotes 69472ammonish08No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure JEE Main and Advanced (Theory)Document19 pagesAtomic Structure JEE Main and Advanced (Theory)Er. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)No ratings yet
- Chem 9th Unit 2 Org ApsDocument5 pagesChem 9th Unit 2 Org ApsMohammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Class Xi CH 2 NotesDocument14 pagesClass Xi CH 2 NotesPrabhjot SinghNo ratings yet
- AIDSDocument15 pagesAIDSMohit PathakNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument9 pagesNuclear Physics NotesNashae Hall-Pass AllenNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamental ParticlesDocument7 pages1.1 Fundamental ParticlesAman ImranNo ratings yet
- Revised Atomic StructureDocument43 pagesRevised Atomic StructureUdy MaudyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NewDocument6 pagesChapter 2 NewMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-PaperDocument7 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-PaperHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity-Notes-Dr. KK-Physics-BMSCEDocument15 pagesSuperconductivity-Notes-Dr. KK-Physics-BMSCEamritanshu.is22No ratings yet
- ARCO SAT Subject Chemistry Practice TestDocument25 pagesARCO SAT Subject Chemistry Practice TesthamdardiNo ratings yet
- 22 Scehme - Cse-Vtu-Question PapersDocument10 pages22 Scehme - Cse-Vtu-Question Papersjayanthibalasubramani2No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument56 pagesChemistryJaxon Isack90% (10)
- DP William Ruto's ManifestoDocument59 pagesDP William Ruto's ManifestoThe Star Kenya100% (1)
- Vibrational Sound Therapy ManualDocument12 pagesVibrational Sound Therapy ManualScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary SurfactantDocument7 pagesPulmonary SurfactantRohan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Biology 11th Edition StarrDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Human Biology 11th Edition StarrTabithaWatsonwbrc100% (50)
- Experiment Design in PhysicsDocument11 pagesExperiment Design in Physicsmedha0% (1)
- ET2008Document16 pagesET2008Soban Maan100% (1)
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Characteristics Properties of PhotonDocument18 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter Characteristics Properties of PhotonDevansh UppalNo ratings yet
- Full Thesis 1Document113 pagesFull Thesis 1Murtaza SieamNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Sci 502 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Sci 502 Physics For TeachersDocument4 pagesFinal Exam in Sci 502 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Sci 502 Physics For TeachersKenneth Roy MatuguinaNo ratings yet
- OCNA Sept 2009 Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy For Benign Skull Base TumorsDocument140 pagesOCNA Sept 2009 Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy For Benign Skull Base TumorsNeeraj MathurNo ratings yet
- Light As WaveDocument39 pagesLight As WaveJhon Vincent C. PerezNo ratings yet
- Fire Detection and Alarm System BasicsDocument115 pagesFire Detection and Alarm System Basicsscribd8421100% (8)
- Date Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet - 3 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level - 1 Exact DurationDocument2 pagesDate Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet - 3 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level - 1 Exact Durationmuhammad AYAANNo ratings yet
- 12P 25 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity PDFDocument78 pages12P 25 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity PDFadimegha100% (1)
- Quiz: Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds: Answers KeyDocument9 pagesQuiz: Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds: Answers KeyMegan CabahugNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewDocument15 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewPhirun ChengNo ratings yet
- Neet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Document27 pagesNeet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Deev SoniNo ratings yet
- Role of The Cesium Antimonide Layer in The Na 2 Ksb/Cs 3 SB PhotocathodeDocument7 pagesRole of The Cesium Antimonide Layer in The Na 2 Ksb/Cs 3 SB PhotocathodeDayti JuniorNo ratings yet
- June 2017 MS - Component 2 WJEC Physics AS-levelDocument12 pagesJune 2017 MS - Component 2 WJEC Physics AS-levelfadi baqainNo ratings yet
- The Early History of Quantum Tunneling - Merzbacher - Phys Today 2002-08Document6 pagesThe Early History of Quantum Tunneling - Merzbacher - Phys Today 2002-08Carlos AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom Solution PaperDocument3 pagesStructure of Atom Solution Paperlustmord688No ratings yet
- DPP-2 Moving ChargeDocument7 pagesDPP-2 Moving ChargeCharles DownsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-DongPanDocument28 pagesChapter 2-DongPanSri JunkNo ratings yet