Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Report
Lab Report
Uploaded by
Fabrizio NEBESSEOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Report
Lab Report
Uploaded by
Fabrizio NEBESSECopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty of Engineering
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Laboratory Report
CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
Pumps in Series and Parallel
Lecturer: O. Nemraoui
Subject: FLM3B0S
Date: 16 November 2023
[Click here and type name] [Click here and type student number] Signed:
[Click here and type name] [Click here and type student number] Signed:
[Click here and type name] [Click here and type student number] Signed:
[Click here and type name] [Click here and type student number] Signed:
I (We) swear that this is the original work of the author(s). All information obtained
directly or indirectly from other sources has been fully acknowledged.
“ We learn through experiments!!”
Aim:
To determine the H vs Q curves for two pumps operating in series and parallel, and
compare with their corresponding published curves.
Apparatus:
Two identical single stage centrifugal pumps driven independently by variable speed
motors. Gate valve for regulating flow rate. Pressure transducers. Revolution counters.
Flow meter.
Procedure:
(a) Connect the pumps in series and record the suction, discharge pressure, flow rate and
input power at a constant speed for varying flow rates. Also record the pump speed.
(b) Repeat (a) above with the pumps connected in parallel instead. Maintain the speed
used in (a)
Theory:
Results:
Series connection
Pump 1 Pump 1 Pump
Sample Motor
Inlet Outlet Volume Pump 1 Inlet Outlet 1
Number 1
pressure Pressure Torque Flowrate Differential Velocity Velocity Total
Speed
Pump 1 Pump 1 Nm Pressure Head
bar bar Q bar V1 V2 H1
n1
[m³/h] [m/s] [m/s] [m]
[rpm]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Pump 2 Pump 2 Pump
Sample Motor
Inlet Outlet Volume Pump 2 Inlet Outlet 2
Number 2
pressure Pressure Torque Flowrate Differential Velocity Velocity Total
Speed
Pump 2 Pump 2 Nm Pressure Head
bar bar Q bar V 1 V 2 H2
n1
[m³/h] [m/s] [m/s] [m]
[rpm]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Sample
Number Volume flowrate Total combined head
[m³/h] [m]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Parallel connection
Pump 1 Pump 1 Pump 1
Sample Motor
Inlet Outlet Volume Pump 1 Inlet Outlet
Number 1
pressure Pressure Torque Flowrate Differential Velocity Velocity Total
Speed
Pump 1 Pump 1 Nm Pressure Head
bar bar Q bar V1 V2 H1
n1
[m³/h] [m/s] [m/s] [m]
[rpm]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Pump 2 Pump 2 Pump
Sample Motor
Inlet Outlet Volume Pump 2 Inlet Outlet 2
Number 2
pressure Pressure Torque Flowrate Differential Velocity Velocity Total
Speed
Pump 2 Pump 2 Nm Pressure Head
bar bar Q bar V1 V2 H2
n1
[m³/h] [m/s] [m/s] [m]
[rpm]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Sample
Number Total Volume flowrate Head
[m³/h] [m]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Discussion:
Conclusion:
Recommendations:
References:
Appendices
Note:
All the above sections need to expanded upon and written up in your words - the
format (e.g. theory omitted here) above serves only as a guide.
All graphs to be drawn manually first, before any computer generated graphs are
drawn.
All manually drawn graphs to be included in appendices, if computer graphs are
included in body of report.
A conclusions section is a requirement of any laboratory report; recommendations are
advisable – often the conclusions and recommendations can be combined into one
section.
You might also like
- C175 Fuel Inlet CalculationDocument5 pagesC175 Fuel Inlet CalculationlamNo ratings yet
- Lab # 5 Plunger Pump: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesLab # 5 Plunger Pump: ObjectiveNioNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4, 5, 6 (Single, Series and Parallel Centrifugal Pumps)Document11 pagesExperiment 4, 5, 6 (Single, Series and Parallel Centrifugal Pumps)Safi Ullah WarraichNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Pump PerformanceDocument20 pagesLab Report Pump Performanceamirshafiq67% (3)
- Fluid Machinery HandoutDocument19 pagesFluid Machinery Handoutأحمد صلاح الدين100% (2)
- Centrifugal Pumps R7Document9 pagesCentrifugal Pumps R7b.jefferson4738123No ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 Test On Vane Pump and Plotting of Performance CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesExperiment No.1 Test On Vane Pump and Plotting of Performance CharacteristicsShivanand TalwarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Pump PerformanceDocument8 pagesExperiment 4 Pump Performanceiskandar.qatarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: To Create A Pump Characteristic Curve & Be Able To Interpret ItDocument6 pagesExperiment 5: To Create A Pump Characteristic Curve & Be Able To Interpret ItKamil Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and Technology University: Fluid Mechanics Lab ReportDocument8 pagesAddis Ababa Science and Technology University: Fluid Mechanics Lab ReportNurye NigusNo ratings yet
- SGB G2 Informe7Document19 pagesSGB G2 Informe7David MuñozNo ratings yet
- Basic Theory PumpDocument37 pagesBasic Theory PumpkunkzNo ratings yet
- Open Ended LabDocument6 pagesOpen Ended LabVishal DhimanNo ratings yet
- FM Lab 6Document6 pagesFM Lab 6Kamil Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Pumps Lab ReportDocument16 pagesSeries and Parallel Pumps Lab ReportHannan AyubNo ratings yet
- ME 422 Experiment No 4Document15 pagesME 422 Experiment No 4Tousif SadmanNo ratings yet
- ESD Projects IVDocument2 pagesESD Projects IVsara48mohaNo ratings yet
- Pump and Compressor Design & Heuristics:: Dr. Chandra Mouli M.RDocument38 pagesPump and Compressor Design & Heuristics:: Dr. Chandra Mouli M.RRayan HassanNo ratings yet
- Manual of Gear PumpDocument5 pagesManual of Gear PumpJaianshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating PumpDocument4 pagesReciprocating PumpTejashri Pote100% (1)
- Hydraulic Pumps, SpecificationsDocument3 pagesHydraulic Pumps, Specificationsalikuncoro1005No ratings yet
- Serial and Parallel Pump Operations-Variable Speed Pump DriveDocument10 pagesSerial and Parallel Pump Operations-Variable Speed Pump DriveAyberk ArdıçNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document37 pagesCH 5zeheeNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal ExperimentDocument8 pagesCentrifugal ExperimentNizar NanoNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating PumpDocument16 pagesReciprocating PumpKavin KabilanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Report 2 AliDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Report 2 AliAli ArshadNo ratings yet
- Study of Centrifugal PumpDocument5 pagesStudy of Centrifugal Pumpउमेश गावंडेNo ratings yet
- ME2135-1 Lab Manual (Characteristics of Centrifugal Pump)Document12 pagesME2135-1 Lab Manual (Characteristics of Centrifugal Pump)meowyNo ratings yet
- 147 2 PDFDocument11 pages147 2 PDFTijana MrdakovicNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7+8+9Document32 pagesExperiment No 7+8+9Muhammad kamran AmjadNo ratings yet
- Numerical Calculation of Energy Performance and Transient Characteristics of Centrifugal Pump Under Gas-Liquid Two-Phase ConditionDocument14 pagesNumerical Calculation of Energy Performance and Transient Characteristics of Centrifugal Pump Under Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Conditionoussema baddediNo ratings yet
- Pumps Chapter 11Document87 pagesPumps Chapter 11Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- 2,4 Pipes&PumpsDocument226 pages2,4 Pipes&PumpsShankar Angappan100% (1)
- ESD Projects IDocument2 pagesESD Projects IDN CoverNo ratings yet
- M Y91 WWTi 58 Eh QHAM629Document5 pagesM Y91 WWTi 58 Eh QHAM629Black CanaryNo ratings yet
- TP Turbomachine1 Pelton Wheel Lab SheetDocument7 pagesTP Turbomachine1 Pelton Wheel Lab SheetAbdelwahab.gfNo ratings yet
- Activity 7Document5 pagesActivity 7Katy PerryNo ratings yet
- Lift Station Pump Head Calculation-UseDocument44 pagesLift Station Pump Head Calculation-Usekdpmansi50% (2)
- Engineering Lesson Guide 4: Pumps, Valves, and FansDocument34 pagesEngineering Lesson Guide 4: Pumps, Valves, and FansNader Ragab AmmarNo ratings yet
- Additional Material-Pumps CurvesDocument65 pagesAdditional Material-Pumps CurvesMannel matuidiNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: ME-422 Fluid Machinery SessionalDocument28 pagesBangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: ME-422 Fluid Machinery Sessionalakib ajadNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump TestDocument7 pagesCentrifugal Pump TestiJeng RalluNo ratings yet
- F4 Centrifugal PumpDocument5 pagesF4 Centrifugal PumpSzeQiLungNo ratings yet
- 7Document59 pages7Zainab Salman AliNo ratings yet
- Single Pump: Sample CalculationDocument4 pagesSingle Pump: Sample CalculationtareqNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Multi Pump Test RigDocument9 pagesExperiment 5: Multi Pump Test RigHahaNo ratings yet
- 3 Centrifugal PumpDocument36 pages3 Centrifugal PumpReza Dhony WijayaNo ratings yet
- Design calculation sheet: V V n−1) - ΔH. SDocument8 pagesDesign calculation sheet: V V n−1) - ΔH. SMoh Amm0% (2)
- Reciprocating Pump Test RigDocument7 pagesReciprocating Pump Test RigPurtain MENo ratings yet
- MELAB3 Experiment 1Document19 pagesMELAB3 Experiment 1Russelle GoNo ratings yet
- 9852 2493 01 - Startup Protocol - EditableDocument6 pages9852 2493 01 - Startup Protocol - EditableSamit JorgeNo ratings yet
- Section 5 Equipment Selection, Sizing & DesignDocument43 pagesSection 5 Equipment Selection, Sizing & Designgad480No ratings yet
- Pump Basics1Document34 pagesPump Basics1sambasivammeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery Manual 2022-23Document40 pagesFluid Machinery Manual 2022-23Aviansh MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Design of Submersible PumpsDocument5 pagesDesign of Submersible PumpsNoorNo ratings yet
- Pump Design Data Parameter S Pump Capacity Lps Water Horse Power Brake Horse PowerDocument8 pagesPump Design Data Parameter S Pump Capacity Lps Water Horse Power Brake Horse PowerGleen TapiaNo ratings yet
- Skema Scada WTP - STP LVDocument7 pagesSkema Scada WTP - STP LVFrans Cisco IcoNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument20 pagesCentrifugal PumpKavin KabilanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Lecture 1Document32 pagesCHAPTER 2 Lecture 1amanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GTU-Paper-Analysis PDF All 20052019030432PM PDFDocument11 pagesGTU-Paper-Analysis PDF All 20052019030432PM PDFAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Davis Shirtliff Manual 2015Document328 pagesDavis Shirtliff Manual 2015Tonui JohnNo ratings yet
- Sulzer Pump Familiarization Rev2Document90 pagesSulzer Pump Familiarization Rev2Jack Lali100% (1)
- Selecting The Best Pump: Guide ToDocument11 pagesSelecting The Best Pump: Guide ToTamani MoyoNo ratings yet
- Seal FluentDocument4 pagesSeal FluentrhbazziNo ratings yet
- Training - Flowserve Apm Pump CW Pump Part4Document11 pagesTraining - Flowserve Apm Pump CW Pump Part4hasan099No ratings yet
- HH220i - JAN 11Document1 pageHH220i - JAN 11Achmad GazaliNo ratings yet
- SBTET AP C-14 SYLLABUS DME IV SemesterDocument36 pagesSBTET AP C-14 SYLLABUS DME IV Semesterthirukumar50% (2)
- Gas Plant 3Document90 pagesGas Plant 3Anthony SiuNo ratings yet
- Ust Mock Boards - PipeDocument8 pagesUst Mock Boards - PipeVon Eric DamirezNo ratings yet
- Pumps Pump Is A Machine Used To Add Energy To A Liquid To Transfer The Liquid From AnotherDocument21 pagesPumps Pump Is A Machine Used To Add Energy To A Liquid To Transfer The Liquid From AnotherNygel CanamanNo ratings yet
- CO COR - Helix V CC Pressure BoostingDocument37 pagesCO COR - Helix V CC Pressure BoostingPaun ValentinNo ratings yet
- Tapflo Centrifugal PumpsDocument30 pagesTapflo Centrifugal PumpssergiofelipeNo ratings yet
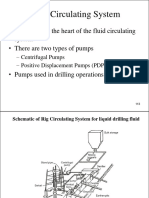
- Fluid Circulating System: - Mud Pump Is The Heart of The Fluid Circulating System - There Are Two Types of PumpsDocument46 pagesFluid Circulating System: - Mud Pump Is The Heart of The Fluid Circulating System - There Are Two Types of PumpsFreddy Mendoza CoronelNo ratings yet
- 07a3ec02 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pages07a3ec02 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryandhracollegesNo ratings yet
- Harriet 2019Document24 pagesHarriet 2019Felipe CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Draft IntegrationDocument53 pagesChapter 1 Draft IntegrationJonhel GatbuntonNo ratings yet
- Desmi DSL PumpeDocument2 pagesDesmi DSL PumpeZoranNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of A Selected Pump and FanDocument2 pagesPerformance Evaluation of A Selected Pump and Fanashier dave calulotNo ratings yet
- Esv Ie2 TD en PDFDocument68 pagesEsv Ie2 TD en PDFCristian Muñoz AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Fracture Analysis of A Cooling Water Pump Shaft: DimitrisDocument7 pagesFracture Analysis of A Cooling Water Pump Shaft: DimitrisT. LimNo ratings yet
- Waste Water Lift Station Design ManualDocument42 pagesWaste Water Lift Station Design ManualVarun Kewal100% (4)
- Slurry PumpsDocument69 pagesSlurry PumpsJhonny AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Progressing Cavity Pump ApplicationsDocument63 pagesProgressing Cavity Pump Applicationsadtijanic-1100% (1)
- GS&P 2 Pump SelectionDocument35 pagesGS&P 2 Pump SelectionMiick NuñeezNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions On PumpsDocument2 pagesExam Questions On PumpsTarek AzizNo ratings yet
- Hyd Micro ProjectDocument20 pagesHyd Micro ProjectOmkar Moze CE - J1 - 88No ratings yet
- Product Portfolio Goulds en Low PDFDocument13 pagesProduct Portfolio Goulds en Low PDFfaisal andreansyahNo ratings yet