Professional Documents
Culture Documents
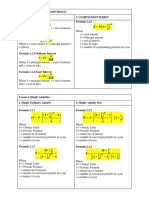
Formula Sheet - Tutorial 1
Formula Sheet - Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
peterpeterovic12345Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- FNCE 623 Formulae For Mid Term ExamDocument3 pagesFNCE 623 Formulae For Mid Term Examleili fallahNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Continuous Compounding, Nominal and Effective Rate of ItenrestDocument7 pagesTopic 2-Continuous Compounding, Nominal and Effective Rate of ItenrestHENRICK IGLENo ratings yet
- Anual 1Document18 pagesAnual 1Gussyck Agus PsicologistaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income Security Analysis Note 2Document61 pagesFixed Income Security Analysis Note 2Kevin CowanNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember Unit 3 Math of InvestmentDocument4 pagesPoints To Remember Unit 3 Math of InvestmentCamille DavidNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms and FormulasDocument2 pagesDefinition of Terms and Formulascarladrian.cruz.abNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Interest and Money-Time RelationshipDocument8 pagesLesson 2 - Interest and Money-Time RelationshipExcel MigsNo ratings yet
- Finance Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinance Formula SheetChris HolmanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Formulas For Time Value of MoneyDocument3 pagesSummary of Formulas For Time Value of MoneyMarilyn Varquez100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6NHƯ NGUYỄN LÂM TÂMNo ratings yet
- RP - CF1 - Time Value of MoneyDocument28 pagesRP - CF1 - Time Value of MoneySamyu KNo ratings yet
- Finanical Management Ch4Document60 pagesFinanical Management Ch4Chucky ChungNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document37 pagesLesson 1Joshua Miguel MejiasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Investment FormulasDocument4 pagesMathematics of Investment FormulasaileeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Equations NotesDocument4 pagesCorporate Finance Equations NotesSotiris HarisNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument10 pagesSummarykhoaphn22413cNo ratings yet
- Las q2w3-4Document5 pagesLas q2w3-4Mark Anthony Bell BacangNo ratings yet
- ECONDocument38 pagesECONjoeyNo ratings yet
- FIN222 Equations NotesDocument49 pagesFIN222 Equations NotesSotiris HarisNo ratings yet
- 1/ Valuation:: Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Timing Value of MoneyDocument12 pages1/ Valuation:: Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Timing Value of MoneyBẢO NGUYỄN HUY100% (1)
- Annuities PDFDocument2 pagesAnnuities PDFKenneth LewisNo ratings yet
- Mock Final 2021 - 2Document5 pagesMock Final 2021 - 2anthony.schzNo ratings yet
- FM Formula Sheet 01Document2 pagesFM Formula Sheet 01Aninda DuttaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1janice ngNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document25 pagesWeek 2ziyue wangNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Formula Sheet: Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesTime Value of Money Formula Sheet: Financial ManagementTechbotix AppsNo ratings yet
- Dejesus, Phoebekate - MMWDocument1 pageDejesus, Phoebekate - MMWPhoebe Kate Sanchez de JesusNo ratings yet
- Helpful Formulas For Finance 1Document2 pagesHelpful Formulas For Finance 1Falguni ShomeNo ratings yet
- Econ 3Document45 pagesEcon 3Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- NPV12Document6 pagesNPV12Rakib RabbyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document28 pagesChapter 2SHIRISH KNo ratings yet
- FM FormulasDocument24 pagesFM FormulasMd. Nafiz ShahrierNo ratings yet
- Sesi 1 Fabozzi Bmas8 PPT Ch02geDocument36 pagesSesi 1 Fabozzi Bmas8 PPT Ch02geLauraNo ratings yet
- Simple Annuity DueDocument28 pagesSimple Annuity DueNimrod CarolinoNo ratings yet
- McsformulaDocument1 pageMcsformulaHirat BrarNo ratings yet
- 12.02 Constant-Growth AnnuitiesDocument8 pages12.02 Constant-Growth Annuitiesmusic niNo ratings yet
- Discounted Cash Flow Valuations: Time Value of Money.: An Example of Finding The Future Value and Present ValueDocument3 pagesDiscounted Cash Flow Valuations: Time Value of Money.: An Example of Finding The Future Value and Present ValueTolulope AkandeNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Time Value of MoneyDocument15 pagesCH 2 Time Value of MoneyNikita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ema Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 04Document13 pagesEma Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 04Duygu ÇınarNo ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument96 pagesCorporate FinanceRohit Kumar83% (6)
- Mathematics of Investment FormulaDocument23 pagesMathematics of Investment FormulaFatima Ira ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Annuity: Interval or Rent Period. Term Is Defined As The Time Between The First and Last Payment IntervalsDocument2 pagesAnnuity: Interval or Rent Period. Term Is Defined As The Time Between The First and Last Payment IntervalsElcie AldeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 AnnuityDocument35 pagesChapter 6 AnnuityfatinNo ratings yet
- Simple AnnuitiesDocument33 pagesSimple Annuitieselma anacletoNo ratings yet
- The Term Structure of Interest Rates Lecture Notes PDFDocument25 pagesThe Term Structure of Interest Rates Lecture Notes PDFMuhammad Zahid FaridNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: Lumpsum Cases: in This Case, We Calculate The Present Value and Future Value For ADocument10 pagesTime Value of Money: Lumpsum Cases: in This Case, We Calculate The Present Value and Future Value For Asuman chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Part 2Document13 pagesChapter 2-Part 2Puji dyukeNo ratings yet
- FINA 1310 - Lecture 3 NotesDocument6 pagesFINA 1310 - Lecture 3 NotesAayushi ReddyNo ratings yet
- RSM 332 Lecture 3: Tina TanDocument17 pagesRSM 332 Lecture 3: Tina TanBella ChungNo ratings yet
- Em5 Lesson 3 Economic Study MethodDocument7 pagesEm5 Lesson 3 Economic Study MethodParisNo ratings yet
- Math101 FinanceDocument2 pagesMath101 FinanceMathew SpurlockNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5Jayesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Topic 3 UpdatedDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Topic 3 UpdatedJAN ERWIN LACUESTANo ratings yet
- Present Values and Accumulations: A S. M Volume 3, Pp. 1331-1336 inDocument6 pagesPresent Values and Accumulations: A S. M Volume 3, Pp. 1331-1336 inRishi SinghNo ratings yet
- To Find The Interest To Find The Principal To Find The Rate To Find The TimeDocument1 pageTo Find The Interest To Find The Principal To Find The Rate To Find The Timebonifacio gianga jrNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument7 pagesTime Value of Moneysincere sincereNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasJi ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 2Document20 pagesStudy Unit 2pphelokazi54No ratings yet
Formula Sheet - Tutorial 1
Formula Sheet - Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
peterpeterovic12345Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Sheet - Tutorial 1
Formula Sheet - Tutorial 1
Uploaded by
peterpeterovic12345Copyright:
Available Formats
Principles of Finance
Formula Sheet – Tutorial 2
Compounding Periods and Interest Rates
𝑛
𝑅 = (1 + 𝑖⁄𝑛) -1
Where,
R is the effective annual rate, i the nominal rate, and n the number of compounding periods
per year (for example, 12 for monthly compounding)
Present Value of a Lump Sum
𝐶
𝑃𝑉 =
(1 + 𝑖)𝑡
Where,
C is the future amount of money that must be discounted, t is the number of compounding
periods between the present date and the date where the sum is worth C, i is the interest
rate for one compounding period (the end of a compounding period is when interest is
applied, for example, annually, semi-annually, quarterly, monthly, daily).
The interest rate, i, is given as a percentage, but expressed as a decimal in this formula.
Present value factor: 𝑣 𝑛 = (1 + 𝑖)−𝑡
Future value
𝐹𝑉 = 𝑃𝑉 × (1 + 𝑖)𝑡
Where,
Where PV is the present value, t is the number of compounding periods (not necessarily an
integer), and i is the interest rate for that period.
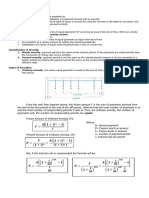
Present Value of Ordinary Annuity
1 − (1 + 𝑖)−𝑛
𝑃𝑉𝑂𝐴 = 𝐶 × [ ]
𝑖
Where,
C is the cash flow per period, i is the interest rate and n is the number of payments
Annuity Due
1 − (1 + 𝑖)−𝑛
𝑃𝑉𝑂𝐴 = 𝐶 × [ ] × (1 + 𝑖)
𝑖
Where,
C is the cash flow per period, i is the interest rate and n is the number of payments
You might also like
- FNCE 623 Formulae For Mid Term ExamDocument3 pagesFNCE 623 Formulae For Mid Term Examleili fallahNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Continuous Compounding, Nominal and Effective Rate of ItenrestDocument7 pagesTopic 2-Continuous Compounding, Nominal and Effective Rate of ItenrestHENRICK IGLENo ratings yet
- Anual 1Document18 pagesAnual 1Gussyck Agus PsicologistaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income Security Analysis Note 2Document61 pagesFixed Income Security Analysis Note 2Kevin CowanNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember Unit 3 Math of InvestmentDocument4 pagesPoints To Remember Unit 3 Math of InvestmentCamille DavidNo ratings yet
- Definition of Terms and FormulasDocument2 pagesDefinition of Terms and Formulascarladrian.cruz.abNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Interest and Money-Time RelationshipDocument8 pagesLesson 2 - Interest and Money-Time RelationshipExcel MigsNo ratings yet
- Finance Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFinance Formula SheetChris HolmanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Formulas For Time Value of MoneyDocument3 pagesSummary of Formulas For Time Value of MoneyMarilyn Varquez100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6NHƯ NGUYỄN LÂM TÂMNo ratings yet
- RP - CF1 - Time Value of MoneyDocument28 pagesRP - CF1 - Time Value of MoneySamyu KNo ratings yet
- Finanical Management Ch4Document60 pagesFinanical Management Ch4Chucky ChungNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document37 pagesLesson 1Joshua Miguel MejiasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Investment FormulasDocument4 pagesMathematics of Investment FormulasaileeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Equations NotesDocument4 pagesCorporate Finance Equations NotesSotiris HarisNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument10 pagesSummarykhoaphn22413cNo ratings yet
- Las q2w3-4Document5 pagesLas q2w3-4Mark Anthony Bell BacangNo ratings yet
- ECONDocument38 pagesECONjoeyNo ratings yet
- FIN222 Equations NotesDocument49 pagesFIN222 Equations NotesSotiris HarisNo ratings yet
- 1/ Valuation:: Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Timing Value of MoneyDocument12 pages1/ Valuation:: Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Timing Value of MoneyBẢO NGUYỄN HUY100% (1)
- Annuities PDFDocument2 pagesAnnuities PDFKenneth LewisNo ratings yet
- Mock Final 2021 - 2Document5 pagesMock Final 2021 - 2anthony.schzNo ratings yet
- FM Formula Sheet 01Document2 pagesFM Formula Sheet 01Aninda DuttaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1janice ngNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document25 pagesWeek 2ziyue wangNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Formula Sheet: Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesTime Value of Money Formula Sheet: Financial ManagementTechbotix AppsNo ratings yet
- Dejesus, Phoebekate - MMWDocument1 pageDejesus, Phoebekate - MMWPhoebe Kate Sanchez de JesusNo ratings yet
- Helpful Formulas For Finance 1Document2 pagesHelpful Formulas For Finance 1Falguni ShomeNo ratings yet
- Econ 3Document45 pagesEcon 3Trebob GardayaNo ratings yet
- NPV12Document6 pagesNPV12Rakib RabbyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document28 pagesChapter 2SHIRISH KNo ratings yet
- FM FormulasDocument24 pagesFM FormulasMd. Nafiz ShahrierNo ratings yet
- Sesi 1 Fabozzi Bmas8 PPT Ch02geDocument36 pagesSesi 1 Fabozzi Bmas8 PPT Ch02geLauraNo ratings yet
- Simple Annuity DueDocument28 pagesSimple Annuity DueNimrod CarolinoNo ratings yet
- McsformulaDocument1 pageMcsformulaHirat BrarNo ratings yet
- 12.02 Constant-Growth AnnuitiesDocument8 pages12.02 Constant-Growth Annuitiesmusic niNo ratings yet
- Discounted Cash Flow Valuations: Time Value of Money.: An Example of Finding The Future Value and Present ValueDocument3 pagesDiscounted Cash Flow Valuations: Time Value of Money.: An Example of Finding The Future Value and Present ValueTolulope AkandeNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Time Value of MoneyDocument15 pagesCH 2 Time Value of MoneyNikita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ema Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 04Document13 pagesEma Ge Berk CF 2GE SG 04Duygu ÇınarNo ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument96 pagesCorporate FinanceRohit Kumar83% (6)
- Mathematics of Investment FormulaDocument23 pagesMathematics of Investment FormulaFatima Ira ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Annuity: Interval or Rent Period. Term Is Defined As The Time Between The First and Last Payment IntervalsDocument2 pagesAnnuity: Interval or Rent Period. Term Is Defined As The Time Between The First and Last Payment IntervalsElcie AldeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 AnnuityDocument35 pagesChapter 6 AnnuityfatinNo ratings yet
- Simple AnnuitiesDocument33 pagesSimple Annuitieselma anacletoNo ratings yet
- The Term Structure of Interest Rates Lecture Notes PDFDocument25 pagesThe Term Structure of Interest Rates Lecture Notes PDFMuhammad Zahid FaridNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money: Lumpsum Cases: in This Case, We Calculate The Present Value and Future Value For ADocument10 pagesTime Value of Money: Lumpsum Cases: in This Case, We Calculate The Present Value and Future Value For Asuman chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Part 2Document13 pagesChapter 2-Part 2Puji dyukeNo ratings yet
- FINA 1310 - Lecture 3 NotesDocument6 pagesFINA 1310 - Lecture 3 NotesAayushi ReddyNo ratings yet
- RSM 332 Lecture 3: Tina TanDocument17 pagesRSM 332 Lecture 3: Tina TanBella ChungNo ratings yet
- Em5 Lesson 3 Economic Study MethodDocument7 pagesEm5 Lesson 3 Economic Study MethodParisNo ratings yet
- Math101 FinanceDocument2 pagesMath101 FinanceMathew SpurlockNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5Jayesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Topic 3 UpdatedDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Topic 3 UpdatedJAN ERWIN LACUESTANo ratings yet
- Present Values and Accumulations: A S. M Volume 3, Pp. 1331-1336 inDocument6 pagesPresent Values and Accumulations: A S. M Volume 3, Pp. 1331-1336 inRishi SinghNo ratings yet
- To Find The Interest To Find The Principal To Find The Rate To Find The TimeDocument1 pageTo Find The Interest To Find The Principal To Find The Rate To Find The Timebonifacio gianga jrNo ratings yet
- Time Value of MoneyDocument7 pagesTime Value of Moneysincere sincereNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasJi ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 2Document20 pagesStudy Unit 2pphelokazi54No ratings yet