Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 viewsRebyuwer
Rebyuwer
Uploaded by
JamesPython is an interpreted, high-level programming language created in the 1980s. It supports multiple programming paradigms and has a simple syntax. Programs are created by defining functions within modules. The standard Python distribution includes an interactive development environment called IDLE that can be used to write and test programs. Python uses indentation to denote code blocks rather than brackets. It supports various data types including strings, integers, floats, lists, and Boolean values. Control flow is implemented using conditionals, loops, functions and modules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Introduction To PythonDocument62 pagesIntroduction To PythonNurfatin Nadhirah100% (1)
- Advance Computer Programming: NotesDocument4 pagesAdvance Computer Programming: NotesGlyza Marie Sederio ButronNo ratings yet
- CP Lec Finals ReviewerDocument15 pagesCP Lec Finals Reviewerww8jpsy8w6No ratings yet
- BLOG Quiz FinalsDocument5 pagesBLOG Quiz FinalsJun Martine SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Comprog 1 ReviewerDocument2 pagesComprog 1 ReviewerrbxwmnNo ratings yet
- ComProg ReviewerDocument4 pagesComProg ReviewerJailyn Ribleza SamosaNo ratings yet
- Hci Finals W1&2Document3 pagesHci Finals W1&2ASAP BOI GAMEZNo ratings yet
- PLSQL Interview Question With Answer-6Document7 pagesPLSQL Interview Question With Answer-6민수자가디스No ratings yet
- 28 - PHP - Looping and FunctionsDocument31 pages28 - PHP - Looping and FunctionsAhsan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Procedural Paradigm: Algol - 2 Generation LanguageDocument50 pagesProcedural Paradigm: Algol - 2 Generation LanguageBuddhika Indrajith GunawardenaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Perl PDFDocument25 pagesAn Introduction To Perl PDFTanmay McGrathNo ratings yet
- Ict Q3Document8 pagesIct Q3MMALTEZ, RALPH CHRISTIAN, R.No ratings yet
- Training Seminar On "Python For Beginners"Document28 pagesTraining Seminar On "Python For Beginners"Rashi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2696445817745910253Document10 pagesInbound 2696445817745910253kristyllemaebNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 Introduction To Java Programming LanguageDocument33 pagesHandout 2 Introduction To Java Programming Languageeugenemwangi08No ratings yet
- SummarySC025 2018-2019Document8 pagesSummarySC025 2018-2019zeytaNo ratings yet
- PHP Infomatics 3Document22 pagesPHP Infomatics 3Jus WaNo ratings yet
- Pyhton ProgrmmingDocument97 pagesPyhton ProgrmmingbharathvajkvcetNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals Week 2 Notes Variables and ExpressionsDocument9 pagesProgramming Fundamentals Week 2 Notes Variables and ExpressionsPablo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Introduction To JavaDocument34 pagesSession 1 Introduction To JavaJomer Robas TadenaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Comprog 2Document15 pagesReviewer - Comprog 2limariokun02No ratings yet
- Basic, Function and Turtle GraphicsDocument35 pagesBasic, Function and Turtle Graphicsabebeyonas88No ratings yet
- RefDocument53 pagesRefawstestacc34No ratings yet
- JavaDocument8 pagesJavaColen LUMAMBANo ratings yet
- Functional ProgrammingDocument46 pagesFunctional ProgrammingJohn Paul Anthony ArlosNo ratings yet
- BIT205-HO1-Basic Concepts of JAVA ProgrammingDocument73 pagesBIT205-HO1-Basic Concepts of JAVA ProgrammingBahaa HaneneNo ratings yet
- Python Preparation QuestionsDocument3 pagesPython Preparation QuestionsnagasanjaysharmaNo ratings yet
- Pds 1Document6 pagesPds 1vkforytNo ratings yet
- Working With Functions-2 2022-23Document55 pagesWorking With Functions-2 2022-23sharanshajiixc36No ratings yet
- Python KeywordsDocument17 pagesPython Keywordsshalinikasera157No ratings yet
- Ch4 - PHPDocument151 pagesCh4 - PHPTrầm Tiến Anh B1706971No ratings yet
- CSE100 wk3 4Document21 pagesCSE100 wk3 4Razia Sultana Ankhy StudentNo ratings yet
- Create PDF in Your Applications With The Pdfcrowd: HTML To PDF ApiDocument437 pagesCreate PDF in Your Applications With The Pdfcrowd: HTML To PDF Apipg rNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PythonDocument13 pagesIntroduction To PythonKartik MahajanNo ratings yet
- Python RevisionDocument96 pagesPython Revisionen21cs301471No ratings yet
- Comp 7Document3 pagesComp 7Tristan Michael G. PanchoNo ratings yet
- Python Unit 1 Part 1Document47 pagesPython Unit 1 Part 1kiranmaijilakara325No ratings yet
- Computer Programming Languages: Lecture - 1Document38 pagesComputer Programming Languages: Lecture - 1Gul khanNo ratings yet
- Ansible - Interview Q&A-2Document11 pagesAnsible - Interview Q&A-2Vignesh PanneerselvamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 JAVA Programming Theoretical FrameworkDocument118 pagesChapter 2 JAVA Programming Theoretical FrameworkronaldbvirinyangweNo ratings yet
- Python Learning (Basics I & II)Document33 pagesPython Learning (Basics I & II)Adventure WorldNo ratings yet
- Java 1Document112 pagesJava 1Malathi NNo ratings yet
- CS121Document2 pagesCS121Ikon TrashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Python Lecture 2Document25 pagesIntroduction To Python Lecture 2Maraña Kelvin LouieNo ratings yet
- Interview Level QA On CDocument20 pagesInterview Level QA On CRam BhardwajNo ratings yet
- IT PF Reviewer MergedDocument15 pagesIT PF Reviewer Mergedpauljustinabelgas.neustNo ratings yet
- ThikDocument8 pagesThikIstamsetty HanumantharaoNo ratings yet
- Python Scripting in Grasshopper SPMDocument15 pagesPython Scripting in Grasshopper SPMVictor CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Computer ProgrammingDocument10 pagesComputer ProgrammingAlesha BanaagNo ratings yet
- IoT Lab Manual Removed RemovedDocument25 pagesIoT Lab Manual Removed Removedansariisrafil03No ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument74 pagesFunctionsvoduykhoa2504No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Data Structure: Unit 1Document40 pagesObject Oriented Data Structure: Unit 1shivanshNo ratings yet
- Computer Science - Introduction To Java ISC NotesDocument10 pagesComputer Science - Introduction To Java ISC NotesVarun Dhawan100% (1)
- Unit 1 Core Java - 240510 - 125907Document165 pagesUnit 1 Core Java - 240510 - 125907manyab009No ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument5 pagesUnit IiAashi JainNo ratings yet
- Chpater 2 Basic in Java ProgrammingDocument60 pagesChpater 2 Basic in Java ProgrammingDesyilalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Python - Basic - SyntaxDocument9 pagesLesson 2 - Python - Basic - SyntaxSherlita YbañezNo ratings yet
- Quiz #3Document4 pagesQuiz #3Uno Ferreras FaustoNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Introduction To JavaDocument36 pagesSession 1 - Introduction To Javat0eberriesNo ratings yet
- PYTHONDocument20 pagesPYTHONahmalik1012No ratings yet
- Python programming for beginners: Python programming for beginners by Tanjimul Islam TareqFrom EverandPython programming for beginners: Python programming for beginners by Tanjimul Islam TareqNo ratings yet
- New in Spring 5: Functional Web Framework: Arjen Poutsma PivotalDocument23 pagesNew in Spring 5: Functional Web Framework: Arjen Poutsma PivotalFaiçal YahiaNo ratings yet
- Java NotesDocument29 pagesJava NotessreenivasnairNo ratings yet
- PST Book - Unit 1 - 5Document192 pagesPST Book - Unit 1 - 5Saipriya VempalliNo ratings yet
- Python Quick NoteDocument23 pagesPython Quick NoteJyotirmay SahuNo ratings yet
- Python:: Data HandlingDocument6 pagesPython:: Data HandlingMeena SharmaNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument44 pagesPythonakbisoi1No ratings yet
- Python - Basic - 1 - Jupyter Notebook (Student)Document44 pagesPython - Basic - 1 - Jupyter Notebook (Student)Mesbahur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 13 - Abstract Classes and InterfacesDocument46 pages13 - Abstract Classes and InterfacesHanNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL REPORT On PythonDocument39 pagesINDUSTRIAL REPORT On PythonAnant PrakashNo ratings yet
- Java 1Document164 pagesJava 1akbala08No ratings yet
- 02 Programming PythonDocument48 pages02 Programming Pythongiordano manciniNo ratings yet
- Kotlin Cheat Sheet 1p - by Ekito 1.2Document4 pagesKotlin Cheat Sheet 1p - by Ekito 1.2Valmir BekteshiNo ratings yet
- C++ Keyboard Shortcut 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesC++ Keyboard Shortcut 2019 PDFJADU FRIENDSNo ratings yet
- Ruby Deep Dive (Jesus Castello)Document250 pagesRuby Deep Dive (Jesus Castello)William Yánez DevNo ratings yet
- 11 - Ip - Hy - Setb - 2022-23 - QP Set BDocument5 pages11 - Ip - Hy - Setb - 2022-23 - QP Set Bspiagent2007No ratings yet
- Python MCQsDocument39 pagesPython MCQsKanadam Karteeka Pavan100% (3)
- Cocoa FundamentalsDocument238 pagesCocoa FundamentalsDaniel MaccarroneNo ratings yet
- Ebook Fluent Python Luciano Ramalho Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Fluent Python Luciano Ramalho Online PDF All Chaptermarcus.keyes538100% (7)
- OOP ExamplesDocument8 pagesOOP ExamplesAdam ButterworthNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction & Syntax of Python ProgramDocument7 pagesUnit1 - Introduction & Syntax of Python Programsanju pawarNo ratings yet
- Python (3) Leaflet: Roland Becker December 16, 2020Document15 pagesPython (3) Leaflet: Roland Becker December 16, 2020beckerrolandhNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Ios 10 Programming Fundamentals With Swift Swift Xcode and Cocoa Basics 3Rd Edition Matt Neuburg PDFDocument43 pagesFull Chapter Ios 10 Programming Fundamentals With Swift Swift Xcode and Cocoa Basics 3Rd Edition Matt Neuburg PDFpatricia.chaney584100% (5)
- BRKSDN-1009 - Python 101 For Network Engineers (2017 Berlin) - 90 MinsDocument181 pagesBRKSDN-1009 - Python 101 For Network Engineers (2017 Berlin) - 90 MinsKevin Kim0% (1)
- Python Notes PDFDocument7 pagesPython Notes PDFSarath RamineniNo ratings yet
- React PropsDocument19 pagesReact PropsYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Javascript Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesAdvanced Javascript Interview Questionsparas1999998No ratings yet
- Python With Data ScienceDocument102 pagesPython With Data ScienceIrfanstudymeterialsNo ratings yet
- What's New in Python: A. M. KuchlingDocument37 pagesWhat's New in Python: A. M. KuchlingPlesa AlexandruNo ratings yet
- PFSD Unit 1 (Autosaved)Document65 pagesPFSD Unit 1 (Autosaved)Sayantan DeNo ratings yet
Rebyuwer
Rebyuwer
Uploaded by
James0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesPython is an interpreted, high-level programming language created in the 1980s. It supports multiple programming paradigms and has a simple syntax. Programs are created by defining functions within modules. The standard Python distribution includes an interactive development environment called IDLE that can be used to write and test programs. Python uses indentation to denote code blocks rather than brackets. It supports various data types including strings, integers, floats, lists, and Boolean values. Control flow is implemented using conditionals, loops, functions and modules.
Original Description:
Original Title
rebyuwer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPython is an interpreted, high-level programming language created in the 1980s. It supports multiple programming paradigms and has a simple syntax. Programs are created by defining functions within modules. The standard Python distribution includes an interactive development environment called IDLE that can be used to write and test programs. Python uses indentation to denote code blocks rather than brackets. It supports various data types including strings, integers, floats, lists, and Boolean values. Control flow is implemented using conditionals, loops, functions and modules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesRebyuwer
Rebyuwer
Uploaded by
JamesPython is an interpreted, high-level programming language created in the 1980s. It supports multiple programming paradigms and has a simple syntax. Programs are created by defining functions within modules. The standard Python distribution includes an interactive development environment called IDLE that can be used to write and test programs. Python uses indentation to denote code blocks rather than brackets. It supports various data types including strings, integers, floats, lists, and Boolean values. Control flow is implemented using conditionals, loops, functions and modules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
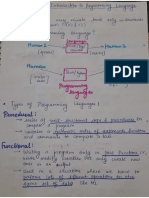
Python - Takes place automa cally during run me
between ONLY numeric value
- Development started in the 1980’s by Guido
- Float + integer = float
van Rossum
- Integer + string = error
- Supports a mul tude of programming
paradigm Modules
- Interpreted, very-high-level programming
- Programs are usually created by typing
language
defini ons into a separate file called a
Notable Features of python module or a script.
- Python module must be a text file with a .py
- Easy to learn
extension
- Cross-pla orm
- Open Source Programming Environment and IDLE
- Supports quick development
- A special type of so ware that simplifies the
- Extensible
process of crea ng modules/programs
- Embeddable
- Helps programmers write programs and
Literals include features such as automa c
inden ng, color highligh ng, and interac ve
print (“Hello”)
development
print (“geng geng”) - The standard python distribu on includes a
programming environment called IDLE that
- “Hello” and “geng geng” are the literals you can use for working on the programs of
- Used to indicate a specific value, which can this course
be assigned to a variable
Strings
Garbage Collec on
- Le ers, special characters, spaces, digits
- Python will automa cally clear old values - Enclose in quota on marks or single quotes
out of memory - “Borbs” “Acups”
Iden fiers Print
- Must begin with a le er or underscore, - Used to output stuff to console
which can be followed by any sequence of - Print(“sheesh”)
le ers, digits, or underscores
- Case-sensi ve Input(“ “)
- Keywords – part of python and cant be used
- Prints whatever is in the quotes
as ordinary iden fiers
- User types in something and hits enter and
Expression binds that value to a variable
- Text = input(“type anything”)
- Can produce new data (numeric or text) - Num = int(input(“type anything”))
values in your program using expressions.
- +, -, *, /, **, abs(), //, % Inden on
Data Conversion - Ma ers in Python
- How you denote block of code
while LOOPS Rela onal Operator
- Know numbers of itera ons - Evaluate a Boolean expression
- Can end early via break - < , <=, ==, >=, >, !=
- Uses a counter
In
- Can rewrite a for loop using a while loop
- Operator is used to determine if a specific
for LOOPS
value is in a given list
- Unbounded numbers for itera ons
Not in
- Can end early via break
- Can use a counter but must ini alize before - Operator returns the opposite result
loop and increment it inside loop
- May not be able to rewrite a while loop Two-Way Decisions
using a for loop - Can be implemented by a aching an else
Range (start, stop, step) clause onto an if clause.
- Default values are “start = 0” and “step = 1’ Mul -Way Decisions
and op onal - Use nested if-else statement to implement
- Loop un l value is stop – 1 mul -way decisions
Break - Else-if can be combined into elif
- Immediately exits whatever loop it is in Indefinite loops
Control Statement - Keeps itera ng un l certain condi ons are
met
- Is a statement that determines the control - if-else loop
flow of a set of statements
Definite loops
Control structure
- Number of itera ons is determined when
- Is a set of statements and the control the loops starts.
statements controlling their execu on. - for loop
3 fundamental forms of control Nested loops
- Sequen al - loop within a loop
- Selec on
- Itera on Pre-test loop
Boolean data type - one that checks for a condi on prior to
running the block of code
- Contains two Boolean values, denoted as
True and False in python Post-test loop
Boolean expression - execute the statements uncondi onally and
only check the condi on a er to determine
- Is an expression that evaluates to a Boolean if the statements should be executed again
value
Input valida on - Causes the variable to refer to the previously
bound variable in the closets enclosing
- If the user types an incorrect input, the
scope
programs ask for another value un l a valid
value has been entered Closure
Func ons - Closures are func on objects that
remembers values in enclosing scopes, even
- Sub-programs which performs tasks which
if they are no longer present in memory
may need to be repeated
- If you call closure without parentheses, only
- Similar to methods, but may not be
the type of the object will be returned
connected with objects
- Some func ons are bundled in standard The LEGB Rule
libraries
- Local
Func on Elements - Enclosed
- Global
- Define – Can appear at the beginning or end
- Built-in
of the program file
- Invoke or call – Usually happens in the body Lists
of the main() func on, but subfunc ons can
- Lists are one of the most powerful tools in
call other subfunc ons too.
python
Func on defini ons - They are just like the arrays declared in other
languages
- Two major parts: defini on head and
- Need not be always homogenous
defini on body
- Can contain strings, integers, as well as
- Defini on Head - has three main parts: the
objects in a single list
keyword def, the iden fier or name of the
- Can be used for implemen ng stacks and
func on, and the parameters in
queues
parentheses.
- Lists are mutable, they can be altered once
- Defini on body - The colon at the end of the
declared
defini on head marks the start of the body,
the block of statements Things we typically want to do with lists:
Variables - Retrieve (or set) an item at a specific
posi on via indexing
- References or pointers to an object in
- Concatenate two lists together
memory
- Get the length of the list
Global Keyword - Add an item to the list
- Remove an item from the list
- Telling python to use the globally defined - Check for membership
variable instead of locally defining it
Indexing
Nonlocal Keyword
- Can use listname[idx] to get and set an item
- Useful in nested func ons at a specific index
- Indexing syntax in python is quite powerful
- Can get a range of elements using what is - Returns the number of mes a specified
called a slice value occurs in a tuple
- Nega ve indices, which count from the back
Index()
of the list
- Can specify a third part of the slice called the - Searches the tuple for a specified value and
stride, by default the stride is one returns the posi on of where it was found
Len() Dic onaries
- Func on to get the length of a list. - Collec on of key-value pairs, unordered,
changeable and indexed
Pop()
- Wri en with curly brackets
- By default remove the first item in a list and
Get()
returns it.
- Get the value of a key
Remove()
Values()
- Remove items by value in a list
- Return values of a dic onary
Append()
Items()
- Add an item to the end of the list
- Loop through both keys and values
Insert()
Popitem()
- Add to posi ons other than the end, such as
the beginning - Removes the last inserted item
Extend() Del
- You can combine another list or tuple at the - The del keyword removes the item with the
end of the list. All items are added to the end specified key name
of the original list
Clear()
Clear()
- Emp es the dic onary
- Remove all items from the list
Copy()
Tuple
- Make a copy of a dic onary
- Is a sequence of immutable Python objects
- Tuple are immutable, they cannot be Dict()
changed once declared. - Also makes a copy of a dic onary
- Usually faster than lists
Tuple()
- Can make a tuple
Count()
You might also like
- Introduction To PythonDocument62 pagesIntroduction To PythonNurfatin Nadhirah100% (1)
- Advance Computer Programming: NotesDocument4 pagesAdvance Computer Programming: NotesGlyza Marie Sederio ButronNo ratings yet
- CP Lec Finals ReviewerDocument15 pagesCP Lec Finals Reviewerww8jpsy8w6No ratings yet
- BLOG Quiz FinalsDocument5 pagesBLOG Quiz FinalsJun Martine SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Comprog 1 ReviewerDocument2 pagesComprog 1 ReviewerrbxwmnNo ratings yet
- ComProg ReviewerDocument4 pagesComProg ReviewerJailyn Ribleza SamosaNo ratings yet
- Hci Finals W1&2Document3 pagesHci Finals W1&2ASAP BOI GAMEZNo ratings yet
- PLSQL Interview Question With Answer-6Document7 pagesPLSQL Interview Question With Answer-6민수자가디스No ratings yet
- 28 - PHP - Looping and FunctionsDocument31 pages28 - PHP - Looping and FunctionsAhsan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Procedural Paradigm: Algol - 2 Generation LanguageDocument50 pagesProcedural Paradigm: Algol - 2 Generation LanguageBuddhika Indrajith GunawardenaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Perl PDFDocument25 pagesAn Introduction To Perl PDFTanmay McGrathNo ratings yet
- Ict Q3Document8 pagesIct Q3MMALTEZ, RALPH CHRISTIAN, R.No ratings yet
- Training Seminar On "Python For Beginners"Document28 pagesTraining Seminar On "Python For Beginners"Rashi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2696445817745910253Document10 pagesInbound 2696445817745910253kristyllemaebNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 Introduction To Java Programming LanguageDocument33 pagesHandout 2 Introduction To Java Programming Languageeugenemwangi08No ratings yet
- SummarySC025 2018-2019Document8 pagesSummarySC025 2018-2019zeytaNo ratings yet
- PHP Infomatics 3Document22 pagesPHP Infomatics 3Jus WaNo ratings yet
- Pyhton ProgrmmingDocument97 pagesPyhton ProgrmmingbharathvajkvcetNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals Week 2 Notes Variables and ExpressionsDocument9 pagesProgramming Fundamentals Week 2 Notes Variables and ExpressionsPablo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Introduction To JavaDocument34 pagesSession 1 Introduction To JavaJomer Robas TadenaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Comprog 2Document15 pagesReviewer - Comprog 2limariokun02No ratings yet
- Basic, Function and Turtle GraphicsDocument35 pagesBasic, Function and Turtle Graphicsabebeyonas88No ratings yet
- RefDocument53 pagesRefawstestacc34No ratings yet
- JavaDocument8 pagesJavaColen LUMAMBANo ratings yet
- Functional ProgrammingDocument46 pagesFunctional ProgrammingJohn Paul Anthony ArlosNo ratings yet
- BIT205-HO1-Basic Concepts of JAVA ProgrammingDocument73 pagesBIT205-HO1-Basic Concepts of JAVA ProgrammingBahaa HaneneNo ratings yet
- Python Preparation QuestionsDocument3 pagesPython Preparation QuestionsnagasanjaysharmaNo ratings yet
- Pds 1Document6 pagesPds 1vkforytNo ratings yet
- Working With Functions-2 2022-23Document55 pagesWorking With Functions-2 2022-23sharanshajiixc36No ratings yet
- Python KeywordsDocument17 pagesPython Keywordsshalinikasera157No ratings yet
- Ch4 - PHPDocument151 pagesCh4 - PHPTrầm Tiến Anh B1706971No ratings yet
- CSE100 wk3 4Document21 pagesCSE100 wk3 4Razia Sultana Ankhy StudentNo ratings yet
- Create PDF in Your Applications With The Pdfcrowd: HTML To PDF ApiDocument437 pagesCreate PDF in Your Applications With The Pdfcrowd: HTML To PDF Apipg rNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PythonDocument13 pagesIntroduction To PythonKartik MahajanNo ratings yet
- Python RevisionDocument96 pagesPython Revisionen21cs301471No ratings yet
- Comp 7Document3 pagesComp 7Tristan Michael G. PanchoNo ratings yet
- Python Unit 1 Part 1Document47 pagesPython Unit 1 Part 1kiranmaijilakara325No ratings yet
- Computer Programming Languages: Lecture - 1Document38 pagesComputer Programming Languages: Lecture - 1Gul khanNo ratings yet
- Ansible - Interview Q&A-2Document11 pagesAnsible - Interview Q&A-2Vignesh PanneerselvamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 JAVA Programming Theoretical FrameworkDocument118 pagesChapter 2 JAVA Programming Theoretical FrameworkronaldbvirinyangweNo ratings yet
- Python Learning (Basics I & II)Document33 pagesPython Learning (Basics I & II)Adventure WorldNo ratings yet
- Java 1Document112 pagesJava 1Malathi NNo ratings yet
- CS121Document2 pagesCS121Ikon TrashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Python Lecture 2Document25 pagesIntroduction To Python Lecture 2Maraña Kelvin LouieNo ratings yet
- Interview Level QA On CDocument20 pagesInterview Level QA On CRam BhardwajNo ratings yet
- IT PF Reviewer MergedDocument15 pagesIT PF Reviewer Mergedpauljustinabelgas.neustNo ratings yet
- ThikDocument8 pagesThikIstamsetty HanumantharaoNo ratings yet
- Python Scripting in Grasshopper SPMDocument15 pagesPython Scripting in Grasshopper SPMVictor CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Computer ProgrammingDocument10 pagesComputer ProgrammingAlesha BanaagNo ratings yet
- IoT Lab Manual Removed RemovedDocument25 pagesIoT Lab Manual Removed Removedansariisrafil03No ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument74 pagesFunctionsvoduykhoa2504No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Data Structure: Unit 1Document40 pagesObject Oriented Data Structure: Unit 1shivanshNo ratings yet
- Computer Science - Introduction To Java ISC NotesDocument10 pagesComputer Science - Introduction To Java ISC NotesVarun Dhawan100% (1)
- Unit 1 Core Java - 240510 - 125907Document165 pagesUnit 1 Core Java - 240510 - 125907manyab009No ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument5 pagesUnit IiAashi JainNo ratings yet
- Chpater 2 Basic in Java ProgrammingDocument60 pagesChpater 2 Basic in Java ProgrammingDesyilalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Python - Basic - SyntaxDocument9 pagesLesson 2 - Python - Basic - SyntaxSherlita YbañezNo ratings yet
- Quiz #3Document4 pagesQuiz #3Uno Ferreras FaustoNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Introduction To JavaDocument36 pagesSession 1 - Introduction To Javat0eberriesNo ratings yet
- PYTHONDocument20 pagesPYTHONahmalik1012No ratings yet
- Python programming for beginners: Python programming for beginners by Tanjimul Islam TareqFrom EverandPython programming for beginners: Python programming for beginners by Tanjimul Islam TareqNo ratings yet
- New in Spring 5: Functional Web Framework: Arjen Poutsma PivotalDocument23 pagesNew in Spring 5: Functional Web Framework: Arjen Poutsma PivotalFaiçal YahiaNo ratings yet
- Java NotesDocument29 pagesJava NotessreenivasnairNo ratings yet
- PST Book - Unit 1 - 5Document192 pagesPST Book - Unit 1 - 5Saipriya VempalliNo ratings yet
- Python Quick NoteDocument23 pagesPython Quick NoteJyotirmay SahuNo ratings yet
- Python:: Data HandlingDocument6 pagesPython:: Data HandlingMeena SharmaNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument44 pagesPythonakbisoi1No ratings yet
- Python - Basic - 1 - Jupyter Notebook (Student)Document44 pagesPython - Basic - 1 - Jupyter Notebook (Student)Mesbahur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 13 - Abstract Classes and InterfacesDocument46 pages13 - Abstract Classes and InterfacesHanNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL REPORT On PythonDocument39 pagesINDUSTRIAL REPORT On PythonAnant PrakashNo ratings yet
- Java 1Document164 pagesJava 1akbala08No ratings yet
- 02 Programming PythonDocument48 pages02 Programming Pythongiordano manciniNo ratings yet
- Kotlin Cheat Sheet 1p - by Ekito 1.2Document4 pagesKotlin Cheat Sheet 1p - by Ekito 1.2Valmir BekteshiNo ratings yet
- C++ Keyboard Shortcut 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesC++ Keyboard Shortcut 2019 PDFJADU FRIENDSNo ratings yet
- Ruby Deep Dive (Jesus Castello)Document250 pagesRuby Deep Dive (Jesus Castello)William Yánez DevNo ratings yet
- 11 - Ip - Hy - Setb - 2022-23 - QP Set BDocument5 pages11 - Ip - Hy - Setb - 2022-23 - QP Set Bspiagent2007No ratings yet
- Python MCQsDocument39 pagesPython MCQsKanadam Karteeka Pavan100% (3)
- Cocoa FundamentalsDocument238 pagesCocoa FundamentalsDaniel MaccarroneNo ratings yet
- Ebook Fluent Python Luciano Ramalho Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Fluent Python Luciano Ramalho Online PDF All Chaptermarcus.keyes538100% (7)
- OOP ExamplesDocument8 pagesOOP ExamplesAdam ButterworthNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction & Syntax of Python ProgramDocument7 pagesUnit1 - Introduction & Syntax of Python Programsanju pawarNo ratings yet
- Python (3) Leaflet: Roland Becker December 16, 2020Document15 pagesPython (3) Leaflet: Roland Becker December 16, 2020beckerrolandhNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Ios 10 Programming Fundamentals With Swift Swift Xcode and Cocoa Basics 3Rd Edition Matt Neuburg PDFDocument43 pagesFull Chapter Ios 10 Programming Fundamentals With Swift Swift Xcode and Cocoa Basics 3Rd Edition Matt Neuburg PDFpatricia.chaney584100% (5)
- BRKSDN-1009 - Python 101 For Network Engineers (2017 Berlin) - 90 MinsDocument181 pagesBRKSDN-1009 - Python 101 For Network Engineers (2017 Berlin) - 90 MinsKevin Kim0% (1)
- Python Notes PDFDocument7 pagesPython Notes PDFSarath RamineniNo ratings yet
- React PropsDocument19 pagesReact PropsYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Javascript Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesAdvanced Javascript Interview Questionsparas1999998No ratings yet
- Python With Data ScienceDocument102 pagesPython With Data ScienceIrfanstudymeterialsNo ratings yet
- What's New in Python: A. M. KuchlingDocument37 pagesWhat's New in Python: A. M. KuchlingPlesa AlexandruNo ratings yet
- PFSD Unit 1 (Autosaved)Document65 pagesPFSD Unit 1 (Autosaved)Sayantan DeNo ratings yet