Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 13
Module 13
Uploaded by
A. MagnoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 13
Module 13
Uploaded by
A. MagnoCopyright:
Available Formats
THE PULSE and BLOOD PRESSURE
Your pulse is your heart rate or the number of times your heart beats in one minute.
Pulse rates vary from person to person. Your pulse is lower when you are at rest and increases
when you exercise (more oxygen-rich blood is needed by the body when you exercise).
Pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle by trained fingertips. The pulse
may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the
body, such as at the neck, wrist, at the groin, behind the knee, near the ankle joint, and on foot.
The best places to take your pulse are at your wrist, inside the elbow, at the side of your neck, or
on the top of your foot. You can also take your pulse at your groin, on your temple, or behind
your knees. The pulse felt on the neck is called the carotid pulse
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure exerted by blood on the walls of a blood vessel that helps to
push blood through the body. Systolic blood pressure measures the amount of pressure that
blood exerts on vessels while the heart is beating. ... Blood pressure is related to the blood
velocity in the arteries and arterioles.
The primary function of blood pressure is to move blood around the body through the
circulatory system. Our blood is full of oxygen and nutrients that feed the body's tissues
and organs.
A sphygmomanometer, also known as a blood pressure meter, blood pressure monitor,
or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an
inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled
manner. A mercury or aneroid manometer to measure the pressure.
You might also like
- High Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Radial and Ulnar Pulse (Wrist) : Located On The Medial of The Wrist (Ulnar Artery)Document4 pagesRadial and Ulnar Pulse (Wrist) : Located On The Medial of The Wrist (Ulnar Artery)Riza MongoteNo ratings yet
- The Heart Is A Muscle: BloodDocument8 pagesThe Heart Is A Muscle: BloodJhoewil QuintuaNo ratings yet
- CBR Report - Vital SignsDocument6 pagesCBR Report - Vital Signsteddy_tudsNo ratings yet
- Arterial Pulse Sites PDFDocument1 pageArterial Pulse Sites PDFRigor MortisNo ratings yet
- Your Heart & Circulatory System: The Heart Is A MuscleDocument4 pagesYour Heart & Circulatory System: The Heart Is A MuscleNguyen Viet SonNo ratings yet
- Cardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDocument13 pagesCardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDavid GoliathNo ratings yet
- Vital Sign:Pulse: Prepared By: Mrs Bemina Ja Assistant Professor ESIC College of Nursing KalaburagiDocument38 pagesVital Sign:Pulse: Prepared By: Mrs Bemina Ja Assistant Professor ESIC College of Nursing Kalaburagibemina jaNo ratings yet
- Isi Jurnal KardioDocument6 pagesIsi Jurnal KardioZulvi RiriNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate Design Lab 1Document4 pagesHeart Rate Design Lab 1Alexandra McGinnNo ratings yet
- PulseDocument13 pagesPulseArdi EroNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs: DiaphragmDocument18 pagesVital Signs: DiaphragmLenjoy CabatbatNo ratings yet
- 170 Anatomy Circulatory SystemDocument26 pages170 Anatomy Circulatory SystemGenevieve MerroNo ratings yet
- Medical History and Physical Examination For Heart andDocument90 pagesMedical History and Physical Examination For Heart andhibaNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument17 pagesBlood VesselsmhycauNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9Document17 pagesThe Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9hareem FatimaNo ratings yet
- BP Monitors PADDocument7 pagesBP Monitors PADLinNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System Group 2Document17 pagesThe Circulatory System Group 2sanique peterkinNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument28 pagesThe Muscular SystemGazelle Piyokcka Mapagmahal AquiloNo ratings yet
- Vital Sign: Blood Pressure and Its AlterationsDocument55 pagesVital Sign: Blood Pressure and Its Alterationsbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Edison Vincent A. Olegario, RN, LPTDocument25 pagesCardiovascular System: Edison Vincent A. Olegario, RN, LPTEdison OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Assignment Anatomy and Physiology NewDocument9 pagesAssignment Anatomy and Physiology Newcassidy DyaletNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Cardiac CycleDocument24 pagesLesson 4 Cardiac CycleTristan PereyNo ratings yet
- A Pulse Is Felt As The Expansion of The Arteries During Ventricular SystoleDocument2 pagesA Pulse Is Felt As The Expansion of The Arteries During Ventricular SystoleShahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- When Should Blood Pressure Be Measured?: Stage Approximate Age Systolic DiastolicDocument6 pagesWhen Should Blood Pressure Be Measured?: Stage Approximate Age Systolic DiastolicJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Through The Human HeartDocument14 pagesThrough The Human HeartAsemed AsemedNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument10 pagesVital SignsEdelou Alegria JumawanNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: OCS Applied Science Mrs. BonifayDocument18 pagesThe Human Heart: OCS Applied Science Mrs. BonifaysudhirNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Noel Lea 4Document16 pagesPpt-Noel Lea 4bossamogahiNo ratings yet
- Circulation DisordersDocument11 pagesCirculation DisordersFred MomanyiNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument19 pagesThe Human HeartbeshlyNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure and Pulse RateDocument7 pagesBlood Pressure and Pulse Ratehjaffer2001100% (1)
- Measuring Heart Rate: Manual MethodDocument1 pageMeasuring Heart Rate: Manual MethodRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeDocument9 pagesThe Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeL I G-Arijit HisabiaNo ratings yet
- The Heart Heart RateDocument16 pagesThe Heart Heart RateAira Mae HasalNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Veins, and CapillariesDocument12 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Veins, and Capillariesvmfmqnf2cpNo ratings yet
- Overview of The HeartDocument3 pagesOverview of The HeartSamanthaKhallanNo ratings yet
- Assessing Radial PulseDocument18 pagesAssessing Radial PulseJoisy AloorNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment BSN 1-Ruby: SUBMITTED TO: Miss Rossini Birad SUBMITTED BY: Shandy PansaDocument7 pagesHealth Assessment BSN 1-Ruby: SUBMITTED TO: Miss Rossini Birad SUBMITTED BY: Shandy PansaShan DyNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle HardDocument2 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle HardMilvic Jean BernardoNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument6 pagesBlood PressuremohitNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Pumping Function of Heart: Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Ejection Fraction Cardiac IndexDocument53 pagesEvaluation of Pumping Function of Heart: Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Ejection Fraction Cardiac Indexapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Recording of Blood PressureDocument4 pagesRecording of Blood PressureSinger Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Journey Through The Human HeartDocument14 pagesA Journey Through The Human HeartVidhi BansalNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument3 pagesBlood Pressurefiras qasimNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Control CentreDocument8 pagesCardiac Control CentregeorgeloxdaleNo ratings yet
- 10 Blood VesselsDocument2 pages10 Blood VesselsDaniellaRuth Cajurao CanalesNo ratings yet
- (Practical) Peripheral Pulses & Blood PressureDocument13 pages(Practical) Peripheral Pulses & Blood PressuremeewhayNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesCirculation and Cardiovascular SystemSatria MandalaNo ratings yet
- Sport & Exercise PhysiologyDocument24 pagesSport & Exercise PhysiologyDeclan SavageNo ratings yet
- PDM 1 - BP HR LabDocument16 pagesPDM 1 - BP HR Labapi-637092426No ratings yet
- Pulseandheartsound 181202083753Document21 pagesPulseandheartsound 181202083753Akanksha LahaseNo ratings yet
- How To Take A PulseDocument1 pageHow To Take A Pulseeilma apriliaNo ratings yet
- KN 4@enzl 8 Ha 4 B 6 CC 9 eDocument26 pagesKN 4@enzl 8 Ha 4 B 6 CC 9 eRamzen Raphael DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemCallie ParkNo ratings yet
- 2017 Labkomp - Auskultation-Bloodpressure - Niklas IvarssonDocument19 pages2017 Labkomp - Auskultation-Bloodpressure - Niklas IvarssonJohn Paolo JosonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesCirculatory SystemJeus BatadlanNo ratings yet
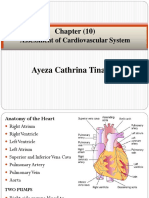
- Chapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesChapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemSandra GabasNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab 11Document5 pagesBio Lab 11Sarah JaglalNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument3 pagesAuditingA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Potential ClientDocument3 pagesApproach To A Potential ClientA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Auditing QuesDocument4 pagesAuditing QuesA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Engl ReviewerDocument22 pagesEngl ReviewerA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Incremental and Radical Innovation: Design Research vs. Technology and Meaning ChangeDocument20 pagesIncremental and Radical Innovation: Design Research vs. Technology and Meaning ChangeA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Module 13Document1 pageModule 13A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument7 pagesVital SignsA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 1 1Document2 pagesCellular Respiration 1 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Reviewquiz4 Lit PDFDocument3 pagesReviewquiz4 Lit PDFA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Sci FiniteDocument5 pagesSci FiniteA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- FehlingsDocument2 pagesFehlingsA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Labster Finals ReviewDocument1 pageLabster Finals ReviewA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 LittDocument9 pagesMod 2 LittA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Art 15Document3 pagesArt 15A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Student Take Quiz Assignmentstart38387006Document5 pagesStudent Take Quiz Assignmentstart38387006A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- FLUOROCARBONDocument3 pagesFLUOROCARBONA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- John Smith 1612Document19 pagesJohn Smith 1612A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Enviii Sci SaDocument6 pagesEnviii Sci SaA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- EA Flora 1Document3 pagesEA Flora 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- What Is EthicsDocument1 pageWhat Is EthicsA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Ecology and EthicsDocument25 pagesLesson 1 Ecology and EthicsA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Overview and Intro 2 Env SciDocument15 pagesModule 2 - Overview and Intro 2 Env SciA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- End of Quiz: G-Litt001 Bsa33 Classic Literatures of The World 2Nd Sem (2022-2023) Review Quiz 6Document3 pagesEnd of Quiz: G-Litt001 Bsa33 Classic Literatures of The World 2Nd Sem (2022-2023) Review Quiz 6A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- What Happened Till The First Supply 1Document10 pagesWhat Happened Till The First Supply 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- ED621826Document56 pagesED621826A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 Litt 3Document2 pagesMod 2 Litt 3A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 Litt 2Document2 pagesMod 2 Litt 2A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS - Partnership DissolutionDocument4 pagesPROBLEMS - Partnership DissolutionA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- 6573 18176 1 PBDocument12 pages6573 18176 1 PBA. MagnoNo ratings yet