Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SS - GENANA LAB - Pelvis I
SS - GENANA LAB - Pelvis I
Uploaded by
Moyeonie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesThe document summarizes key anatomical features of the male and female pelvis. It identifies the structures that make up the pelvic walls, floor, and roof. It also labels important ligaments and joints like the sacroiliac and pubic symphysis. The document outlines the measurements of the female pelvis and defines different pelvic types including gynecoid, android, and anthropoid. The blood vessels, nerves, and internal iliac artery branches entering the pelvis are illustrated. Finally, the major differences between the male and female pelvis are compared such as inlet shape, cavity structure, and bone formation.
Original Description:
Original Title
SS- GENANA LAB_Pelvis I
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key anatomical features of the male and female pelvis. It identifies the structures that make up the pelvic walls, floor, and roof. It also labels important ligaments and joints like the sacroiliac and pubic symphysis. The document outlines the measurements of the female pelvis and defines different pelvic types including gynecoid, android, and anthropoid. The blood vessels, nerves, and internal iliac artery branches entering the pelvis are illustrated. Finally, the major differences between the male and female pelvis are compared such as inlet shape, cavity structure, and bone formation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesSS - GENANA LAB - Pelvis I
SS - GENANA LAB - Pelvis I
Uploaded by
MoyeonieThe document summarizes key anatomical features of the male and female pelvis. It identifies the structures that make up the pelvic walls, floor, and roof. It also labels important ligaments and joints like the sacroiliac and pubic symphysis. The document outlines the measurements of the female pelvis and defines different pelvic types including gynecoid, android, and anthropoid. The blood vessels, nerves, and internal iliac artery branches entering the pelvis are illustrated. Finally, the major differences between the male and female pelvis are compared such as inlet shape, cavity structure, and bone formation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
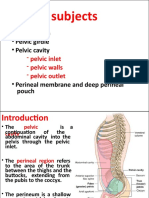
PELVIS I
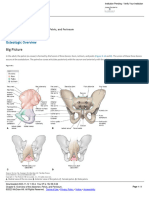
A. Label the parts of the pelvis and identify the view of the pictures below.
B. What comprises the pelvic wall on each side?
PELVIC WALL
ANTERIOR Bodies of pubic bone, Pubic rami, and symphysis pubis
POSTERIOR Sacrum, Coccyx, piriformis muscle, and parietal pelvic fascia
LATERAL Hip bone, obturator membrane, sacrotuberous and
sacrospinous ligaments, obturator internus muscle and its
covering fascia.
ROOF Paired levator ani and coccyges muscle and their covering
fasciae from the pelvic diaphragm
FLOOR Pelvic viscera (pelvic diaphragm and associated fascia)
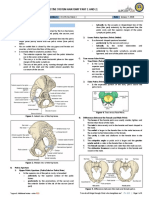
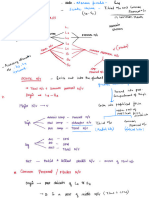
C. Identify the structures that stabilize and hold the pelvic wall together and identify
what parts of the pelvis it connects
1) Levator Ani Muscle: Anterior part of the pelvic diaphragm.
2) Coccygeus Muscle: Forms the posterior portion of the pelvic diaphragm.
3) Sacroiliac joints: between articular surface of sacrum and iliac bones.
4) Sacrococcygeal joints: Between the last sacral vertebrae and first coccygeal
vertebrae.
5) Symphysis Pubis: Between two public bone.
D. Identify and illustrate the different pelvic measurements on the picture below and its
approximate numeric Value
E. Illustrate the different types of pelvic and define its characteristics
Gynecoid Present in 41% of women. It is the typical pelvis.
Android Present in 33% of White female and 16% of Black females, is
the male or funnel-shaped pelvis with a contracted outlet.
Anthropoid Present in 24% of White female and 16% of Black females, is
long, narrow, and oval shaped.
Platypelloid Present in only about 2% of women, is a wide pelvis flattened
at the brim, with the promontory of the sacrum pushed forward.
F. illustrate the pelvic floor and label all its parts
F. Illustrate and identify the blood vessels that enter and exit the pelvic wall
G. Label the sacral plexus and identify their nerve distribution
H. Draw and label the branchings of the internal iliac artery as it enters the pelvis
I. Differentiate the male and female pelvis in terms of the following:
MALE FEMALE
Inlet Heart-shaped Transversely oval
Cavity funnel shaped Roomier
Outlet Smaller Larger
Depth triangle cone circular curved
Sacrum long, narrow, and straight short, wider, and flatter
Subpubic angle narrower 70 degrees V- rounded and wider
shaped
Bone Structure heavier and sturdier lighter and Broad
False pelvis Deep Shallow
Function For Heavy Body build For Childbearing
You might also like
- Choices-Stories-You-Play-Fandom-Blades of Light and Shadow Book 1 ChoicesDocument66 pagesChoices-Stories-You-Play-Fandom-Blades of Light and Shadow Book 1 ChoicesVasudha Singh100% (1)
- Female PelvisDocument41 pagesFemale Pelvissanthiyasandy88% (8)
- Anat 5.2 Pelvis and Perineum - ElevazoDocument14 pagesAnat 5.2 Pelvis and Perineum - Elevazolovelots1234No ratings yet
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormFrom EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Mooring OperationsDocument1 pageMooring OperationsTom AlexNo ratings yet
- Wound Assessment: Michelle Moore RN, MSN, WCC Wound Care Education InstituteDocument20 pagesWound Assessment: Michelle Moore RN, MSN, WCC Wound Care Education InstituteSunjaya TunggalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy by DR - Alaa (END 207)Document57 pagesAnatomy by DR - Alaa (END 207)salmahanykarawiaNo ratings yet
- Physiol and OT Pelvic and Perineal Regions 2022Document51 pagesPhysiol and OT Pelvic and Perineal Regions 2022Zuko JamangileNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics AnatomyDocument19 pagesObstetrics AnatomyCheryl OrtizNo ratings yet
- Assignment5 - Female PelvisDocument8 pagesAssignment5 - Female PelvisMahenurNo ratings yet
- Obg Lab ModuleDocument217 pagesObg Lab Moduleaiswarya ppNo ratings yet
- Assignment5 - Female PelvisDocument7 pagesAssignment5 - Female Pelvispriyanka100% (1)
- Female PelvisDocument7 pagesFemale PelvissubashikNo ratings yet
- LAB Anterior Abdominal Wall & Inguinal RegionDocument12 pagesLAB Anterior Abdominal Wall & Inguinal RegionnanaNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Human ReproductiveDocument68 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproductivesavita hanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Pelvis and Perineum Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesPelvis and Perineum Lecture NotesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- 4 - Anatomy of PelvisDocument10 pages4 - Anatomy of PelvisJISHNU TKNo ratings yet
- 3.. Anatomy of The Female Pelvis and Fetal-1Document24 pages3.. Anatomy of The Female Pelvis and Fetal-1wairimuagatha9No ratings yet
- 7-Pelvis ND SacrumDocument25 pages7-Pelvis ND Sacrumnandiniparashar853No ratings yet
- Seminar On Female Pelvis and Pelvic FloorDocument11 pagesSeminar On Female Pelvis and Pelvic FloorJasmin SabnaNo ratings yet
- 11A U2 Male Reproductive Tract 2024 MI V10 3Document29 pages11A U2 Male Reproductive Tract 2024 MI V10 3Chawka AlbadehNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Obstetrics & GynecologyDocument37 pagesTextbook of Obstetrics & Gynecologysanjivdas0% (1)
- The Pelvic GirdleDocument22 pagesThe Pelvic GirdleJudithNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemMahad Maxamed AxmedNo ratings yet
- Review Anatomy For ClerksDocument163 pagesReview Anatomy For ClerksNicole Alexandra KhoNo ratings yet
- Female PelvisDocument21 pagesFemale PelvisArjumand ZargarNo ratings yet
- 11.pelvic Walls, Joints, Vessels & NervesDocument36 pages11.pelvic Walls, Joints, Vessels & NervespashaNo ratings yet
- Pelvis: The Pelvis/Bony Gridle/Pelvic GridleDocument18 pagesPelvis: The Pelvis/Bony Gridle/Pelvic GridlepreezaNo ratings yet
- Question No 01: PART A) Define Pelvis?Document5 pagesQuestion No 01: PART A) Define Pelvis?aminaNo ratings yet
- Pelvis and PerineumDocument5 pagesPelvis and PerineumK ZarabianNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument106 pagesReproductive Systemduded5187No ratings yet
- Review Notes - Radiographic Positioning and Radiologic Procedures I PDFDocument30 pagesReview Notes - Radiographic Positioning and Radiologic Procedures I PDFCziara JustineNo ratings yet
- B-Anatomy Unit-6 - Pelivc Girdle Horse Pig Dog FowlsDocument18 pagesB-Anatomy Unit-6 - Pelivc Girdle Horse Pig Dog FowlsimajitavpatroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Overview of The Abdomen, Pelvis, and PerineumDocument5 pagesChapter 6. Overview of The Abdomen, Pelvis, and Perineumleafyislucky 91No ratings yet
- 01 Jan7 Trans Female Anatomy Group 1and 2Document8 pages01 Jan7 Trans Female Anatomy Group 1and 2Delsie VicenteNo ratings yet
- PelvisDocument10 pagesPelvisPranidhi ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The PelvisDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Pelvisapi-195986134No ratings yet
- Joints of The Lower LimbDocument63 pagesJoints of The Lower LimbEliud MbuteNo ratings yet
- BY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)Document52 pagesBY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)DCRUZNo ratings yet
- Anatomi PanggulDocument34 pagesAnatomi Panggulel hadidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument62 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- LECT 1.anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 1.Document37 pagesLECT 1.anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 1.Umer RafiqNo ratings yet
- LowerLimbExam NurDocument108 pagesLowerLimbExam Nuralina nguynNo ratings yet
- Female PelvisDocument4 pagesFemale Pelvisvarshasharma05100% (1)
- MCN Book ProjectDocument74 pagesMCN Book ProjectRonnie De Vera IINo ratings yet
- Subjects: - Introduction - Pelvic Girdle - Pelvic CavityDocument39 pagesSubjects: - Introduction - Pelvic Girdle - Pelvic CavityAshraf SidrahNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To The Pelvis and The Pelvic Peritoneum DIYADocument38 pages1 Introduction To The Pelvis and The Pelvic Peritoneum DIYAOmotosho DavidNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument36 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- Osseous Question BankDocument11 pagesOsseous Question Bankarpitsonone16No ratings yet
- 2-Pelvic Walls, Joints, Vessels & NervesDocument32 pages2-Pelvic Walls, Joints, Vessels & NervesAbdul Rafay ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomi Organ PanggulDocument45 pages1 Anatomi Organ PanggulHutomo Budi Hasnian SyahNo ratings yet
- Anatomi PelvisDocument44 pagesAnatomi Pelvisari naNo ratings yet
- Bony Pelvis, Pelvic Walls, and Pelvic Measurements Text - PDocument0 pagesBony Pelvis, Pelvic Walls, and Pelvic Measurements Text - PShouq Khair AllaNo ratings yet
- Thorax 1Document109 pagesThorax 1Insyirah JohariNo ratings yet
- Inguinal Canal and ScrotumDocument55 pagesInguinal Canal and ScrotumAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 2anatomyoflscoccyxandsacrum 200218190905Document35 pages2anatomyoflscoccyxandsacrum 200218190905ravikop43No ratings yet
- MCN Module 3Document9 pagesMCN Module 3Fatrick BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Ebook Notes PDFDocument89 pagesObstetrics and Gynecology Ebook Notes PDFGaurav ShyamaniNo ratings yet
- Maternalpelvis 160311112407Document22 pagesMaternalpelvis 160311112407Sunil YadavNo ratings yet
- 1 InroductionDocument44 pages1 Inroductiondemeke andebetNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument36 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- A New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasFrom EverandA New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasNo ratings yet
- PEH 2 WK 7Document9 pagesPEH 2 WK 7memeNo ratings yet
- Self Myofascial ReleaseDocument22 pagesSelf Myofascial ReleaseMuhammad Fahmy100% (1)
- The Peripheral Nervous System: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesThe Peripheral Nervous System: ObjectivesIbra TutorNo ratings yet
- Osteopetrosis (Marble Bones, Albers-Schönberg Disease) DefinitionDocument9 pagesOsteopetrosis (Marble Bones, Albers-Schönberg Disease) DefinitionRustin Dale EnriquezNo ratings yet
- New Holland CX5080, CX5090, CX5090 Laterale, CX5090 Hillside, CX6080, CX6090, CX6090 Laterale Combine Service Repair ManualDocument31 pagesNew Holland CX5080, CX5090, CX5090 Laterale, CX5090 Hillside, CX6080, CX6090, CX6090 Laterale Combine Service Repair ManualggjjjjotonesNo ratings yet
- Shattered StarsDocument314 pagesShattered Starsanshikamittal1807No ratings yet
- Rotator Cuff TearsDocument5 pagesRotator Cuff TearsdrjorgewtorresNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture Points - Acupuncture School Online - Learning Acupuncture and Moxibustion Courses OnlineDocument7 pagesAcupuncture Points - Acupuncture School Online - Learning Acupuncture and Moxibustion Courses Onlinecarlos coelhoNo ratings yet
- Background PF The StudyDocument3 pagesBackground PF The StudyZT EstreraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lower Limb by DR AzamDocument19 pagesAnatomy Lower Limb by DR AzamroulprayashNo ratings yet
- 2023-03-02 St. Mary's County TimesDocument32 pages2023-03-02 St. Mary's County TimesSouthern Maryland OnlineNo ratings yet
- Accessory Navicular SyndromeDocument6 pagesAccessory Navicular SyndromeXin YiNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide For FirstAidCPR en 8Document233 pagesComprehensive Guide For FirstAidCPR en 8Richard Guiriba100% (1)
- WM Eus MFL71728908 03 230322 00 Om Web enDocument64 pagesWM Eus MFL71728908 03 230322 00 Om Web eni wNo ratings yet
- BT 710 Op Manual 710 Eng Opm Eur r02Document38 pagesBT 710 Op Manual 710 Eng Opm Eur r02Sulay Avila LlanosNo ratings yet
- Tos PDFDocument12 pagesTos PDFDiana ChirilăNo ratings yet
- Thermal Heat Pad: Chemistry Research ProjectDocument24 pagesThermal Heat Pad: Chemistry Research ProjectSiva NeshNo ratings yet
- Law549 (Torts) Assignment: Personal Injuries (June 2020)Document13 pagesLaw549 (Torts) Assignment: Personal Injuries (June 2020)Nurul SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Efa 2019-05Document96 pagesEfa 2019-05Mark JhunNo ratings yet
- Pitch-Side Management of Acute Shoulder Dislocations: A Conceptual ReviewDocument9 pagesPitch-Side Management of Acute Shoulder Dislocations: A Conceptual ReviewElan R.S.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology 7 EDITION: Concepts of Health and Disease: American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (Orthoinfo)Document2 pagesPathophysiology 7 EDITION: Concepts of Health and Disease: American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (Orthoinfo)Justine Simeon lagunzadNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY - 19.03.20 - The Vertebral ColumnDocument29 pagesANATOMY - 19.03.20 - The Vertebral ColumnArianna RomanoNo ratings yet
- Triage in Emergency Department: Triage Waiting Room Team LeaderDocument27 pagesTriage in Emergency Department: Triage Waiting Room Team LeaderJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument3 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryMilla TanNo ratings yet
- Geria NotesDocument8 pagesGeria NotesPCIs DR RotationNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Triage CategoryDocument2 pagesMalaysian Triage CategoryArnold Daniel70% (10)
- Why Does My Body Stiffen Up?Document6 pagesWhy Does My Body Stiffen Up?BMMPDPP1020 Aldrin Anak JaparNo ratings yet