Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre-Cal Formulas
Pre-Cal Formulas
Uploaded by
shannenkrishagwapaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-Cal Formulas
Pre-Cal Formulas
Uploaded by
shannenkrishagwapaCopyright:
Available Formats
PRE-CALCULUS (1ST QUARTER)
FORMULAS
CIRCLE
Center Standard Form
(ℎ, 𝑘) (𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2
(0, 0) 𝑥2 + 𝑦2 = 𝑟2
𝑏 2
Completing the square 𝑐=( )
2𝑎
PARABOLA
Principal Axis Vertex Directrix Focus Standard Form
Case 1: (ℎ, 𝑘) 𝑦 = 𝑘−𝑝 (ℎ, 𝑘 + 𝑝) (𝑥 − ℎ)2 = 4𝑝(𝑦 − 𝑘)
Vertical (0, 0) 𝑦 = −𝑝 (0, 𝑝) 𝑥 2 = 4𝑝𝑦
Case 2: (ℎ, 𝑘) 𝑥 =ℎ−𝑝 (ℎ + 𝑝, 𝑘 ) (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 4𝑝(𝑥 − ℎ)
Horizontal (0, 0) 𝑥 = −𝑝 (𝑝, 0) 𝑦 2 = 4𝑝𝑥
Latus Rectum 𝐿𝑅 = |4𝑝|
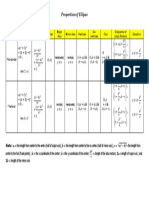
ELLIPSE
Principal Axis Center Vertices Co-vertices Foci Standard Form
(ℎ, 𝑘) (ℎ ± 𝑎, 𝑘) (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑏) (ℎ ± 𝑐, 𝑘)
(𝑥 − ℎ )2 (𝑦 − 𝑘 )2
+ =1
Case 1: 𝑎2 𝑏2
Horizontal
𝑥2 𝑦2
(0, 0) (±𝑎, 0) (0, ± 𝑏) (±𝑐, 0) + =1
𝑎2 𝑏 2
(ℎ, 𝑘) (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑎) (ℎ ± 𝑏, 𝑘) (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑐)
(𝑥 − ℎ )2 (𝑦 − 𝑘 )2
+ =1
Case 2: 𝑏2 𝑎2
Vertical
𝑥2 𝑦2
(0, 0) (0, ± 𝑎) (±𝑏, 0) (0, ± 𝑐) + =1
𝑏 2 𝑎2
Length of major axis 2𝑎
Length of minor axis 2𝑏
Pythagorean Theorem (solving for 𝒄) 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 − 𝑏 2
HYPERBOLA
Principal
Center Vertices Co-vertices Foci Asymptotes Standard Form
Axis
(ℎ, 𝑘) (ℎ ± 𝑎, 𝑘) (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑏) (ℎ ± 𝑐, 𝑘)
𝑏 (𝑥 − ℎ )2 (𝑦 − 𝑘 )2
(𝑦 − 𝑘) = ± (𝑥 − ℎ) − =1
Case 1: 𝑎 𝑎2 𝑏2
Horizontal
𝑏 𝑥2 𝑦2
(0, 0) (±𝑎, 0) (0, ± 𝑏) (±𝑐, 0) 𝑦=± 𝑥 − =1
𝑎 𝑎2 𝑏 2
(ℎ, 𝑘) (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑎) (ℎ ± 𝑏, 𝑘) (ℎ, 𝑘 ± 𝑐)
𝑎
(𝑦 − 𝑘) = ± (𝑥 − ℎ) (𝑦 − 𝑘 )2 (𝑥 − ℎ )2
𝑏 − =1
Case 2: 𝑎2 𝑏2
Vertical 𝑎 𝑦2 𝑥2
(0, 0) (0, ± 𝑎) (±𝑏, 0) (0, ± 𝑐) 𝑦=± 𝑥 − =1
𝑏 𝑎2 𝑏 2
Length of transverse axis 2𝑎
Length of conjugate axis 2𝑏
Pythagorean Theorem (solving for 𝒄) 𝑐 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2
2
2𝑏 2
Latus Rectum 𝐿𝑅 =
𝑎
You might also like
- Engineering Mathematics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEngineering Mathematics Cheat Sheettevin sessa67% (3)
- Krishna's Question Bank Analytical GeometryDocument291 pagesKrishna's Question Bank Analytical Geometryijoky63% (8)
- 2D Model Monoatomic ChainDocument29 pages2D Model Monoatomic ChainM Irfan100% (1)
- Formula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Document1 pageFormula Sheet 1 (Precalculus)Roberto DiscutidoNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus ConicsectionsDocument1 pagePre Calculus ConicsectionsBCamacho UrielNo ratings yet
- The Ellipse: X y A B B A eDocument1 pageThe Ellipse: X y A B B A eJaff LawrenceNo ratings yet
- (Distance Between The Vertex and The Focus) : (Parabola)Document2 pages(Distance Between The Vertex and The Focus) : (Parabola)Karen LeonorNo ratings yet
- Sturm-Liouville & FourierDocument36 pagesSturm-Liouville & FourierEhab WilsonNo ratings yet
- Wave Function: Quantum Chemistry - Exercise Set 2Document8 pagesWave Function: Quantum Chemistry - Exercise Set 2mozNo ratings yet
- Ellipse Guide TableDocument2 pagesEllipse Guide TableJelaine GalvezNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - CSE - 381 PDFDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet - CSE - 381 PDFYasmine A. SabryNo ratings yet
- POWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsDocument3 pagesPOWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsLorniel GraxielNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 19 11 2022Document5 pagesLecture 7 19 11 2022owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument12 pagesConic SectionJohn Aldwin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Suprafata Cilindru Paralel Generatoare Rotire DRPT)Document1 pageSuprafata Cilindru Paralel Generatoare Rotire DRPT)chiricacosmin97No ratings yet
- Geometry - The EllipseDocument2 pagesGeometry - The EllipseJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- NCS21 - 02 - Phase Plane Analysis of Nonlinear Systems - 03Document7 pagesNCS21 - 02 - Phase Plane Analysis of Nonlinear Systems - 03zain khuramNo ratings yet
- Properties of EllipseDocument1 pageProperties of EllipseWeCareNo ratings yet
- Formulario LaPlaceDocument1 pageFormulario LaPlaceandres.castellonNo ratings yet
- Textbook Calculus Single Variable Bretscher Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Calculus Single Variable Bretscher Ebook All Chapter PDFshannon.millender193100% (20)
- Precalculus q1 FormulasDocument1 pagePrecalculus q1 FormulasGeronimo LucesNo ratings yet
- gr10t2 Functions Parabola Function MemoDocument8 pagesgr10t2 Functions Parabola Function MemoaaronmaburutseNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series Multiple Variable FunctionDocument1 pageTaylor Series Multiple Variable Functionmakrosha11816No ratings yet
- Taylor Series - Multiple Var Summer 22-23Document1 pageTaylor Series - Multiple Var Summer 22-23MRM MuhidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-2.3 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 2-2.3 PDFNorshahida MustarNo ratings yet
- Mat061 Chapter 2Document40 pagesMat061 Chapter 2Enaira100% (1)
- Solution To Extra Problem Set 5Document13 pagesSolution To Extra Problem Set 5物理系小薯No ratings yet
- SAT Formula Sheet: Linear FunctionsDocument8 pagesSAT Formula Sheet: Linear FunctionsShreyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Code 1.2Document17 pagesLesson Code 1.2Eriel MagramoNo ratings yet
- Calculus Reference SheetDocument6 pagesCalculus Reference SheetKevinNo ratings yet
- GraphDocument1 pageGraphKhoiruz ZahraNo ratings yet
- PRE-CALCULUS-W5-SLEM PC11AGfuucc Quarter1 Week5Document6 pagesPRE-CALCULUS-W5-SLEM PC11AGfuucc Quarter1 Week5Lemuel FajutagNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument21 pagesHyperbolaNorman JadumasNo ratings yet
- Cónicas CuadroDocument1 pageCónicas CuadroJuan Ignacio PirosoNo ratings yet
- 11 - HW Partials Gradient ProblemsDocument3 pages11 - HW Partials Gradient ProblemsasdfNo ratings yet
- Problemario Unidad 2 CMDocument5 pagesProblemario Unidad 2 CMRobles Ramírez Angel EliasNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Assignment - No - 4 - EditedDocument13 pagesSolutions - Assignment - No - 4 - EditedJahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DifferentiationDocument19 pagesChapter 2 DifferentiationMNo ratings yet
- Curva Parábola Elipse Hipérbola DefinicionesDocument1 pageCurva Parábola Elipse Hipérbola DefinicionesDante FayanásNo ratings yet
- Clave de Primer Parcial de Matemática IV. 2022Document9 pagesClave de Primer Parcial de Matemática IV. 2022César Augusto GuidoNo ratings yet
- Memo Assignment 1Document6 pagesMemo Assignment 1kideho6173No ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Week 4 Competency 8Document3 pagesPre Calculus Week 4 Competency 8cyriljunaicamaranquezNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous FunctionDocument11 pagesHomogeneous FunctionJOHN DAVID DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis Spring 2023 HW 7Document4 pagesComplex Analysis Spring 2023 HW 7asampathNo ratings yet
- Pptintegraldualipat 170512082355Document26 pagesPptintegraldualipat 170512082355Aisyah KhairaniNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Integral Tentu: Volume TabungDocument14 pagesAplikasi Integral Tentu: Volume TabungKekek LeliyanaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument12 pagesQuadratic EquationsRaymondNo ratings yet
- Answers - Online Daily Test 7 - TrockersDocument7 pagesAnswers - Online Daily Test 7 - TrockersMichael MyamboNo ratings yet
- Cálculo IntegralDocument5 pagesCálculo IntegraldanchanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Suspension Bridge Chapter 0 Parabola CableDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Suspension Bridge Chapter 0 Parabola CableSeungWoo LEENo ratings yet
- DistributionDocument4 pagesDistributionBui DuyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 1.kinematicsDocument12 pagesTutorial 4 1.kinematicsSALVADOR VARGAS DIAZNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise #4 Investigation of The Nonlinear Systems StabilityDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exercise #4 Investigation of The Nonlinear Systems StabilityFarabi AskarNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesAnalytic GeometryJennifer JumaquioNo ratings yet
- HIGH ORDER SLIP BOUNDARY SOLUTIONS For Two-Dimensional Micro-Hartmann Gas FlowsDocument4 pagesHIGH ORDER SLIP BOUNDARY SOLUTIONS For Two-Dimensional Micro-Hartmann Gas FlowsAhmad AlmasriNo ratings yet
- Group Assign CivilDocument1 pageGroup Assign CivilgediongatzNo ratings yet
- Solid of RevolutionDocument4 pagesSolid of RevolutionNicole TiancoNo ratings yet
- Harold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"Document7 pagesHarold's Precalculus Rectangular - Polar - Parametric "Cheat Sheet"HarshNo ratings yet
- Boundary Value Problem PDFDocument30 pagesBoundary Value Problem PDFrazNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Tutorial: SECTION - A (Aimstutorial - In) SECTION - A (Aimstutorial - In)Document4 pagesTutorial Tutorial: SECTION - A (Aimstutorial - In) SECTION - A (Aimstutorial - In)M.SHOURYA VARDHANNo ratings yet
- Scale-& Curves in Engineering GraphicsDocument55 pagesScale-& Curves in Engineering GraphicsUDDALAKNo ratings yet
- 9 Circle (@mrbeastjee)Document39 pages9 Circle (@mrbeastjee)I AM KIM TAEHYUNGNo ratings yet
- Part - I Part - Ii: ResonanceDocument7 pagesPart - I Part - Ii: ResonanceDikshant AsutkarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.0 (Main)Document19 pagesExercise 1.0 (Main)rockydalabehera94No ratings yet
- Hyperbola: Equation of Vertical, Shifted and Rotated Hyperbolas and Parametric Coordinates of HyperbolaDocument13 pagesHyperbola: Equation of Vertical, Shifted and Rotated Hyperbolas and Parametric Coordinates of HyperbolaJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument7 pagesCircles PDFBrijesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- KKKL1103 Week 5 - (AutoCAD) Isometric Drawings-20191007042509Document19 pagesKKKL1103 Week 5 - (AutoCAD) Isometric Drawings-20191007042509Indahnya BersabarNo ratings yet
- Asm 18272Document3 pagesAsm 18272syedmohdhamza0013No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson PlanLowie D GacetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Circle Exercise Ex. 17 (A)Document21 pagesChapter 17 - Circle Exercise Ex. 17 (A)Fahad pathanNo ratings yet
- Circle - Circumference: ExampleDocument2 pagesCircle - Circumference: ExampleMuhamad Zahwan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Discriminant of A Conic: Lesson #10Document6 pagesDiscriminant of A Conic: Lesson #10Daphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Parabolas With Vertex at The Origin: Chapter 10 - Conic SectionsDocument28 pages10.1 Parabolas With Vertex at The Origin: Chapter 10 - Conic SectionsShanelle SantillanaNo ratings yet
- Metric Ellipses in Minkowski PlanesDocument8 pagesMetric Ellipses in Minkowski PlanesJosé Jorge Bueno ContrerasNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Area Under Curve Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)Document2 pagesCH 8 Area Under Curve Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)CRPF School100% (7)
- Ellipse:) 1 e 0 (, A B 1 eDocument16 pagesEllipse:) 1 e 0 (, A B 1 eKamalesh Shenoy0% (2)
- Research Paper MathematicsDocument7 pagesResearch Paper MathematicsSoumik agarwallaNo ratings yet
- IPE Inter II Year Maths IIB Model Paper IDocument2 pagesIPE Inter II Year Maths IIB Model Paper IMohan Veerabomala100% (1)
- 07 Parabola and Ellipse - Handouts PDFDocument28 pages07 Parabola and Ellipse - Handouts PDFMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Equations of CirclesDocument36 pagesEquations of CirclesAzalia SabilaNo ratings yet
- SPLM Analytic Geometry Part 2Document85 pagesSPLM Analytic Geometry Part 2Joey TelinNo ratings yet
- Ellipses: You Should LearnDocument6 pagesEllipses: You Should Learnwyena matandacNo ratings yet
- Charles Jandrei Pereyra Grade 11-PasteurDocument6 pagesCharles Jandrei Pereyra Grade 11-PasteurCharles Jandrei PereyraNo ratings yet
- X - Ntse - Test-1 - Area Related To Circles Test-4Document2 pagesX - Ntse - Test-1 - Area Related To Circles Test-4raghuNo ratings yet
- Precalculus11 q1 Mod5 Identifyingconicsbyinspection v1Document24 pagesPrecalculus11 q1 Mod5 Identifyingconicsbyinspection v1Daine GamiaoNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument23 pagesConic SectionsRohit Kumar AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Prepared By: Prof. Teresita P. Liwanag - ZapantaDocument19 pagesConic Sections: Prepared By: Prof. Teresita P. Liwanag - ZapantaAudie T. MataNo ratings yet