Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Concept of State
The Concept of State
Uploaded by
Kunal SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Astm g23Document12 pagesAstm g23David CastroNo ratings yet
- The Filipino Citizens and Their RightsDocument35 pagesThe Filipino Citizens and Their RightsAntonio C. CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Activity-2 Human RightDocument2 pagesActivity-2 Human Rightbalbinc10No ratings yet
- CitizenshipDocument12 pagesCitizenshipanzala noorNo ratings yet
- PPG ReviewerDocument4 pagesPPG Reviewergasparcielomae12No ratings yet
- Chapter Three & FourDocument34 pagesChapter Three & FourAsfawosen DingamaNo ratings yet
- Citizen Ship CH 1Document15 pagesCitizen Ship CH 1Abdela Aman MtechNo ratings yet
- 1, Liberal Republican..Document1 page1, Liberal Republican..bisetegnbisrat2004No ratings yet
- JurisprudenceDocument17 pagesJurisprudenceShaghil NasidNo ratings yet
- Citizenship PDFDocument4 pagesCitizenship PDFPradhyumna B.RaviNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of ImmigratioinDocument15 pagesThe Ethics of Immigratiointhebusstopworld100% (1)
- EC and SH 3Document27 pagesEC and SH 3RLC TunesNo ratings yet
- Scope of Human RightsDocument14 pagesScope of Human RightsJohn Lester Tan100% (2)
- PLBA 1500 - Assignment #2Document6 pagesPLBA 1500 - Assignment #2damevalencia817No ratings yet
- Judicial Independence Americn Bar Assoc 37Document109 pagesJudicial Independence Americn Bar Assoc 37cyrus dresselhausNo ratings yet
- Investigación - Saúl Alejandro Martínez AlmanzaDocument1 pageInvestigación - Saúl Alejandro Martínez Almanzamsaul6068No ratings yet
- SummaryDocument14 pagesSummaryrobertocampospalmaNo ratings yet
- Блок 2.3docxDocument16 pagesБлок 2.3docxanastasiastepanova0388No ratings yet
- Civil Liberties HelperDocument2 pagesCivil Liberties Helperboumalichaima94No ratings yet
- Citizen and CitizenshipDocument11 pagesCitizen and CitizenshipalemayehuNo ratings yet
- q2h1. Human RightsDocument17 pagesq2h1. Human RightsJenevie MohamadNo ratings yet
- Civics Assignment SolutionDocument5 pagesCivics Assignment SolutionAsfawosen DingamaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-17 at 8.51.53 PMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-17 at 8.51.53 PMBittu SinghNo ratings yet
- JURISPRUDENCEDocument17 pagesJURISPRUDENCEShaghil NasidNo ratings yet
- CitizenshipDocument2 pagesCitizenshipSangeet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document8 pagesLesson 12Azi SierraNo ratings yet
- Citizenship and Good GovernanceDocument19 pagesCitizenship and Good GovernanceKim BautistaNo ratings yet
- Asylum SeekerDocument3 pagesAsylum SeekerAdv Mahmudur RashidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Human Rights Law 1Document43 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Human Rights Law 1ChloeNo ratings yet
- Portfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 SemesterDocument18 pagesPortfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 SemesterDexter SaladinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Pol Gov PPT CRS For Discussion 2Document45 pagesLesson 5 Pol Gov PPT CRS For Discussion 2Lexxy FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Politics - Important QuDocument9 pagesComparative Politics - Important Qusadia.jaman841No ratings yet
- What Is A Constitution PrimerDocument28 pagesWhat Is A Constitution Primerhassan khanNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Human Rights PromisesDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Human Rights Promisesrahulsthakur22No ratings yet
- Portfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 Semester S.Y. 2019-2020Document17 pagesPortfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 Semester S.Y. 2019-2020Dexter SaladinoNo ratings yet
- Tema 7 DCIPDocument9 pagesTema 7 DCIPToporeț AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Civil and Political RightsDocument14 pagesCivil and Political RightsLakshmi Rajan100% (1)
- CitenzenshipDocument14 pagesCitenzenshipMeynard CastroNo ratings yet
- Political SystemDocument3 pagesPolitical Systemaqsatalib106No ratings yet
- Polity Paper 22Document63 pagesPolity Paper 22Abcd WweNo ratings yet
- Civil RightsDocument3 pagesCivil RightsVincent LamNo ratings yet
- Social Interest and National Policies: What Is Public Policy? 1. Public PolicyDocument4 pagesSocial Interest and National Policies: What Is Public Policy? 1. Public PolicyEmmanuel BatinganNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document4 pagesAnswer 1jrmascuudNo ratings yet
- Bhiku ParekhDocument9 pagesBhiku ParekhRupam DubeyNo ratings yet
- Duties and ObiligationDocument4 pagesDuties and ObiligationGodwin EzekielNo ratings yet
- NSTP Lesson 2 Bill of RightsDocument46 pagesNSTP Lesson 2 Bill of RightsJenina Kaye Mostoles Gravides0% (1)
- DemocracyDocument16 pagesDemocracyIrene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Human RightsDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Human RightsJoseph R. SereñoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Constitution PrimerDocument25 pagesWhat Is A Constitution Primersaad aliNo ratings yet
- The Category of Human Rights: ExampleDocument5 pagesThe Category of Human Rights: Examplekeziah mae bagacinaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights Presentation Group3Document30 pagesHuman Rights Presentation Group3rafaelarmildez02No ratings yet
- Lycée MunicipalDocument6 pagesLycée MunicipalIlly JérémieNo ratings yet
- Bill of RightsDocument4 pagesBill of RightsSheena Liegh EntredichoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 - Citizenship FinalDocument64 pagesLesson 13 - Citizenship FinalMai Eu RhaNo ratings yet
- Citizeship Paret 2-1Document10 pagesCitizeship Paret 2-1Bililign GeremewNo ratings yet
- Lesson For Sep. 25Document12 pagesLesson For Sep. 25Donna LedesmaNo ratings yet
- CGW AssignmentDocument4 pagesCGW AssignmentIsha khobragadeNo ratings yet
- Role of International Society in Political ObligatioDocument6 pagesRole of International Society in Political ObligatioVibhutiNo ratings yet
- CDVsDocument2 pagesCDVsAndyScheelNo ratings yet
- Human RightsDocument5 pagesHuman RightsJerlyn SaplaNo ratings yet
- Elements of State, BY - Strictly - Student - 1637130994426Document4 pagesElements of State, BY - Strictly - Student - 1637130994426Kunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Formation of IncDocument9 pagesFormation of IncKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kartik EnvironmeDocument12 pagesKartik EnvironmeKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Important Sites of Indus Valley CivilisationDocument1 pageImportant Sites of Indus Valley CivilisationKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- TCPv3 TOCDocument4 pagesTCPv3 TOCKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- AmericanDocument19 pagesAmericanKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BallbDocument164 pagesSyllabus BallbKunal Sharma100% (1)
- Indian Legal HistoryDocument31 pagesIndian Legal HistoryKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contract Act MemoDocument13 pagesContract Act MemoKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Republic v. NaguiatDocument2 pagesRepublic v. NaguiatStephen Roy ArgosinoNo ratings yet
- CS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data SheetDocument4 pagesCS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data SheetJen OrfrecioNo ratings yet
- Eo 211Document2 pagesEo 211mark paul cortejosNo ratings yet
- Missingpage MergedDocument29 pagesMissingpage Mergedsuguna deviNo ratings yet
- DD 2527Document2 pagesDD 2527Paul MilesNo ratings yet
- Petitioners Vs Vs Respondent George Erwin M. Garcia Nicolas P. Lapena, JRDocument9 pagesPetitioners Vs Vs Respondent George Erwin M. Garcia Nicolas P. Lapena, JRCJ N PiNo ratings yet
- PAN PACIFIC SERVICE V Equitable PCI BankDocument3 pagesPAN PACIFIC SERVICE V Equitable PCI BanksiyaonNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Fundamentals of Arbitration Law - Part 2Document47 pagesTopic 4 - Fundamentals of Arbitration Law - Part 2Sanjay JainNo ratings yet
- Abangan v. AbanganDocument2 pagesAbangan v. AbanganLucas Gabriel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Glosario de MigraciónDocument92 pagesGlosario de Migraciónmangogo18No ratings yet
- Proprty Law Research PaperDocument9 pagesProprty Law Research Papermokshaa govilNo ratings yet
- Standard Mutual NDADocument7 pagesStandard Mutual NDAPRASAD THOMBARENo ratings yet
- Introducer 2 WayDocument5 pagesIntroducer 2 WayJohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Political LawDocument3 pagesLecture - Political LawchristineNo ratings yet
- Political Parties and Pressure Groups - Indian Polity NotesDocument8 pagesPolitical Parties and Pressure Groups - Indian Polity NotesHarshita satwaniNo ratings yet
- Law of TortsDocument16 pagesLaw of TortsSubhankar AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law Demistified - Uganda's PerspectiveDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Law Demistified - Uganda's PerspectiveGukiina PatrickNo ratings yet
- AmicusDocument2 pagesAmicusissaNo ratings yet
- GST Compensation To StatesDocument24 pagesGST Compensation To StatesBarun GargNo ratings yet
- Corrected NRI Marriages in India Socio Legal Perspectives of Women HarassmentDocument14 pagesCorrected NRI Marriages in India Socio Legal Perspectives of Women HarassmentMeenu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nature and Function of Tortious LiabilityDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Nature and Function of Tortious LiabilityYoushreen Washeelah Choomka100% (1)
- Forms of Government: Based On Power & Authority Distribution Muhammad Mustafa RazaDocument17 pagesForms of Government: Based On Power & Authority Distribution Muhammad Mustafa RazaMuhammad Mustafa RazaNo ratings yet
- Burgum V JaegerDocument10 pagesBurgum V JaegerRob PortNo ratings yet
- 07.06.11 Nycdcc $250-$500 Exaction For Picket DutyDocument17 pages07.06.11 Nycdcc $250-$500 Exaction For Picket DutyLatisha WalkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Limited PartnershipDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Limited PartnershipRica Meryl OcsinNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Lectures - Kinds of ObligationsDocument82 pagesOBLICON Lectures - Kinds of ObligationsRyle Radcliffe100% (1)
- Arihant SST Term 2Document164 pagesArihant SST Term 2Priyanshu Paul100% (2)
- Central Kyc Registration Form For IndividualsDocument5 pagesCentral Kyc Registration Form For IndividualsBKNo ratings yet
- Baker V Carr 369 U S 186Document7 pagesBaker V Carr 369 U S 186MarkNo ratings yet
The Concept of State
The Concept of State
Uploaded by
Kunal SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Concept of State
The Concept of State
Uploaded by
Kunal SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
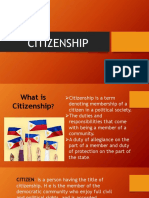
The concept of "state inclusion and exclusion from its ambit" in jurisprudence refers to the processes
through which a state determines who is considered a part of its legal and political community
(inclusion) and who is not (exclusion). This involves defining the boundaries of citizenship,
membership, and legal protection within the state.
Key elements related to this concept include:
1. **Citizenship**: States typically have criteria for determining who qualifies as a citizen. Citizenship
confers certain rights and responsibilities, such as the right to vote, work, and receive protection
under the law. Inclusion in the ambit of the state often implies citizenship, while exclusion may mean
lack of citizenship or denial of certain rights to non-citizens.
2. **Immigration and Emigration**: States regulate the movement of people across their borders
through immigration and emigration policies. Inclusion may involve allowing individuals to enter and
settle within the state's territory, while exclusion may take the form of immigration restrictions or
deportation.
3. **Legal Rights and Protections**: Inclusion within the state's ambit ensures that individuals enjoy
legal rights and protections. Exclusion, on the other hand, may result in a lack of legal standing or
limited access to the justice system.
4. **Social and Political Inclusion**: Beyond legal considerations, inclusion can extend to social and
political participation. This involves the recognition and acceptance of diverse groups within the
state, promoting a sense of belonging and participation in the political process.
5. **Human Rights**: The concept of inclusion and exclusion is also relevant in the context of human
rights. Inclusion involves ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their background, enjoy
fundamental human rights. Exclusion, in this context, may involve discrimination or the denial of
rights to certain groups.
6. **Sovereignty and Borders**: States exercise control over their territory and assert sovereignty
through the establishment of borders. Inclusion and exclusion are integral to defining the limits of
state authority and the scope of its legal and political jurisdiction.
Understanding the dynamics of inclusion and exclusion in jurisprudence is essential for analyzing
issues related to citizenship, immigration, human rights, and the overall relationship between
individuals and the state. Legal scholars, policymakers, and human rights advocates often engage
with these concepts to address questions of justice, equality, and the rule of law.
You might also like
- Astm g23Document12 pagesAstm g23David CastroNo ratings yet
- The Filipino Citizens and Their RightsDocument35 pagesThe Filipino Citizens and Their RightsAntonio C. CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Activity-2 Human RightDocument2 pagesActivity-2 Human Rightbalbinc10No ratings yet
- CitizenshipDocument12 pagesCitizenshipanzala noorNo ratings yet
- PPG ReviewerDocument4 pagesPPG Reviewergasparcielomae12No ratings yet
- Chapter Three & FourDocument34 pagesChapter Three & FourAsfawosen DingamaNo ratings yet
- Citizen Ship CH 1Document15 pagesCitizen Ship CH 1Abdela Aman MtechNo ratings yet
- 1, Liberal Republican..Document1 page1, Liberal Republican..bisetegnbisrat2004No ratings yet
- JurisprudenceDocument17 pagesJurisprudenceShaghil NasidNo ratings yet
- Citizenship PDFDocument4 pagesCitizenship PDFPradhyumna B.RaviNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of ImmigratioinDocument15 pagesThe Ethics of Immigratiointhebusstopworld100% (1)
- EC and SH 3Document27 pagesEC and SH 3RLC TunesNo ratings yet
- Scope of Human RightsDocument14 pagesScope of Human RightsJohn Lester Tan100% (2)
- PLBA 1500 - Assignment #2Document6 pagesPLBA 1500 - Assignment #2damevalencia817No ratings yet
- Judicial Independence Americn Bar Assoc 37Document109 pagesJudicial Independence Americn Bar Assoc 37cyrus dresselhausNo ratings yet
- Investigación - Saúl Alejandro Martínez AlmanzaDocument1 pageInvestigación - Saúl Alejandro Martínez Almanzamsaul6068No ratings yet
- SummaryDocument14 pagesSummaryrobertocampospalmaNo ratings yet
- Блок 2.3docxDocument16 pagesБлок 2.3docxanastasiastepanova0388No ratings yet
- Civil Liberties HelperDocument2 pagesCivil Liberties Helperboumalichaima94No ratings yet
- Citizen and CitizenshipDocument11 pagesCitizen and CitizenshipalemayehuNo ratings yet
- q2h1. Human RightsDocument17 pagesq2h1. Human RightsJenevie MohamadNo ratings yet
- Civics Assignment SolutionDocument5 pagesCivics Assignment SolutionAsfawosen DingamaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-03-17 at 8.51.53 PMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-17 at 8.51.53 PMBittu SinghNo ratings yet
- JURISPRUDENCEDocument17 pagesJURISPRUDENCEShaghil NasidNo ratings yet
- CitizenshipDocument2 pagesCitizenshipSangeet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document8 pagesLesson 12Azi SierraNo ratings yet
- Citizenship and Good GovernanceDocument19 pagesCitizenship and Good GovernanceKim BautistaNo ratings yet
- Asylum SeekerDocument3 pagesAsylum SeekerAdv Mahmudur RashidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Human Rights Law 1Document43 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Human Rights Law 1ChloeNo ratings yet
- Portfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 SemesterDocument18 pagesPortfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 SemesterDexter SaladinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Pol Gov PPT CRS For Discussion 2Document45 pagesLesson 5 Pol Gov PPT CRS For Discussion 2Lexxy FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Politics - Important QuDocument9 pagesComparative Politics - Important Qusadia.jaman841No ratings yet
- What Is A Constitution PrimerDocument28 pagesWhat Is A Constitution Primerhassan khanNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Human Rights PromisesDocument1 pageThe Evolution of Human Rights Promisesrahulsthakur22No ratings yet
- Portfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 Semester S.Y. 2019-2020Document17 pagesPortfolio On Philippine Politics and Governance: 1 Quarter, 1 Semester S.Y. 2019-2020Dexter SaladinoNo ratings yet
- Tema 7 DCIPDocument9 pagesTema 7 DCIPToporeț AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Civil and Political RightsDocument14 pagesCivil and Political RightsLakshmi Rajan100% (1)
- CitenzenshipDocument14 pagesCitenzenshipMeynard CastroNo ratings yet
- Political SystemDocument3 pagesPolitical Systemaqsatalib106No ratings yet
- Polity Paper 22Document63 pagesPolity Paper 22Abcd WweNo ratings yet
- Civil RightsDocument3 pagesCivil RightsVincent LamNo ratings yet
- Social Interest and National Policies: What Is Public Policy? 1. Public PolicyDocument4 pagesSocial Interest and National Policies: What Is Public Policy? 1. Public PolicyEmmanuel BatinganNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document4 pagesAnswer 1jrmascuudNo ratings yet
- Bhiku ParekhDocument9 pagesBhiku ParekhRupam DubeyNo ratings yet
- Duties and ObiligationDocument4 pagesDuties and ObiligationGodwin EzekielNo ratings yet
- NSTP Lesson 2 Bill of RightsDocument46 pagesNSTP Lesson 2 Bill of RightsJenina Kaye Mostoles Gravides0% (1)
- DemocracyDocument16 pagesDemocracyIrene MendozaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Human RightsDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Human RightsJoseph R. SereñoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Constitution PrimerDocument25 pagesWhat Is A Constitution Primersaad aliNo ratings yet
- The Category of Human Rights: ExampleDocument5 pagesThe Category of Human Rights: Examplekeziah mae bagacinaNo ratings yet
- Human Rights Presentation Group3Document30 pagesHuman Rights Presentation Group3rafaelarmildez02No ratings yet
- Lycée MunicipalDocument6 pagesLycée MunicipalIlly JérémieNo ratings yet
- Bill of RightsDocument4 pagesBill of RightsSheena Liegh EntredichoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 - Citizenship FinalDocument64 pagesLesson 13 - Citizenship FinalMai Eu RhaNo ratings yet
- Citizeship Paret 2-1Document10 pagesCitizeship Paret 2-1Bililign GeremewNo ratings yet
- Lesson For Sep. 25Document12 pagesLesson For Sep. 25Donna LedesmaNo ratings yet
- CGW AssignmentDocument4 pagesCGW AssignmentIsha khobragadeNo ratings yet
- Role of International Society in Political ObligatioDocument6 pagesRole of International Society in Political ObligatioVibhutiNo ratings yet
- CDVsDocument2 pagesCDVsAndyScheelNo ratings yet
- Human RightsDocument5 pagesHuman RightsJerlyn SaplaNo ratings yet
- Elements of State, BY - Strictly - Student - 1637130994426Document4 pagesElements of State, BY - Strictly - Student - 1637130994426Kunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Formation of IncDocument9 pagesFormation of IncKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kartik EnvironmeDocument12 pagesKartik EnvironmeKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Important Sites of Indus Valley CivilisationDocument1 pageImportant Sites of Indus Valley CivilisationKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- TCPv3 TOCDocument4 pagesTCPv3 TOCKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- AmericanDocument19 pagesAmericanKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BallbDocument164 pagesSyllabus BallbKunal Sharma100% (1)
- Indian Legal HistoryDocument31 pagesIndian Legal HistoryKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Contract Act MemoDocument13 pagesContract Act MemoKunal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Republic v. NaguiatDocument2 pagesRepublic v. NaguiatStephen Roy ArgosinoNo ratings yet
- CS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data SheetDocument4 pagesCS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data SheetJen OrfrecioNo ratings yet
- Eo 211Document2 pagesEo 211mark paul cortejosNo ratings yet
- Missingpage MergedDocument29 pagesMissingpage Mergedsuguna deviNo ratings yet
- DD 2527Document2 pagesDD 2527Paul MilesNo ratings yet
- Petitioners Vs Vs Respondent George Erwin M. Garcia Nicolas P. Lapena, JRDocument9 pagesPetitioners Vs Vs Respondent George Erwin M. Garcia Nicolas P. Lapena, JRCJ N PiNo ratings yet
- PAN PACIFIC SERVICE V Equitable PCI BankDocument3 pagesPAN PACIFIC SERVICE V Equitable PCI BanksiyaonNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Fundamentals of Arbitration Law - Part 2Document47 pagesTopic 4 - Fundamentals of Arbitration Law - Part 2Sanjay JainNo ratings yet
- Abangan v. AbanganDocument2 pagesAbangan v. AbanganLucas Gabriel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Glosario de MigraciónDocument92 pagesGlosario de Migraciónmangogo18No ratings yet
- Proprty Law Research PaperDocument9 pagesProprty Law Research Papermokshaa govilNo ratings yet
- Standard Mutual NDADocument7 pagesStandard Mutual NDAPRASAD THOMBARENo ratings yet
- Introducer 2 WayDocument5 pagesIntroducer 2 WayJohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Political LawDocument3 pagesLecture - Political LawchristineNo ratings yet
- Political Parties and Pressure Groups - Indian Polity NotesDocument8 pagesPolitical Parties and Pressure Groups - Indian Polity NotesHarshita satwaniNo ratings yet
- Law of TortsDocument16 pagesLaw of TortsSubhankar AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law Demistified - Uganda's PerspectiveDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Law Demistified - Uganda's PerspectiveGukiina PatrickNo ratings yet
- AmicusDocument2 pagesAmicusissaNo ratings yet
- GST Compensation To StatesDocument24 pagesGST Compensation To StatesBarun GargNo ratings yet
- Corrected NRI Marriages in India Socio Legal Perspectives of Women HarassmentDocument14 pagesCorrected NRI Marriages in India Socio Legal Perspectives of Women HarassmentMeenu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nature and Function of Tortious LiabilityDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Nature and Function of Tortious LiabilityYoushreen Washeelah Choomka100% (1)
- Forms of Government: Based On Power & Authority Distribution Muhammad Mustafa RazaDocument17 pagesForms of Government: Based On Power & Authority Distribution Muhammad Mustafa RazaMuhammad Mustafa RazaNo ratings yet
- Burgum V JaegerDocument10 pagesBurgum V JaegerRob PortNo ratings yet
- 07.06.11 Nycdcc $250-$500 Exaction For Picket DutyDocument17 pages07.06.11 Nycdcc $250-$500 Exaction For Picket DutyLatisha WalkerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Limited PartnershipDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Limited PartnershipRica Meryl OcsinNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Lectures - Kinds of ObligationsDocument82 pagesOBLICON Lectures - Kinds of ObligationsRyle Radcliffe100% (1)
- Arihant SST Term 2Document164 pagesArihant SST Term 2Priyanshu Paul100% (2)
- Central Kyc Registration Form For IndividualsDocument5 pagesCentral Kyc Registration Form For IndividualsBKNo ratings yet
- Baker V Carr 369 U S 186Document7 pagesBaker V Carr 369 U S 186MarkNo ratings yet