Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 Aldket Reduc
01 Aldket Reduc
Uploaded by
Sarvik The Pokémon Master RaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 Aldket Reduc
01 Aldket Reduc
Uploaded by
Sarvik The Pokémon Master RaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem
345 – Organic Reactions Chapter 19
Prepared by José Laboy, MS
http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page)
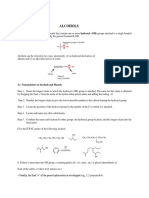
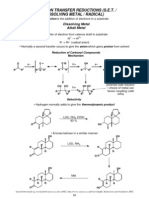
Aldehyde and Ketone Reduction
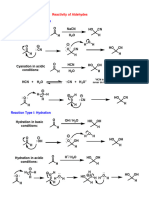
Reaction:
O
1) LiAlH4
H 3C H 2) Acid workup OH
or
Aldehydes
are
reduced
to
1o
alcohols
NaBH4 / CH3OH
Ketones
are
reduced
to
2o
alcohols
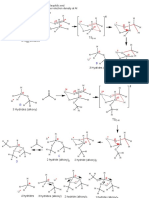
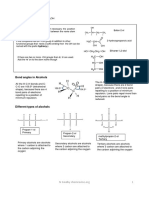
Mechanism:
O O Li
H
+ Al
H H
H
H C 3 H H 3C
H
H
H Al H
Li
H
H H
Al Li
Li and Al salts
O H O O
H
H
Li Al
4 H 3C OH
H O
H 3C
H
3
more
times
O O
H
Occurs
during
acid
workup
The
reduction
of
an
aldehyde
or
ketone
is
like
another
addition
reaction
to
carbonyls.
Either
reagent,
LiAlH4
or
NaBH4
will
do
the
job.
Use
of
H2
under
high
pressure
in
the
presence
of
a
precious
metal
can
also
provide
a
reduction.
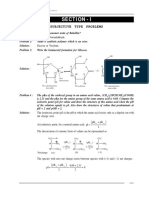
O OH
H2 102 atm / Ni
Because
of
the
harsh
conditions
necessary
to
reduce
the
carbonyl
groups
using
catalytic
hydrogenation
milder
conditions
will
selectively
hydrogenate
alkene
compounds,
e.g.,
H2
/
Pd(C).
O
O
H2 / Pd (C)
Room Temp.
You might also like
- 8thdec2022 Asymmetric Synthesis Using Chiral ReagentDocument14 pages8thdec2022 Asymmetric Synthesis Using Chiral ReagentPrince MeliodasNo ratings yet
- 6 - Organic ChemistryDocument27 pages6 - Organic ChemistryAlvaro CatalaNo ratings yet
- Reductions PPT 29-08-2020Document12 pagesReductions PPT 29-08-2020jkc collegeNo ratings yet
- 6 Organic Chemistry IDocument27 pages6 Organic Chemistry IAwil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Org Chem RxnsDocument4 pagesOrg Chem RxnsAkshit agarwalNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Naming TableDocument1 pageFunctional Group Naming Tableinfo.acc231No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Hydrocarbons PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Concepts and Hydrocarbons PDFDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- Copia de Aldehyde ReactionsDocument5 pagesCopia de Aldehyde Reactionsileanajaiseh26No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I EdexcelDocument28 pagesOrganic Chemistry I EdexcelAinara Román MacíasNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I EdexcelDocument28 pagesOrganic Chemistry I Edexcelvyb8qpq57yNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of CarbohydratesDocument27 pagesStructure and Function of CarbohydratesAli SeenaNo ratings yet
- Module2 Reduction PDFDocument55 pagesModule2 Reduction PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Oxoacids of Chlorine by H To O ChemistryDocument44 pagesOxoacids of Chlorine by H To O ChemistryRitu JoharNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 7: Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds - Achiral and Chiral ReductionDocument13 pagesEXPERIMENT 7: Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds - Achiral and Chiral ReductionHawra JawadNo ratings yet
- Alcohols PDFDocument8 pagesAlcohols PDFVon Valentine MhuteNo ratings yet
- The Logic of Chemical Synthesis Corey E J Amp Cheng X M 331 463Document133 pagesThe Logic of Chemical Synthesis Corey E J Amp Cheng X M 331 463bann tvNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesAlcohol and Carboxylic AcidPutri Nur SyafieqahNo ratings yet
- Week 13 WorkshopDocument3 pagesWeek 13 Workshoplayla_loveNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Revision Guide Introduction Organic AqaDocument9 pages3.1 Revision Guide Introduction Organic AqaIman KhanNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Revision Guide Alcohols AqaDocument7 pages3.5 Revision Guide Alcohols Aqashafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- 19.8 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones To Alcohols: Cyclobutanone Lithium Aluminum Hydride CyclobutanolDocument5 pages19.8 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones To Alcohols: Cyclobutanone Lithium Aluminum Hydride CyclobutanolHimanshu Panchal100% (1)
- Experiment 5 Properties of Carbohydrates: Solubility, Reactivity, and Specific RotationDocument9 pagesExperiment 5 Properties of Carbohydrates: Solubility, Reactivity, and Specific RotationCiara marie BernardoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Revision Guide Introduction Organic AqaDocument9 pages3.1 Revision Guide Introduction Organic Aqashafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionsTiffany LiuNo ratings yet
- HalogenalkaneDocument4 pagesHalogenalkanePutri Nur SyafieqahNo ratings yet
- Che 91165 FlashcardsDocument5 pagesChe 91165 FlashcardsLê Minh DuyNo ratings yet
- Drawing Haworth ProjectionsDocument6 pagesDrawing Haworth ProjectionschoconoodlesNo ratings yet
- Isomers of Coordination ComplexesDocument12 pagesIsomers of Coordination ComplexesNov IndaNo ratings yet
- 4 Introductory Organic Chemistry and AlkanesDocument12 pages4 Introductory Organic Chemistry and AlkanesChristina HerculesNo ratings yet
- 6: Organic Chemistry I: 6A. Introduction To Organic Chemistry Basic Definitions To KnowDocument27 pages6: Organic Chemistry I: 6A. Introduction To Organic Chemistry Basic Definitions To KnowJam GeejeeNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesOrganic Chemistryj.obriain94No ratings yet
- Mike Virnig - Crud PresentationDocument34 pagesMike Virnig - Crud Presentationworquera2507No ratings yet
- Pertemuan 5 Reguler Pagi & Sore 2021-2022 - 2Document53 pagesPertemuan 5 Reguler Pagi & Sore 2021-2022 - 2Amelia Dwi Ramadhani AjitiaNo ratings yet
- Grupos FuncionalesDocument1 pageGrupos FuncionalesHelena EspañaNo ratings yet
- CY2102Document2 pagesCY2102Prarabdha SharmaNo ratings yet
- TABORADA - Act8 (Ketones and Aldehydes)Document4 pagesTABORADA - Act8 (Ketones and Aldehydes)Justin Habaña TaboradaNo ratings yet
- No Experiment Tittle/ Subtittle Reagent Used Function of Reagent ReactionDocument9 pagesNo Experiment Tittle/ Subtittle Reagent Used Function of Reagent ReactionLailatul BadriyahNo ratings yet
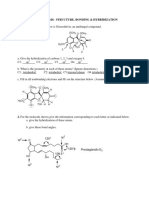
- Homework Problems: Structure, Bonding & Hybridization 1. The Molecule Shown Below Is Griseofulvin, An Antifungal CompoundDocument8 pagesHomework Problems: Structure, Bonding & Hybridization 1. The Molecule Shown Below Is Griseofulvin, An Antifungal CompoundPrachi KaushikNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - AlcoholsDocument7 pagesTopic 5 - AlcoholsRichard WalkerNo ratings yet
- CH-105 - (4) Chemistry of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCH-105 - (4) Chemistry of Carbonyl CompoundsK T Prajwal PrathikshNo ratings yet
- Carbohidratos Estructura PDFDocument6 pagesCarbohidratos Estructura PDFPatricia NarvaezNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Alcohols: O H H H HDocument15 pages6.5 Alcohols: O H H H HPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- P1-Hidrolisis de CarbohidratosDocument7 pagesP1-Hidrolisis de CarbohidratosgOnZo_86100% (1)
- AlcoholsDocument16 pagesAlcoholsLucas “Khumalo” KaunduNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionsDocument15 pagesNamed ReactionsSony mulgundNo ratings yet
- Hydration of Ketones and AldehydesDocument10 pagesHydration of Ketones and AldehydesPranjal SinghalNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2: CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CLDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2: CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CL CLTrung VõNo ratings yet
- Metal ReductionDocument11 pagesMetal Reductiondeepthimahanthi sabithaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.8 Amino Acids Structure Acid-Base Properties Condensation Reactions ProteinsDocument8 pagesTopic 4.8 Amino Acids Structure Acid-Base Properties Condensation Reactions ProteinsSammyJayNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 6 Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesKami Export - 6 Biological MoleculesNicholas Crowell100% (1)
- ch18 SummaryDocument1 pagech18 Summaryapi-465421809No ratings yet
- NEPHAR 305 Metabolism - 12Document61 pagesNEPHAR 305 Metabolism - 12Ra'fat RaheemNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Polymers-02 - Solved ProblemsDocument11 pagesBiomolecules and Polymers-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Kraft Reactin-Dye SynthesisDocument7 pagesKraft Reactin-Dye Synthesisgulft1777No ratings yet
- An Aldol Condensation To Synthesize ChalconesDocument6 pagesAn Aldol Condensation To Synthesize ChalconesAssyakurNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EthersDocument23 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and EthersKunal ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Experiment: CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesExperiment: CarbohydratesAriane Kyle GlodoveNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl Compounds (Alcohols)Document7 pagesHydroxyl Compounds (Alcohols)Nazmul NayeemNo ratings yet
- Overview of Alcohol Production 07042020Document66 pagesOverview of Alcohol Production 07042020PujitNo ratings yet
- BS 534 1990Document27 pagesBS 534 1990Upendranath BhupalNo ratings yet
- 6 Quarter 1 Module 6-STRUCTURE-OF-DNADocument21 pages6 Quarter 1 Module 6-STRUCTURE-OF-DNAMah Jane Divina100% (2)
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument12 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYChangha ParkNo ratings yet
- Final ReviewDocument43 pagesFinal ReviewKaththi KathirNo ratings yet
- Asm 3789Document6 pagesAsm 3789Mohammad Farhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Name - : (Excludes Brønsted-Lowry)Document22 pagesName - : (Excludes Brønsted-Lowry)John23No ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument5 pagesChemistry AssignmentNebal IsmailNo ratings yet
- Concentrations of Solutions: Unified Learning Activity Sheet in Science G7 Quarter 1 - Week 6Document2 pagesConcentrations of Solutions: Unified Learning Activity Sheet in Science G7 Quarter 1 - Week 6fitz zamoraNo ratings yet
- Water Food and Beverages Catalogue Line Plast Group 2019 AugustDocument5 pagesWater Food and Beverages Catalogue Line Plast Group 2019 AugustkukutestNo ratings yet
- RCE Varnisch+Removal Part+2 PDFA TGDocument52 pagesRCE Varnisch+Removal Part+2 PDFA TGdvfbckqfwqNo ratings yet
- Purificiation and Characterisation of Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesPurificiation and Characterisation of Organic CompoundsHari BabuNo ratings yet
- Final Histopath Notes.Document19 pagesFinal Histopath Notes.anneorigmtNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 2. Familiarization With ApparatusesDocument28 pagesLecture Note 2. Familiarization With ApparatuseskkkNo ratings yet
- 04 Unit Operations in Food Processing Contact Equilibrium Separation Processes-3: ExtractionDocument15 pages04 Unit Operations in Food Processing Contact Equilibrium Separation Processes-3: Extractionjackson100% (1)
- Class 10 Chemistry QuestionerDocument23 pagesClass 10 Chemistry QuestionerAnand HiremathNo ratings yet
- Natural Polymeric Biomaterials: Processing and Properties: R 2017 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument6 pagesNatural Polymeric Biomaterials: Processing and Properties: R 2017 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedAndres Felipe Rojas RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Weld Overlay Procedure For InconelDocument3 pagesWeld Overlay Procedure For InconelArash Mohamadi100% (3)
- Thermodynamic - Tables and GraphicsDocument46 pagesThermodynamic - Tables and GraphicsBruno MeloNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Layout Plan: Ground FloorDocument1 pageSanitary Layout Plan: Ground FloorFrancis KoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Science Presentation in Blue Light Blue Hand Drawn StyleDocument16 pagesChemical Reactions Science Presentation in Blue Light Blue Hand Drawn StyleMary Grace FacularinNo ratings yet
- GBT 24186Document5 pagesGBT 24186Cao Mạnh CườngNo ratings yet
- Practicals VivaDocument23 pagesPracticals Viva9C /Thanyasri.D TNo ratings yet
- Concure 1316Document4 pagesConcure 1316Rituraj RNo ratings yet
- GUID - 8 en-USDocument23 pagesGUID - 8 en-USHammam HafidzurahmanNo ratings yet
- PC 2004 - Proceedings PDFDocument905 pagesPC 2004 - Proceedings PDFkizaIIINo ratings yet
- Catalogo Bicos Lavagem ProMaxDocument20 pagesCatalogo Bicos Lavagem ProMaxSérgio GomesNo ratings yet
- 1974 - Soga - Copolymerization of Carbon Dioxide With PropyleneimineDocument11 pages1974 - Soga - Copolymerization of Carbon Dioxide With PropyleneimineViraj EdirisingheNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Composite Sleepers (17102023) - Maam CorrectionDocument44 pagesProject Report On Composite Sleepers (17102023) - Maam Correctionsmitirupa.pradhanfmeNo ratings yet
- U.S. Department of Transportation: Laboratory Test Procedure FOR Fmvss 116 Motor Vehicle Brake FluidsDocument5 pagesU.S. Department of Transportation: Laboratory Test Procedure FOR Fmvss 116 Motor Vehicle Brake FluidsMuhammad RNo ratings yet
- BP603T Unit 4-6Document69 pagesBP603T Unit 4-6Gyampoh SolomonNo ratings yet