Professional Documents
Culture Documents
para Lec - Flagellates-Giardia Lamblia
para Lec - Flagellates-Giardia Lamblia
Uploaded by
foxgod183Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Breast Cancer Multidisciplinary Pathways For Cancer Care in The Community (True PDFDocument220 pagesBreast Cancer Multidisciplinary Pathways For Cancer Care in The Community (True PDFDuk Han KimNo ratings yet
- giardiaDocument28 pagesgiardiawaleed wainsNo ratings yet
- Q. Necrotizing EnterocolitisDocument3 pagesQ. Necrotizing EnterocolitisRoselle Joy D. RosalejosNo ratings yet
- GIT InfectionDocument43 pagesGIT InfectionRaja RuzannaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Pathogenic FlagellatesDocument63 pages4.1 Pathogenic Flagellateskaartikey dubeNo ratings yet
- Flagellates (New Version) PDFDocument91 pagesFlagellates (New Version) PDFjan9paeiamsubNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument18 pagesHandoutschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections II IBDDocument8 pagesBacterial Infections II IBDRozeanneNo ratings yet
- GenitoDocument12 pagesGenitofatima_antonioNo ratings yet
- (HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestDocument2 pages(HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestHan SoloNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Basic TerminologiesDocument4 pagesParasitology: Basic TerminologiesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Pelvic TuberculosisDocument6 pagesPelvic TuberculosisJoan TimbolNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus-Midterm - 2ND SemDocument6 pagesStreptococcus-Midterm - 2ND Semrhenzyl ganoNo ratings yet
- Uti, Rheumatic Fever & ArthritisDocument2 pagesUti, Rheumatic Fever & ArthritisKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Kitten WholeDocument5 pagesKitten WholeAlexander GintingNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach To Children With Chronic Refractory Constipation Consensus Report by The SIGENP Motility Working GroupDocument15 pagesDiagnostic and Therapeutic Approach To Children With Chronic Refractory Constipation Consensus Report by The SIGENP Motility Working GroupEduardo Rios DuboisNo ratings yet
- Infection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Document109 pagesInfection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Sirawit Namkaeng ChoksuchatNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyDocument72 pagesParasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyanaNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsDocument2 pagesChlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsPetrisor GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- A. Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura (Whipworm)Document2 pagesA. Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura (Whipworm)Thea PepitoNo ratings yet
- IntussDocument4 pagesIntussemman_abzNo ratings yet
- L7.1 PEDIA Genitourinary Disorders (Feb0822)Document2 pagesL7.1 PEDIA Genitourinary Disorders (Feb0822)Erald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #4) TransDocument4 pagesParasitology (Lect #4) TransSherlyn Giban InditaNo ratings yet
- Lascano, Joanne Alyssa H. - Parasitology SGDDocument8 pagesLascano, Joanne Alyssa H. - Parasitology SGDJoanne Alyssa Hernandez LascanoNo ratings yet
- p1319 PDFDocument4 pagesp1319 PDFSyairodhiNo ratings yet
- Usm1 2 Is Lec Finals TransDocument49 pagesUsm1 2 Is Lec Finals TransArianne Grace GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 6DehydrationRefArticle6 PDFDocument11 pages6DehydrationRefArticle6 PDFMaya LarasNo ratings yet
- NS1 Case PresDocument8 pagesNS1 Case PresjoanaalpayNo ratings yet
- Luminal FlagellatesDocument55 pagesLuminal FlagellateseliwajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - StaphylococciDocument36 pagesChapter 14 - StaphylococciVincent Reyes100% (1)
- Paediatric Vaginal DischargeDocument3 pagesPaediatric Vaginal DischargeTanwi SinghNo ratings yet
- Anaerobes of Clinical ImportanceDocument13 pagesAnaerobes of Clinical ImportanceEarl John SepayaNo ratings yet
- IM Assignment#4 Part5Section15Chapter202 MumpsDocument3 pagesIM Assignment#4 Part5Section15Chapter202 MumpsJason OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesDocument18 pagesWeek 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesAngie BaylonNo ratings yet
- Physician Licensure Exam March 2019 Recall: MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesPhysician Licensure Exam March 2019 Recall: MicrobiologyNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Rest SlidesDocument44 pagesRest SlidesMohed LipanNo ratings yet
- AmoebiasisDocument3 pagesAmoebiasisKrista CabelloNo ratings yet
- Common Urological Problems in Children: Prepuce, Phimosis, and Buried PenisDocument7 pagesCommon Urological Problems in Children: Prepuce, Phimosis, and Buried PenisAbdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Virology NotesDocument7 pagesMtap - Virology NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Johns Hopkins Guides - CholecystitisDocument4 pagesJohns Hopkins Guides - CholecystitisTruly Dian AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric 23 Aug 2022Document36 pagesPediatric 23 Aug 2022GrInDoVe9097No ratings yet
- Dumlao, Michelin H.Document20 pagesDumlao, Michelin H.Mich DumlaoNo ratings yet
- ObsNGyn - Common Gyne Disorders AtfDocument21 pagesObsNGyn - Common Gyne Disorders AtfarongeremewNo ratings yet
- MBP Lab ReviewerDocument9 pagesMBP Lab ReviewerTrisha PaolaNo ratings yet
- Team 2 CPC - 2mor RangersDocument15 pagesTeam 2 CPC - 2mor Rangersdenzel0711No ratings yet
- Autoimmune DisordersDocument13 pagesAutoimmune Disordersinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Is Module 14Document33 pagesIs Module 14gladyskheyagamNo ratings yet
- Symptom Flow Chart: DiarrheaDocument1 pageSymptom Flow Chart: DiarrheaJeff ZhouNo ratings yet
- 4 - Malabsorption With NotesDocument34 pages4 - Malabsorption With NotesFGHFGHYFNo ratings yet
- Pedia Trans Respi Part 1Document8 pagesPedia Trans Respi Part 1Gen XNo ratings yet
- Pediatric CardiologyDocument7 pagesPediatric CardiologyMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Obstruction Due To Ascariasis - Management IssuesDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal Obstruction Due To Ascariasis - Management IssuesRachel DoloksaribuNo ratings yet
- 11small Pleomorphic Gram Negative BacilliDocument53 pages11small Pleomorphic Gram Negative BacilliClarence SantosNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesMicrobiologyDerek AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 4 Prelim - Atrial FlagellatesDocument52 pages4 Prelim - Atrial FlagellatesHersey MiayoNo ratings yet
- Travellers' Diarrhoea: A Guide For GpsDocument5 pagesTravellers' Diarrhoea: A Guide For GpsHafizuddin RazidNo ratings yet
- Disease of Colon and RectumDocument393 pagesDisease of Colon and Rectum6130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Bacteriology FinalsDocument6 pagesMtap - Bacteriology FinalsMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal and Urinogenital System: Giardia, Trichomonas, Dientamoeba Blood and Tissues: Trypanosoma and LeishmaniaDocument22 pagesIntestinal and Urinogenital System: Giardia, Trichomonas, Dientamoeba Blood and Tissues: Trypanosoma and LeishmaniaGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Microbio (Bacte)Document22 pagesMicrobio (Bacte)Carl PinedaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine AgentsDocument10 pagesEndocrine AgentsWendy VasquezNo ratings yet
- MSNHaemorrhoidsDocument17 pagesMSNHaemorrhoidsBrittany JordanNo ratings yet
- NE For StrokeDocument22 pagesNE For StrokeJacky LinNo ratings yet
- Nevid CH12 TBDocument85 pagesNevid CH12 TBAngela MarisNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology For The Equine Practitioner 2002-2002Document2 pagesOphthalmology For The Equine Practitioner 2002-2002Francisco JulianNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR 3 Neoplastic, Myeloproliferative and Myelodysplastic DisordersDocument6 pagesSEMINAR 3 Neoplastic, Myeloproliferative and Myelodysplastic DisordersMICHELLE RAPELONo ratings yet
- Immunotherapy For Lung CancerDocument3 pagesImmunotherapy For Lung CancerPongwirat ChantasoontornNo ratings yet
- STS 1 Act 6 Gene TherapyDocument1 pageSTS 1 Act 6 Gene TherapyJustine EscotoNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease DayaDocument74 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease DayarajhiniNo ratings yet
- BL BreastDocument14 pagesBL Breastsandhu27152715No ratings yet
- New Term 3Document2 pagesNew Term 3ابراهيم عتبانيNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument22 pagesNeonatal JaundiceNivedita Charan100% (2)
- 2023 Esc Cardiomiopatii SlidesDocument161 pages2023 Esc Cardiomiopatii SlidesCostică dascăluNo ratings yet
- Alopecia Totalis Following HFMDDocument3 pagesAlopecia Totalis Following HFMDVilt VilNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - DM (Tantsa Tamia)Document58 pagesCase Presentation - DM (Tantsa Tamia)tantsaNo ratings yet
- Cancer PainDocument12 pagesCancer Painsaranya.tNo ratings yet
- Ischemic StrokeDocument7 pagesIschemic StrokeAlly Juaneza100% (1)
- Dapa-CKD - Applying Clinical Evidence To Clinical PracticeDocument45 pagesDapa-CKD - Applying Clinical Evidence To Clinical Practicedevikumar kelkarNo ratings yet
- Dehghan 2018Document5 pagesDehghan 2018Nguyễn Văn HoạchNo ratings yet
- Guideline MERS Management in Malaysia, 2023Document123 pagesGuideline MERS Management in Malaysia, 2023Nezly IderusNo ratings yet
- BMI For AgeDocument2 pagesBMI For AgeNeil AtanacioNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Klinikopatologi Karsinoma Kolorektal PDFDocument5 pagesKarakteristik Klinikopatologi Karsinoma Kolorektal PDFMuhammad RizqiNo ratings yet
- Actualizacion Consenso Manejo Paciente Anciano Cancer ColorrectalDocument16 pagesActualizacion Consenso Manejo Paciente Anciano Cancer Colorrectalbreenda.rubioNo ratings yet
- Tot TCM in Pain Management.v1 2018Document41 pagesTot TCM in Pain Management.v1 2018AHNo ratings yet
- Biology File Project FileDocument22 pagesBiology File Project Filebhaskarganguly1976No ratings yet
- Prognostic Value and Adverse Events of Cytoreductive Surgery With Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Primary Advanced and PlatinumDocument14 pagesPrognostic Value and Adverse Events of Cytoreductive Surgery With Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Primary Advanced and PlatinumChris El HadiNo ratings yet
- Family Case SampleDocument25 pagesFamily Case SampleGrInDoVe9097No ratings yet
- Praktik Audit Kepatuhan Kebersihan TanganDocument19 pagesPraktik Audit Kepatuhan Kebersihan TanganTitiNo ratings yet
- Afp For MbbsDocument65 pagesAfp For MbbsShyam Sundar SNo ratings yet
para Lec - Flagellates-Giardia Lamblia
para Lec - Flagellates-Giardia Lamblia
Uploaded by
foxgod183Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
para Lec - Flagellates-Giardia Lamblia
para Lec - Flagellates-Giardia Lamblia
Uploaded by
foxgod183Copyright:
Available Formats
MLS 306 – CLINICAL PARASITOLOGY (LECTURE)
FLAGELLATES - GIARDIA LAMBLIA
1st SEMESTER | S.Y. 2022-2023 TRANSCRIBED BY: CAILENE S. INFANTE
LECTURER: DOC KISHAN BHALANI
TOPIC OUTLINE
I. Flagellates
a. Giardia lamblia
FLAGELLATES
3 BASIC GROUPS OF FLAGELLATES
➔ Intestinal flagellates
➔ Tissue flagellates
➔ Blood flagellates
GENERAL BODY STRUCTURES OF FLAGELLATES
➔ Kinetosome
➔ Costa
➔ Cystotome
➔ Cytostome
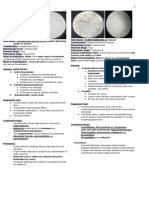
GIARDIA LAMBLIA
Figure 2 giardia lamblia trophozoite
➔ Final Habitat:
➢ Duodenum of the small intestine
➔ Duodenal aspirate can be a laboratory sample
➔ Associated with:
➢ Malabsorption syndrome
➢ Steatorrhea
➔ It causes traveler's diarrhea and epidemic diarrhea
TROPHOZOITE
➔ Pear-shaped or teardrop shaped
➔ The only bilaterally symmetrical protozoan with
medial line called AXOSTYLE
➔ Referred to as:
➢ “Old Man’s Face / Old Man with Eyeglasses”
➢ Old man with whiskers
➢ Cartoon character Figure 3 Trophozoite in the Intestine
➢ Monkey’s face
➔ FALLING LEAF MOTILITY CYST
➔ With 2 anterior nuclei ➔ Footballshaped/ovoid
➢ four pairs of flagella ➔ With 2-4 nuclei
➔ With 2 sucking disks ➔ Cytoplasm often appears retracted
➔ The AXOSTYLE is made up of two axonemes, defined
as the interior portion of the flagella
➔ Two slightly curved rodlike structures, known as
Median Bodies, sit on the axonemes posterior to the
nuclei
Figure 4 Giardia lamblia cyst
Figure 1 Giardia lamblia trophozoite
Infante, Cailene S. [BS MLS 3F] 1
DIAGNOSIS
➔ Demonstration of trophozoite and or cyst
➔ Duodeno-jejunal aspiration
➔ Biopsy
➔ Entero Test
➔ Antigen detection test
➢ Immunofluorescence
➢ immunochromatographic assays
➢ direct flourescent antibody
◼ gold standard
➢ PCR
EPIDEMIOLOGY
➔ The prevalence in the Philippines is less than 20%
and more common in children than in adults ( 6%)
➔ Homosexual
➔ Cysts have been found in dogs, cats, farm animals
and some wild animals
➔ Can be transmitted from fecally contaminated food
Figure 5 Giardia lamblia cyst ➔ Important risk factors include:
➢ Poor hygiene
➢ Poor sanitation
➢ Overcrowding
➢ Immunodeficiency
➢ Bacterial and fungal overgrowth in the small
intestine
➢ Homosexual practices.
➔ Related to “gay bowel syndrome”.
TREATMENT , PREVENTION AND CONTROL
➔ Proper water treatment
➢ chemical therapy and filtration
➔ Proper disposal of feces to prevent contamination of
water supply
➔ Prevent food from contamination due to the use of
human excreta as fertilizer for vegetables
➔ Prevent food from contamination from flies and
infected food handlers
➔ Avoidance of unprotected oral-anal sex
Figure 6 Giardia lamblia life cycle
PATHOLOGY
➔ It causes:
➢ traveller’s diarrhea
➢ epidemic diarrhea
➔ Associated with:
➢ Nausea
➢ anorexia
➢ crampy stomach
➔ The stool become light colored but not blood
streaked
➔ The diarrhea may become persistent, chronic and
associated with malabsorption so that the stool may
become steatorrheic
➔ Produce lectin
➔ Cause villous flattening and cyst hypertrophy.
➔ Typical incubation period is 10- 36 days
➔ Produce watery, foul-smelling diarrhea
➔ Self-limiting condition that typically is over in 10-14
days after onset
Infante, Cailene S. [BS MLS 3F] 2
You might also like
- Breast Cancer Multidisciplinary Pathways For Cancer Care in The Community (True PDFDocument220 pagesBreast Cancer Multidisciplinary Pathways For Cancer Care in The Community (True PDFDuk Han KimNo ratings yet
- giardiaDocument28 pagesgiardiawaleed wainsNo ratings yet
- Q. Necrotizing EnterocolitisDocument3 pagesQ. Necrotizing EnterocolitisRoselle Joy D. RosalejosNo ratings yet
- GIT InfectionDocument43 pagesGIT InfectionRaja RuzannaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Pathogenic FlagellatesDocument63 pages4.1 Pathogenic Flagellateskaartikey dubeNo ratings yet
- Flagellates (New Version) PDFDocument91 pagesFlagellates (New Version) PDFjan9paeiamsubNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument18 pagesHandoutschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections II IBDDocument8 pagesBacterial Infections II IBDRozeanneNo ratings yet
- GenitoDocument12 pagesGenitofatima_antonioNo ratings yet
- (HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestDocument2 pages(HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestHan SoloNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Basic TerminologiesDocument4 pagesParasitology: Basic TerminologiesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Pelvic TuberculosisDocument6 pagesPelvic TuberculosisJoan TimbolNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus-Midterm - 2ND SemDocument6 pagesStreptococcus-Midterm - 2ND Semrhenzyl ganoNo ratings yet
- Uti, Rheumatic Fever & ArthritisDocument2 pagesUti, Rheumatic Fever & ArthritisKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Kitten WholeDocument5 pagesKitten WholeAlexander GintingNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach To Children With Chronic Refractory Constipation Consensus Report by The SIGENP Motility Working GroupDocument15 pagesDiagnostic and Therapeutic Approach To Children With Chronic Refractory Constipation Consensus Report by The SIGENP Motility Working GroupEduardo Rios DuboisNo ratings yet
- Infection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Document109 pagesInfection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Sirawit Namkaeng ChoksuchatNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyDocument72 pagesParasitology: Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara Discipline of ParasitologyanaNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsDocument2 pagesChlamydia Felis: Infection in CatsPetrisor GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- A. Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura (Whipworm)Document2 pagesA. Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura (Whipworm)Thea PepitoNo ratings yet
- IntussDocument4 pagesIntussemman_abzNo ratings yet
- L7.1 PEDIA Genitourinary Disorders (Feb0822)Document2 pagesL7.1 PEDIA Genitourinary Disorders (Feb0822)Erald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology (Lect #4) TransDocument4 pagesParasitology (Lect #4) TransSherlyn Giban InditaNo ratings yet
- Lascano, Joanne Alyssa H. - Parasitology SGDDocument8 pagesLascano, Joanne Alyssa H. - Parasitology SGDJoanne Alyssa Hernandez LascanoNo ratings yet
- p1319 PDFDocument4 pagesp1319 PDFSyairodhiNo ratings yet
- Usm1 2 Is Lec Finals TransDocument49 pagesUsm1 2 Is Lec Finals TransArianne Grace GuerreroNo ratings yet
- 6DehydrationRefArticle6 PDFDocument11 pages6DehydrationRefArticle6 PDFMaya LarasNo ratings yet
- NS1 Case PresDocument8 pagesNS1 Case PresjoanaalpayNo ratings yet
- Luminal FlagellatesDocument55 pagesLuminal FlagellateseliwajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - StaphylococciDocument36 pagesChapter 14 - StaphylococciVincent Reyes100% (1)
- Paediatric Vaginal DischargeDocument3 pagesPaediatric Vaginal DischargeTanwi SinghNo ratings yet
- Anaerobes of Clinical ImportanceDocument13 pagesAnaerobes of Clinical ImportanceEarl John SepayaNo ratings yet
- IM Assignment#4 Part5Section15Chapter202 MumpsDocument3 pagesIM Assignment#4 Part5Section15Chapter202 MumpsJason OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesDocument18 pagesWeek 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesAngie BaylonNo ratings yet
- Physician Licensure Exam March 2019 Recall: MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesPhysician Licensure Exam March 2019 Recall: MicrobiologyNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Rest SlidesDocument44 pagesRest SlidesMohed LipanNo ratings yet
- AmoebiasisDocument3 pagesAmoebiasisKrista CabelloNo ratings yet
- Common Urological Problems in Children: Prepuce, Phimosis, and Buried PenisDocument7 pagesCommon Urological Problems in Children: Prepuce, Phimosis, and Buried PenisAbdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Virology NotesDocument7 pagesMtap - Virology NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Johns Hopkins Guides - CholecystitisDocument4 pagesJohns Hopkins Guides - CholecystitisTruly Dian AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric 23 Aug 2022Document36 pagesPediatric 23 Aug 2022GrInDoVe9097No ratings yet
- Dumlao, Michelin H.Document20 pagesDumlao, Michelin H.Mich DumlaoNo ratings yet
- ObsNGyn - Common Gyne Disorders AtfDocument21 pagesObsNGyn - Common Gyne Disorders AtfarongeremewNo ratings yet
- MBP Lab ReviewerDocument9 pagesMBP Lab ReviewerTrisha PaolaNo ratings yet
- Team 2 CPC - 2mor RangersDocument15 pagesTeam 2 CPC - 2mor Rangersdenzel0711No ratings yet
- Autoimmune DisordersDocument13 pagesAutoimmune Disordersinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Is Module 14Document33 pagesIs Module 14gladyskheyagamNo ratings yet
- Symptom Flow Chart: DiarrheaDocument1 pageSymptom Flow Chart: DiarrheaJeff ZhouNo ratings yet
- 4 - Malabsorption With NotesDocument34 pages4 - Malabsorption With NotesFGHFGHYFNo ratings yet
- Pedia Trans Respi Part 1Document8 pagesPedia Trans Respi Part 1Gen XNo ratings yet
- Pediatric CardiologyDocument7 pagesPediatric CardiologyMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Obstruction Due To Ascariasis - Management IssuesDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal Obstruction Due To Ascariasis - Management IssuesRachel DoloksaribuNo ratings yet
- 11small Pleomorphic Gram Negative BacilliDocument53 pages11small Pleomorphic Gram Negative BacilliClarence SantosNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesMicrobiologyDerek AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 4 Prelim - Atrial FlagellatesDocument52 pages4 Prelim - Atrial FlagellatesHersey MiayoNo ratings yet
- Travellers' Diarrhoea: A Guide For GpsDocument5 pagesTravellers' Diarrhoea: A Guide For GpsHafizuddin RazidNo ratings yet
- Disease of Colon and RectumDocument393 pagesDisease of Colon and Rectum6130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Bacteriology FinalsDocument6 pagesMtap - Bacteriology FinalsMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal and Urinogenital System: Giardia, Trichomonas, Dientamoeba Blood and Tissues: Trypanosoma and LeishmaniaDocument22 pagesIntestinal and Urinogenital System: Giardia, Trichomonas, Dientamoeba Blood and Tissues: Trypanosoma and LeishmaniaGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Microbio (Bacte)Document22 pagesMicrobio (Bacte)Carl PinedaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine AgentsDocument10 pagesEndocrine AgentsWendy VasquezNo ratings yet
- MSNHaemorrhoidsDocument17 pagesMSNHaemorrhoidsBrittany JordanNo ratings yet
- NE For StrokeDocument22 pagesNE For StrokeJacky LinNo ratings yet
- Nevid CH12 TBDocument85 pagesNevid CH12 TBAngela MarisNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology For The Equine Practitioner 2002-2002Document2 pagesOphthalmology For The Equine Practitioner 2002-2002Francisco JulianNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR 3 Neoplastic, Myeloproliferative and Myelodysplastic DisordersDocument6 pagesSEMINAR 3 Neoplastic, Myeloproliferative and Myelodysplastic DisordersMICHELLE RAPELONo ratings yet
- Immunotherapy For Lung CancerDocument3 pagesImmunotherapy For Lung CancerPongwirat ChantasoontornNo ratings yet
- STS 1 Act 6 Gene TherapyDocument1 pageSTS 1 Act 6 Gene TherapyJustine EscotoNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease DayaDocument74 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease DayarajhiniNo ratings yet
- BL BreastDocument14 pagesBL Breastsandhu27152715No ratings yet
- New Term 3Document2 pagesNew Term 3ابراهيم عتبانيNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument22 pagesNeonatal JaundiceNivedita Charan100% (2)
- 2023 Esc Cardiomiopatii SlidesDocument161 pages2023 Esc Cardiomiopatii SlidesCostică dascăluNo ratings yet
- Alopecia Totalis Following HFMDDocument3 pagesAlopecia Totalis Following HFMDVilt VilNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - DM (Tantsa Tamia)Document58 pagesCase Presentation - DM (Tantsa Tamia)tantsaNo ratings yet
- Cancer PainDocument12 pagesCancer Painsaranya.tNo ratings yet
- Ischemic StrokeDocument7 pagesIschemic StrokeAlly Juaneza100% (1)
- Dapa-CKD - Applying Clinical Evidence To Clinical PracticeDocument45 pagesDapa-CKD - Applying Clinical Evidence To Clinical Practicedevikumar kelkarNo ratings yet
- Dehghan 2018Document5 pagesDehghan 2018Nguyễn Văn HoạchNo ratings yet
- Guideline MERS Management in Malaysia, 2023Document123 pagesGuideline MERS Management in Malaysia, 2023Nezly IderusNo ratings yet
- BMI For AgeDocument2 pagesBMI For AgeNeil AtanacioNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Klinikopatologi Karsinoma Kolorektal PDFDocument5 pagesKarakteristik Klinikopatologi Karsinoma Kolorektal PDFMuhammad RizqiNo ratings yet
- Actualizacion Consenso Manejo Paciente Anciano Cancer ColorrectalDocument16 pagesActualizacion Consenso Manejo Paciente Anciano Cancer Colorrectalbreenda.rubioNo ratings yet
- Tot TCM in Pain Management.v1 2018Document41 pagesTot TCM in Pain Management.v1 2018AHNo ratings yet
- Biology File Project FileDocument22 pagesBiology File Project Filebhaskarganguly1976No ratings yet
- Prognostic Value and Adverse Events of Cytoreductive Surgery With Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Primary Advanced and PlatinumDocument14 pagesPrognostic Value and Adverse Events of Cytoreductive Surgery With Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Primary Advanced and PlatinumChris El HadiNo ratings yet
- Family Case SampleDocument25 pagesFamily Case SampleGrInDoVe9097No ratings yet
- Praktik Audit Kepatuhan Kebersihan TanganDocument19 pagesPraktik Audit Kepatuhan Kebersihan TanganTitiNo ratings yet
- Afp For MbbsDocument65 pagesAfp For MbbsShyam Sundar SNo ratings yet