Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Audit Planning
Audit Planning
Uploaded by
lied27106Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Audit Planning
Audit Planning
Uploaded by
lied27106Copyright:
Available Formats
Audit Planning
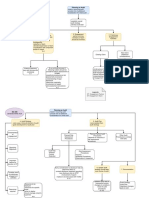
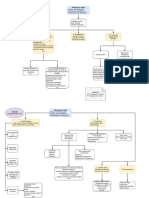
Objective : to plan the audit so that it will be perform in an
effective manner .
Output of Planning (2)
Audit
1 .
strategy
2. Audit Plan
F- actors that appeals the Natures Extent
op Planing
i. Size and complexity
a. key engagement team members previous experience w/ entity
3- din the
circumstances that occur during engagement
4. Timing of the appointment of the Auditor
Major Planning Activities
t
2 3
identifying and assessing 42mm through understanding the entity
and it's environment
Planned RISK assessment procedure ^
Establish Overall Strategy Develop Audit Man
Identify and asses Risk of Material Mi statement
AUDIT PLAN
to establish overall strategy
Generally ; In order audit
plan
detailed than overall
-
Auditor shall
• more
strategy
i. Obtain an
understanding of the entity and its environment .
§!!!!!!
Identify risk of material misktement
s assess
pnimewak It Include descriptions
.
2.
i. Identify the characteristics of the reporting of
engagement that define its scope requirement i. N T E
-
-
of the risk assessment procedures
Detailed steps 2. ascertain the location
reporting objectives of components Further audit procedures
.
2.
OF the
obtdtadgfhnty engagement to plan
3. Other planned audit PSA 's
internal control
including it's Risk the timing and nature procedures required by
assessment
procedures
419nificant in directing
3. consider Factors that are
consider
Materiality the engagement teams ' effort AUDIT PROGRAM
Inherent risk
Contains !
'
4 Consider the result
.
Identify and assess the risk of material mi statement control risk
.
of preliminary engagement activities t
knowledge gained on other engagements performed by the i. audit objectives for each area
engagement partner to entity is relevant totter
significant
Determine the acceptable level of Audit risk
factors 2. N T E of audit
-
-
procedures required
to implement over all audit plan
5. ascertain the N T E of resources necessary
- -
3. time budget for various audit area /procedures
Identify detection risk to determine N T E of - -
further audit
procedures .
to perform the engagement .
serves as a:
Riskassessment
procedure :
1. set
of instructions
Objective :
obtain an understanding of the entity and its environment .tk Financial RF
proper execution
µ 1-
applicable means to control and record
2.
2.
Identify 4 assess RMM
OF work
why ? provide basis fir design
and implementation of response
to the assessed risk .
Communication phase
during planning
Auditor 0¥ with
entity's management
to facilitate the conduct and
management
of the audit engagement -
(e.g coordinate planned audit procedures w/ work
of personnel)
b-
4
Direction / Supervision and Review Other Planning Considerations
need
i. Determine the
of an auditors expert
1
expert in field other than
accounting or auditing
what happens ?
Auditor uses expert 's work to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence
internal Cinside the firm )
expert can be :
fwm
external (outside the firm )
Note : When an audit is carried out
by an entirely by an audit engagement partner 55010 )
His okay to consult w/ other suitably experienced auditors or auditors professional body
⑨ INHERENT RISK
at
@btadtadgfhnty
,
1 Fs level and Assertion level for classes of transactions
including it's internal control , RAP and Related Activities
( inherent rsk)
/accounts balances and disclosures
HOW ?
•
By performing risk assessment procedures
determine whether tguch risks
}
•
µ performing , use
professional skepticism appeals the assessment of risk @ take into account :
purpose : obtain sufficient appropriate ext denote assertion level
degree which inherent factors affect the
susceptibility to mistatement
meut]
unbiased manner i. the
remain alert to audit evidence that
•
" not biased Evaluate the Nature 4 Extent oftheir b4
•
consideration
For what ? Basis for of confab
.
pervasive effect on FS
identifying risk
of material mistake
design further audit
procedures Significant Risk
.
1- - an
Identified RMM
for which assessment of Inherent Risk is close to the
upper and oplhe Spectrum
.
Sources
of Audit evidence Responses to
significant risk
1. Identify controls that
Note : Auditor is NOT required to
identify ALL possible sources
of Audit exldenoe 2. test } actresses significant risks
3 Obtain more evidence
1-
Interaction w/ management TCWG ,
other key personell
identified
,
4- Communicate to TCWG the significant risk
5. Timely tell ew of document
2. External parties cnhelher gotten directly / indirectly )
3 Publicly available info about the
entity ⑤ Control risk assessment
process [ see Handouts for consideration of IC )
RHP CRISK assessmentprocedures )
i. Inquiry all to better understand
the entity 4 Determine the acceptable level of Audit risk
2. Observation
How to determine ? By professional judgement
3
Inspection linen) used in :
} :÷::÷
-
a. Substantive test
4. analytical procedure
steps :
i. Develop expectations regarding
FS accepted
2 Compare expectations ys Actual
Define and Investigate SIGNIFICANT differences Identify detection risk to audit
3
g-
determine N T E of - -
further procedures .
Detection risk -
Audit risk
✓ accepted
Inherent risk ✗ Control Risk
2 Consider
Materiality
How to determine materiality ?
When is
information material ?
Used of assessed level of DR
it's or mi statement
When omission could influence through !
the economic decisions of users .
whether Professional Judgement Lower DR Higher DR
aggregately
Natunemoreeffeohvepnceduteslessefpechvepnc.ec#
individual
depends on may be
applied may be
applied
nature and/or size timing .
Procedure Performed
year end -
closer to Procedure performed
dates
at interim or several
'
uses
of materiality in
planning Extent Larger sample size is tested smaller sample size is tested
statement
i. identify and asses risks of material
helps determine N T E
of audit procedures
inverse relationship
- '
2
Audit risk
-
Materiality vs :
Levels of materiality (3) the Higher the level the lower the and it risk
materiality
.
can be based on continued) .
}
' CFP )
benchmark ✗%
(overall Materiality ) determined at overall financial level total assets
statement total revenue CIS
represents the smallest aggregate
2
A. FS Materiality
amount of mi
that is Acceptable trail FS total income
ltolerablemistakment )
""a" Matri
}
"
4
"
(specific/ individual
B. Materiality to specific class
of transaction /account balance /disclosure materiality) -
expected uncorrected mistakemerits on
classes
of transaction
-
c. Performance Materiality calculated as certain materiality
g. of overall
(planning 1 scoping materiality ) ( total amount may
exceed overall materiality)
Audit Risk
risk material mistakemeat C inherent risk ✗ control risk )
of
components
risk of not detecting the mistntement (detection risk)
detection rusk = risk that SUB STAHNKE PROCEDURES
Will NOT detect a mistatement that could be material
Formula :
Audit risk =
ROMM ✗ RISK of non detection
OR
Inherent risk✗ control risk ✗ detection risk
3 Identify and assess the risk of material mistalement
① INHERENT RISK assec.me/-
process
:
objective to identify : how INHERENT risk
factors affect the susceptibility of assertions TO MLsHtEMENB
the preparation
in
of Fs .
result :
auditor knows how to and plan
perform
•
further audit procedures ENITFIEDRMM
asses
riske assertion level
.
effect on
FS
Petras we effect
-
on
@ FS level
.
assertion about class of transaction/ account balance /disclosure
}
i. Relevant assertions a
- -
- an
when it has an IDENTIFIED HSKOFNM
assess
ii significant class contains 1 more relevant assertions determines where
llkekhood 9
-
or
opgansach.ph/*pgpp
on
@ assertion level -
(magnitude of } mstatetnent ①
"
SPECTRUM
of
Inherent risk
"
is the
identified
② RMM
determines
-
significant risks
You might also like
- Bok CMRPDocument56 pagesBok CMRPjaviermvs100% (7)
- Planning and Budgeting - PPT NotesDocument44 pagesPlanning and Budgeting - PPT NotesEmma WongNo ratings yet
- NADCAP AC7114 Rev FDocument23 pagesNADCAP AC7114 Rev FAnonymous gFcnQ4go100% (3)
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Chapter 2 - Audit Strategy, Planning and ProgrammingDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Chapter 2 - Audit Strategy, Planning and ProgrammingNavneet NandaNo ratings yet
- Section 2 Comparative AnalysisDocument35 pagesSection 2 Comparative AnalysisShiela Marie GadayosNo ratings yet
- Section 2 Comparative AnalysisDocument34 pagesSection 2 Comparative AnalysisShiela Marie GadayosNo ratings yet
- Detailed Audit PlanDocument3 pagesDetailed Audit PlanPhrexilyn PajarilloNo ratings yet
- Planning - Prelims Seatwork No. 1Document35 pagesPlanning - Prelims Seatwork No. 1Shiela Marie GadayosNo ratings yet
- Study Notes On Auditing: Planning An Audit of Financial Statements (ISA-300)Document11 pagesStudy Notes On Auditing: Planning An Audit of Financial Statements (ISA-300)sajedulNo ratings yet
- Revised Audit Plan Template - ApprovedDocument57 pagesRevised Audit Plan Template - ApprovedRiza Mae Ramos AddatuNo ratings yet
- Audit QB Ch2Document12 pagesAudit QB Ch2Piyush ChhimwalNo ratings yet
- Ch_2_Audit_Strategy__Planning___Execution__CA_Study_NotesDocument2 pagesCh_2_Audit_Strategy__Planning___Execution__CA_Study_NotesbabugenuNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document1 pageTopic 5sofianasery28No ratings yet
- DOH AG III - Accomplishment ReportDocument18 pagesDOH AG III - Accomplishment Reportshane natividadNo ratings yet
- Mind Map 5Document1 pageMind Map 5darylle roblesNo ratings yet
- Aars Isa 300 Series Flowcharts by Sir Jamshaid AkhtarDocument13 pagesAars Isa 300 Series Flowcharts by Sir Jamshaid AkhtarahmadNo ratings yet
- JBSESB-MP004 Quality Management PlanDocument1 pageJBSESB-MP004 Quality Management PlanNaqib Levis SolNo ratings yet
- Budgeting HandbookDocument1 pageBudgeting HandbookTamer ŞenerNo ratings yet
- 06-BOC Gensan - 2022 - AAPSIDocument5 pages06-BOC Gensan - 2022 - AAPSIReihannah Paguital-MagnoNo ratings yet
- Jordan Short Training Course Kpis en PDFDocument140 pagesJordan Short Training Course Kpis en PDFmohamed elgammlNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning Asuncion Et Al. 2021Document8 pagesAudit Planning Asuncion Et Al. 2021tjasonkiddNo ratings yet
- Audit Notes Ca BosDocument30 pagesAudit Notes Ca BosBijay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Pre0131 Midterm Reviewer - PDF PlanningDocument2 pagesPre0131 Midterm Reviewer - PDF PlanningEliny CruzNo ratings yet
- (Resa2019) Preweek (AP)Document30 pages(Resa2019) Preweek (AP)Dawson Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PM 2Document67 pagesPM 2KhushbuNo ratings yet
- Proficiency StageDocument10 pagesProficiency StageFLORITA SERRANO50% (2)
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.1808-Audit Planning-An Overview MAY 2015Document8 pagesLecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.1808-Audit Planning-An Overview MAY 2015Misa AmaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document9 pagesChapter 04Trang Lê Thị ThùyNo ratings yet
- Audits & Inspections ProcessDocument1 pageAudits & Inspections ProcessAmaline PrataNo ratings yet
- Oga Se2 Ework Programmes July 2019Document9 pagesOga Se2 Ework Programmes July 2019Par MadNo ratings yet
- Commonwealth Avenue, Quezon City, Philippines: Republic of The Philippines Commission On AuditDocument4 pagesCommonwealth Avenue, Quezon City, Philippines: Republic of The Philippines Commission On AuditMJ BajaNo ratings yet
- Improve MaterialDocument130 pagesImprove MaterialbillNo ratings yet
- Strategik ManegementDocument15 pagesStrategik ManegementnitaNo ratings yet
- 62549studentjournal-Jan2021a (1) - RemovedDocument15 pages62549studentjournal-Jan2021a (1) - RemovedTimepass MungfuliNo ratings yet
- At.3206-Planning An Audit of Financial StatementsDocument6 pagesAt.3206-Planning An Audit of Financial StatementsDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Planning An Audit ISA 300: EP: Engagement Partner ET: Engagement TeamDocument2 pagesPlanning An Audit ISA 300: EP: Engagement Partner ET: Engagement TeamMuhammad AslamNo ratings yet
- Cia Review: Part 2 Study Unit 4: Engagement PlanningDocument12 pagesCia Review: Part 2 Study Unit 4: Engagement PlanningjorgeNo ratings yet
- P7 - Planning PartDocument15 pagesP7 - Planning PartArab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Auditing-Techniques-Audit Performance 2022Document50 pagesAuditing-Techniques-Audit Performance 2022kyawNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document6 pagesCH 4K60 Phạm Tuấn KiệtNo ratings yet
- Assurance - Chapter 3 - STDocument67 pagesAssurance - Chapter 3 - STLinh KhanhNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance Speclized Industries - 18 Sep 2023Document29 pagesAuditing and Assurance Speclized Industries - 18 Sep 2023Renelyn FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - Audit Planning P2Document14 pagesChap 4 - Audit Planning P2hangNo ratings yet
- Risk Management, Internal Controls and Audit: Status Update - November 4, 2019Document9 pagesRisk Management, Internal Controls and Audit: Status Update - November 4, 2019skand.knath23No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Audit Strategy, Planning and ProgrammingDocument1 pageChapter 2 - Audit Strategy, Planning and Programmingthuzh007No ratings yet
- Audit 7Document26 pagesAudit 7Harold Dan AcebedoNo ratings yet
- Audit Strategy, Audit Planning and Audit Programme: Learning OutcomesDocument31 pagesAudit Strategy, Audit Planning and Audit Programme: Learning OutcomesMayank JainNo ratings yet
- CSU2021 Audit ReportDocument155 pagesCSU2021 Audit ReportMiss_AccountantNo ratings yet
- Ppas TemplateDocument4 pagesPpas TemplatejhaneberteNo ratings yet
- Intended Learning Outcomes:: SESSION 3: Estimating and Resource EstimateDocument11 pagesIntended Learning Outcomes:: SESSION 3: Estimating and Resource EstimatemateojullieanneNo ratings yet
- At.3509 - Overall Audit Strategy and Audit ProgramDocument11 pagesAt.3509 - Overall Audit Strategy and Audit ProgramJohn MaynardNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document35 pagesWeek 5flora tasiNo ratings yet
- BPM - 3 - HalaDocument12 pagesBPM - 3 - HalaAsadulla KhanNo ratings yet
- Action Plan DetailsDocument1 pageAction Plan DetailsDon James VillaroNo ratings yet
- Tug and Barge Survey ReportDocument4 pagesTug and Barge Survey ReportFoad MirzaieNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Planning or Profit Planning - 5 of Financial and Other Resources of The Company InaDocument3 pagesShort-Term Planning or Profit Planning - 5 of Financial and Other Resources of The Company InaAngela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Planning & Supervising The EngagementDocument13 pagesPlanning & Supervising The EngagementJuris Renier MendozaNo ratings yet
- At.2505 Planning The AuditDocument28 pagesAt.2505 Planning The Auditawesome bloggersNo ratings yet
- Process PlanDocument5 pagesProcess PlanKashif SamadNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Audit PlanningDocument3 pagesCh-2 Audit PlanningSavya Sachi100% (1)
- STRATEGYDEVELOPMENTDocument7 pagesSTRATEGYDEVELOPMENTJonathan WenNo ratings yet
- PROJECT MONITORING AND EVALUATION- A PRIMER: Every Student's Handbook on Project M & EFrom EverandPROJECT MONITORING AND EVALUATION- A PRIMER: Every Student's Handbook on Project M & ENo ratings yet
- Understanding QMS 9001 2015 PDFDocument108 pagesUnderstanding QMS 9001 2015 PDFLeoncio Lumaban100% (2)
- Project Management: A Managerial Approach: - Auditing ProjectsDocument18 pagesProject Management: A Managerial Approach: - Auditing ProjectsRaihan MuflihhamimNo ratings yet
- SA 8000 AuditDocument7 pagesSA 8000 Auditjohnthep2009100% (1)
- Chapter 1 BADocument17 pagesChapter 1 BAHEMA NAIRNo ratings yet
- Personnel AuditDocument19 pagesPersonnel AuditHappy MehraNo ratings yet
- Dugayon Vs People (G.R. No. 147333 August 12, 2004)Document6 pagesDugayon Vs People (G.R. No. 147333 August 12, 2004)Amir Nazri KaibingNo ratings yet
- National Energy Audit InitiativeDocument37 pagesNational Energy Audit InitiativeSALMANNo ratings yet
- Niño Mary N. Savillo BSADocument2 pagesNiño Mary N. Savillo BSAKyohyunNo ratings yet
- 2019 Systems Engineering SBAreportDocument8 pages2019 Systems Engineering SBAreportUD SinghNo ratings yet
- WBHO Integrated Report 2018Document61 pagesWBHO Integrated Report 2018Wachama j SwanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 AnsDocument14 pagesChapter 11 AnsZen TungpalanNo ratings yet
- Quizbowl M7&M8Document54 pagesQuizbowl M7&M8Ann Christine C. ChuaNo ratings yet
- FAM Reviewer by NANDocument86 pagesFAM Reviewer by NANshane natividadNo ratings yet
- Louw 4Document32 pagesLouw 4Qianyue HeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument34 pagesFundamentals of Auditing and Assurance ServicesPeter BanjaoNo ratings yet
- Risk Response PlanningDocument5 pagesRisk Response Planningubadjate100% (1)
- 4.3 Scope of QMSDocument8 pages4.3 Scope of QMSVijayendran VijayNo ratings yet
- Auditing As Profession in BangladeshDocument11 pagesAuditing As Profession in BangladeshIshan_Bhowmik50% (2)
- 01A Audit of Limited CompaniesDocument34 pages01A Audit of Limited CompaniesSai VardhanNo ratings yet
- CA Final Mock Test Papers and Solutions For May 2017 ICAIDocument9 pagesCA Final Mock Test Papers and Solutions For May 2017 ICAIRithik VisuNo ratings yet
- IT AuditingDocument48 pagesIT AuditingQueen Arianne Rafols SingcolanNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document24 pagesModule 5Naruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Plan For CateringDocument80 pagesFood Safety Plan For CateringNghia Khang100% (1)
- Local Church Audit ReportDocument5 pagesLocal Church Audit ReportJennie HastingsNo ratings yet
- بشير 7Document23 pagesبشير 7Basheer Yousif IsmailNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Implementing The POPIADocument21 pagesA Guide To Implementing The POPIABheki TshimedziNo ratings yet
- Hamid Fabrics Limited: ProspectusDocument173 pagesHamid Fabrics Limited: ProspectusI U Asif AhmadNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory ReviewerDocument9 pagesAuditing Theory ReviewerChristian MaritoNo ratings yet