Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics 1
Thermodynamics 1
Uploaded by
manvir270508Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BBC English Book Class 12 PDFDocument3 pagesBBC English Book Class 12 PDFmanvir27050850% (2)
- Solar Energy Engineering 2nd Edition Kalogirou Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesSolar Energy Engineering 2nd Edition Kalogirou Solutions Manualjoshuarussellbmrgzkdeia100% (11)
- Answers For Tutorial No. 2: ME1202 Introduction To Thermodynamics - Academic Year 2017Document9 pagesAnswers For Tutorial No. 2: ME1202 Introduction To Thermodynamics - Academic Year 2017manaraj100% (1)
- PHY 205 Exam 1 Fall 2014 URIDocument5 pagesPHY 205 Exam 1 Fall 2014 URIlyndsey_erin_aguiarNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document120 pagesCH 12PhimjunkieNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Indicators Disclosed in Corporate Sustainability Reports PDFDocument16 pagesAn Analysis of Indicators Disclosed in Corporate Sustainability Reports PDFRahul PramaniNo ratings yet
- Examview - Biology 1st Semester Exam With Standards W-O AnwsDocument4 pagesExamview - Biology 1st Semester Exam With Standards W-O Anwsapi-232424041No ratings yet
- TemplateDocument2 pagesTemplateJoemar SubongNo ratings yet
- شيت واجبDocument3 pagesشيت واجبhussamjamal432No ratings yet
- TS 1 To 6Document11 pagesTS 1 To 6Anshul Gautam100% (1)
- Thermodynamics - Weekly Test 01 - Test PaperDocument4 pagesThermodynamics - Weekly Test 01 - Test PaperAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Weekly Test 02 - Test PaperDocument4 pagesThermodynamics - Weekly Test 02 - Test PaperAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (Lecture 1-3)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (Lecture 1-3)eja70No ratings yet
- Practice Problems Thermodynamic Relations CyclesDocument2 pagesPractice Problems Thermodynamic Relations CyclesSanu SouravNo ratings yet
- DPP-18 (Thermodynamics)Document4 pagesDPP-18 (Thermodynamics)Dushyanth S JNo ratings yet
- hw9 PDFDocument2 pageshw9 PDFtesfaye awelNo ratings yet
- S 5 XNWWG FF P42 C JBC C8 CGDocument8 pagesS 5 XNWWG FF P42 C JBC C8 CGanshbhatnagar002No ratings yet
- Heat & Thermodynamics Qns Asked in IITDocument7 pagesHeat & Thermodynamics Qns Asked in IITBiprodeep14No ratings yet
- KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument37 pagesKTG & ThermodynamicsveereshgajwelNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesThermodynamicsjashsumedhaNo ratings yet
- Tuttherm2 PDFDocument6 pagesTuttherm2 PDFPrabir BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Question 1152296Document3 pagesQuestion 1152296Navya VaishnaviNo ratings yet
- THER206 Tut 2nd LawDocument2 pagesTHER206 Tut 2nd Law5432167890OOOONo ratings yet
- 11 GasesDocument17 pages11 Gasespuja ritongaNo ratings yet
- Processes and Carnot CycleDocument4 pagesProcesses and Carnot CycleRagh AhmedNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics Ib Q MarkschemeDocument26 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics Ib Q MarkschemeLaila HassanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Spring 2018-19Document3 pagesTutorial 2 Spring 2018-19ANMOLNo ratings yet
- P6. Hukum 1 TermodinamikaDocument6 pagesP6. Hukum 1 TermodinamikaAnis AnisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)Document4 pagesTutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)kkhimatiNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument54 pagesThermodynamicsArbeeChrystelV.AleraNo ratings yet
- (W - 9,460 J/mol) : ST NDDocument2 pages(W - 9,460 J/mol) : ST NDMubasharNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsbybjDocument25 pagesThermodynamicsbybjdhairyatiwari1222No ratings yet
- Che 325-345 (Module 4) EntropyDocument33 pagesChe 325-345 (Module 4) Entropyraina205macNo ratings yet
- 2023 MteDocument6 pages2023 MteISHAAN JAIN 22114039No ratings yet
- Sem 1 PhysicsDocument25 pagesSem 1 PhysicsShiu Ping Wong100% (1)
- Thermodynamics 1655870560521Document26 pagesThermodynamics 1655870560521Singh DhruvNo ratings yet
- ETD Question Bank 2021-22Document14 pagesETD Question Bank 2021-22Vinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- ThermodymanicsDocument6 pagesThermodymanicsnavy.aulakh11No ratings yet
- 1 - GasesDocument5 pages1 - GasesVon Joby RomeroNo ratings yet
- Physics - 2k18Document5 pagesPhysics - 2k18Pragyanshu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- ChE211 HW2Document1 pageChE211 HW2Nathan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas LawDocument7 pagesCombined Gas LawAllenWORXNo ratings yet
- Example 4Document41 pagesExample 4Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Adiabatik Prosess Ok 2020Document15 pagesAdiabatik Prosess Ok 2020Pemri Yangrit SaeNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 ReviewDocument45 pagesPertemuan 7 ReviewAna Sholikhatus Sa'diyah100% (1)
- Thermal Physics Home Work Sheet-6 1640756934272Document1 pageThermal Physics Home Work Sheet-6 1640756934272Vivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1 - Intro To Combustion, Principles of ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesLearning Material 1 - Intro To Combustion, Principles of ThermodynamicsVELASCO JULIE-ANN G.No ratings yet
- Subjective Questions: KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesSubjective Questions: KTG & ThermodynamicsTanvir ShafalNo ratings yet
- Thermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFDocument33 pagesThermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFFattihiEkhmalNo ratings yet
- Question PART 3 (2023)Document5 pagesQuestion PART 3 (2023)qbao2806k4No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Unit 4Document10 pagesThermodynamic Unit 4Bhavani .SNo ratings yet
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedDocument2 pagesAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedPruthvi HareeshNo ratings yet
- Ch-Thermodynamics DPP 03Document4 pagesCh-Thermodynamics DPP 03soumyadipmaity902No ratings yet
- EOC Chapter12Document11 pagesEOC Chapter12Armando LiosNo ratings yet
- Adhwat World Academy: Class 11 - PhysicsDocument5 pagesAdhwat World Academy: Class 11 - PhysicsUtkarsh VaishNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Equation and EntropyDocument27 pagesIdeal Gas Equation and EntropyJude Roswel GenerilloNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics: Second GradeDocument13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics: Second GradeMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- TALLER 3 - 2do CorteDocument9 pagesTALLER 3 - 2do Corteeylen OviedoNo ratings yet
- 4.thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Exercise 1 PDFDocument49 pages4.thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Exercise 1 PDFtwinkle varuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Continued Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Study Guide in PowerpointDocument53 pagesChapter 7 Continued Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Study Guide in Powerpointbrayan CortezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment 2 2014Document5 pagesThermodynamics Assignment 2 2014ravikr950% (1)
- Solution Part 3 (2023)Document9 pagesSolution Part 3 (2023)01khanh26No ratings yet
- BCM Electrostati Field 2024Document1 pageBCM Electrostati Field 2024manvir270508No ratings yet
- 1-C-73970-Dear ParentsDocument1 page1-C-73970-Dear Parentsmanvir270508No ratings yet
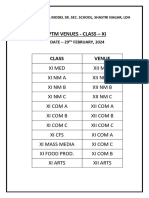
- PTM VENUES XiDocument1 pagePTM VENUES Ximanvir270508No ratings yet
- PTM Circular December 2023-1Document1 pagePTM Circular December 2023-1manvir270508No ratings yet
- History of Indian TelevisionDocument14 pagesHistory of Indian Televisionmanvir270508No ratings yet
- 09-17.5 E MicroCal T SeriesDocument4 pages09-17.5 E MicroCal T SeriesIlic MiroslavNo ratings yet
- D - Internet - Myiemorgmy - Intranet - Assets - Doc - Alldoc - Document - 20574 - Flyer HD - Ir. Hj. Arul Hisham - 31 Mac 2021Document4 pagesD - Internet - Myiemorgmy - Intranet - Assets - Doc - Alldoc - Document - 20574 - Flyer HD - Ir. Hj. Arul Hisham - 31 Mac 2021Tan Kang YaoNo ratings yet
- mtv1000 UsermanDocument95 pagesmtv1000 UsermanJuan Carlos Quispe LopezNo ratings yet
- Vibro-Acoustics: A New Springer PublicationDocument9 pagesVibro-Acoustics: A New Springer PublicationcharcharNo ratings yet
- Aron GideyDocument141 pagesAron Gideydere100% (1)
- Swot Analysis of OgdclDocument2 pagesSwot Analysis of OgdclMuhammad Ahmer100% (2)
- Share MarketDocument84 pagesShare MarketSai TharunNo ratings yet
- BD418 External - Annunciator - BTTY ANN 003 FiplexDocument1 pageBD418 External - Annunciator - BTTY ANN 003 Fiplexculeros1No ratings yet
- Bronze Data SheetDocument3 pagesBronze Data SheetAnonymous xkKyD8fBouNo ratings yet
- Cop. 1132Document4 pagesCop. 1132r2drill50% (2)
- WCH01 01 Que 20170111Document24 pagesWCH01 01 Que 20170111Niranjan BhuvanaratnamNo ratings yet
- K Single - TS - EngDocument13 pagesK Single - TS - Engguy doohNo ratings yet
- Waste-to-Energy in The PhilippinesDocument54 pagesWaste-to-Energy in The PhilippinesEleazar Ante TalabongNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Motorized LiftDocument62 pagesFabrication of Motorized LiftANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Bottle Washers, Factors Affecting Washing Operations, Power Requirements of Can and Bottle WashersDocument3 pagesBottle Washers, Factors Affecting Washing Operations, Power Requirements of Can and Bottle WashersMonty KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Early dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]Document2 pagesEarly dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]abhywaNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Quantum MechanicsDocument3 pagesQuiz On Quantum MechanicsAnge1196No ratings yet
- Investigation of Polarization and Depolarization Current For Evaluation of Moisture in Oil-Pressboard InsulationDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Polarization and Depolarization Current For Evaluation of Moisture in Oil-Pressboard InsulationmersiumNo ratings yet
- Table 4B1 and 4E4ADocument2 pagesTable 4B1 and 4E4Ahachan100% (2)
- Generator Set Data Sheet: 825 kVA StandbyDocument3 pagesGenerator Set Data Sheet: 825 kVA StandbydukegarrikNo ratings yet
- BIO Battery: Power For FutureDocument15 pagesBIO Battery: Power For Futurekavya2smart100% (2)
- Gas Turbines Siemens Interactive PDFDocument22 pagesGas Turbines Siemens Interactive PDF'Izzad AfifNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Mild HybirdDocument12 pagesPresentation On Mild HybirdAkshay S BhatNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval CB10 / CBH10: Brazed Plate Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesAlfa Laval CB10 / CBH10: Brazed Plate Heat ExchangerAfonso LopesNo ratings yet
- Content Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2020Document111 pagesContent Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2020Fabiola Marella PardedeNo ratings yet
- Diesel Exhaust FluidDocument7 pagesDiesel Exhaust FluidCISHAC FPNo ratings yet
- 9.5 Giant Metallic StructuresDocument2 pages9.5 Giant Metallic StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
Thermodynamics 1
Thermodynamics 1
Uploaded by
manvir270508Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermodynamics 1
Thermodynamics 1
Uploaded by
manvir270508Copyright:
Available Formats
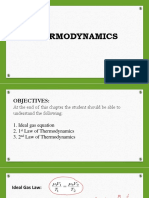
PROBLEMS FOR PRACTICE
7. One gram mole of an ideal gas at N.T.P. is first
SOTHERMAL AND
expanded isothermalily to twice the original
ADIABATIC PROCESSESS
volume. It is then compressed at constant voBume.
1. A cylinder containing 1 gram mole oí a gas was till its pressure is raised to the original value.
compressed adiabaticaily until its temperafure rose Calculate the total amount of work done. Given R
from 27C to 97C.Calculate work done and heat 8-3 J mole-l K-l. [Ans. 1-57 x 10* J]
produced in the gas. Take y = 1-5. 8. A tyre pumped to a pressure of6 atmosphere bursts
[Ans. 1162 J, 276-7 cals] suddenly. Calculate the temperature of escaping
2. A sample of gas (y 1-5) is compressed air. Given initial
temperature is 15°C and y
=
room
adiabatically from a volume of 1600 c.c to 400 for air is 14. [Ans. 172-6 K]
C.c. If the initial pressure is 150 kPa, what is the 9. Find the final volume of a
gram molecule of a gas
final pressure. How much work is done on the gas after an isothermal
in the process ?
expansion at 127°C, if the
[Ans. 1200 kPa ; - 480 J] original volume is 400 c.c. Given the amount of
3. 200 cm of a gas is compressed to 100 cm at work done by a gram molecule
of a gas during
atmospheric pressure (10 dyne/cm). Find the expansion is 2302-6 joule, R 8-3 =
joule mole
resultant pressure if the change is (i) slow K-
10. A
[Ans. 800 c.e.]
(i)sudden. Take y= 14. quantity of air at normal
temperature com- is
[Ans. ) 2 atm (i) 2638 atm] pressed (a) slowly (b) suddenly to one third of its
4. An ideal monoatomic gas is taken around the cycle
volume. Find the rise in
case, y= 14. temperature, if any in each
ABCDA, where co-ordinates of A, B, C andD on [Ans. (a) Zero (b) 150-6°C]
11. Two different
P-V diagram are A (p, V), B (2 p. V), C (2p, 2 V) adiabatic for the same gas
curves
and D (p. 2 V). Cakculate work done during the intersect two isothermals at
in P-V T, and T as shown
Cycle [Ans.p diagram, Fig. 8.23. How does the ratio
5. A quantity of air at 27C and atmospheric pressure (VVcompare with the
ratio (V,/V)?
is suddeniy compressed to half its original volume.
FIGURE 8.23
Find the final (i pressure and (i) temperaure.
Given y for air = 1-42. T1
[Ans. (i) 2675 atmosphere (i) 128:3°CT
6. A cylinder containingone gram mole of a gas was
put on boiling water bath and compressed D
adiabatically till its temperature rose by 70°C.
Calculate the work done and heat developed in
he gas, = 15, R=2 cal. moleK-,
[Ans. 1176 joule, 280 cal.]
[Ans. Same]
urlm
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S
50°C and 75 em of
ercury pressure, a definite
12. Ifat while doing 70 J of work. How much heat has to
mass of a gas is compressed (i) slowly (i) enly,
be the final pressure and be supplied in taking the same gas from state a to
then what will temp. of
each case, if the final volume : state b via another path when it perförms 200 J of
the gas in one
work ?
initial volume ? y= 15. [Ans. 235 J]
fourth of the 22. One gram mole of an ideal
Ans. ) 300 em; 50°C i) 600 cm; 373°C1 gas at S.T.P. is subjected
to a reversible adiabatic expansion to double its
13, An ideal monoatomic gas is taken round the eycle
volume. Find the change in internal energy in the
ABCDA where co-ordinates of A, B, C, D on P-V
diagram are A (p, V), B(2p, V). C(2p, 2 V) and D
process. Take y= 14. [Ans. 1373-2 J]
23. If 1 gram of oxygen at 760 mm pressure and 0°CC
(p, 2 V). Calculate work done during the cycle.
has its volume doubled in an adiabatic change;
[Ans. pV]1 calculate the change in internal energy. Take R=2
14. Calculate net work done by the gas whose cal. mole- K-, J = 4-2 J cal. and y = 1.4.
thermodynamical behaviour is represented by right
[Ans.-43-37J]
angled triangle ABC on P-V diagram. The P-V 24. Ten mole of hydrogen at N.T.P. is compressed
co-ordinates are: A (20, 6), B (10, 12) and
C(10, 6) where P is in Nm and Vis in m3
adiabatically so that its temperature becomes
400°C. How much work is done on the gas ? Also,
[Ans. 30 J calculate the increase in internal energy of the gas.
15. One mole of an ideal gas is heated from 273 K to Take R = 8-4 J mole K and y = 14.
546 K at constant pressure of 1 atmosphere. [Ans.-8-4 x 104 J : 8-4 x 104 J
Calculate the work done by the gas in the process. 25. Calculate the increase in internal energy of 1 kg of
LAns. 2-26 x 105 J] water at 100°C when it is converted into steam at
the same temp. and at 1 atmosphere (100 kPa).
16. Three moles of an ideal gas at 127°C expand
The density of water and steam are 1000 kg/m*
isothermally until the volume is doubled. Calculate
and 0-6 kg/m' respectively. The latent heat of
the amount of work done and heat absorbed. vaporization of water = 2-25 x 10° J/kg.
[Ans. 6912J, 6912 J] [Ans. 2-08x 106 J]
FIRST LAW 26. The internal energy of a monoatomic ideal gas is
PE
OF THERMODYNAMICS 1-5 nR AT. One mole of He is kept in a cylinder of
cross section 8-5 cm. The cylinder is closed by a
17. A volume' of 10 m3 of a liquid is supplied with
light frictionless piston. The gas is heated slowly
100 kcal ofheat and expands at a constant pressure
in a process during which a total of 42 J heat is
of 10 atm to a final volume of 10-2 m'. Calculate
given to the gas. If the temperature rises through
the work done and change in internal energy.
2°C, find the distance moved by the piston. Take 1
[Ans. 48 kcal. 52 kcall atmospheric pressure = 100 k Pa. [Ans. 20 eml
. At
o°C and
normal atmospheric pressure, the
g of water increases from 1 cm
to
volume of 1
T-091 cm on freezing. What is the change
n internal energy ? Normal atmospheric pressure
1-013 x 10 N/m2 and latent heat of melting ice
80 cal g [Ans. 80-0022 cal]
A sample of ideal gas (y= 1-4) is heated at constant
pressure. If 140 J of heat is supplied to the gas.
Find (i) change in internal energy of the gas
(i) work done by the [Ans. 100J; 40 J]
gas.
One kg of water at 373 K is converted into steam
Lne same temperature. The volume 1 cm or
water becomes1671 em3 on boiling. Calculate the
hange in internal energyof the system, if heat of
Vaporisation is 540 calg-1, Given standara
nOSpheric pressure =1-013[Ans.
x10° 499-84
Nm kcal]
21.
hen a gas is taken from one state a to another
stateb via one path, it absorbs 25 calories of heat
You might also like
- BBC English Book Class 12 PDFDocument3 pagesBBC English Book Class 12 PDFmanvir27050850% (2)
- Solar Energy Engineering 2nd Edition Kalogirou Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesSolar Energy Engineering 2nd Edition Kalogirou Solutions Manualjoshuarussellbmrgzkdeia100% (11)
- Answers For Tutorial No. 2: ME1202 Introduction To Thermodynamics - Academic Year 2017Document9 pagesAnswers For Tutorial No. 2: ME1202 Introduction To Thermodynamics - Academic Year 2017manaraj100% (1)
- PHY 205 Exam 1 Fall 2014 URIDocument5 pagesPHY 205 Exam 1 Fall 2014 URIlyndsey_erin_aguiarNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document120 pagesCH 12PhimjunkieNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Indicators Disclosed in Corporate Sustainability Reports PDFDocument16 pagesAn Analysis of Indicators Disclosed in Corporate Sustainability Reports PDFRahul PramaniNo ratings yet
- Examview - Biology 1st Semester Exam With Standards W-O AnwsDocument4 pagesExamview - Biology 1st Semester Exam With Standards W-O Anwsapi-232424041No ratings yet
- TemplateDocument2 pagesTemplateJoemar SubongNo ratings yet
- شيت واجبDocument3 pagesشيت واجبhussamjamal432No ratings yet
- TS 1 To 6Document11 pagesTS 1 To 6Anshul Gautam100% (1)
- Thermodynamics - Weekly Test 01 - Test PaperDocument4 pagesThermodynamics - Weekly Test 01 - Test PaperAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Weekly Test 02 - Test PaperDocument4 pagesThermodynamics - Weekly Test 02 - Test PaperAbhijeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (Lecture 1-3)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (Lecture 1-3)eja70No ratings yet
- Practice Problems Thermodynamic Relations CyclesDocument2 pagesPractice Problems Thermodynamic Relations CyclesSanu SouravNo ratings yet
- DPP-18 (Thermodynamics)Document4 pagesDPP-18 (Thermodynamics)Dushyanth S JNo ratings yet
- hw9 PDFDocument2 pageshw9 PDFtesfaye awelNo ratings yet
- S 5 XNWWG FF P42 C JBC C8 CGDocument8 pagesS 5 XNWWG FF P42 C JBC C8 CGanshbhatnagar002No ratings yet
- Heat & Thermodynamics Qns Asked in IITDocument7 pagesHeat & Thermodynamics Qns Asked in IITBiprodeep14No ratings yet
- KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument37 pagesKTG & ThermodynamicsveereshgajwelNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesThermodynamicsjashsumedhaNo ratings yet
- Tuttherm2 PDFDocument6 pagesTuttherm2 PDFPrabir BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Question 1152296Document3 pagesQuestion 1152296Navya VaishnaviNo ratings yet
- THER206 Tut 2nd LawDocument2 pagesTHER206 Tut 2nd Law5432167890OOOONo ratings yet
- 11 GasesDocument17 pages11 Gasespuja ritongaNo ratings yet
- Processes and Carnot CycleDocument4 pagesProcesses and Carnot CycleRagh AhmedNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics Ib Q MarkschemeDocument26 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics Ib Q MarkschemeLaila HassanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Spring 2018-19Document3 pagesTutorial 2 Spring 2018-19ANMOLNo ratings yet
- P6. Hukum 1 TermodinamikaDocument6 pagesP6. Hukum 1 TermodinamikaAnis AnisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)Document4 pagesTutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)kkhimatiNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument54 pagesThermodynamicsArbeeChrystelV.AleraNo ratings yet
- (W - 9,460 J/mol) : ST NDDocument2 pages(W - 9,460 J/mol) : ST NDMubasharNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsbybjDocument25 pagesThermodynamicsbybjdhairyatiwari1222No ratings yet
- Che 325-345 (Module 4) EntropyDocument33 pagesChe 325-345 (Module 4) Entropyraina205macNo ratings yet
- 2023 MteDocument6 pages2023 MteISHAAN JAIN 22114039No ratings yet
- Sem 1 PhysicsDocument25 pagesSem 1 PhysicsShiu Ping Wong100% (1)
- Thermodynamics 1655870560521Document26 pagesThermodynamics 1655870560521Singh DhruvNo ratings yet
- ETD Question Bank 2021-22Document14 pagesETD Question Bank 2021-22Vinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- ThermodymanicsDocument6 pagesThermodymanicsnavy.aulakh11No ratings yet
- 1 - GasesDocument5 pages1 - GasesVon Joby RomeroNo ratings yet
- Physics - 2k18Document5 pagesPhysics - 2k18Pragyanshu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- ChE211 HW2Document1 pageChE211 HW2Nathan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas LawDocument7 pagesCombined Gas LawAllenWORXNo ratings yet
- Example 4Document41 pagesExample 4Akatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- Adiabatik Prosess Ok 2020Document15 pagesAdiabatik Prosess Ok 2020Pemri Yangrit SaeNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 ReviewDocument45 pagesPertemuan 7 ReviewAna Sholikhatus Sa'diyah100% (1)
- Thermal Physics Home Work Sheet-6 1640756934272Document1 pageThermal Physics Home Work Sheet-6 1640756934272Vivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1 - Intro To Combustion, Principles of ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesLearning Material 1 - Intro To Combustion, Principles of ThermodynamicsVELASCO JULIE-ANN G.No ratings yet
- Subjective Questions: KTG & ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesSubjective Questions: KTG & ThermodynamicsTanvir ShafalNo ratings yet
- Thermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFDocument33 pagesThermo EXAMPLE 7.2-CHAPTER 7 PDFFattihiEkhmalNo ratings yet
- Question PART 3 (2023)Document5 pagesQuestion PART 3 (2023)qbao2806k4No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Unit 4Document10 pagesThermodynamic Unit 4Bhavani .SNo ratings yet
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedDocument2 pagesAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part. Data Hand Book and Steam Tables Is PermittedPruthvi HareeshNo ratings yet
- Ch-Thermodynamics DPP 03Document4 pagesCh-Thermodynamics DPP 03soumyadipmaity902No ratings yet
- EOC Chapter12Document11 pagesEOC Chapter12Armando LiosNo ratings yet
- Adhwat World Academy: Class 11 - PhysicsDocument5 pagesAdhwat World Academy: Class 11 - PhysicsUtkarsh VaishNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Equation and EntropyDocument27 pagesIdeal Gas Equation and EntropyJude Roswel GenerilloNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics: Second GradeDocument13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics: Second GradeMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- TALLER 3 - 2do CorteDocument9 pagesTALLER 3 - 2do Corteeylen OviedoNo ratings yet
- 4.thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Exercise 1 PDFDocument49 pages4.thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Exercise 1 PDFtwinkle varuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Continued Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Study Guide in PowerpointDocument53 pagesChapter 7 Continued Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Study Guide in Powerpointbrayan CortezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment 2 2014Document5 pagesThermodynamics Assignment 2 2014ravikr950% (1)
- Solution Part 3 (2023)Document9 pagesSolution Part 3 (2023)01khanh26No ratings yet
- BCM Electrostati Field 2024Document1 pageBCM Electrostati Field 2024manvir270508No ratings yet
- 1-C-73970-Dear ParentsDocument1 page1-C-73970-Dear Parentsmanvir270508No ratings yet
- PTM VENUES XiDocument1 pagePTM VENUES Ximanvir270508No ratings yet
- PTM Circular December 2023-1Document1 pagePTM Circular December 2023-1manvir270508No ratings yet
- History of Indian TelevisionDocument14 pagesHistory of Indian Televisionmanvir270508No ratings yet
- 09-17.5 E MicroCal T SeriesDocument4 pages09-17.5 E MicroCal T SeriesIlic MiroslavNo ratings yet
- D - Internet - Myiemorgmy - Intranet - Assets - Doc - Alldoc - Document - 20574 - Flyer HD - Ir. Hj. Arul Hisham - 31 Mac 2021Document4 pagesD - Internet - Myiemorgmy - Intranet - Assets - Doc - Alldoc - Document - 20574 - Flyer HD - Ir. Hj. Arul Hisham - 31 Mac 2021Tan Kang YaoNo ratings yet
- mtv1000 UsermanDocument95 pagesmtv1000 UsermanJuan Carlos Quispe LopezNo ratings yet
- Vibro-Acoustics: A New Springer PublicationDocument9 pagesVibro-Acoustics: A New Springer PublicationcharcharNo ratings yet
- Aron GideyDocument141 pagesAron Gideydere100% (1)
- Swot Analysis of OgdclDocument2 pagesSwot Analysis of OgdclMuhammad Ahmer100% (2)
- Share MarketDocument84 pagesShare MarketSai TharunNo ratings yet
- BD418 External - Annunciator - BTTY ANN 003 FiplexDocument1 pageBD418 External - Annunciator - BTTY ANN 003 Fiplexculeros1No ratings yet
- Bronze Data SheetDocument3 pagesBronze Data SheetAnonymous xkKyD8fBouNo ratings yet
- Cop. 1132Document4 pagesCop. 1132r2drill50% (2)
- WCH01 01 Que 20170111Document24 pagesWCH01 01 Que 20170111Niranjan BhuvanaratnamNo ratings yet
- K Single - TS - EngDocument13 pagesK Single - TS - Engguy doohNo ratings yet
- Waste-to-Energy in The PhilippinesDocument54 pagesWaste-to-Energy in The PhilippinesEleazar Ante TalabongNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Motorized LiftDocument62 pagesFabrication of Motorized LiftANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Bottle Washers, Factors Affecting Washing Operations, Power Requirements of Can and Bottle WashersDocument3 pagesBottle Washers, Factors Affecting Washing Operations, Power Requirements of Can and Bottle WashersMonty KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Early dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]Document2 pagesEarly dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]abhywaNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Quantum MechanicsDocument3 pagesQuiz On Quantum MechanicsAnge1196No ratings yet
- Investigation of Polarization and Depolarization Current For Evaluation of Moisture in Oil-Pressboard InsulationDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Polarization and Depolarization Current For Evaluation of Moisture in Oil-Pressboard InsulationmersiumNo ratings yet
- Table 4B1 and 4E4ADocument2 pagesTable 4B1 and 4E4Ahachan100% (2)
- Generator Set Data Sheet: 825 kVA StandbyDocument3 pagesGenerator Set Data Sheet: 825 kVA StandbydukegarrikNo ratings yet
- BIO Battery: Power For FutureDocument15 pagesBIO Battery: Power For Futurekavya2smart100% (2)
- Gas Turbines Siemens Interactive PDFDocument22 pagesGas Turbines Siemens Interactive PDF'Izzad AfifNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Mild HybirdDocument12 pagesPresentation On Mild HybirdAkshay S BhatNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval CB10 / CBH10: Brazed Plate Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesAlfa Laval CB10 / CBH10: Brazed Plate Heat ExchangerAfonso LopesNo ratings yet
- Content Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2020Document111 pagesContent Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2020Fabiola Marella PardedeNo ratings yet
- Diesel Exhaust FluidDocument7 pagesDiesel Exhaust FluidCISHAC FPNo ratings yet
- 9.5 Giant Metallic StructuresDocument2 pages9.5 Giant Metallic StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet


















































































![Early dimmers were directly controlled through the manual manipulation of large dimmer panels. This required all power to come through the lighting control location, which could be inconvenient, inefficient and potentially dangerous for large or high-powered systems, such as those used for stage lighting. In 1896, Granville Woods patented his "Safety Dimmer", which greatly reduced wasted energy by reducing the amount of energy generated to match desired demand rather than burning off unwanted energy.[1] In 1959, Joel S. Spira, who would found the Lutron Electronics Company in 1961, invented a dimmer based on a diode and a tapped autotransformer, saving energy and allowing the dimmer to be installed in a standard electrical wallbox.[2][3]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/318437784/149x198/2f1fbec41e/1468638713?v=1)










