Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Em Spectrum
Em Spectrum
Uploaded by
Fender Coomstone0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
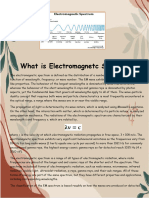
8 views24 pages1. Electromagnetic radiation comes in waves that can travel through space without a medium. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
2. Radio waves have long wavelengths and low frequencies. They are used for broadcasting music, news, and other information.
3. Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They are used in devices like microwave ovens, cell phones, and Wi-Fi.
Original Description:
em waves
Original Title
EM-SPECTRUM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Electromagnetic radiation comes in waves that can travel through space without a medium. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
2. Radio waves have long wavelengths and low frequencies. They are used for broadcasting music, news, and other information.
3. Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They are used in devices like microwave ovens, cell phones, and Wi-Fi.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views24 pagesEm Spectrum
Em Spectrum
Uploaded by
Fender Coomstone1. Electromagnetic radiation comes in waves that can travel through space without a medium. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
2. Radio waves have long wavelengths and low frequencies. They are used for broadcasting music, news, and other information.
3. Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They are used in devices like microwave ovens, cell phones, and Wi-Fi.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 24
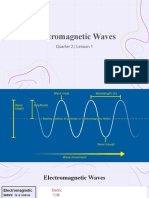
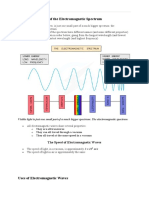
Electromagnetic radiation is a special
kind of energy that travels in waves
through space. It is like a wave of
energy that can move without
needing anything else to carry it,
even in empty space.
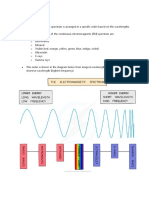
Radio waves Microwaves Infrared Visible Light
Visible Light Ultraviolet X-Radiation Gamma Ray
These are the waves that allow us to
listen to the radio. They have long
wavelengths and low frequencies.
Radio waves are used for
broadcasting music, news, and other
information.
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths
and higher frequencies than radio
waves. They are used in microwave
ovens to cook and heat food. They are
also used for communication, such as
cell phones and Wi-Fi.
Infrared radiation is sometimes called
"heat radiation" because we feel it as
warmth. It has longer wavelengths
than visible light. Infrared radiation is
used in devices like TV remote
controls and thermal cameras.
Visible light is a critical component of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum,
occupying a small yet essential portion that the human eye can perceive. This
spectrum encompasses a broad range of 1.electromagnetic waves, characterized by
varying wavelengths and frequencies. Visible light falls within the wavelengths of
approximately 400 to 700 nanometers, transitioning seamlessly from shorter 2.violet
and blue wavelengths to longer 3.orange and 4.red wavelengths. This limited band of
wavelengths corresponds to the colors of the 5.rainbow, and when these colors blend
harmoniously, they form the 6.white light that is commonly associated with
7.sunlight.
The human eye's sensitivity to visible light is a remarkable adaptation, allowing us to
interpret the world around us based on the 8.colors we perceive. Each color
corresponds to a specific 9.wavelength within the visible spectrum, with red having the
10.longest wavelength and violet the 11.shortest. Beyond its role in perception, visible
light plays a crucial role in various natural processes, such as 12.photosynthesis in
plants and the creation of rainbows through the 13.dispersion of sunlight in
14.water droplets. Scientifically, understanding the characteristics of visible light is
fundamental to fields like optics and astronomy, where the study of these wavelengths
provides insights into the composition, temperature, and motion of celestial objects.
This is the type of electromagnetic
radiation that allows us to see the
world around us. Visible light comes in
different colors, like red, orange,
yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Each color has a different wavelength.
UV rays, or ultraviolet rays, find diverse applications across various fields. In
medicine, UV radiation is utilized for disinfection purposes, where it effectively
eliminates bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms, contributing to the
sterilization of medical equipment and environments. In the realm of technology,
UV rays play a crucial role in semiconductor manufacturing processes, facilitating
the creation of intricate microelectronics. Additionally, UV radiation is employed in
forensic investigations to reveal latent fingerprints and detect bodily fluids. Beyond
these applications, UV rays have a pivotal role in phototherapy for certain skin
conditions and are integral in the creation of UV-based curing systems for adhesives
and coatings in industries. Despite its potential benefits, it is essential to note that
prolonged exposure to UV rays poses health risks, necessitating careful
consideration and regulation in various applications.
UV radiation has shorter wavelengths
and higher frequencies than visible
light. It comes from the sun and is
responsible for causing sunburns. We
can't see UV radiation, but it can be
harmful to our skin and eyes.
for blur for confetti for a drumroll
for mic drop for bubbles for quiet
for unveil Any number from 0-9 for a timer
*Please delete this section before downloading.
You might also like
- Sci 10 PPT - em WavesDocument27 pagesSci 10 PPT - em WavesDioscora S. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneFrom EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Nov Dec 2017Document22 pagesNov Dec 2017arr2604No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument6 pagesUntitled DocumentMichaela CuarteroNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument11 pagesEM WavesHomok Noki100% (1)
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Document7 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum 3Nur-shima SakilinNo ratings yet
- EM SpectrumDocument6 pagesEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Uses of Electromagnetic WavesDocument4 pagesUses of Electromagnetic WavesMarlou PrincesaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic RadiationDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic RadiationAyman BashirNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module 2Document2 pagesUnit 2 Module 2heide100% (1)
- THE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilDocument10 pagesTHE Electromagnetic Spectrum: Unit 2, Module 2 Kiziah F. GranilHannah Joy DulayNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- EM WaveDocument12 pagesEM Waveshikhaar24No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic WavesNjike ChigbuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- 2NDQ Science NotesDocument38 pages2NDQ Science NotesEzekiel BayocotNo ratings yet
- By NaanaDocument29 pagesBy Naanajuicypine14No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumamyrulerzNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Speed of Light Photon SpectrumFOODHEALTHNo ratings yet
- Applications of MicrowavesDocument6 pagesApplications of MicrowavesorculloNo ratings yet
- Radiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyDocument42 pagesRadiant Energy & Nuclear EnergyChristine Marielle Claroniño ApoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceLorin Louise P. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Waves Reading PassageDocument2 pagesWaves Reading PassagedavidNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic WavesCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMaria ArshadNo ratings yet
- Radio WavesDocument4 pagesRadio WavesSophia Nicole ZaraNo ratings yet
- Light EnergyDocument2 pagesLight EnergyMa Catherine DiazNo ratings yet
- Sia83 3notesDocument5 pagesSia83 3notesAmaechi ZalNo ratings yet
- Uses of EM WavesDocument3 pagesUses of EM WavesPallika DhingraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic WavesSherazNo ratings yet
- Elctronic RadiationDocument4 pagesElctronic RadiationTia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Lesson2 EM Waves ApplicationsDocument32 pagesScience 10 Lesson2 EM Waves ApplicationsJean LaguitanNo ratings yet
- Visible LightDocument26 pagesVisible LightDotty dottyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAk R71No ratings yet
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Science PT 2nd QRTR 1Document29 pagesScience PT 2nd QRTR 1Rayver Chris VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- (51014) Javier Prelab6Document2 pages(51014) Javier Prelab6Jesse JavierNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum 20232024Document15 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum 20232024WowNo ratings yet
- The Effects of EM Radiation On Living ThingsDocument23 pagesThe Effects of EM Radiation On Living ThingsCharm VergaraNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument13 pagesPhysics ProjectGanesh harkalNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic Waves M@trix FoundationDocument7 pagesElectro Magnetic Waves M@trix FoundationdjbabuNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument4 pages3.3 Electromagnetic SpectrumDhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Engineering Electromagnetism Assignment: Gaurav Kumar, Roll No.-108110029. 10/27/2011Document4 pagesEngineering Electromagnetism Assignment: Gaurav Kumar, Roll No.-108110029. 10/27/2011Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument9 pagesDocumentVijay DhoniNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesDocument4 pagesConcept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesLunaNo ratings yet
- Spectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveDocument10 pagesSpectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveJabez Edwin SivaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Electromagnetic Waves FADRIGONDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Electromagnetic Waves FADRIGONNarahmie RuadoNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter Science ReviewerDocument26 pages3RD Quarter Science ReviewerKristha Tejerero GuiaNo ratings yet
- Input 1 To 5Document57 pagesInput 1 To 5Starskie MonacarNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument15 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumJohnRenzoMolinarNo ratings yet
- Source of EnergyDocument6 pagesSource of Energypg2No ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument2 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumShamoose AlaaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesDocument45 pagesGrade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesMary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Physics 10 UV ScriptDocument3 pagesGroup 5 Physics 10 UV ScriptEmilrie RogeroNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument34 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumShinpay doodles100% (1)
- 1 - Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pages1 - Electromagnetic Spectrumbinyang lalaNo ratings yet
- GyroDocument14 pagesGyroatinder13No ratings yet
- Mechanical Testing and Structure AnalysisDocument6 pagesMechanical Testing and Structure AnalysisAbdullah AlkalaliNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy: Solubility and Distribution PhenomenaDocument6 pagesPhysical Pharmacy: Solubility and Distribution PhenomenaAishwarya PawarNo ratings yet
- CAS NO 61791-53-5 - Duomeen-TdoDocument2 pagesCAS NO 61791-53-5 - Duomeen-TdoVirender KumarNo ratings yet
- Boq PCWDocument1 pageBoq PCWNARMADA ENGINEERINGNo ratings yet
- SDS Gta 733Document12 pagesSDS Gta 733harlendri STNo ratings yet
- Thesis Results Chapter SampleDocument6 pagesThesis Results Chapter Samplewinstinakennedybaltimore100% (2)
- Science 10 9.3 Diverging LensDocument34 pagesScience 10 9.3 Diverging Lensjeane san cel arciagaNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Bee ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Quiz Bee ReviewerMonica Morales MaañoNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Properties of SoilDocument6 pages10.1 Properties of Soilcory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
- Emf HW 1Document1 pageEmf HW 1Krunal PatelNo ratings yet
- Induction NotesDocument15 pagesInduction NotesKartikNo ratings yet
- Kaolite Insulating CastablesDocument2 pagesKaolite Insulating CastablesChan Keng ChunNo ratings yet
- On Agents of MutationDocument22 pagesOn Agents of Mutationmine_ne361No ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 3.1 Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 3.1 Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneFadhliana UzalliNo ratings yet
- Weight-Volume Relationships: Quiz Gt102Document8 pagesWeight-Volume Relationships: Quiz Gt102Sharon Rose OcampoNo ratings yet
- Qui PDFDocument206 pagesQui PDFPeter CardenasNo ratings yet
- Arjuna NEET (2024) Yakeen NEET 2.0 (2024) : Practice Test-15Document18 pagesArjuna NEET (2024) Yakeen NEET 2.0 (2024) : Practice Test-15suryanshnaarayan2023No ratings yet
- Algol Oy Mail - FWD - Carbon Black India - PCBL GroupDocument2 pagesAlgol Oy Mail - FWD - Carbon Black India - PCBL GroupAnshu SahniNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Particles and Approximately 35 Sub-Atomic ParticlesDocument35 pagesFundamental Particles and Approximately 35 Sub-Atomic ParticlesKunj VermaNo ratings yet
- 5070 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument4 pages5070 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersMian zainNo ratings yet
- The Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 2023Document2 pagesThe Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 2023Yuchen WuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document87 pagesUnit 2SavitaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions in ChemistryDocument3 pagesImportant Questions in ChemistrySumaiya RahmanNo ratings yet
- All Other Details Are Same As 2661 3510 71 12: (Add Friction Welding Allowances For Final Length) 1274Document1 pageAll Other Details Are Same As 2661 3510 71 12: (Add Friction Welding Allowances For Final Length) 1274sachin pataneNo ratings yet
- Pertamina-Dex English VersionDocument1 pagePertamina-Dex English VersionrekaelektraNo ratings yet
- Pre-Treatment - ClasssDocument202 pagesPre-Treatment - ClasssAbel TayeNo ratings yet
- Radiographic TestingDocument42 pagesRadiographic TestingBiNuLAlB75% (8)
- Cell Membrane and Transport 4-Practical ActivityDocument13 pagesCell Membrane and Transport 4-Practical ActivityRohan PaneruNo ratings yet