Professional Documents
Culture Documents
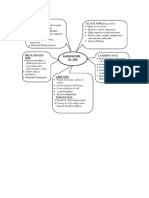
Soil Types
Soil Types
Uploaded by
mrtblisus0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
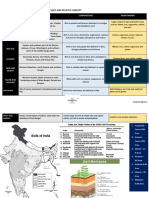
17 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the key characteristics of different soil types found in India. It provides information on the formation, features, minerals, crops grown, and areas found for each soil type including alluvial, black, red and yellow, laterite, arid, and forest soils. The different soil types vary in their texture, composition, pH, moisture, and suitability for different crops depending on factors like parent material, climate, terrain, and level of weathering. Proper soil management techniques are required for some soil types to improve fertility and cultivability.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the key characteristics of different soil types found in India. It provides information on the formation, features, minerals, crops grown, and areas found for each soil type including alluvial, black, red and yellow, laterite, arid, and forest soils. The different soil types vary in their texture, composition, pH, moisture, and suitability for different crops depending on factors like parent material, climate, terrain, and level of weathering. Proper soil management techniques are required for some soil types to improve fertility and cultivability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesSoil Types
Soil Types
Uploaded by
mrtblisusThe document summarizes the key characteristics of different soil types found in India. It provides information on the formation, features, minerals, crops grown, and areas found for each soil type including alluvial, black, red and yellow, laterite, arid, and forest soils. The different soil types vary in their texture, composition, pH, moisture, and suitability for different crops depending on factors like parent material, climate, terrain, and level of weathering. Proper soil management techniques are required for some soil types to improve fertility and cultivability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xlsx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
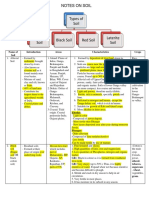
Name Formation Features Minerals Crops Areas found
Sugarcane, Paddy, N. Plains, Gujarat, Rajasthan,
Depositions of Brahmaputra, Most widely spread and fertile soil; Potash, Phosphoric Acid, Wheat, Other cereal Delta of Mahanadi, Krishna and
Alluvial Indus, Ganga {BIG} consists of sand, silt and clay{SSC}. and lime and Pulse crops Kaveri
Calcium Carbonate,
Magnesium, Potash, Lime Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malva,
Climatic conditions and Made up of clayey materials. AKA and poor in Phosphoric MP, Chhattisgarh, Godavri and
Black parent rock. Regur soil and black cotton soil content Cotton Krishna Valleys
Dev reddish color due to diffusion of
Red and Dev on Crystalline igneous Iron in crystalline and metamorphic Eastern and Southern Deccan
yellow rocks in areas of low rain fall rocks. Yellow in hydrated form. Iron N/A Plateau, Odisha and Chhattisgarh
Mostly deep to very deep,
Develops under tropical and acidic{pH<6}, prone to soil erosion
sub-tropical climate with and degradation, deficient in plant Tea, Coffee, Cashew
Laterite alternate wet and dry seasons. nutrients N/A nuts S Ind, W Ghats, WB, NE Ind.
Red-Brown color, sandy in texture,
saline in nature, cultivable with
proper irrigation, lacks humus and Calcium due to Kanker
moisture, In some areas salt content {restricts infiltration of
Arid N/A very high. water} N/A Thar-W Rajasthan
Loamy silty-Valleys, Coarse grained-
upper slopes, Acidic with low
humus-snow covered Himalayas, Hilly and Mountainous areas
Fertile-lower parts of valley and river where sufficient rain forests are
Forest N/A terraces. N/A N/A available
X - Factor
Its two types are Khadar and
bangar
N/A
N/A
Intense leaching due to
heavy rain,
Brought under irrigation-
implimenting appropriate
soil conservation techniques
and irrigation{Laterite and
arid}
N/A
You might also like
- Soils TableDocument2 pagesSoils TablePakhshi Luthra100% (4)
- Classification of Soils in IndiaDocument2 pagesClassification of Soils in IndiaArmaan PruthiNo ratings yet
- Type Features Regions CropsDocument1 pageType Features Regions CropsKaran PatelNo ratings yet
- Soil Types in India Upsc Notes 50Document9 pagesSoil Types in India Upsc Notes 50AmrithNo ratings yet
- Resources and Developemnt - Types of Soil TableDocument1 pageResources and Developemnt - Types of Soil TablePRATHAMNo ratings yet
- Indus Ganga Brahmaputra Potash Phosphoric LimeDocument6 pagesIndus Ganga Brahmaputra Potash Phosphoric LimeNATASHA AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Geography SoilDocument4 pagesGeography Soilhamarirasoi0803No ratings yet
- Soil ClassificationDocument2 pagesSoil ClassificationDC MSME AttendanceNo ratings yet
- Major Classification of Indian SoilsDocument4 pagesMajor Classification of Indian SoilsALABANI MANGANo ratings yet
- Resources and Development One Short RevisionDocument1 pageResources and Development One Short RevisionAayush YadavNo ratings yet
- Geo LN 1 Types of SoDocument2 pagesGeo LN 1 Types of SoParveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Krmvp/2024-25/Class X/Geography/Ch 1-Resources and Development Types of Soil (Refer To Page 7 and 9 of Ncert For Details) 1) Alluvial SoilDocument2 pagesKrmvp/2024-25/Class X/Geography/Ch 1-Resources and Development Types of Soil (Refer To Page 7 and 9 of Ncert For Details) 1) Alluvial Soilmohdshahid1333No ratings yet
- Resources and Development (Part - 2)Document48 pagesResources and Development (Part - 2)Krishna VijayNo ratings yet
- Soils in IndiaDocument2 pagesSoils in IndiaNagesh Kshirsagar NKNo ratings yet
- Type of Soil Formation of Soil Characteristi C Feature Major CropDocument3 pagesType of Soil Formation of Soil Characteristi C Feature Major CropJenish PadshalaNo ratings yet
- Soils in India and Natural VegetationDocument3 pagesSoils in India and Natural VegetationPixel AragamiNo ratings yet
- Krmvp/2021-22/Class X/Geography/Ch 1-Resources and Development Types of SoilDocument2 pagesKrmvp/2021-22/Class X/Geography/Ch 1-Resources and Development Types of SoilUnknown PersonNo ratings yet
- Soils of IndiaDocument8 pagesSoils of Indiaomkumar7349No ratings yet
- Resource and Development Part C - Soil ResourceDocument7 pagesResource and Development Part C - Soil ResourceDarsh TodiNo ratings yet
- Indian SoilDocument40 pagesIndian SoilHarshNo ratings yet
- Classification of SoilDocument8 pagesClassification of SoilAranya KarraNo ratings yet
- Geo - X - SoilDocument9 pagesGeo - X - SoilAdvait BajoriaNo ratings yet
- 10 Relative Density & Types of Soils in IndiaDocument18 pages10 Relative Density & Types of Soils in IndiaASWIN padmakumarNo ratings yet
- 381 Soils of India IndiashastraDocument2 pages381 Soils of India IndiashastraKarambir Singh DhayalNo ratings yet
- 381 Soils of India Indiashastra PDFDocument2 pages381 Soils of India Indiashastra PDFKarambir Singh DhayalNo ratings yet
- Ftre-2017-C-X - Paper-1 - At+pcmDocument4 pagesFtre-2017-C-X - Paper-1 - At+pcmSharad GhatpandeNo ratings yet
- Resource Final 1Document12 pagesResource Final 1abhirajyadav216No ratings yet
- Soil in India: Soil Type Expansion/Regions DescriptionDocument8 pagesSoil in India: Soil Type Expansion/Regions Descriptionparthasarathi.dhal777No ratings yet
- Soil TypeDocument4 pagesSoil Typepriya sahniNo ratings yet
- Soil Table Legend BhaiyaDocument2 pagesSoil Table Legend BhaiyaPaokhongam KipgenNo ratings yet
- Major Soil Deposits of IndiaDocument6 pagesMajor Soil Deposits of Indiatvennela28No ratings yet
- Soil TypesDocument3 pagesSoil TypesKaran RavalNo ratings yet
- Soils of India: - Factors Affecting Soil FormationDocument21 pagesSoils of India: - Factors Affecting Soil FormationRathod Sasidhar NaikNo ratings yet
- Soil in IndiaDocument19 pagesSoil in IndiaAbhishek KakkarNo ratings yet
- IGP CSAT Paper 1 Geography Indian Geography Physical India Physical Part 2Document12 pagesIGP CSAT Paper 1 Geography Indian Geography Physical India Physical Part 2Ankit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1055185791soils of India (Ug) - India - GeographyDocument7 pages1055185791soils of India (Ug) - India - GeographyAmrithNo ratings yet
- Grd10-Geog-Soil Notes - 1011684742963138563 - 1011684742963138563 - 1011684742963138563Document8 pagesGrd10-Geog-Soil Notes - 1011684742963138563 - 1011684742963138563 - 1011684742963138563Sohan VernekarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Geography Revision Notes - 230307 - 112823Document47 pagesClass 10 Geography Revision Notes - 230307 - 112823Aryan DeshwalNo ratings yet
- Types of Soils: Sneha TikooDocument20 pagesTypes of Soils: Sneha TikooSanjay Sharma100% (2)
- Classification of Soil in India Geography Notes For UPSC1Document5 pagesClassification of Soil in India Geography Notes For UPSC1vijaya luckyNo ratings yet
- Soil Classification TableDocument2 pagesSoil Classification TablekkNo ratings yet
- Apne Desh Ki MittiDocument17 pagesApne Desh Ki MittiKunal GautamNo ratings yet
- Types of Soil PDFDocument4 pagesTypes of Soil PDFmanishNo ratings yet
- Types of Soil PDFDocument4 pagesTypes of Soil PDFmanishNo ratings yet
- Types of SoilDocument4 pagesTypes of Soilpriyanka goenkaNo ratings yet
- L-4 Soils of IndiaDocument22 pagesL-4 Soils of IndiaAarav JoshiNo ratings yet
- Geography 21-22 Class 10 Synopsis and Assignment Part 3Document4 pagesGeography 21-22 Class 10 Synopsis and Assignment Part 3Aquib IrshadNo ratings yet
- Soils: Sasmika Shinoj Grade 4Document6 pagesSoils: Sasmika Shinoj Grade 4Sasmika ShinojNo ratings yet
- Soil Type of IndiaDocument8 pagesSoil Type of IndiaAr Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Soil - Short SummDocument4 pagesChapter 8 - Soil - Short Summmail2shanthithevarNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Soil in India and Their Specific Crops: Made ByDocument20 pagesDifferent Types of Soil in India and Their Specific Crops: Made ByriddhisnewworldNo ratings yet
- Geography SEA Term 2 AY 2023-24 by Rishita PankajDocument7 pagesGeography SEA Term 2 AY 2023-24 by Rishita PankajrajneeshNo ratings yet
- Soils of IndiaDocument10 pagesSoils of IndiaAllieNo ratings yet
- Desert & Forest SoilDocument5 pagesDesert & Forest Soilbacibe1488No ratings yet
- Alluvial SoilsDocument3 pagesAlluvial SoilsP-0050-11 DEVIKA SHAILENDRA RATHORENo ratings yet
- 52445indian Soil Geography Semester III 07 09 2020Document6 pages52445indian Soil Geography Semester III 07 09 2020AmrithNo ratings yet
- Types 1. Alluvial Soils: 3. Red and Yellow SoilDocument1 pageTypes 1. Alluvial Soils: 3. Red and Yellow SoilbinalamitNo ratings yet
- Different Soil Types in India Understand The Differences Using An Easy-To-Learn TableDocument3 pagesDifferent Soil Types in India Understand The Differences Using An Easy-To-Learn TableDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Birthstones - A Collection of Historical Articles on the Gemstones Linked to AstrologyFrom EverandA Guide to Birthstones - A Collection of Historical Articles on the Gemstones Linked to AstrologyNo ratings yet
- Ce2251 Soil Mechanics QBDocument17 pagesCe2251 Soil Mechanics QBmanisaibabaNo ratings yet
- Index Propertis BH 2Document7 pagesIndex Propertis BH 2Andrea AsvaniNo ratings yet
- Effect of Antecedent Rainfall Patterns On Rainfall-Induced Slope FailureDocument9 pagesEffect of Antecedent Rainfall Patterns On Rainfall-Induced Slope FailuresonNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 6-8Document7 pagesLab Report 6-8Lawrence TuliaoNo ratings yet
- College of Soil Physics: 22 October - 9 November, 2007Document26 pagesCollege of Soil Physics: 22 October - 9 November, 2007Abdusalam IdirisNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Principles of GeologyDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Principles of GeologyVince Sharman AureNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8: Soil CompactionDocument14 pagesExercise 8: Soil CompactionKenzo Braye GeraleNo ratings yet
- Soil GSB WMM by Sand Replacement MethodDocument2 pagesSoil GSB WMM by Sand Replacement MethodBrahammanand BairwaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Soils 1Document12 pagesMechanical Properties of Soils 1muhammedssebatindira3No ratings yet
- Plate 4 Effective Stresses in SoilDocument14 pagesPlate 4 Effective Stresses in SoilSofia Isabelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Index Properties of Soil: Er. Shatrudhan Prasad Yadav Constructor Instructor LTS, LahanDocument14 pagesUNIT-3 Index Properties of Soil: Er. Shatrudhan Prasad Yadav Constructor Instructor LTS, Lahanajai chyNo ratings yet
- Crop Rotation - Wikipedia PDFDocument59 pagesCrop Rotation - Wikipedia PDFRinchen LhadenNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Science Grade 7 Weathering of Rocks and Soil Formation 1Document5 pagesStudy Guide Science Grade 7 Weathering of Rocks and Soil Formation 1Srijita RoyNo ratings yet
- Soil Research GateDocument20 pagesSoil Research GatejatinNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Lecture Notes - 2018 - FullDocument207 pagesSoil Mechanics Lecture Notes - 2018 - FullkakaNo ratings yet
- Torsion BalanceDocument39 pagesTorsion BalanceSai Ganesh100% (4)
- Review MODULE - GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (Soil Properties)Document4 pagesReview MODULE - GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (Soil Properties)Ma Ella Mae LogronioNo ratings yet
- Settlement CalculationDocument16 pagesSettlement Calculationalicarlos13No ratings yet
- Soil Exam1.pdf Soil Exam2.pdf Soil Exam3 PDFDocument63 pagesSoil Exam1.pdf Soil Exam2.pdf Soil Exam3 PDFArchie MilanoNo ratings yet
- Allah Se Mangiye اللہ سے مانگیےDocument48 pagesAllah Se Mangiye اللہ سے مانگیےArshad Ayoub KhanNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Tanah I: Dr. Ir. Ahmad RIFA'I, M.T. Bagian - 2Document28 pagesMekanika Tanah I: Dr. Ir. Ahmad RIFA'I, M.T. Bagian - 2Vicco TanadyNo ratings yet
- Bore Pile Design in SandDocument6 pagesBore Pile Design in SandAbhijit HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Soil BMP Manual PDFDocument46 pagesSoil BMP Manual PDFसुनिल बाबु खत्रीNo ratings yet
- GRIHA Criterion 3Document10 pagesGRIHA Criterion 3VarunPatyalNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Asentamientos - CraigDocument2 pagesEjercicios Asentamientos - Craigsebastian huerfanoNo ratings yet
- Answer For Assignment #2Document10 pagesAnswer For Assignment #2Duge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- Midterm RequirementDocument6 pagesMidterm RequirementPaula Rodalyn MateoNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text, A LandslideDocument2 pagesExplanation Text, A LandslideFatehah DevaNo ratings yet