Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCIENCE10 WLAS EM Week 1 FINALIST
SCIENCE10 WLAS EM Week 1 FINALIST
Uploaded by
Wendelyn Bacalso AcigaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Surge Analysis and The Wave Plan MethodDocument126 pagesSurge Analysis and The Wave Plan Methodmailmaverick8167No ratings yet
- MurraylightemDocument2 pagesMurraylightemapi-26383090433% (3)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Wavesputri_latifah100% (3)
- Waves and em Spectrum Ws PDFDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Ws PDFJv Loo Caguioa100% (1)
- Karen May P. UrlandaDocument47 pagesKaren May P. UrlandaKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- S10FE-11a-b-47 MELC: Compare The Relative Wavelengths of Different Forms of ConceptsDocument5 pagesS10FE-11a-b-47 MELC: Compare The Relative Wavelengths of Different Forms of ConceptsMikaela Julianne Erada100% (1)
- Quarter 2: MODULE 1: Different Forms of EM WavesDocument30 pagesQuarter 2: MODULE 1: Different Forms of EM WavesPepito Rosario Baniqued, Jr100% (2)
- FilipinoDocument6 pagesFilipinoVinz JaneNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Module 2Document73 pagesQuarter 2 Module 2princesslayshoNo ratings yet
- Science10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Document15 pagesScience10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Christine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction EM Waves WorksheetDocument3 pagesIntroduction EM Waves WorksheetUmer AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Clem Waves Lesson04 NotesasDocument1 pageClem Waves Lesson04 NotesasdanaNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmDocument3 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmDocument3 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction em Waves Worksheet 2Document2 pagesIntroduction em Waves Worksheet 2api-2605470450% (1)
- The Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmDocument3 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmJhet Ardian CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Eem wiveSZDocument3 pagesEem wiveSZJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Grade 10 (De Guzman)Document19 pagesModule 2 Grade 10 (De Guzman)Kim De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 - EM WavesDocument8 pagesLecture 2.1 - EM WavesAPPLE CAGUNGUN-BELGICANo ratings yet
- Final Sci10 q2 m2 Edited-16Document16 pagesFinal Sci10 q2 m2 Edited-16Fe GullodNo ratings yet
- Long TestDocument2 pagesLong TestJow DualanNo ratings yet
- G10 Physics CompendiumDocument41 pagesG10 Physics CompendiumJhin CortezNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Different Forms of EM WavesDocument13 pagesLAS 1 Different Forms of EM WavesaquesamabiniNo ratings yet
- Em SpectrumDocument13 pagesEm SpectrumKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument40 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrummike ebioNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science 10 MODULE 4Document13 pagesQ2 Science 10 MODULE 4princesslayshoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument40 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrumtripathiansh447No ratings yet
- EM Waves and Spectrum Worksheet AlnahdaDocument3 pagesEM Waves and Spectrum Worksheet AlnahdaMaryem Nabawi100% (1)
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2. Calculating Wavelengtdytrjycghh and FrequencyDocument37 pagesLESSON 2. Calculating Wavelengtdytrjycghh and FrequencyRyan Aint simpNo ratings yet
- EVS SeminarDocument30 pagesEVS SeminarMonica SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument22 pagesEM WavesJane Reyes100% (1)
- EM Spectrum Worksheets PDFDocument2 pagesEM Spectrum Worksheets PDFMarian Galoso100% (1)
- Properties of LightDocument25 pagesProperties of LightAhmad Dhiyaul WahidNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum FormsDocument32 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum FormsRuih PadillaNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Module 1 (Q2-Week 1-5)Document20 pagesSci10 Module 1 (Q2-Week 1-5)CHRIS JOHN A. SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Science 10Document5 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Science 10soriachristellejade8No ratings yet
- Sci10 Practical Applications of em WavesDocument17 pagesSci10 Practical Applications of em WavesChristina PlataNo ratings yet
- G10 Physics CompendiumDocument41 pagesG10 Physics CompendiumAlodia Carlos PastorizoNo ratings yet
- Science10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Document19 pagesScience10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Renmarie LaborNo ratings yet
- (51014) Javier Prelab6Document2 pages(51014) Javier Prelab6Jesse JavierNo ratings yet
- 2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1Document2 pages2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1pranitjadhav0407No ratings yet
- G10 Science Q2 - W2 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument13 pagesG10 Science Q2 - W2 - Electromagnetic WavesKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- em Spectrum 2Document26 pagesem Spectrum 2Juliever EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Different Regions of Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument20 pagesLesson 1 The Different Regions of Electromagnetic SpectrumsubaldojenniferNo ratings yet
- Wave C12Document9 pagesWave C12Wajira Sanjaya PereraNo ratings yet
- Research PDFDocument28 pagesResearch PDFJeon ManobanNo ratings yet
- Science10 q2 Mod3of6 Effectsofemwavesonlivingthingsandenvironment v2Document15 pagesScience10 q2 Mod3of6 Effectsofemwavesonlivingthingsandenvironment v2Christine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum Work SheetDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Work SheetSenpai ChibiNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum Ws PDFDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Ws PDFAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum WsDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum WsTracey LaRussoNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum Ws PDFDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Ws PDFJv Loo CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 MindScape - Science Intervention For StudentsDocument16 pagesQuarter 2 MindScape - Science Intervention For StudentsadrianquininezaNo ratings yet
- Chem Waves Lesson LectureDocument11 pagesChem Waves Lesson LectureMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrumroziel A.mabitasanNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument30 pagesEM WavesCLarence De ClaroNo ratings yet
- Mechanik Ruina Pratap ContentDocument2 pagesMechanik Ruina Pratap Contentapi-129423309No ratings yet
- Physics EeeercDocument5 pagesPhysics EeeercJessabelle RamosNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of Light WavesDocument24 pagesDiffraction of Light Wavesbenjamin swokaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 2 PDFRohan Ghosh DastidarNo ratings yet
- Pump Sizing Calculation SheetDocument7 pagesPump Sizing Calculation SheetManik Kandan100% (1)
- Problem. A 5-Sided Lot ABCDE Is Surveyed Inside Its Perimeter From A Point Named F. The Horizontal Distances andDocument4 pagesProblem. A 5-Sided Lot ABCDE Is Surveyed Inside Its Perimeter From A Point Named F. The Horizontal Distances andwoi mariaNo ratings yet
- Waves-Quantum and Nuclear-Resolution-Atomic and NuclearDocument45 pagesWaves-Quantum and Nuclear-Resolution-Atomic and NuclearMartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document4 pagesTutorial Chapter 2batrisyaNo ratings yet
- SPM 2010 Paper 2Document78 pagesSPM 2010 Paper 2Suriyati YusoffNo ratings yet
- Space Weight LabDocument3 pagesSpace Weight Labapi-403198825100% (1)
- Physics Worksheet For Grade 9Document4 pagesPhysics Worksheet For Grade 9Kassahun100% (1)
- RAE3601-2023 Assignment 2Document9 pagesRAE3601-2023 Assignment 2thabisoNo ratings yet
- Pascal Archimedes BernoulliDocument2 pagesPascal Archimedes BernoulliRj Bengil100% (1)
- Sample Solution Manual For Orbital Mechanics For Engineer 3rd CurtisDocument16 pagesSample Solution Manual For Orbital Mechanics For Engineer 3rd CurtisSumon SwiftNo ratings yet
- Lec 16 CDocument66 pagesLec 16 CSalman MemonNo ratings yet
- A Quasi-Optical: Converter With BifocalDocument5 pagesA Quasi-Optical: Converter With BifocalAnonymous DGq0O15nNzNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Physics Model Examination For Grade 12 Ginbot .: General DirectionDocument8 pagesAddis Ababa Physics Model Examination For Grade 12 Ginbot .: General DirectionKhalid A.100% (3)
- Equation of Continuity and Bernoulli's EquationDocument16 pagesEquation of Continuity and Bernoulli's Equationdimitris1936No ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument18 pagesSimple Harmonic Motionieja03100% (2)
- Engineering VibrationsDocument43 pagesEngineering VibrationsClayton Roe100% (3)
- Board PhysicsDocument9 pagesBoard PhysicsDurgesh Yadav100% (1)
- Lesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaDocument34 pagesLesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- THE APPLICATION OF QUATERNION ALGEBRA TO GYROSCOPIC MOTION, NAVIGATION, AND GUIDANCE George P. Davailus Old Dominion University Aerospace Engineering Department Advisor: Brett A. NewmanDocument7 pagesTHE APPLICATION OF QUATERNION ALGEBRA TO GYROSCOPIC MOTION, NAVIGATION, AND GUIDANCE George P. Davailus Old Dominion University Aerospace Engineering Department Advisor: Brett A. NewmanmarkrichardmuradNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesDocument42 pagesLecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesPercival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Fluid ForcesDocument16 pagesFluid ForcesGeorge OparNo ratings yet
- Oblique Shock WavesDocument25 pagesOblique Shock WavesDhinasuga DhinakaranNo ratings yet
- 1-Newton Second Law-ForMATDocument5 pages1-Newton Second Law-ForMATVAIBHAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1642990216class 9 Questions - Sound ChapterDocument9 pages1642990216class 9 Questions - Sound ChapterMANISHA GARGNo ratings yet
SCIENCE10 WLAS EM Week 1 FINALIST
SCIENCE10 WLAS EM Week 1 FINALIST
Uploaded by
Wendelyn Bacalso AcigaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE10 WLAS EM Week 1 FINALIST
SCIENCE10 WLAS EM Week 1 FINALIST
Uploaded by
Wendelyn Bacalso AcigaCopyright:
Available Formats
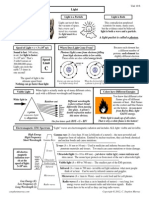
WEEKLY LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET
Science 10, Quarter 2, Week 1
Electromagnetic Spectrum
(Different Regions of the Electromagnetic Spectrum)
Name: ___________________________________________ Section: ____________________
Most Essential Learning Competency (MELC)
Learning Objective:
Compare the relative wavelengths of different forms of electromagnetic waves.
(S10FE-IIab-47)
Sub-tasked competency:
a. describe the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of wavelength, frequency
and energy;
b. relate wavelength to frequency and energy;
c. solve problems involving wavelength, frequency and energy.
Time Allotment: (6 days)
Key Concepts
In this learning activity sheet, you will learn about the different regions of the
electromagnetic spectrum. This will lead you to understand how electromagnetic waves transport
energy.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuum of electromagnetic waves arranged according
to frequency and wavelength. It is a gradual progression from the waves of lowest frequencies to
the waves of highest frequencies. According to increasing frequency, the EM spectrum includes:
radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves
do not have exact dividing region.
(The Electromagnetic Spectrum; LM pages 142&147)
Exercises / Activities
Activity 1.1. Fill Me!
Direction: Study the diagram and read the reading material. Fill in each blank with the word
that best completes the reading comprehension.
http://www.geditorial.com/blog/sunday-science-the-electromagnetic-spectrum
Author: Bria F. Singson
School/Station: Agay National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
The Electromagnetic Spectrum is the complete/entire range of EM waves in order of increasing
frequency and decreasing wavelength. As you look from left to right on a diagram of the spectrum;
this means that the wavelengths get smaller and the frequency gets larger. It is an inverse
relationship exists between size of the wave and frequency. We all know that all EM waves travel
at the same speed: 300,000km/s. If you can recall the formula for speed, it is the wavelength times
the frequency. For the answer is always be 300,000km/s, as one number goes up, the other must
go down. All EM waves is radiation; it’s just that the longer wavelengths do not carry enough
energy in them to damage cells. Always remember that the higher the frequency, the more energy
in the wave.
Waves in the Spectrum
• Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies; wavelengths range from
1000s of meters to 0.001 m; and the shortest radio waves are microwaves. Radio waves are
used in RADAR; the radio detection and ranging; it’s sending sound, pictures (TV), cell
phones, cooking and satellite transmissions.
• Infrared waves (heat) have shorter wavelengths, from 0.001 m to 700 nm and higher
frequencies (a nm is one billionth of a meter). Infrared is used to find people in the dark and
in TV remotes.
• Visible light is what we can see in the EM spectrum. Wavelengths of visible light range from
about 700 nm (red light) to 400 nm (violet light). Visible light frequencies are usually higher
than the frequencies of infrared waves. We can identify how visible light is such a small
portion of the entire spectrum.
• Ultraviolet wavelengths range from about 400 nm to 10 nm; the frequency (and therefore
the energy) is high enough with UV rays to penetrate living cells and cause them damage.
We need UV rays to produce vitamin D in our bodies. Even though too much can lead to
sunburn and skin cancer; and UV rays are easily stopped by clothing and used for
sterilization of materials because they kill bacteria in high enough concentrations. Although
humans cannot see UV light, bees and butterflies. Some small rodents, and some birds can.
• X-rays have wavelengths from 10 nm to 0.001 nm. They have enough energy to penetrate
and closer deep into tissues, but are stopped by dense materials, such as bones. And used
for examining solid structures (such as looking for cracks in bones and bridges), and for
cancer treatments.
• Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths (less than one trillionth of a meter: 10 to the
negative 12), therefore the highest frequencies, carries the most energy. These are the most
harmful/damaging to tissues that can penetrate the deepest. They are hard to stop! and
you would need a 3-4foot thick concrete wall to stop them. Gamma rays are released in
nuclear power plants, by nuclear bombs, and by naturally occurring elements on Earth.
They are actually used in the treatment of cancer.
A.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum is the 1.__________ range of EM waves in order of 2._________
frequency and 3.__________ wavelength. As you look from left to right on a diagram of the spectrum;
this means that the wavelengths get 4.________ and the frequency gets 5.________. It is an
6.________ relationship exists between size of the wave and frequency. We all know that all EM
waves travel at the same 7.___________. If you can recall the formula for speed, it is the 8.________
times the 9._________. For the answer is always be 300,000km/s, as one number goes 10._____,
the other must go 1._____. All EM waves is 12.________; it’s just that the longer wavelengths do not
Author: Bria F. Singson
School/Station: Agay National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
carry enough energy in them to damage cells. Always remember that the higher the 13._______,
the more 14.________ in the wave.
B.
1.___________have the ________ wavelengths and _________ frequencies; wavelengths range from
1000s of meters to 0.001 m; and the shortest radio waves are _________ Radio waves are used in
RADAR; the radio detection and ranging; it’s sending sound, ___________, __________, __________
and ___________________.
2. _________ waves (heat) have ________ wavelengths, from 0.001 m to 700 nm and _________
frequencies (a nm is one billionth of a meter). Infrared is used to ___________ and in __________.
3.___________ is what we can _____ in the EM spectrum. Wavelengths of visible light range from
about 700 nm (____ light) to 400 nm (_______ light). Visible light frequencies are usually _______
than the frequencies of infrared waves. We can identify how visible light is such a small portion of
the entire spectrum.
4. Ultraviolet wavelengths range from about 400 nm to 10 nm; the _________ (and therefore the
________) is high enough with UV rays to ________ living ______ and cause them ________. We need
UV rays to produce _________ in our bodies. Even though too much can lead to ________ and
___________; and UV rays are ______ stopped by clothing and used for sterilization of materials
because they kill bacteria in high enough concentrations. Although humans cannot see UV light,
______ and butterflies. Some small rodents, and some ______ can.
5.___-rays have wavelengths from 10 nm to 0.001 nm. They have enough _______ to penetrate and
closer ______ into tissues, but are ________ by ______ materials, such as bones. And used for
________________ (such as looking for cracks in bones and bridges), and for _____________.
6. Gamma _____ have the _________ wavelengths (less than one _________ of a meter: 10 to the
negative 12), therefore the _________ frequencies, carries the most ________. These are the most
_____________ to tissues that can penetrate the deepest. They are ______ to stop! and you would
need a _______ thick concrete wall to stop them. Gamma rays are released in nuclear power plants,
by nuclear bombs, and by naturally occurring elements on Earth. They are actually used in the
treatment of cancer.
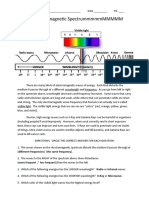
Activity 1.2. Name Me!
Direction: Name the different parts of the Electromagnetic Spectrum in the box.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
https://www.univie.ac.at/geographie/fachdidaktik/FD/site/external_htmls/imagers.gsfc.nasa.g
ov/ems/waves3.html
Author: Bria F. Singson
School/Station: Agay National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
Activity 2. Compare Me!
Direction: Study and compare the relative wavelength, frequencies and energies of the different
regions of the electromagnetic spectrum below.
https://quizlet.com/284710064/physics-electromagnetic-spectrum-diagram/
Compare the following waves Description
(lower, higher, longer, shorter)
1. Radio waves are ______ in wavelength than the gamma-ray.
2. Microwave is ______ in energy than infrared.
3. Visible light is ______ in frequency than x-ray.
4. Radio wave is ______ in energy than gamma-ray.
5. Infrared is ______ in wavelength than UV.
6. Visible light is _____ in frequency than radio wave.
Author: Bria F. Singson
School/Station: Agay National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
Which of the EM wave has the following characteristics? (Gamma ray, X-ray, UV, Visible
light, Microwave, Infrared,
Radio wave)
7. highest energy?
8. lowest energy?
9. longest wavelength
10. shortest wavelength
11. lowest frequency
12. highest frequency
Activity 3. Solve me!
Direction: Study below how the energy of a photon can be calculated. Answer the questions
that follow.
The Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation
When we talk of electromagnetic radiation as a particle, we refer to photons, which are packets of
energy. The energy of the photon is related to the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation
according to: h is called Planck’s constant.
Planck’s constant is a physical constant named after Max Planck. h = 6.626× 10-34 J.s
The energy of a photon can be calculated using the formula: E = hf or E = h c/ λ. Where E is the
energy of the photon in joules (J), h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, f is the frequency
in hertz (Hz) and λ is the wavelength in metres (m).
Worked Example 1: Calculating the energy of a photon I
Problem: Calculate the energy of a photon with a frequency of 3× 1018 Hz.
Answer We use the formula: E = hf
E = hf = 6.6×10-34 ×(3× 1018) = 2×10-15 J
Worked Example 2: Calculating the energy of a photon II
Problem: What is the energy of an ultraviolet photon with a wavelength of 200 nm? Where 200nm
= 200 x 10-9 m or 2 x 10-7m
Answer Step 1: Determine what is required and how to approach the problem. We are required to
calculate the energy associated with a photon of ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 200 nm. We
can use: E = h c/ λ
Where c is the speed of light equal to 3 x 10-8 m/s
Step 2: Solve the problem
E = h(c/ λ) = (6.626×10-34) 3× 108)/200×10-9 = 9,939× 10-10 J
Author: Bria F. Singson
School/Station: Agay National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
Now, try these!
Particle nature of EM waves
1. How is the energy of a photon related to its frequency and wavelength?
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
2. Calculate the energy of a photon of EM radiation with a frequency of 10 12 Hz.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Determine the energy of a photon of EM radiation with a wavelength of 600 nm.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
(Mark Horner. et al., The Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation: Textbook for High School
Students Studying the Sciences Physics Grades 10-12 p. 55-56)
Rubric for scoring: (adapted from courser.org)
Is the response correct?
___ 0 points- No, the response was incorrect.
___ 2 points- The response was partially incorrect.
___ 4 points- Yes, the response was correct.
___ 5 points- Yes, the response was correct and especially insightful or detailed.
Reflection
Try to relate your insights/learning in a short poem, then answer the question that follow.
Sunrise, Sunset
The sun that ensuing every day is a tale
Every day was born with a sunrise and edge with a sunset
One and the same way we open our eyes to spot the light
And near them to hear the dark.
“Oh, Sunlight!” the pretentious gold to be found on Universe
Makes a beautiful life with a sunrise and sunset in every single day, and they’re perfectly free.
1. If molecules in the sky scattered low-frequency light instead of high frequency light, how
would the colors of the sky and sunsets appear? Justify your answer.
________________________________________________________________________________________
Author: Bria F. Singson
School/Station: Agay National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
References for learners:
Acosta H. D. et al. Electromagnetic Spectrum: Science Module 10. Pasay City: DepEd, 2017.
Dumlao,D. Electromagnetic Spectrum: SIM Grade 10. Don Salustiano Aquino MNHS: 2016.
Department of Education. Teaching Guide Science 10 p.115 – 125.
Horner M. et al. The Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation: Textbook for High School
Students Studying the Sciences Physics Grades 10-12 p. 55-56.
EASE/OHSP Physics Module 17: Electromagnetic Waves and Wireless Communication. Accessed
on November 4, 2020. Retrieved from https://lrmds.deped.gov.ph/detail/7660
Sunday Science: The Electromagnetic Spectrum. Accessed on November 4, 2020. Retrieved from
http://www.geditorial.com/blog/sunday-science-the-electromagnetic-spectrum
Physics: Electromagnetic Spectrum. Accessed on November 5, 2020. Retrieved from
https://quizlet.com/284710064/physics-electromagnetic-spectrum-diagram/
The Electromagnetic Spectrum. Accessed on November 5, 2020. Retrieved from
https://www.univie.ac.at/geographie/fachdidaktik/FD/site/external_htmls/imagers.gsfc.nasa.g
ov/ems/waves3.html
Author: Bria F. Singson
School/Station: Agay National High School
Division: Agusan del Norte
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
email address: bria.singson@deped.gov.ph
Division: Agusan del Norte
School/Station: Agay National High School
Author: Bria F. Singson
Activity 1.2 Activity 1.1 Activity 1.1
Name Me! Fill Me! Fill Me!
A.
1. Building 4. 1. complete
2. Human Frequency 2. increasing
3. Honey Bee Energy 3. decreasing
4. Pinpoint Penetrate 4. smaller
5.Protozoans Cells 5. larger
6. Molecules damage 6. inverse
7. Atoms Sunburn 7. speed: 300,000km/s
8. Atomic Nuclei Skin cancer 8. wavelength
Need 9. frequency
Activity 2 Compare Me! Vitamin D 10. up
1. longer Easily 11. down
2. lower Bees 12. radiation
3. lower Small rodents and some birds 13. frequency
4. lower 5. 14. energy
5. longer X B.
6. higher Enough 1. Radio waves
7. gamma ray Deep Longest
8. radio wave Stopped Lowest
9. radio wave Dense Microwaves
10. gamma ray Examining solid structures RADAR
11. radio wave Cancer treatments Sending sound
12. gamma ray 6. Pictures (TV)
Rays Cell phones
Activity 3 Solve Me! Shortest Cooking
Trillionth Satellites
1. Inversely promotional- Highest Transmissions
the higher the frequency, Energy 2. Infrared waves
the shorter the Damaging Shorter
wavelength. Hard Higher
2. 6.6 x 10-22 J 3-4 foot Find people in the dark
3. 3.3-19 J In TV remotes
3. Visible light
See
Red
Violet
Higher
Answer Key
You might also like
- Surge Analysis and The Wave Plan MethodDocument126 pagesSurge Analysis and The Wave Plan Methodmailmaverick8167No ratings yet
- MurraylightemDocument2 pagesMurraylightemapi-26383090433% (3)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Wavesputri_latifah100% (3)
- Waves and em Spectrum Ws PDFDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Ws PDFJv Loo Caguioa100% (1)
- Karen May P. UrlandaDocument47 pagesKaren May P. UrlandaKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2W3-4Document15 pagesScience 10 - Q2W3-4quackity obamaNo ratings yet
- S10FE-11a-b-47 MELC: Compare The Relative Wavelengths of Different Forms of ConceptsDocument5 pagesS10FE-11a-b-47 MELC: Compare The Relative Wavelengths of Different Forms of ConceptsMikaela Julianne Erada100% (1)
- Quarter 2: MODULE 1: Different Forms of EM WavesDocument30 pagesQuarter 2: MODULE 1: Different Forms of EM WavesPepito Rosario Baniqued, Jr100% (2)
- FilipinoDocument6 pagesFilipinoVinz JaneNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Module 2Document73 pagesQuarter 2 Module 2princesslayshoNo ratings yet
- Science10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Document15 pagesScience10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Christine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction EM Waves WorksheetDocument3 pagesIntroduction EM Waves WorksheetUmer AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Clem Waves Lesson04 NotesasDocument1 pageClem Waves Lesson04 NotesasdanaNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmDocument3 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmDocument3 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction em Waves Worksheet 2Document2 pagesIntroduction em Waves Worksheet 2api-2605470450% (1)
- The Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmDocument3 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrummmmmmmmmmJhet Ardian CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Eem wiveSZDocument3 pagesEem wiveSZJhet CoritanaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Grade 10 (De Guzman)Document19 pagesModule 2 Grade 10 (De Guzman)Kim De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 - EM WavesDocument8 pagesLecture 2.1 - EM WavesAPPLE CAGUNGUN-BELGICANo ratings yet
- Final Sci10 q2 m2 Edited-16Document16 pagesFinal Sci10 q2 m2 Edited-16Fe GullodNo ratings yet
- Long TestDocument2 pagesLong TestJow DualanNo ratings yet
- G10 Physics CompendiumDocument41 pagesG10 Physics CompendiumJhin CortezNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Different Forms of EM WavesDocument13 pagesLAS 1 Different Forms of EM WavesaquesamabiniNo ratings yet
- Em SpectrumDocument13 pagesEm SpectrumKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument40 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrummike ebioNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science 10 MODULE 4Document13 pagesQ2 Science 10 MODULE 4princesslayshoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument40 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrumtripathiansh447No ratings yet
- EM Waves and Spectrum Worksheet AlnahdaDocument3 pagesEM Waves and Spectrum Worksheet AlnahdaMaryem Nabawi100% (1)
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2. Calculating Wavelengtdytrjycghh and FrequencyDocument37 pagesLESSON 2. Calculating Wavelengtdytrjycghh and FrequencyRyan Aint simpNo ratings yet
- EVS SeminarDocument30 pagesEVS SeminarMonica SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument22 pagesEM WavesJane Reyes100% (1)
- EM Spectrum Worksheets PDFDocument2 pagesEM Spectrum Worksheets PDFMarian Galoso100% (1)
- Properties of LightDocument25 pagesProperties of LightAhmad Dhiyaul WahidNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum FormsDocument32 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum FormsRuih PadillaNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Module 1 (Q2-Week 1-5)Document20 pagesSci10 Module 1 (Q2-Week 1-5)CHRIS JOHN A. SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Science 10Document5 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Science 10soriachristellejade8No ratings yet
- Sci10 Practical Applications of em WavesDocument17 pagesSci10 Practical Applications of em WavesChristina PlataNo ratings yet
- G10 Physics CompendiumDocument41 pagesG10 Physics CompendiumAlodia Carlos PastorizoNo ratings yet
- Science10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Document19 pagesScience10 q2 Mod1of6 Electromagneticspectrum v2Renmarie LaborNo ratings yet
- (51014) Javier Prelab6Document2 pages(51014) Javier Prelab6Jesse JavierNo ratings yet
- 2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1Document2 pages2023-11-10 11 - 13 - 50.563 - 1pranitjadhav0407No ratings yet
- G10 Science Q2 - W2 - Electromagnetic WavesDocument13 pagesG10 Science Q2 - W2 - Electromagnetic WavesKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- Science 10 SECOND QuarterDocument152 pagesScience 10 SECOND QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIAN100% (1)
- em Spectrum 2Document26 pagesem Spectrum 2Juliever EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Different Regions of Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument20 pagesLesson 1 The Different Regions of Electromagnetic SpectrumsubaldojenniferNo ratings yet
- Wave C12Document9 pagesWave C12Wajira Sanjaya PereraNo ratings yet
- Research PDFDocument28 pagesResearch PDFJeon ManobanNo ratings yet
- Science10 q2 Mod3of6 Effectsofemwavesonlivingthingsandenvironment v2Document15 pagesScience10 q2 Mod3of6 Effectsofemwavesonlivingthingsandenvironment v2Christine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum Work SheetDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Work SheetSenpai ChibiNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum Ws PDFDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Ws PDFAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum WsDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum WsTracey LaRussoNo ratings yet
- Waves and em Spectrum Ws PDFDocument2 pagesWaves and em Spectrum Ws PDFJv Loo CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 MindScape - Science Intervention For StudentsDocument16 pagesQuarter 2 MindScape - Science Intervention For StudentsadrianquininezaNo ratings yet
- Chem Waves Lesson LectureDocument11 pagesChem Waves Lesson LectureMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhysicsDocument7 pagesModule 8 PhysicsLopez AeraNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument11 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrumroziel A.mabitasanNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument30 pagesEM WavesCLarence De ClaroNo ratings yet
- Mechanik Ruina Pratap ContentDocument2 pagesMechanik Ruina Pratap Contentapi-129423309No ratings yet
- Physics EeeercDocument5 pagesPhysics EeeercJessabelle RamosNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of Light WavesDocument24 pagesDiffraction of Light Wavesbenjamin swokaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 2 PDFRohan Ghosh DastidarNo ratings yet
- Pump Sizing Calculation SheetDocument7 pagesPump Sizing Calculation SheetManik Kandan100% (1)
- Problem. A 5-Sided Lot ABCDE Is Surveyed Inside Its Perimeter From A Point Named F. The Horizontal Distances andDocument4 pagesProblem. A 5-Sided Lot ABCDE Is Surveyed Inside Its Perimeter From A Point Named F. The Horizontal Distances andwoi mariaNo ratings yet
- Waves-Quantum and Nuclear-Resolution-Atomic and NuclearDocument45 pagesWaves-Quantum and Nuclear-Resolution-Atomic and NuclearMartinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document4 pagesTutorial Chapter 2batrisyaNo ratings yet
- SPM 2010 Paper 2Document78 pagesSPM 2010 Paper 2Suriyati YusoffNo ratings yet
- Space Weight LabDocument3 pagesSpace Weight Labapi-403198825100% (1)
- Physics Worksheet For Grade 9Document4 pagesPhysics Worksheet For Grade 9Kassahun100% (1)
- RAE3601-2023 Assignment 2Document9 pagesRAE3601-2023 Assignment 2thabisoNo ratings yet
- Pascal Archimedes BernoulliDocument2 pagesPascal Archimedes BernoulliRj Bengil100% (1)
- Sample Solution Manual For Orbital Mechanics For Engineer 3rd CurtisDocument16 pagesSample Solution Manual For Orbital Mechanics For Engineer 3rd CurtisSumon SwiftNo ratings yet
- Lec 16 CDocument66 pagesLec 16 CSalman MemonNo ratings yet
- A Quasi-Optical: Converter With BifocalDocument5 pagesA Quasi-Optical: Converter With BifocalAnonymous DGq0O15nNzNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Physics Model Examination For Grade 12 Ginbot .: General DirectionDocument8 pagesAddis Ababa Physics Model Examination For Grade 12 Ginbot .: General DirectionKhalid A.100% (3)
- Equation of Continuity and Bernoulli's EquationDocument16 pagesEquation of Continuity and Bernoulli's Equationdimitris1936No ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument18 pagesSimple Harmonic Motionieja03100% (2)
- Engineering VibrationsDocument43 pagesEngineering VibrationsClayton Roe100% (3)
- Board PhysicsDocument9 pagesBoard PhysicsDurgesh Yadav100% (1)
- Lesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaDocument34 pagesLesson Explainer - Velocity - NagwaMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- THE APPLICATION OF QUATERNION ALGEBRA TO GYROSCOPIC MOTION, NAVIGATION, AND GUIDANCE George P. Davailus Old Dominion University Aerospace Engineering Department Advisor: Brett A. NewmanDocument7 pagesTHE APPLICATION OF QUATERNION ALGEBRA TO GYROSCOPIC MOTION, NAVIGATION, AND GUIDANCE George P. Davailus Old Dominion University Aerospace Engineering Department Advisor: Brett A. NewmanmarkrichardmuradNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesDocument42 pagesLecture 6 - Fluid Flow in PipesPercival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Fluid ForcesDocument16 pagesFluid ForcesGeorge OparNo ratings yet
- Oblique Shock WavesDocument25 pagesOblique Shock WavesDhinasuga DhinakaranNo ratings yet
- 1-Newton Second Law-ForMATDocument5 pages1-Newton Second Law-ForMATVAIBHAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- 1642990216class 9 Questions - Sound ChapterDocument9 pages1642990216class 9 Questions - Sound ChapterMANISHA GARGNo ratings yet