Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inbound 3476607779425663890
Inbound 3476607779425663890
Uploaded by
Johanna RullanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inbound 3476607779425663890
Inbound 3476607779425663890
Uploaded by
Johanna RullanCopyright:
Available Formats
International Business and Trade
Module 3
Mercantilism
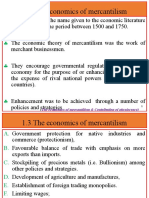
Mercantilism is a nationalist economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and
minimize the imports for an economy. In other words, it seeks to maximize the accumulation of
resources within the country and use those resources for one-sided trade.
What is mercantilism in simple terms?
Mercantilism is an economic practice by which governments used their economies to augment
state power at the expense of other countries. Governments sought to ensure that exports
exceeded imports and to accumulate wealth in the form of bullion (mostly gold and silver).Oct
23, 2023
History of Mercantilism
First seen in Europe during the 1500s, mercantilism was based on the idea that a nation's
wealth and power were best served by increasing exports and limiting imports.
Mercantilism replaced the feudal economic system in Western Europe. At the time, England
was the epicenter of the British Empire but had relatively few natural resources.
To grow its wealth, England introduced fiscal policies that discouraged colonists from buying
foreign products and created incentives to buy only British goods. For example, the Sugar Act
of 1764 raised duties on foreign refined sugar and molasses imported by the colonies. This
increased taxation was meant to give British sugar growers in the West Indies a monopoly on
the colonial market.
You might also like
- International Business-2nd Major AssignmentDocument5 pagesInternational Business-2nd Major AssignmentvikramNo ratings yet
- What Is Mercantilism?: Balance of TradeDocument6 pagesWhat Is Mercantilism?: Balance of TradeMarjorie Cabauatan BirungNo ratings yet
- International Trade Law NotesDocument41 pagesInternational Trade Law NotesSMCC 26 Speaker 2No ratings yet
- MERCANTILISMDocument2 pagesMERCANTILISMAsad KhanNo ratings yet
- MithunDocument81 pagesMithunMeghana RaoNo ratings yet
- International Trade NotesDocument8 pagesInternational Trade NotesKomal SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Mercantilism: A) Meaning and Definition of MercantilismDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Mercantilism: A) Meaning and Definition of MercantilismHasnath AhmedNo ratings yet
- Final Exam TopicsDocument33 pagesFinal Exam Topicsaziangamerz87No ratings yet
- MercantilismDocument3 pagesMercantilismarciblue67% (3)
- History of Economic Thought Lecture2 (UN 1)Document27 pagesHistory of Economic Thought Lecture2 (UN 1)Chewaka TemenaNo ratings yet
- MercantilismDocument2 pagesMercantilismCC RiriNo ratings yet
- Classical Macroeconomics - Mercantilism and Neo-MercantilismDocument12 pagesClassical Macroeconomics - Mercantilism and Neo-MercantilismBHANU TYAGINo ratings yet
- MercantilismDocument3 pagesMercantilismMicca DeynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document47 pagesChapter 3Maurice ZorillaNo ratings yet
- MERCENTILISM Hidayat UllahDocument5 pagesMERCENTILISM Hidayat UllahWaqas khanNo ratings yet
- Mercantilism Is An: Political Economy, Published in 1767Document1 pageMercantilism Is An: Political Economy, Published in 1767Nandani VermaNo ratings yet
- LuckyDocument3 pagesLuckymr haldarNo ratings yet
- MercantilismDocument3 pagesMercantilismjeraldtomas12No ratings yet
- MERCENTILISM HasnainDocument5 pagesMERCENTILISM HasnainWaqas khanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-History of Economic ThoughtDocument42 pagesLecture 3-History of Economic ThoughtMurad QarayevNo ratings yet
- Public Finance Module 2.0Document36 pagesPublic Finance Module 2.0Pamela R. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Drivers of GlobalizationDocument141 pagesDrivers of GlobalizationBhavesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- MercantilismDocument2 pagesMercantilismBapu FinuNo ratings yet
- Fina Notes of IPEDocument5 pagesFina Notes of IPEMaheen AliNo ratings yet
- Classical Country Based Theories of International TradeDocument27 pagesClassical Country Based Theories of International TradeMadrogaba, Paulo Robert P. BSBA-MM 1-1No ratings yet
- Cas Ii Assignment ON Mercantilism: Created By: Sanchali Gorai and Surabhi Dikshit Subject: International FinanceDocument7 pagesCas Ii Assignment ON Mercantilism: Created By: Sanchali Gorai and Surabhi Dikshit Subject: International FinanceSanchali GoraiNo ratings yet
- Mercantilism and Economic NationalismDocument25 pagesMercantilism and Economic NationalismPrinces Danica ArconadoNo ratings yet
- MERCANTILISMDocument8 pagesMERCANTILISMBushy KilayNo ratings yet
- International Trade TheoriesDocument3 pagesInternational Trade TheoriesAbidullahNo ratings yet
- International Trade With Classical and Contemporary TheoriesDocument20 pagesInternational Trade With Classical and Contemporary TheoriesNaomi Alberg-BlijdNo ratings yet
- MercantilismDocument15 pagesMercantilismjohn jamesNo ratings yet
- ZeeshanDocument5 pagesZeeshanWaqas khanNo ratings yet
- Classical and Neo-MercantilismDocument20 pagesClassical and Neo-Mercantilismfarirehman96No ratings yet
- History of Economic Thought: Lecture 1& 2 Pre-Classical Economics Mercantilism & PhysciocratsDocument31 pagesHistory of Economic Thought: Lecture 1& 2 Pre-Classical Economics Mercantilism & PhysciocratssmcNo ratings yet
- Mercantilism: Definition: Mercantilism Is An Economic Theory Where The Government Seeks ToDocument10 pagesMercantilism: Definition: Mercantilism Is An Economic Theory Where The Government Seeks Tosavia mirNo ratings yet
- Mercantalism 1Document11 pagesMercantalism 1TammanaNo ratings yet
- MERCANTALISMDocument6 pagesMERCANTALISMKiran SyedNo ratings yet
- C2 MercantilistDocument23 pagesC2 MercantilistCarmen ChangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document1 pageLesson 3Francin AdriaticoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of MercantilismDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of MercantilismSchezad AfrįdįNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MercantilismDocument21 pagesChapter 4 MercantilismGorangoNo ratings yet
- MercantilismDocument55 pagesMercantilismRam PareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 WVES 222Document9 pagesChapter 5 WVES 222olebile.tlholoNo ratings yet
- SS1-Introduction To HEADocument21 pagesSS1-Introduction To HEAAh NinNo ratings yet
- Econ 412 Lecture Combined Notes 2021 KabuDocument56 pagesEcon 412 Lecture Combined Notes 2021 Kabugedionkipkoech214No ratings yet
- International Political Economy (IPE), Also Known As Global Political Economy (GPE), Refers ToDocument8 pagesInternational Political Economy (IPE), Also Known As Global Political Economy (GPE), Refers Toenih carolNo ratings yet
- Theories of Intl TradeDocument35 pagesTheories of Intl TradePrakshi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Mercantilism ReadingDocument2 pagesMercantilism Readingrrrrrrrr rrrrrrrrNo ratings yet
- History of Economic ThoughtDocument5 pagesHistory of Economic ThoughtBrock NavarroNo ratings yet
- Rise of France and NetherlandsDocument23 pagesRise of France and NetherlandsShristi ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 7586423486975915125Document4 pagesInbound 7586423486975915125Johanna RullanNo ratings yet
- Ba Core 6 - Unit 2 - ReviewerDocument3 pagesBa Core 6 - Unit 2 - ReviewerJohnloyd daracanNo ratings yet
- History of Economic ThoughtDocument39 pagesHistory of Economic ThoughtAditi RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Theroies of International TradeDocument12 pagesTheroies of International TradeBantoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 ONLINEDocument10 pagesLesson 2 ONLINEFrancis Dave Nagum Mabborang IINo ratings yet
- Mercantilism Another VersionDocument44 pagesMercantilism Another VersionDeepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 3.+IB +protectionismDocument11 pages3.+IB +protectionismkioshitienNo ratings yet