Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson - Plan 1
Lesson - Plan 1
Uploaded by
Rina Marie Besin CartesianoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Picture-Perfect STEM Lessons, Kindergarten: Using Children's Books for Three-Dimensional LearningFrom EverandPicture-Perfect STEM Lessons, Kindergarten: Using Children's Books for Three-Dimensional LearningNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Sustainability Multidisciplinary Ubd UnitDocument11 pages4th Grade Sustainability Multidisciplinary Ubd Unitapi-267230750No ratings yet
- Sehs9124 - Limpieza y Secado de Grupos ElectrogenosDocument10 pagesSehs9124 - Limpieza y Secado de Grupos ElectrogenosOscar Curimanya100% (1)
- Sample Lesson Plan Endangered SpeciesDocument6 pagesSample Lesson Plan Endangered Speciesapi-239781441100% (1)
- Float Sink Lesson Plan 2Document6 pagesFloat Sink Lesson Plan 2api-388627256No ratings yet
- Educ 5025 Teaching English Learners Integrated Eld Lesson Plan 7th Grade ScienceDocument11 pagesEduc 5025 Teaching English Learners Integrated Eld Lesson Plan 7th Grade Scienceapi-338433169No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanMarijoy Marge RafaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledGwendolyn CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesScience Lesson PlanronalynbotobaraNo ratings yet
- Final Curriculum PlanDocument40 pagesFinal Curriculum Planapi-122605596No ratings yet
- Biodiversity, Food and Farming For A Healthy Planet: Lesson PlansDocument30 pagesBiodiversity, Food and Farming For A Healthy Planet: Lesson PlansMARY ROSENo ratings yet
- Sierra Nevada College Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesSierra Nevada College Lesson Planapi-266778770No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant UnitDocument8 pagesAnimal and Plant Unitapi-252935769No ratings yet
- Earth Science Lesson - PlanDocument3 pagesEarth Science Lesson - Planpedro braulioNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Lesson ExemplarDocument11 pagesBiodiversity Lesson ExemplarNelma Faye MadambaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument14 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceAlren SaberonNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson Planjrm.tinoyNo ratings yet
- Ict 22Document5 pagesIct 22api-250192253No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanluigivallespinpiñeroNo ratings yet
- Friends of Our Environment FridayDocument8 pagesFriends of Our Environment Fridayapi-319166569No ratings yet
- Carlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeDocument3 pagesCarlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeJanine Gevero MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanglifoneaailenekrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanJonas CabusbusanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan WasteDocument9 pagesLesson Plan Wastemydel campehiosNo ratings yet
- Forum 502 ExtractDocument6 pagesForum 502 Extractjmobando1No ratings yet
- A Frogs Skin - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesA Frogs Skin - Lesson Planapi-255425919No ratings yet
- Create To Educate: Title of Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesCreate To Educate: Title of Lesson Planapi-282594826No ratings yet
- Water Systems On Earth Water Systems On Earth: Grade 8 Science Lessons Grade 8 Science LessonsDocument39 pagesWater Systems On Earth Water Systems On Earth: Grade 8 Science Lessons Grade 8 Science Lessonsapi-215899543No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanMark Jay LegoNo ratings yet
- Bio@Lp 2012Document46 pagesBio@Lp 2012Mariah ThezNo ratings yet
- Ross 16te802 Glt1reportDocument9 pagesRoss 16te802 Glt1reportapi-325792607No ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar BiodiversityDocument5 pagesLesson Exemplar BiodiversityArnold C. LasitNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan EvolutionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan EvolutionnorjanahpasagueNo ratings yet
- Environmental BiologyDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Biology1799647611No ratings yet
- Science 9 BiodiversityDocument3 pagesScience 9 BiodiversityJayNo ratings yet
- Mjacksoninstructional Tech UnitDocument11 pagesMjacksoninstructional Tech Unitapi-215826593No ratings yet
- LP 2022Document6 pagesLP 2022Bert RoseteNo ratings yet
- GwapakoDocument2 pagesGwapakoangelinelokinaNo ratings yet
- Ladnscc Assignment 1Document14 pagesLadnscc Assignment 1mbiwan AchareNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan: Lesson Cross CurricularDocument10 pagesUnit Plan: Lesson Cross Curricularapi-311724683No ratings yet
- Title of Unit: Evolution Grade Level: 10th Grade Subject: Biology Time Frame: Five WeeksDocument8 pagesTitle of Unit: Evolution Grade Level: 10th Grade Subject: Biology Time Frame: Five Weeksapi-281582336No ratings yet
- Thursday LessonDocument4 pagesThursday Lessonapi-372343626No ratings yet
- Animal HomesDocument1 pageAnimal Homesapi-218762447No ratings yet
- ProjectDocument26 pagesProjectapi-340166683No ratings yet
- Ubd EcologyDocument13 pagesUbd EcologyPaul Michael Vial Boncayo100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanSantillan Charity MayNo ratings yet
- Snail Unit Plan Lesson 1Document3 pagesSnail Unit Plan Lesson 1api-464689903No ratings yet
- Course Guide - 9 EcologyDocument281 pagesCourse Guide - 9 EcologyNora LeeNo ratings yet
- M6 L6 FinalDocument45 pagesM6 L6 FinalUrban EcoLab CurriculumNo ratings yet
- Science 3Document2 pagesScience 3api-239852387No ratings yet
- Ed508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Template 1Document6 pagesEd508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Template 1api-740167831No ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Prototype Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 Third Quarter, WeekDocument4 pagesI. Objectives:: Prototype Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 Third Quarter, WeekCherry MaeNo ratings yet
- Tiffany Washington 5e Lesson Plan 1Document8 pagesTiffany Washington 5e Lesson Plan 1api-644963967No ratings yet
- Design DocumentDocument9 pagesDesign Documentapi-208533376No ratings yet
- Learningguide 3rdsustanability 2Document7 pagesLearningguide 3rdsustanability 2api-300007613No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document3 pagesLesson 5api-709748758No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanluigivallespinpiñeroNo ratings yet
- Weird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionDocument28 pagesWeird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionBecky BrownNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1-3 ReviewDocument2 pagesLesson Plan 1-3 Reviewapi-237688616No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson Planyen yenNo ratings yet
- API 6A Gate ValvesDocument12 pagesAPI 6A Gate ValvesLee Sweningson100% (1)
- (Download PDF) Water Resources of Chile Bonifacio Fernandez Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument40 pages(Download PDF) Water Resources of Chile Bonifacio Fernandez Online Ebook All Chapter PDFannie.cormier901100% (9)
- ScriptDocument7 pagesScriptSaiyam Chaudhary0% (1)
- AA#27 Bitterroot Briar (L2-4) - Expeditious Retreat PressDocument13 pagesAA#27 Bitterroot Briar (L2-4) - Expeditious Retreat PressYankeeinHawaii100% (3)
- The Role of Shopping Malls in An Environment A Case of Oluwole Shopping Mall in Lagos Island Lagos State, NigeriaDocument6 pagesThe Role of Shopping Malls in An Environment A Case of Oluwole Shopping Mall in Lagos Island Lagos State, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- PVC Wire Flexible CablesDocument10 pagesPVC Wire Flexible CablesPrinasen NaiduNo ratings yet
- Question 1. A. Booked B. Missed D. Pronounced: JaneDocument4 pagesQuestion 1. A. Booked B. Missed D. Pronounced: JaneThuận NgyễnNo ratings yet
- Resurgence Issue 260Document84 pagesResurgence Issue 260imperativecureNo ratings yet
- The Artist SpectrumDocument132 pagesThe Artist SpectrumsumendersinghNo ratings yet
- Ess420 Vce Unit 1 Aos 2Document10 pagesEss420 Vce Unit 1 Aos 2api-267133657No ratings yet
- 040 - Ekistics TheoryDocument4 pages040 - Ekistics TheoryAbdurrehman AzeemNo ratings yet
- 17.4 Boiler and Feed-Water TreatmentDocument28 pages17.4 Boiler and Feed-Water Treatmentnomeacuerdo1No ratings yet
- Shell - Lubricants - Product Data GuideDocument20 pagesShell - Lubricants - Product Data GuideRolando DaclanNo ratings yet
- Chapman 2009 NumbersofLivingSpecies Oz World DEHDocument85 pagesChapman 2009 NumbersofLivingSpecies Oz World DEHvero adaroNo ratings yet
- Environmental Weeds of The Wet TropicsDocument94 pagesEnvironmental Weeds of The Wet TropicsSadao MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity by Design Maximising The Biodiversit-Groen Kennisnet 468095Document122 pagesBiodiversity by Design Maximising The Biodiversit-Groen Kennisnet 468095komal shinde100% (1)
- CULTURAL STUDY ChapterDocument17 pagesCULTURAL STUDY Chapterchristeena joseNo ratings yet
- How Natural and Built Environments Impact Human Health: Dr. Nancy WellsDocument4 pagesHow Natural and Built Environments Impact Human Health: Dr. Nancy WellsBettina TiongcoNo ratings yet
- Ore Textures and Wall Rock AlterationDocument6 pagesOre Textures and Wall Rock AlterationIrwan EPNo ratings yet
- Authorial Comments in Tess of D'urbervilles by Thomas HardyDocument4 pagesAuthorial Comments in Tess of D'urbervilles by Thomas HardydilipbaradNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education: History GoalsDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Education: History GoalskhaidhirNo ratings yet
- Presentation About The RA 9147 The LawPhDocument14 pagesPresentation About The RA 9147 The LawPhMarianne R. De TorresNo ratings yet
- Short Moral StoriesDocument24 pagesShort Moral StoriesVarsha RayNo ratings yet
- Grace Lalawmpuii Sailo, EvsDocument177 pagesGrace Lalawmpuii Sailo, Evsatul pandeyNo ratings yet
- Mobilith AW SeriesDocument3 pagesMobilith AW SeriesDavid SalgueroNo ratings yet
- II. Ecoliteracy and The Different ApproachesDocument34 pagesII. Ecoliteracy and The Different Approachesgerrie anne untoNo ratings yet
- Corbett Epithermal 2006 Paper 2nd DraftDocument32 pagesCorbett Epithermal 2006 Paper 2nd DrafthistorysilviaNo ratings yet
- RN Parkins-The Stress Corrosion Cracking of C-MN Steek Ub CO2-HCO3-CO3 Solutions I, Stress Corrosion DataDocument15 pagesRN Parkins-The Stress Corrosion Cracking of C-MN Steek Ub CO2-HCO3-CO3 Solutions I, Stress Corrosion DataAlondra HermosoNo ratings yet
- The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019Document129 pagesThe Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019Hugo Barata GomesNo ratings yet
Lesson - Plan 1
Lesson - Plan 1
Uploaded by
Rina Marie Besin CartesianoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson - Plan 1
Lesson - Plan 1
Uploaded by
Rina Marie Besin CartesianoCopyright:
Available Formats
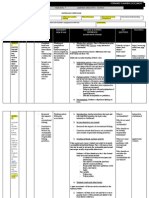
Subject: Science
Grade Level: Grade 9
Objective:
1. Define extinction.
2. Explain the importance of biodiversity.
3. Differentiate the rate of extinction in the past and in the present.
4. Enumerate the causes of extinction.
5. Infer the causes why some species are vulnerable to extinction.
Learning across the curriculum:
- Mathematics: Graph the rate of extinction in the past and present.
- Social Studies: Investigate the impact of extinction on ecosystems throughout history.
- Language Arts: Write a persuasive essay on the importance of conserving biodiversity.
Elicit:
- Ask students if they have heard of the term "extinction" and what they understand about it.
Translate to English.
Engage:
1. Show a short video clip about the impact of animal extinction on ecosystems. Discuss the
emotional and ecological effects with the students. Translate to English.
2. Present a series of images of endangered species and ask students to reflect on the
importance of protecting biodiversity. Translate to English.
3. Conduct a class survey on the students' favorite animals and discuss how extinction can
affect these species. Translate to English.
Explore:
Activity 1: Extinction Timeline
Materials: Chart paper, markers, images or descriptions of extinct animals
Instructions: In small groups, create a timeline showcasing the different extinct animals
throughout history. Discuss the possible reasons for their extinction. Use the rubric
provided for grading.
Rubric:
- Accuracy of timeline: 10 points
- Identification of reasons for extinction: 10 points
Assessment questions:
1. What is the purpose of creating a timeline of extinct animals?
2. Why is it important to understand the reasons for their extinction?
Activity 2: Rate of Extinction Comparison
Materials: Graph paper, data on past and present extinction rates
Instructions: In pairs, graph the rate of extinction in the past and present. Compare the
two graphs and discuss the differences. Use the rubric provided for grading.
Rubric:
- Accuracy of graphs: 10 points
- Analysis of differences: 10 points
Assessment questions:
1. What do the graphs show about the rate of extinction in the past and present?
2. Why do you think there is a difference in the rate of extinction?
Activity 3: Causes of Extinction Card Sort
Materials: Cards with causes of extinction, such as habitat loss, pollution, and climate
change
Instructions: In groups, sort the cards into categories based on the causes of extinction.
Discuss the impact of each cause on biodiversity. Use the rubric provided for grading.
Rubric:
- Accuracy of card sorting: 10 points
- Explanation of cause and impact: 10 points
Assessment questions:
1. Why is it important to identify the causes of extinction?
2. How do these causes affect biodiversity?
Explain:
1. Teacher-led discussion on the definition of extinction, emphasizing the irreversible loss of
species. Translate to English.
2. Interactive presentation on the importance of biodiversity and its role in maintaining
ecological balance. Encourage student participation and discussion. Translate to English.
Elaborate:
1. Divide the class into pairs. Assign each pair a vulnerable species and have them research
and create a presentation on the factors contributing to its vulnerability. Translate to English.
2. Conduct a debate on whether human activities or natural causes are more responsible for
the current rate of extinction. Translate to English.
Evaluate:
- Design a multiple-choice quiz to assess students' understanding of the causes of extinction
and the importance of biodiversity. Translate to English.
- Assign a project where students create an infographic highlighting the impacts of extinction
on different ecosystems. Translate to English.
Extend:
- Organize a field trip to a local conservation area or zoo to observe endangered species in
their natural or protected habitats. Translate to English.
Assignment:
Write a reflection paper on the role of individuals in conserving biodiversity. Translate to
English.
You might also like
- Picture-Perfect STEM Lessons, Kindergarten: Using Children's Books for Three-Dimensional LearningFrom EverandPicture-Perfect STEM Lessons, Kindergarten: Using Children's Books for Three-Dimensional LearningNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Sustainability Multidisciplinary Ubd UnitDocument11 pages4th Grade Sustainability Multidisciplinary Ubd Unitapi-267230750No ratings yet
- Sehs9124 - Limpieza y Secado de Grupos ElectrogenosDocument10 pagesSehs9124 - Limpieza y Secado de Grupos ElectrogenosOscar Curimanya100% (1)
- Sample Lesson Plan Endangered SpeciesDocument6 pagesSample Lesson Plan Endangered Speciesapi-239781441100% (1)
- Float Sink Lesson Plan 2Document6 pagesFloat Sink Lesson Plan 2api-388627256No ratings yet
- Educ 5025 Teaching English Learners Integrated Eld Lesson Plan 7th Grade ScienceDocument11 pagesEduc 5025 Teaching English Learners Integrated Eld Lesson Plan 7th Grade Scienceapi-338433169No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanMarijoy Marge RafaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledGwendolyn CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesScience Lesson PlanronalynbotobaraNo ratings yet
- Final Curriculum PlanDocument40 pagesFinal Curriculum Planapi-122605596No ratings yet
- Biodiversity, Food and Farming For A Healthy Planet: Lesson PlansDocument30 pagesBiodiversity, Food and Farming For A Healthy Planet: Lesson PlansMARY ROSENo ratings yet
- Sierra Nevada College Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesSierra Nevada College Lesson Planapi-266778770No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant UnitDocument8 pagesAnimal and Plant Unitapi-252935769No ratings yet
- Earth Science Lesson - PlanDocument3 pagesEarth Science Lesson - Planpedro braulioNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Lesson ExemplarDocument11 pagesBiodiversity Lesson ExemplarNelma Faye MadambaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument14 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceAlren SaberonNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson Planjrm.tinoyNo ratings yet
- Ict 22Document5 pagesIct 22api-250192253No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanluigivallespinpiñeroNo ratings yet
- Friends of Our Environment FridayDocument8 pagesFriends of Our Environment Fridayapi-319166569No ratings yet
- Carlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeDocument3 pagesCarlos Hilado Memorial State CollegeJanine Gevero MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanglifoneaailenekrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanJonas CabusbusanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan WasteDocument9 pagesLesson Plan Wastemydel campehiosNo ratings yet
- Forum 502 ExtractDocument6 pagesForum 502 Extractjmobando1No ratings yet
- A Frogs Skin - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesA Frogs Skin - Lesson Planapi-255425919No ratings yet
- Create To Educate: Title of Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesCreate To Educate: Title of Lesson Planapi-282594826No ratings yet
- Water Systems On Earth Water Systems On Earth: Grade 8 Science Lessons Grade 8 Science LessonsDocument39 pagesWater Systems On Earth Water Systems On Earth: Grade 8 Science Lessons Grade 8 Science Lessonsapi-215899543No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanMark Jay LegoNo ratings yet
- Bio@Lp 2012Document46 pagesBio@Lp 2012Mariah ThezNo ratings yet
- Ross 16te802 Glt1reportDocument9 pagesRoss 16te802 Glt1reportapi-325792607No ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar BiodiversityDocument5 pagesLesson Exemplar BiodiversityArnold C. LasitNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan EvolutionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan EvolutionnorjanahpasagueNo ratings yet
- Environmental BiologyDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Biology1799647611No ratings yet
- Science 9 BiodiversityDocument3 pagesScience 9 BiodiversityJayNo ratings yet
- Mjacksoninstructional Tech UnitDocument11 pagesMjacksoninstructional Tech Unitapi-215826593No ratings yet
- LP 2022Document6 pagesLP 2022Bert RoseteNo ratings yet
- GwapakoDocument2 pagesGwapakoangelinelokinaNo ratings yet
- Ladnscc Assignment 1Document14 pagesLadnscc Assignment 1mbiwan AchareNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan: Lesson Cross CurricularDocument10 pagesUnit Plan: Lesson Cross Curricularapi-311724683No ratings yet
- Title of Unit: Evolution Grade Level: 10th Grade Subject: Biology Time Frame: Five WeeksDocument8 pagesTitle of Unit: Evolution Grade Level: 10th Grade Subject: Biology Time Frame: Five Weeksapi-281582336No ratings yet
- Thursday LessonDocument4 pagesThursday Lessonapi-372343626No ratings yet
- Animal HomesDocument1 pageAnimal Homesapi-218762447No ratings yet
- ProjectDocument26 pagesProjectapi-340166683No ratings yet
- Ubd EcologyDocument13 pagesUbd EcologyPaul Michael Vial Boncayo100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanSantillan Charity MayNo ratings yet
- Snail Unit Plan Lesson 1Document3 pagesSnail Unit Plan Lesson 1api-464689903No ratings yet
- Course Guide - 9 EcologyDocument281 pagesCourse Guide - 9 EcologyNora LeeNo ratings yet
- M6 L6 FinalDocument45 pagesM6 L6 FinalUrban EcoLab CurriculumNo ratings yet
- Science 3Document2 pagesScience 3api-239852387No ratings yet
- Ed508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Template 1Document6 pagesEd508-5e-Lesson-Plan-Template 1api-740167831No ratings yet
- I. Objectives:: Prototype Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 Third Quarter, WeekDocument4 pagesI. Objectives:: Prototype Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 Third Quarter, WeekCherry MaeNo ratings yet
- Tiffany Washington 5e Lesson Plan 1Document8 pagesTiffany Washington 5e Lesson Plan 1api-644963967No ratings yet
- Design DocumentDocument9 pagesDesign Documentapi-208533376No ratings yet
- Learningguide 3rdsustanability 2Document7 pagesLearningguide 3rdsustanability 2api-300007613No ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document3 pagesLesson 5api-709748758No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanluigivallespinpiñeroNo ratings yet
- Weird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionDocument28 pagesWeird & Wild: Teacher Guide Grades 3 - 5 Program DescriptionBecky BrownNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1-3 ReviewDocument2 pagesLesson Plan 1-3 Reviewapi-237688616No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson Planyen yenNo ratings yet
- API 6A Gate ValvesDocument12 pagesAPI 6A Gate ValvesLee Sweningson100% (1)
- (Download PDF) Water Resources of Chile Bonifacio Fernandez Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument40 pages(Download PDF) Water Resources of Chile Bonifacio Fernandez Online Ebook All Chapter PDFannie.cormier901100% (9)
- ScriptDocument7 pagesScriptSaiyam Chaudhary0% (1)
- AA#27 Bitterroot Briar (L2-4) - Expeditious Retreat PressDocument13 pagesAA#27 Bitterroot Briar (L2-4) - Expeditious Retreat PressYankeeinHawaii100% (3)
- The Role of Shopping Malls in An Environment A Case of Oluwole Shopping Mall in Lagos Island Lagos State, NigeriaDocument6 pagesThe Role of Shopping Malls in An Environment A Case of Oluwole Shopping Mall in Lagos Island Lagos State, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- PVC Wire Flexible CablesDocument10 pagesPVC Wire Flexible CablesPrinasen NaiduNo ratings yet
- Question 1. A. Booked B. Missed D. Pronounced: JaneDocument4 pagesQuestion 1. A. Booked B. Missed D. Pronounced: JaneThuận NgyễnNo ratings yet
- Resurgence Issue 260Document84 pagesResurgence Issue 260imperativecureNo ratings yet
- The Artist SpectrumDocument132 pagesThe Artist SpectrumsumendersinghNo ratings yet
- Ess420 Vce Unit 1 Aos 2Document10 pagesEss420 Vce Unit 1 Aos 2api-267133657No ratings yet
- 040 - Ekistics TheoryDocument4 pages040 - Ekistics TheoryAbdurrehman AzeemNo ratings yet
- 17.4 Boiler and Feed-Water TreatmentDocument28 pages17.4 Boiler and Feed-Water Treatmentnomeacuerdo1No ratings yet
- Shell - Lubricants - Product Data GuideDocument20 pagesShell - Lubricants - Product Data GuideRolando DaclanNo ratings yet
- Chapman 2009 NumbersofLivingSpecies Oz World DEHDocument85 pagesChapman 2009 NumbersofLivingSpecies Oz World DEHvero adaroNo ratings yet
- Environmental Weeds of The Wet TropicsDocument94 pagesEnvironmental Weeds of The Wet TropicsSadao MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity by Design Maximising The Biodiversit-Groen Kennisnet 468095Document122 pagesBiodiversity by Design Maximising The Biodiversit-Groen Kennisnet 468095komal shinde100% (1)
- CULTURAL STUDY ChapterDocument17 pagesCULTURAL STUDY Chapterchristeena joseNo ratings yet
- How Natural and Built Environments Impact Human Health: Dr. Nancy WellsDocument4 pagesHow Natural and Built Environments Impact Human Health: Dr. Nancy WellsBettina TiongcoNo ratings yet
- Ore Textures and Wall Rock AlterationDocument6 pagesOre Textures and Wall Rock AlterationIrwan EPNo ratings yet
- Authorial Comments in Tess of D'urbervilles by Thomas HardyDocument4 pagesAuthorial Comments in Tess of D'urbervilles by Thomas HardydilipbaradNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education: History GoalsDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Education: History GoalskhaidhirNo ratings yet
- Presentation About The RA 9147 The LawPhDocument14 pagesPresentation About The RA 9147 The LawPhMarianne R. De TorresNo ratings yet
- Short Moral StoriesDocument24 pagesShort Moral StoriesVarsha RayNo ratings yet
- Grace Lalawmpuii Sailo, EvsDocument177 pagesGrace Lalawmpuii Sailo, Evsatul pandeyNo ratings yet
- Mobilith AW SeriesDocument3 pagesMobilith AW SeriesDavid SalgueroNo ratings yet
- II. Ecoliteracy and The Different ApproachesDocument34 pagesII. Ecoliteracy and The Different Approachesgerrie anne untoNo ratings yet
- Corbett Epithermal 2006 Paper 2nd DraftDocument32 pagesCorbett Epithermal 2006 Paper 2nd DrafthistorysilviaNo ratings yet
- RN Parkins-The Stress Corrosion Cracking of C-MN Steek Ub CO2-HCO3-CO3 Solutions I, Stress Corrosion DataDocument15 pagesRN Parkins-The Stress Corrosion Cracking of C-MN Steek Ub CO2-HCO3-CO3 Solutions I, Stress Corrosion DataAlondra HermosoNo ratings yet
- The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019Document129 pagesThe Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019Hugo Barata GomesNo ratings yet