Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsChild Asd
Child Asd
Uploaded by
Abdualaziz AlmalkiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Daft12eIM - 17 - CH 17Document23 pagesDaft12eIM - 17 - CH 17miah haNo ratings yet
- Defferentiated Lesson Plan (Detailed)Document14 pagesDefferentiated Lesson Plan (Detailed)Jo Celyn90% (10)
- The Trauma of Birth - RowanDocument47 pagesThe Trauma of Birth - RowanWombaten50% (2)
- Behavioural DisordersDocument18 pagesBehavioural DisordersAnsu MaliyakalNo ratings yet
- ADHD - Group PresentationDocument28 pagesADHD - Group PresentationDhayaneeDruAinsleyII100% (1)
- Child, MotorDocument4 pagesChild, MotorAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument1 pageAutism Spectrum DisorderkatNo ratings yet
- Developmental DisordersDocument4 pagesDevelopmental DisordersMary Belle OrtegaNo ratings yet
- AdhdDocument2 pagesAdhdAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder Conduct DisorderDocument1 pageOppositional Defiant Disorder Conduct DisorderkatNo ratings yet
- Developmental & Behavioral DisordersDocument29 pagesDevelopmental & Behavioral DisordersJoko Pratama AtmayudhaNo ratings yet
- Pervasive Developmental DisordersDocument20 pagesPervasive Developmental DisordersHikari 光 Shidou100% (1)
- Neurodevelopmental DisordersDocument3 pagesNeurodevelopmental DisordersJustine BayabosNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent PsychiatryDocument57 pagesChild and Adolescent PsychiatrySajaratul Syifaa'No ratings yet
- Disorders Usually 1 Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, & AdolescenceDocument31 pagesDisorders Usually 1 Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, & AdolescenceShahzad Bashir ShamsNo ratings yet
- Asperger BrochureDocument2 pagesAsperger BrochureGraciela CalderónNo ratings yet
- M A DDocument19 pagesM A DjoycesiosonNo ratings yet
- Disruptive Behaviours IN ChildrenDocument54 pagesDisruptive Behaviours IN Childrenman_sengalNo ratings yet
- Autistic Spectrum Disorders: Prepared By: Dr. Shewikar El Bakry Ass. Prof. of Neuropsychiatry Banha UniversityDocument75 pagesAutistic Spectrum Disorders: Prepared By: Dr. Shewikar El Bakry Ass. Prof. of Neuropsychiatry Banha UniversityChamsonNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument147 pagesAutismcharby12108272No ratings yet
- HFD Slides (1) (Repaired)Document47 pagesHFD Slides (1) (Repaired)Samia Munir100% (3)
- Pervasive Developmental DisordersDocument17 pagesPervasive Developmental DisordersKc ChuaNo ratings yet
- Child and AdolescentDocument89 pagesChild and AdolescentLarry CalivoNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument145 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderDiane Primo50% (2)
- Odd and CDDocument29 pagesOdd and CDRiyaSinghNo ratings yet
- Child Psychiatry Dr. Budi PratitiDocument16 pagesChild Psychiatry Dr. Budi PratitiRed DemonNo ratings yet
- Disorders in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument7 pagesDisorders in Childhood and AdolescenceCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Child Psychiatry1Document21 pagesChild Psychiatry1mariam tarekNo ratings yet
- Copied Y5 Pediatrics Behavior and Emotional Problems in ChildrenDocument50 pagesCopied Y5 Pediatrics Behavior and Emotional Problems in ChildrenAnak mama SayangNo ratings yet
- Autismo 2003Document9 pagesAutismo 2003Victor EscobarNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument26 pagesAutismminangsung minangnengNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior 12 2016Document15 pagesHuman Behavior 12 2016aalijahabbasNo ratings yet
- Disorders in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument6 pagesDisorders in Childhood and AdolescenceCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- INE302 Autism Unit 4 NewDocument30 pagesINE302 Autism Unit 4 NewValencia MohlalaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of ChildhoodDocument61 pagesDisorders of ChildhoodEdom TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Disabilities: Severe and ProfoundDocument31 pagesIntellectual Disabilities: Severe and ProfoundSharza MahrukhNo ratings yet
- Impulsiveness and Inability To Delay Gratification Are CharacteristicDocument1 pageImpulsiveness and Inability To Delay Gratification Are CharacteristickatNo ratings yet
- Anxiety I and II - 2023Document96 pagesAnxiety I and II - 2023annaNo ratings yet
- Case Conference: Autism: Keanu Fontanilla and Lance Gamiao October 31, 2014Document4 pagesCase Conference: Autism: Keanu Fontanilla and Lance Gamiao October 31, 2014Justine UyNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Disorders PDFDocument43 pagesChild and Adolescent Disorders PDFPreslee DulnuanNo ratings yet
- Psychopathologyslideshare 150721015626 Lva1 App6891Document62 pagesPsychopathologyslideshare 150721015626 Lva1 App6891Arun ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- PERSONALITYDocument4 pagesPERSONALITYJustine BayabosNo ratings yet
- Normal MilestonesDocument20 pagesNormal MilestonesSwetha PonugotiNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument25 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderDrSk Samim100% (1)
- Shanz - Pedia 1.02 ASD, ADHD, LDDocument5 pagesShanz - Pedia 1.02 ASD, ADHD, LDPetrina XuNo ratings yet
- FINAL FlipbookDocument14 pagesFINAL FlipbookTrinity PikeNo ratings yet
- Behavior Management PresentationDocument72 pagesBehavior Management PresentationDasta E Lajpal E Ali DanyoreNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia 1.01Document7 pagesShanz - Pedia 1.01Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument6 pagesAutismapi-367611011No ratings yet
- Approach To Developmental Delay: Prof Rashmi Kumar Department of Pediatrics KgmuDocument35 pagesApproach To Developmental Delay: Prof Rashmi Kumar Department of Pediatrics KgmuRishu BujjuNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum Disorders.Document38 pagesAutism Spectrum Disorders.AnoobisNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Reviewer-1Document4 pagesTherapeutic Communication Reviewer-1Amber BlodduweddNo ratings yet
- Promoting Positive Parenting in Children With Neurodevelopmental DisorderDocument20 pagesPromoting Positive Parenting in Children With Neurodevelopmental DisordereeshaNo ratings yet
- A.2 NormalDev 2019Document34 pagesA.2 NormalDev 2019Kibru le EyesusNo ratings yet
- Child DisordersDocument111 pagesChild Disorderspriyanka rajNo ratings yet
- Childhood DisorderDocument7 pagesChildhood DisorderJerryNo ratings yet
- Attention Deficient Hyperactivity Disorders Dr. Rabia Ramadan GajumDocument24 pagesAttention Deficient Hyperactivity Disorders Dr. Rabia Ramadan GajumDr rasha FoadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Disorders of ChildhoodAdolescencePDF - 240222 - 161526Document43 pagesLecture 6 Disorders of ChildhoodAdolescencePDF - 240222 - 161526hui xin ngNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Sports For CWSN (Children With Special Needs - (Divyanag)Document19 pagesPhysical Education and Sports For CWSN (Children With Special Needs - (Divyanag)Saroj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder in CAPDocument73 pagesAnxiety Disorder in CAPkavitha selvam100% (1)
- Chapter 13 - Personality DisordersDocument15 pagesChapter 13 - Personality DisordersnayaddouaihyNo ratings yet
- SCHIZOPHRENIADocument3 pagesSCHIZOPHRENIAsheynmalubayNo ratings yet
- Dudley Dementia Prescribing Guidance Final 1626174181Document9 pagesDudley Dementia Prescribing Guidance Final 1626174181Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 4Document5 pagesRole Play 4Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Addiction SummeryDocument2 pagesAddiction SummeryAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Attitudes of Physicians Toward Forensic Psychiatry in Saudi Arabia - Saudi Medical JournalDocument22 pagesKnowledge and Attitudes of Physicians Toward Forensic Psychiatry in Saudi Arabia - Saudi Medical JournalAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 5Document5 pagesRole Play 5Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 6Document5 pagesRole Play 6Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 4632 - Lecture (8) Forensic PsychiatryDocument13 pages4632 - Lecture (8) Forensic PsychiatryAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Memory Loss FullDocument252 pagesMemory Loss FullAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Admissions - The First Law in Saudi Arabia - Forensic Psychiatry InstituteDocument9 pagesPsychiatric Admissions - The First Law in Saudi Arabia - Forensic Psychiatry InstituteAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- E300630 FullDocument8 pagesE300630 FullAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet - Brain Map and FunctionsDocument4 pagesFact Sheet - Brain Map and FunctionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument3 pagesAntipsychoticsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- FULLTEXT01Document134 pagesFULLTEXT01Abdualaziz Almalki100% (1)
- DrugofchoiceDocument16 pagesDrugofchoiceAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 9-12 Qs Test PreparationDocument1 page9-12 Qs Test PreparationAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- CYP and Smoking Drug InteractionsDocument6 pagesCYP and Smoking Drug InteractionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Child Development 2020-2021Document40 pagesChild Development 2020-2021Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Important TablesDocument22 pagesKaplan Important TablesAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ExamDocument2 pagesAbnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ExamAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Neurocovid Pharmacological Recommendations For Delirium Associated With COVID-19Document12 pagesNeurocovid Pharmacological Recommendations For Delirium Associated With COVID-19Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- ACLP How To Guide Doing A Consult 2020Document5 pagesACLP How To Guide Doing A Consult 2020Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 4-8 Answer Test PreparationDocument1 page4-8 Answer Test PreparationAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Medication Potential Use in COVID19 DeliriumDocument1 pageMedication Potential Use in COVID19 DeliriumAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Epidemiology (Kaplan)Document2 pagesPsychiatric Epidemiology (Kaplan)Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- PrognosisDocument7 pagesPrognosisAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Validation and Cultural Adaptation of The Arabic Versions of The Mini-Mental Status Examination - 2 and Mini-Cog TestDocument10 pagesValidation and Cultural Adaptation of The Arabic Versions of The Mini-Mental Status Examination - 2 and Mini-Cog TestAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Piaget's Developmental StagesDocument1 pageSummary of Piaget's Developmental StagesAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Llr1i: Table 4.1 - 3 Classification of Defense MechanismsDocument2 pagesLlr1i: Table 4.1 - 3 Classification of Defense MechanismsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Red FlagsDocument1 pageDevelopmental Red FlagsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Lesions Location in Brain and AffectsDocument1 pageLesions Location in Brain and AffectsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Francoys Gagne MDDT. Texto en InglésDocument6 pagesFrancoys Gagne MDDT. Texto en InglésBiblioteca Altas Capacidades /Aptitudes sobresalientes...100% (1)
- Uts Lesson 2Document6 pagesUts Lesson 2ANDREA LOUISE ELCANONo ratings yet
- Introduction To Community B.SC Ii Yr CHNDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Community B.SC Ii Yr CHNJOSEPH IVO A. AGUINALDONo ratings yet
- A Psychoanalytic Approach To The Character of KurtzDocument41 pagesA Psychoanalytic Approach To The Character of KurtzSuit Sof100% (17)
- Curriculum Map Sa Edukasyon Sa Pagpapahalaga 7Document10 pagesCurriculum Map Sa Edukasyon Sa Pagpapahalaga 7Cloue Faye I. BasalloNo ratings yet
- 90 Tesfaye AlemayehuDocument8 pages90 Tesfaye AlemayehuchuchuNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument13 pagesContent ServerDorin TriffNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Conceptual FieldsDocument12 pagesThe Theory of Conceptual FieldsAmerika Sánchez LeónNo ratings yet
- Session No. 2 - Cultural Environment and International BusinessDocument23 pagesSession No. 2 - Cultural Environment and International BusinessHeshan Nikitha AmarasinghaNo ratings yet
- Risk Factor of Adolescent AggressionDocument9 pagesRisk Factor of Adolescent AggressionAsih Nor ZahidahNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky TheoryDocument3 pagesVygotsky Theoryvaibhavi BarkaNo ratings yet
- Leadership Amidst Chaos: How Great Managers Transcend Chaos, Lean Economic Times, and Lead Their Staff To SuccessDocument6 pagesLeadership Amidst Chaos: How Great Managers Transcend Chaos, Lean Economic Times, and Lead Their Staff To SuccessImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz and AssignmentDocument5 pagesLong Quiz and AssignmentFai LanelNo ratings yet
- Proposal PTK Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesProposal PTK Bahasa Inggrispepen sunaryaNo ratings yet
- Eric MannDocument130 pagesEric MannMaliga IgaNo ratings yet
- Industrial PsychologyDocument75 pagesIndustrial PsychologyAlam Tareque100% (2)
- CHAPTER 4 Outdoor Learning Environment in ECEDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 4 Outdoor Learning Environment in ECENur AinisyahirahNo ratings yet
- JIN SHIN JYUTSU Three Method CorrectionsDocument2 pagesJIN SHIN JYUTSU Three Method CorrectionsWalfutureNo ratings yet
- Brief COPE - Muller & Spitz (2003)Document10 pagesBrief COPE - Muller & Spitz (2003)patrick telismaNo ratings yet
- Employee Performance Improvement Strategy PresentationDocument15 pagesEmployee Performance Improvement Strategy PresentationCalmly VetgansNo ratings yet
- Nurainna Syuhada Binti Bahri 2021117493 BA2471ADocument8 pagesNurainna Syuhada Binti Bahri 2021117493 BA2471ANurainna SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- LifespanDevelopment 05 EarlyChildhoodDocument38 pagesLifespanDevelopment 05 EarlyChildhoodjapstudyaccNo ratings yet
- "Conditioned Reflexes. Inhibition of Conditioned Reflexes.": Vinnitsia - 2013Document11 pages"Conditioned Reflexes. Inhibition of Conditioned Reflexes.": Vinnitsia - 2013Oumaima EttalibNo ratings yet
- Child Sexual AbuseDocument8 pagesChild Sexual AbuseSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- Impact of Public Examination System On Teaching and LearningDocument12 pagesImpact of Public Examination System On Teaching and LearningZahida Afzal100% (1)
- Values Vs SkillsDocument13 pagesValues Vs SkillsInstantNo ratings yet
- The Art of Listening in CommunicationDocument4 pagesThe Art of Listening in CommunicationZahid Mushtaq100% (1)
Child Asd
Child Asd
Uploaded by
Abdualaziz Almalki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Child asd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesChild Asd
Child Asd
Uploaded by
Abdualaziz AlmalkiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
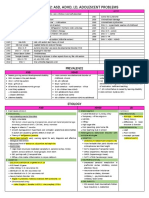
Criteria: Up to 25% of ASD cases some language develops & is
subsequently lost- Decline in social interaction between 1st
A. Persistent deficit in social communication manifested by & 2nd year of life.
• ≠emotional reciprocity
• ≠nonverbal communication Bio-Markers:
• ≠understanding relationships).
• ↑platelet serotonin→ 1st identified.
Specify current severity: • ↑mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin
• GABA alteration
Level I→ require support, lack of support cause noticeable≠ • ↑ total brain volume
Level II→ require substantial support • Head circumference normal→ developed macrocephaly
• ↑ amygdala size in 1st years→ decrease over time
Level III→ require very substantial support • Striatum enlarged, +ve correlation between it’s size and
presence of repetitive behaviors.
B. Restricted repetitive pattern of behaviors 2\4 • Rt. Temporal lobe→ theory of mind= ability to
• stereotyped repetitive behaviors attribute emotional state of others, & to oneself.
• insistence on sameness & inflexible • Frontal lobe atypical activation→ social perception &
• strong attachment & fixed circumscribed emotional reasoning.
• hyper or hypo reactivity to sensory inputs. • Lt. frontal region→ memory & language-based tasks
Specify current severity: Clinical observations:
Level I→ require support • Child è ASD focus on mouth rather than eye contact.
• Extreme anxiety if usual routine is disturbed
Level II→ require substantial support
• Toys not used typically→ manipulated in ritualistic way
Level III→ require very substantial support • Enjoy spinning, banging, & watching water flowing.
• If è sever ID→ ↑ self-injury behaviors
C. Present in early developmental period • ↑ dermatological≠ & risk of infection than general pop.
D. Causes significant impairment in function. • may have special ability→ math, music, hyperlexia
E. Exclude ID
Assessment Tools:
Specify if:
➢ADOS, autism diagnostic observation schedule
• With- without ID ➢CARS, childhood autism rating scale
• With- without language impairment
• è known medical, congenital or environmental problem Rett syndrome:
• è neurodevelopmental, mental, behavioral problem
▪ normal develop. Till 6m→ progressive decline.
• è catatonia
▪ head circumference normal→ @ 1Y decelerate
change in diagnosis in DSM5: ▪ seem primarily in ♀
▪ loss of hand movement, previously acquired speech
• were 5 discrete disorders→ autistic disorder, Asperger, skills, irregular respiration while awake only, scoliosis
childhood disintegrative disorder, Rett syndrome, & ▪ seizure up to 75%
pervasive developmental disorder NOS.
• rather than 3 categories of syx. (social, language, childhood disintegrative disorder:
repetitive behaviors) → there are now only 2 (social
▪ called Heller’s syndrome& disintegrative psychosis
communication & repetitive behaviors).
▪ normal develop. Till 2Y→loss of (2\5): bladder bowel
• If +ve social communication≠ & criterion B not met→
control, social, language, play, motor skills.
diagnosis is social communication disorder.
▪ ♂8:♀1 – associated è seizure
NB. “early infantile autism” described by Kanner
Asperger’s Disorder:
Epidemiology: 1%- or 14\1000- ♂4:♀1- ♀ è ID>♂-
▪ 2\3→ ≠nonverbal communication, ≠peer relationships,
prevalence in siblings in APA 4.5%- Kaplan up to 50%
restricted interest.
siblings of child è ASD ↑ risk of other developmental≠
▪ NO language or cognitive ≠
≥ 1\3 è comorbid seizure- grandma 20%- 30% è ID
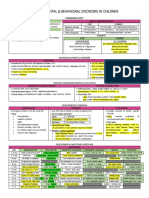
Formulation:
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors
• Genetic • Neglect & maltreatment
➢ Fragile X syndrome: FMNR1 gene, X linked recessive, large face & ear, • ↑ academic & social demands
macroorchidism, ASD+ID
➢ Tuberous sclerosis: autosomal dominant, multiple benign tumor, ASD+ID+seizure
➢ Other chromosomes include: 2-7-16-17
• Advanced maternal & paternal age
• Gestational bleeding, or diabetes, ABO- Rh incompatibility
• First born baby
• Birth complication: trauma, umbilical cord complication, hypoxia
• Fetal distress, low birth wt., small gestational age, low Abgar score
• Infection: Rubella, Toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus.
• Teratogenic: lead- valproic acid
Perpetuating Factors Prognostic Factors
• Lack of support- psychosocial deprivation • Presence of family support→ good
• Presence of comorbidity (medical- mental - behavioral) • Early intensive behavioral intervention→ good
• Children è IQ > 70 & average adaptive skills→ good
• Presence of language disorder→ poor
• Severity
• Presence of comorbid conditions
Management:
Social Psychological pharmacological
❖ Social skill training ❖ Psychoeducation & support to the family ❖ Irritability:
❖ ↑long term skills in independent living ❖ ↓irritable & disturbed behaviors • Risperidone→ 0.5-1.5mg
❖ ↑socially acceptable behaviors ❖ Behavioral therapy for repetitive behavior, self-injury • Aripiprazole→ 5-15mg
❖ Speech therapy if needed ❖ Behavioral therapy for insomnia if present ❖ ADHD like syx:
❖ CBT for anxiety, depression, or OCD if present • stimulant→ methylphenidate
• non-stimulant→ atomoxetine
• clonidine
❖ insomnia: melatonin
❖ mood or OCD: SSRIs
Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS)
The Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) is a 15-items behavioral rating scale developed to identify children with autism and to
categorize these behaviors from mild to moderate to severe. The total CARS score may range from a low of 15 (obtained when the child¹s
behavior is rated as falling within normal limits on all 15 scales) to a high of 60 (obtained when the child¹s behavior is rated as severely
abnormal on all 15 scales). The score represents placement on a continuum: the lower the score, the fewer autistic behaviors the child
exhibits; the higher the score, the more autistic behaviors the child exhibits.
School Rating Completed by …………. The scores were as follows:
Relating to People (1-2-3-4)
Emotional Response (1-2-3-4)
Imitation (1-2-3-4)
Body Use (1-2-3-4)
Object Use (1-2-3-4)
Adaptation to Change (1-2-3-4)
Listening Response (1-2-3-4)
Taste, Smell, Touch (1-2-3-4)
Visual Response (1-2-3-4)
Fear or Nervous (1-2-3-4)
Verbal Communication (1-2-3-4)
Activity Level (1-2-3-4)
Nonverbal Communication (1-2-3-4)
Level & Consistency of Intellectual Response (1-2-3-4)
General Impression (1-2-3-4)
Total Score XX
You might also like
- Daft12eIM - 17 - CH 17Document23 pagesDaft12eIM - 17 - CH 17miah haNo ratings yet
- Defferentiated Lesson Plan (Detailed)Document14 pagesDefferentiated Lesson Plan (Detailed)Jo Celyn90% (10)
- The Trauma of Birth - RowanDocument47 pagesThe Trauma of Birth - RowanWombaten50% (2)
- Behavioural DisordersDocument18 pagesBehavioural DisordersAnsu MaliyakalNo ratings yet
- ADHD - Group PresentationDocument28 pagesADHD - Group PresentationDhayaneeDruAinsleyII100% (1)
- Child, MotorDocument4 pagesChild, MotorAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument1 pageAutism Spectrum DisorderkatNo ratings yet
- Developmental DisordersDocument4 pagesDevelopmental DisordersMary Belle OrtegaNo ratings yet
- AdhdDocument2 pagesAdhdAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder Conduct DisorderDocument1 pageOppositional Defiant Disorder Conduct DisorderkatNo ratings yet
- Developmental & Behavioral DisordersDocument29 pagesDevelopmental & Behavioral DisordersJoko Pratama AtmayudhaNo ratings yet
- Pervasive Developmental DisordersDocument20 pagesPervasive Developmental DisordersHikari 光 Shidou100% (1)
- Neurodevelopmental DisordersDocument3 pagesNeurodevelopmental DisordersJustine BayabosNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent PsychiatryDocument57 pagesChild and Adolescent PsychiatrySajaratul Syifaa'No ratings yet
- Disorders Usually 1 Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, & AdolescenceDocument31 pagesDisorders Usually 1 Diagnosed in Infancy, Childhood, & AdolescenceShahzad Bashir ShamsNo ratings yet
- Asperger BrochureDocument2 pagesAsperger BrochureGraciela CalderónNo ratings yet
- M A DDocument19 pagesM A DjoycesiosonNo ratings yet
- Disruptive Behaviours IN ChildrenDocument54 pagesDisruptive Behaviours IN Childrenman_sengalNo ratings yet
- Autistic Spectrum Disorders: Prepared By: Dr. Shewikar El Bakry Ass. Prof. of Neuropsychiatry Banha UniversityDocument75 pagesAutistic Spectrum Disorders: Prepared By: Dr. Shewikar El Bakry Ass. Prof. of Neuropsychiatry Banha UniversityChamsonNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument147 pagesAutismcharby12108272No ratings yet
- HFD Slides (1) (Repaired)Document47 pagesHFD Slides (1) (Repaired)Samia Munir100% (3)
- Pervasive Developmental DisordersDocument17 pagesPervasive Developmental DisordersKc ChuaNo ratings yet
- Child and AdolescentDocument89 pagesChild and AdolescentLarry CalivoNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument145 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderDiane Primo50% (2)
- Odd and CDDocument29 pagesOdd and CDRiyaSinghNo ratings yet
- Child Psychiatry Dr. Budi PratitiDocument16 pagesChild Psychiatry Dr. Budi PratitiRed DemonNo ratings yet
- Disorders in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument7 pagesDisorders in Childhood and AdolescenceCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Child Psychiatry1Document21 pagesChild Psychiatry1mariam tarekNo ratings yet
- Copied Y5 Pediatrics Behavior and Emotional Problems in ChildrenDocument50 pagesCopied Y5 Pediatrics Behavior and Emotional Problems in ChildrenAnak mama SayangNo ratings yet
- Autismo 2003Document9 pagesAutismo 2003Victor EscobarNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument26 pagesAutismminangsung minangnengNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior 12 2016Document15 pagesHuman Behavior 12 2016aalijahabbasNo ratings yet
- Disorders in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument6 pagesDisorders in Childhood and AdolescenceCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- INE302 Autism Unit 4 NewDocument30 pagesINE302 Autism Unit 4 NewValencia MohlalaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of ChildhoodDocument61 pagesDisorders of ChildhoodEdom TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Disabilities: Severe and ProfoundDocument31 pagesIntellectual Disabilities: Severe and ProfoundSharza MahrukhNo ratings yet
- Impulsiveness and Inability To Delay Gratification Are CharacteristicDocument1 pageImpulsiveness and Inability To Delay Gratification Are CharacteristickatNo ratings yet
- Anxiety I and II - 2023Document96 pagesAnxiety I and II - 2023annaNo ratings yet
- Case Conference: Autism: Keanu Fontanilla and Lance Gamiao October 31, 2014Document4 pagesCase Conference: Autism: Keanu Fontanilla and Lance Gamiao October 31, 2014Justine UyNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Disorders PDFDocument43 pagesChild and Adolescent Disorders PDFPreslee DulnuanNo ratings yet
- Psychopathologyslideshare 150721015626 Lva1 App6891Document62 pagesPsychopathologyslideshare 150721015626 Lva1 App6891Arun ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- PERSONALITYDocument4 pagesPERSONALITYJustine BayabosNo ratings yet
- Normal MilestonesDocument20 pagesNormal MilestonesSwetha PonugotiNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument25 pagesAutism Spectrum DisorderDrSk Samim100% (1)
- Shanz - Pedia 1.02 ASD, ADHD, LDDocument5 pagesShanz - Pedia 1.02 ASD, ADHD, LDPetrina XuNo ratings yet
- FINAL FlipbookDocument14 pagesFINAL FlipbookTrinity PikeNo ratings yet
- Behavior Management PresentationDocument72 pagesBehavior Management PresentationDasta E Lajpal E Ali DanyoreNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia 1.01Document7 pagesShanz - Pedia 1.01Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument6 pagesAutismapi-367611011No ratings yet
- Approach To Developmental Delay: Prof Rashmi Kumar Department of Pediatrics KgmuDocument35 pagesApproach To Developmental Delay: Prof Rashmi Kumar Department of Pediatrics KgmuRishu BujjuNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum Disorders.Document38 pagesAutism Spectrum Disorders.AnoobisNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Reviewer-1Document4 pagesTherapeutic Communication Reviewer-1Amber BlodduweddNo ratings yet
- Promoting Positive Parenting in Children With Neurodevelopmental DisorderDocument20 pagesPromoting Positive Parenting in Children With Neurodevelopmental DisordereeshaNo ratings yet
- A.2 NormalDev 2019Document34 pagesA.2 NormalDev 2019Kibru le EyesusNo ratings yet
- Child DisordersDocument111 pagesChild Disorderspriyanka rajNo ratings yet
- Childhood DisorderDocument7 pagesChildhood DisorderJerryNo ratings yet
- Attention Deficient Hyperactivity Disorders Dr. Rabia Ramadan GajumDocument24 pagesAttention Deficient Hyperactivity Disorders Dr. Rabia Ramadan GajumDr rasha FoadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Disorders of ChildhoodAdolescencePDF - 240222 - 161526Document43 pagesLecture 6 Disorders of ChildhoodAdolescencePDF - 240222 - 161526hui xin ngNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Sports For CWSN (Children With Special Needs - (Divyanag)Document19 pagesPhysical Education and Sports For CWSN (Children With Special Needs - (Divyanag)Saroj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder in CAPDocument73 pagesAnxiety Disorder in CAPkavitha selvam100% (1)
- Chapter 13 - Personality DisordersDocument15 pagesChapter 13 - Personality DisordersnayaddouaihyNo ratings yet
- SCHIZOPHRENIADocument3 pagesSCHIZOPHRENIAsheynmalubayNo ratings yet
- Dudley Dementia Prescribing Guidance Final 1626174181Document9 pagesDudley Dementia Prescribing Guidance Final 1626174181Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 4Document5 pagesRole Play 4Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Addiction SummeryDocument2 pagesAddiction SummeryAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Attitudes of Physicians Toward Forensic Psychiatry in Saudi Arabia - Saudi Medical JournalDocument22 pagesKnowledge and Attitudes of Physicians Toward Forensic Psychiatry in Saudi Arabia - Saudi Medical JournalAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 5Document5 pagesRole Play 5Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Role Play 6Document5 pagesRole Play 6Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 4632 - Lecture (8) Forensic PsychiatryDocument13 pages4632 - Lecture (8) Forensic PsychiatryAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Memory Loss FullDocument252 pagesMemory Loss FullAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Admissions - The First Law in Saudi Arabia - Forensic Psychiatry InstituteDocument9 pagesPsychiatric Admissions - The First Law in Saudi Arabia - Forensic Psychiatry InstituteAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- E300630 FullDocument8 pagesE300630 FullAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet - Brain Map and FunctionsDocument4 pagesFact Sheet - Brain Map and FunctionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- AntipsychoticsDocument3 pagesAntipsychoticsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- FULLTEXT01Document134 pagesFULLTEXT01Abdualaziz Almalki100% (1)
- DrugofchoiceDocument16 pagesDrugofchoiceAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 9-12 Qs Test PreparationDocument1 page9-12 Qs Test PreparationAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- CYP and Smoking Drug InteractionsDocument6 pagesCYP and Smoking Drug InteractionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Child Development 2020-2021Document40 pagesChild Development 2020-2021Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Kaplan Important TablesDocument22 pagesKaplan Important TablesAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ExamDocument2 pagesAbnormal Involuntary Movement Scale ExamAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Neurocovid Pharmacological Recommendations For Delirium Associated With COVID-19Document12 pagesNeurocovid Pharmacological Recommendations For Delirium Associated With COVID-19Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- ACLP How To Guide Doing A Consult 2020Document5 pagesACLP How To Guide Doing A Consult 2020Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- 4-8 Answer Test PreparationDocument1 page4-8 Answer Test PreparationAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Medication Potential Use in COVID19 DeliriumDocument1 pageMedication Potential Use in COVID19 DeliriumAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Epidemiology (Kaplan)Document2 pagesPsychiatric Epidemiology (Kaplan)Abdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- PrognosisDocument7 pagesPrognosisAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Validation and Cultural Adaptation of The Arabic Versions of The Mini-Mental Status Examination - 2 and Mini-Cog TestDocument10 pagesValidation and Cultural Adaptation of The Arabic Versions of The Mini-Mental Status Examination - 2 and Mini-Cog TestAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Piaget's Developmental StagesDocument1 pageSummary of Piaget's Developmental StagesAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Llr1i: Table 4.1 - 3 Classification of Defense MechanismsDocument2 pagesLlr1i: Table 4.1 - 3 Classification of Defense MechanismsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Red FlagsDocument1 pageDevelopmental Red FlagsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Lesions Location in Brain and AffectsDocument1 pageLesions Location in Brain and AffectsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Francoys Gagne MDDT. Texto en InglésDocument6 pagesFrancoys Gagne MDDT. Texto en InglésBiblioteca Altas Capacidades /Aptitudes sobresalientes...100% (1)
- Uts Lesson 2Document6 pagesUts Lesson 2ANDREA LOUISE ELCANONo ratings yet
- Introduction To Community B.SC Ii Yr CHNDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Community B.SC Ii Yr CHNJOSEPH IVO A. AGUINALDONo ratings yet
- A Psychoanalytic Approach To The Character of KurtzDocument41 pagesA Psychoanalytic Approach To The Character of KurtzSuit Sof100% (17)
- Curriculum Map Sa Edukasyon Sa Pagpapahalaga 7Document10 pagesCurriculum Map Sa Edukasyon Sa Pagpapahalaga 7Cloue Faye I. BasalloNo ratings yet
- 90 Tesfaye AlemayehuDocument8 pages90 Tesfaye AlemayehuchuchuNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument13 pagesContent ServerDorin TriffNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Conceptual FieldsDocument12 pagesThe Theory of Conceptual FieldsAmerika Sánchez LeónNo ratings yet
- Session No. 2 - Cultural Environment and International BusinessDocument23 pagesSession No. 2 - Cultural Environment and International BusinessHeshan Nikitha AmarasinghaNo ratings yet
- Risk Factor of Adolescent AggressionDocument9 pagesRisk Factor of Adolescent AggressionAsih Nor ZahidahNo ratings yet
- Vygotsky TheoryDocument3 pagesVygotsky Theoryvaibhavi BarkaNo ratings yet
- Leadership Amidst Chaos: How Great Managers Transcend Chaos, Lean Economic Times, and Lead Their Staff To SuccessDocument6 pagesLeadership Amidst Chaos: How Great Managers Transcend Chaos, Lean Economic Times, and Lead Their Staff To SuccessImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz and AssignmentDocument5 pagesLong Quiz and AssignmentFai LanelNo ratings yet
- Proposal PTK Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesProposal PTK Bahasa Inggrispepen sunaryaNo ratings yet
- Eric MannDocument130 pagesEric MannMaliga IgaNo ratings yet
- Industrial PsychologyDocument75 pagesIndustrial PsychologyAlam Tareque100% (2)
- CHAPTER 4 Outdoor Learning Environment in ECEDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 4 Outdoor Learning Environment in ECENur AinisyahirahNo ratings yet
- JIN SHIN JYUTSU Three Method CorrectionsDocument2 pagesJIN SHIN JYUTSU Three Method CorrectionsWalfutureNo ratings yet
- Brief COPE - Muller & Spitz (2003)Document10 pagesBrief COPE - Muller & Spitz (2003)patrick telismaNo ratings yet
- Employee Performance Improvement Strategy PresentationDocument15 pagesEmployee Performance Improvement Strategy PresentationCalmly VetgansNo ratings yet
- Nurainna Syuhada Binti Bahri 2021117493 BA2471ADocument8 pagesNurainna Syuhada Binti Bahri 2021117493 BA2471ANurainna SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- LifespanDevelopment 05 EarlyChildhoodDocument38 pagesLifespanDevelopment 05 EarlyChildhoodjapstudyaccNo ratings yet
- "Conditioned Reflexes. Inhibition of Conditioned Reflexes.": Vinnitsia - 2013Document11 pages"Conditioned Reflexes. Inhibition of Conditioned Reflexes.": Vinnitsia - 2013Oumaima EttalibNo ratings yet
- Child Sexual AbuseDocument8 pagesChild Sexual AbuseSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- Impact of Public Examination System On Teaching and LearningDocument12 pagesImpact of Public Examination System On Teaching and LearningZahida Afzal100% (1)
- Values Vs SkillsDocument13 pagesValues Vs SkillsInstantNo ratings yet
- The Art of Listening in CommunicationDocument4 pagesThe Art of Listening in CommunicationZahid Mushtaq100% (1)