Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pe 8
Pe 8
Uploaded by
Arul AnandanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pe 8
Pe 8
Uploaded by
Arul AnandanCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Electronics Laboratory (EE 33006)
STUDY OF BASIC TRANSISTOR CONVERTERS
Object:
1. To study a forward converter (Buck).
2. To Study a fly-back converter (Boost).
3. To study a CUK converter (Buck-Boost).
APPARATUS :
1. Experimental Set-up.
2. Rheostat 85Ω.
3. 0 – 30V, 2A Power Supply.
4. Oscilloscope (Double Trace).
PROcEDURE :
A. TO STUDY A FORWARD (BUCK) CONVERTER.
Study the Mosfet used in the circuit. Look up at manual and note the circuit
associated with the mosfet. Note all ratings.
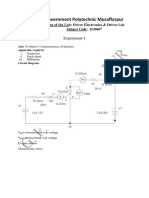
Connect components on the panel as shown in fig. P.E. 14.1. By controlling
the potentiometers on the front panel. Set the driving signal at the base of the
power Transitor to about 30Khz and a low Duty ratio.
Department of Electrical Engineering
Power Electronics Laboratory (EE 33006)
A. With Duty ratio from 0.1 to 0.9 in nine steps note the output DC voltage. Note
for some of these cases voltage across all power components on the panel. The
load current should always be continuous. Keep track of it by observing
inductor voltage. It should never come to Zero (instantaneously). In case it
does come down to zero, adjust load to make current continuous again.
Note the input current waveform for any two values of D.R.
B. With D. R. held at 0.1, adjust load circuit and Tabulate V DCout and I DC ( Load ) .
Repeat with D.R. 2.4, 0.8.
B. FLY – BACK (BOOST) CONVERTER
Connect up the circuit as in Fig. P. E. 14.2. Repeat the steps in part A. The current
should still be continuous. Therefore note the voltage across the inductor and take
steps as in ‘A’.
C. (a) BUCK – BOOST CONVERTER
(b) CUK CONVERTER
Department of Electrical Engineering
Power Electronics Laboratory (EE 33006)
(a) Connect up circuit as in Fig. P.E 14.3. Repeat as in A & B, again
keeping track of the continuity of the current through L. Note
waveforms and observations of D. R. and output DC avg. voltage.
Observe input current waveform and mosfet voltage.
(b) Repeat as above connect and external L2 . Current in both inductors
should be continuous now. C2 is the Non-polarised one of the panel.
Questions :
1. Why are the currents required to remain constant in the experiments?
2. Which circuits allow a continuous input current?
3. Differentiate between the two types of buck-boost converters.
Department of Electrical Engineering
You might also like
- Doble TDR900 User GuideDocument78 pagesDoble TDR900 User GuideJavier Jose Rodriguez50% (2)
- Lab File Basics of Electronics & Electrical Engg. (For PTU B.Tech. 1st Year)Document49 pagesLab File Basics of Electronics & Electrical Engg. (For PTU B.Tech. 1st Year)Cutie33% (3)
- Analog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Lab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticaDocument8 pagesLab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticageovannyNo ratings yet
- Student Workbook PDFDocument103 pagesStudent Workbook PDFCarbon Nano TubeNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Single-Phase Rect2Document6 pagesExp 2 Single-Phase Rect2usmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE852Document20 pagesLab Manual EE852Uzair Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- ECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument20 pagesECCE4466: Power Electronics Student Lab Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineeringsenpai_mendozaNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 Single-Phase Rect1Document9 pagesExp 1 Single-Phase Rect1usmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Edc Lab ManualDocument70 pagesEdc Lab ManualreneeshczNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Three-Phase RectDocument8 pagesExp 3 Three-Phase RectusmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: TheoryDocument9 pagesExperiment # 1: P-N Junction Diode: Theorypoonginithi040% (1)
- Exp 8 Buck ConverterDocument7 pagesExp 8 Buck Converterusmpowerlab50% (2)
- Exp 6 Thyristor 1phase Rect PDFDocument6 pagesExp 6 Thyristor 1phase Rect PDFusmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science and Technology University Collage of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering Department of Electromechanical EngineeringDocument6 pagesAddis Ababa Science and Technology University Collage of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering Department of Electromechanical EngineeringHanan ShayiboNo ratings yet
- Lab PE1Document7 pagesLab PE1Yuci IcuyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE851 PDFDocument20 pagesLab Manual EE851 PDFswarnasrikNo ratings yet
- EEL2026-LabsheetDocument23 pagesEEL2026-LabsheetchandraNo ratings yet
- Aero Lab Manual 2014-2015Document23 pagesAero Lab Manual 2014-2015Muthyala AkhilNo ratings yet
- PH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexDocument28 pagesPH 411 Physics Laboratory I (Electronics) : Instruction Manual IndexReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExperimentDocument7 pagesLaboratory ExperimentFsaskrn XxNo ratings yet
- Expt2 - Single Phase Uncontrolled (Diode) RectifierDocument4 pagesExpt2 - Single Phase Uncontrolled (Diode) RectifierORK BUNSOKRAKMUNYNo ratings yet
- Electric Machines LaboratoryDocument44 pagesElectric Machines Laboratory11mustafa.mNo ratings yet
- EE331 Lab 2 v2Document11 pagesEE331 Lab 2 v2SonDinhQuangNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument41 pagesLab ManualSyaoran7Li80% (5)
- Solid States Final TestDocument7 pagesSolid States Final TestRickel RoweNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Full Wave Bridge ConverterDocument4 pages3 Phase Full Wave Bridge Convertersubhasishpodder100% (1)
- Lab ManualDocument56 pagesLab ManualNishant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- LAB 13 To Investigate Double Bus-Bar Coupling and Switching Sequence For Disconnectors and Power Circuit BreakersDocument5 pagesLAB 13 To Investigate Double Bus-Bar Coupling and Switching Sequence For Disconnectors and Power Circuit BreakersFARYYAD RANANo ratings yet
- Lab 09FDocument5 pagesLab 09FUmar AyubNo ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument70 pagesAEC Lab ManualRohan BoseNo ratings yet
- 2011 Important PDFDocument6 pages2011 Important PDFShaheer DurraniNo ratings yet
- Prelab (To Be Completed INDIVIDUALLY) : Lab 2 - Transformer CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesPrelab (To Be Completed INDIVIDUALLY) : Lab 2 - Transformer CharacteristicshotboangaNo ratings yet
- EEC ActivityDocument19 pagesEEC ActivityKerwin James AustriaNo ratings yet
- Exp03 2019 368Document19 pagesExp03 2019 368Mohammad alhaboob2030No ratings yet
- Sr. No. Name of Experiment: Load Test On 3 Phase Squirrel Cage Induction MotorDocument40 pagesSr. No. Name of Experiment: Load Test On 3 Phase Squirrel Cage Induction MotorSagar G ReddyNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ManualDocument42 pagesPower Electronics ManualJavaria Chiragh50% (2)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectsDocument36 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectsTushar Kush100% (4)
- Lab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Document41 pagesLab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Ilavarasan TamizhNo ratings yet
- 9A02504 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pages9A02504 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Document7 pages20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Usama MughalNo ratings yet
- C-20 P e Practicle ComletetDocument80 pagesC-20 P e Practicle Comletetamrutha cNo ratings yet
- Group-5 - Laboratory No. 4Document32 pagesGroup-5 - Laboratory No. 4Angel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document2 pagesExperiment 1MeghaNo ratings yet
- EEC ActivityDocument13 pagesEEC ActivityKerwin James AustriaNo ratings yet
- PSA Lab 1 and 2Document17 pagesPSA Lab 1 and 2Usama KhanNo ratings yet
- 5.thyristor Three-Phase Rectifier & Inverter NewDocument8 pages5.thyristor Three-Phase Rectifier & Inverter NewSonet HosainNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab Exp3 PDFDocument17 pagesElectronics Lab Exp3 PDFgacc4sitesNo ratings yet
- Exp 12 Single Phase Inverter Part IIDocument7 pagesExp 12 Single Phase Inverter Part IIusmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 1 - Diode v2021Document4 pagesPre-Lab 1 - Diode v2021محمد ابو جرادNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDocument18 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & Drivesshashi kumarNo ratings yet
- Danial Power 3Document8 pagesDanial Power 3Arqam Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Contactless Dynamo Bike Wheel LightsDocument6 pagesContactless Dynamo Bike Wheel Lightsmarandan85No ratings yet
- PE Project EVCSDocument5 pagesPE Project EVCSKrishanSinghNo ratings yet
- Data Input Current Carrying Capacity Overall Dia.: Cable Selection Calculation - LTDocument5 pagesData Input Current Carrying Capacity Overall Dia.: Cable Selection Calculation - LTsunilNo ratings yet
- H1000e I Ema-Emc PDFDocument4 pagesH1000e I Ema-Emc PDFNguyen Van ChungNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University Haramaya Institute of Technology Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument3 pagesHaramaya University Haramaya Institute of Technology Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringBuze TfNo ratings yet
- Pyro Mi Specifiers GuideDocument12 pagesPyro Mi Specifiers Guideashley_moseley1918No ratings yet
- 590G-V2 in A4 CatalogueDocument6 pages590G-V2 in A4 CatalogueMATIAS_CNo ratings yet
- BEE TECHNICAL SUBJECTS 2019 SaveDocument22 pagesBEE TECHNICAL SUBJECTS 2019 Savej deenNo ratings yet
- Crumar Spirit Service Manual PDFDocument11 pagesCrumar Spirit Service Manual PDFFlaco Depaulo CarlosNo ratings yet
- Voltage Peak Limiter Load Vs Power Tables FP+ Series: Dedicated Touring AmplifiersDocument2 pagesVoltage Peak Limiter Load Vs Power Tables FP+ Series: Dedicated Touring AmplifiersDimosthenis MarinidisNo ratings yet
- HPH-20-120kW-Catalogo InglesDocument2 pagesHPH-20-120kW-Catalogo IngleselNo ratings yet
- Solaredge Power Optimizer: Frame-Mounted Module Add-On For Commercial InstallationsDocument2 pagesSolaredge Power Optimizer: Frame-Mounted Module Add-On For Commercial Installationsfadi lamoNo ratings yet
- I2R T2DC 500S TT - Datasheets - USDocument3 pagesI2R T2DC 500S TT - Datasheets - USabdulkawi alasharyNo ratings yet
- Nano SMD 462 Series FuseDocument3 pagesNano SMD 462 Series Fuseedgar_dauzonNo ratings yet
- SD800 TimerDocument1 pageSD800 Timerpatelhet229No ratings yet
- ACT 3 DE INGLÉS The Basics of Motor Control Centers MCCDocument6 pagesACT 3 DE INGLÉS The Basics of Motor Control Centers MCCMaria Fer PerezNo ratings yet
- Datasheet SF7 US 2018Document2 pagesDatasheet SF7 US 2018aslamNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Powered AC GeneratorDocument5 pagesBicycle Powered AC GeneratorUsman DoltanaNo ratings yet
- Panasonic VF0 InvertersDocument4 pagesPanasonic VF0 InvertersTecnico 1 EmbarbaNo ratings yet
- FC16X-P Perkins Leroy GRDocument7 pagesFC16X-P Perkins Leroy GRIsrael GomezNo ratings yet
- Emko ATS10 Eng Short v00 PDFDocument6 pagesEmko ATS10 Eng Short v00 PDFCarmen Serbanoiu33% (3)
- Wind TurbineDocument18 pagesWind TurbineDinesh Inavolu50% (2)
- 250 kVA Transformer Manufacturing and Transformer TestingDocument84 pages250 kVA Transformer Manufacturing and Transformer TestingPronoy Kumar100% (2)
- Multipurpose Watertight Luminaire: Part NoDocument2 pagesMultipurpose Watertight Luminaire: Part NoCarmenNo ratings yet
- 21.SMES Based Excitation System For Doubly-Fed Induction Generator in Wind Power ApplicationDocument4 pages21.SMES Based Excitation System For Doubly-Fed Induction Generator in Wind Power Applicationanji.guvvalaNo ratings yet
- Transformers, Flexible and Reliable - BR009002ENDocument12 pagesTransformers, Flexible and Reliable - BR009002ENKishor JadhavNo ratings yet
- SMPSDocument29 pagesSMPSwcdma1230% (2)
- Connect Series AccesoriesDocument15 pagesConnect Series AccesoriesPablo Gaspar D'Agostini AmengualNo ratings yet
- C1250 D2R PCC3.3 Parts ListDocument110 pagesC1250 D2R PCC3.3 Parts Listengye7ia100% (1)