Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformers
Transformers
Uploaded by
beratgunes543Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- A2 UNIT 4 Test Answer Key HigherDocument2 pagesA2 UNIT 4 Test Answer Key HigherMaxi Comas60% (5)
- (English) MEGACITIES of The World (Season 1 - Complete)Document58 pages(English) MEGACITIES of The World (Season 1 - Complete)Sveta EnglishNo ratings yet
- Transformer Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesTransformer Interview QuestionsAnonymous sAmJfcV50% (4)
- Automation Studio User ManualDocument152 pagesAutomation Studio User ManualS Rao Cheepuri100% (1)
- Transformer QuestionsDocument48 pagesTransformer QuestionsPraveen Chandran100% (1)
- Abc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesFrom EverandAbc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesWürth ElektronikNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 1 PDFDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines 1 PDFThangam MaheshNo ratings yet
- II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IDocument6 pagesII yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IanunilaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument45 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineeringsurya892No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 2 MARKSDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines 2 MARKSdtselvanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine QueationsDocument22 pagesElectrical Machine QueationsAtharva DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines EE1211Document15 pagesElectrical Machines EE1211Atchutharam EceNo ratings yet
- 2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2Document5 pages2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2soumya vollalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Two Marks Noorul Islam Colleege of Engineering KumaracoilDocument6 pagesElectrical Machines Two Marks Noorul Islam Colleege of Engineering KumaracoilSuresh DulamNo ratings yet
- EM1 - Unit 2 - 2marksDocument5 pagesEM1 - Unit 2 - 2marksAmarabalan NarasingamNo ratings yet
- Bee Voltage Regulation EfficiencyDocument8 pagesBee Voltage Regulation EfficiencyrasoolNo ratings yet
- EfficiencyDocument21 pagesEfficiency4zfq8g84rkNo ratings yet
- BEE Module 4 TransformerDocument9 pagesBEE Module 4 TransformerMintu MinjNo ratings yet
- Transformers - Three Phase TransformersDocument25 pagesTransformers - Three Phase TransformersDeepakDeep100% (1)
- Chapter 3 MSDocument42 pagesChapter 3 MSRounak ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Transformer FinalDocument37 pagesChapter 2, Transformer Finaltemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, TransformerDocument28 pagesChapter 2, Transformertemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamDocument52 pagesElectrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamMy EverythingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Transformer: Electrical MachineDocument39 pagesChapter 3: Transformer: Electrical MachineThe zeroNo ratings yet
- Two Marks Question With Answer Magnetic Circuits and Magnetic MaterialDocument9 pagesTwo Marks Question With Answer Magnetic Circuits and Magnetic MaterialChandra SekarNo ratings yet
- Transformers: 1 K Hinds - 2012Document5 pagesTransformers: 1 K Hinds - 2012Jelani GreerNo ratings yet
- Eee PDFDocument19 pagesEee PDFRanchuNo ratings yet
- Dav Public SchoolDocument14 pagesDav Public Schools sundararajan100% (1)
- TransformerDocument22 pagesTransformerIF21 Minit ChitrodaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MCQDocument20 pagesUnit 2 MCQanand anithaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance:: Armature Windings Lap and Wave Windings (Year - 2) - YoutubeDocument6 pagesCapacitance:: Armature Windings Lap and Wave Windings (Year - 2) - YoutubeMukeshKumarMahtoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine I-3140913Document44 pagesElectrical Machine I-3140913Patel KashyapNo ratings yet
- Transformer & MotorDocument92 pagesTransformer & MotorAshutosh Rai100% (1)
- Transformers: Basic Electrical Engineering ECE-133Document23 pagesTransformers: Basic Electrical Engineering ECE-133Pulkit SethiNo ratings yet
- EEE Unit 4Document7 pagesEEE Unit 4pradeepkumarsa980No ratings yet
- Transformer Theory Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesTransformer Theory Questions and AnswersVishal Sawh100% (3)
- Transformer Gec228 2024 2Document26 pagesTransformer Gec228 2024 2eerandomstuff1211No ratings yet
- Electrical TransformerDocument19 pagesElectrical Transformer164ec1f5100% (1)
- Unit IIIDocument11 pagesUnit IIIAshok BNo ratings yet
- Auto Transformer: Auto Transformer Is Kind of Electrical Transformer Where Primary and Secondary Shares SameDocument8 pagesAuto Transformer: Auto Transformer Is Kind of Electrical Transformer Where Primary and Secondary Shares SameAbhishek PareekNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument20 pagesTransformerAjayNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Single Phase Transformers - LA Teacher Guide - ENGDocument15 pagesGrade 11 Single Phase Transformers - LA Teacher Guide - ENGnolotshiaNo ratings yet
- EE8301 Electrical Machines-I Transformers Ms.J.Sumithra, Asp/EeeDocument39 pagesEE8301 Electrical Machines-I Transformers Ms.J.Sumithra, Asp/Eeedaniel alejandro chaparro zipaNo ratings yet
- Autotransformer Connection ExplaineDocument6 pagesAutotransformer Connection ExplaineNepoliyanNo ratings yet
- Kskcet Ee6352-Electrical Engg & Instrm. Year/Sem:Iv/ViiDocument15 pagesKskcet Ee6352-Electrical Engg & Instrm. Year/Sem:Iv/ViimanikandanNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMER (Levinesh)Document16 pagesTRANSFORMER (Levinesh)livinesh05rNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 1Document2 pagesAssignment Unit 1DHANUSH SHIVANANDNo ratings yet
- Electricalprep Com Transformers More 5Document16 pagesElectricalprep Com Transformers More 5gokulchandruNo ratings yet
- UNIT-II Transformers & Alternator-2marksDocument5 pagesUNIT-II Transformers & Alternator-2marksashwen30No ratings yet
- Viva EM LabDocument4 pagesViva EM LabcoolrajeeeNo ratings yet
- Module-1 TransformersDocument27 pagesModule-1 TransformersSuraj Gowda BHNo ratings yet
- Module4 TransformerDocument47 pagesModule4 Transformeranvay.shirsatNo ratings yet
- Transformers 22-02-2023Document25 pagesTransformers 22-02-2023Youth Empowerment and Talent RecognitionNo ratings yet
- Transformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument32 pagesTransformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaParvezKhanNo ratings yet
- Regent Education & Research FoundationDocument28 pagesRegent Education & Research FoundationSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment No3 Beae-EDocument3 pagesAssignment No3 Beae-EAR KhokharNo ratings yet
- Auto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenFrom EverandAuto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Summer Intership ProjectDocument68 pagesSummer Intership ProjectDaksha Milind Patil100% (2)
- Real Time Detection of Human Stress Using Sensors and Machine Learning TechniquesDocument12 pagesReal Time Detection of Human Stress Using Sensors and Machine Learning TechniquesA M WamiqueNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/33Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/33Saleha ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- GPS Tracker Communication ProtocolDocument39 pagesGPS Tracker Communication ProtocolMuhammed EmamNo ratings yet
- Government Engineering College Dahod: Dadhichi HostelDocument5 pagesGovernment Engineering College Dahod: Dadhichi HostelSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Psychology and AdvertisingDocument59 pagesPsychology and AdvertisingEMMA SHAFFU EL CHACARNo ratings yet
- Cathay Pacific Research PaperDocument4 pagesCathay Pacific Research Paperafeawfxlb100% (1)
- EMMVEE - On-Grid PV Modules - DatasheetDocument2 pagesEMMVEE - On-Grid PV Modules - Datasheetmk gandhiNo ratings yet
- Small-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutionDocument81 pagesSmall-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutiondibudkNo ratings yet
- Bettin Bots - False FavouritesDocument41 pagesBettin Bots - False Favouriteskaalingaa starNo ratings yet
- ACK NAK EnhancementDocument15 pagesACK NAK Enhancementbasit_engineerNo ratings yet
- TST2601 - Minor Test 1 - Memo - 2022Document8 pagesTST2601 - Minor Test 1 - Memo - 2022Johan PienaarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Perspective in PsychologyDocument74 pagesCognitive Perspective in PsychologyrubinaNo ratings yet
- Manual - HSIDocument23 pagesManual - HSIrichardfloyd100% (2)
- Chapter 4.5 SC f5Document7 pagesChapter 4.5 SC f5kwongyawNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders:: Identification and ManagementDocument45 pagesMood Disorders:: Identification and ManagementFikatu HugoronNo ratings yet
- 07363769410070872Document15 pages07363769410070872Palak AgarwalNo ratings yet
- HP ProLiant ML370 G6 ServerDocument4 pagesHP ProLiant ML370 G6 ServerTrenell Steffan IsraelNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading 1Document17 pagesDevelopmental Reading 1api-310357012100% (1)
- Instruction Manual For Barber-Colman Series EA Electric High Torque ActuatorsDocument12 pagesInstruction Manual For Barber-Colman Series EA Electric High Torque ActuatorsMaximiliano SanchezNo ratings yet
- Commercial Book ListDocument6 pagesCommercial Book Listoto saviourNo ratings yet
- Funda Finals ReviewerDocument23 pagesFunda Finals Reviewerchloepaxton030No ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSAmanda100% (1)
- Tentative Awards ListDocument121 pagesTentative Awards ListA.R MaheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Project Scheduling Lagging, Crashing and Activity NetworksDocument26 pagesChapter 6 Project Scheduling Lagging, Crashing and Activity NetworksMỹ Mộc LinhNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering ObservationDocument2 pagesCollege of Engineering ObservationFrenz VillasisNo ratings yet
- LearnEnglish Listening B1 Meeting An Old FriendDocument4 pagesLearnEnglish Listening B1 Meeting An Old FriendTr RoseNo ratings yet
Transformers
Transformers
Uploaded by
beratgunes543Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transformers
Transformers
Uploaded by
beratgunes543Copyright:
Available Formats
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH, VIRUDHUNAGAR QUESTION BANK
EE6401– ELECTRICAL MACHINCES-1
QUESTION AND ANSWERS
Unit-II-TRANSFORMERS
PART-A
1. What is the function of a transformer?
Transformers are energy converting devices, converting AC electrical energy with one
level of voltage and current, to AC electrical energy with another level of voltage and current
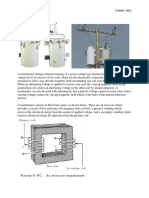
2. Mention the difference between core and shell type transformers.
In core type, the windings surround the core considerably and in shell type the core
surround the winding.
3. What is the purpose of laminating the core in transformers?
To reduce eddy current loss.
4. Give the emf equation of a transformer and define each term.
Emf induced in primary coil E1 = 4.44 fFmN1 volt Emf
induced in secondary coil E2 = 4.44fFmN2 volt
Where,
f is the frequency of AC input
Fm is the maximum value of flux in the core
N1, N2 are the number of primary and secondary turns.
5. Does the transformer draw any current when secondary is open? Why?
Yes, it (primary) will draw the current from the main supply in order to magnetize the
core and to supply iron and copper losses on no load. There will not be any current in the
secondary since secondary is open.
6. Define voltage regulation of a transformer
The change in secondary terminal voltage from no load to full load expressed as a
percentage of no load or full load voltage is termed as regulation.
% regulation = (0V2-V2) x 100/0V2
7. Full load copper loss in a transformer is 1600 watts. What will be the loss at half load?
If x is the ratio of actual load to full load then copper loss = x2(full load copper
loss).Here Wc = (0.5)2 x 1600 = 400 watts
EE6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I-UNIT 2
Page 1 of 6
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH, VIRUDHUNAGAR QUESTION BANK
8. Define all day efficiency of a transformer.
It is the computed on the basis of energy consumed during a certain period, usually a day
of 24 hs.
All day efficiency = output in kWh for 24 hrs /input in kWh for 24 hrs.
9. Why transformers are rated in kVA ?
Copper loss of a transformer depends on current and iron loss on voltage. Hence total
losses depend on Volt- Ampere and not on the power factor. That is why the rating of
transformers is in KVA and not in KW.
10. Why are breathers used in transformers?
Breathers are used to entrap the atmospheric moisture and thereby not allowing it to pass
on to the transformer oil. Also to permit the oil inside the tank to expand and contract as its
temperature increases and decreases. Also to avoid sledging of oil i.e. decomposition of oil.
Addition of 8 parts of water in 1000000 reduces the insulations quantity of oil. Normally silica
gel is filled in the breather having pink color. This color will be changed to white due to
continuous use, which is an indication of bad silica gel, it is normally heated and reused.
11. A 1100/400 V, 50 Hz single phase transformer has 100 turns on the secondary winding.
Calculate the number of turns on its primary.
We know V1 / V2 = k = N2 / N1
Substituting 400/1100 = 100/N1
N1 = 100/400 x 1100
= 275 turns.
12.What are the functions of no-load current in a transformer?
No-load current produces flux and supplies iron loss and copper loss on no-load.
13. Can the voltage regulation of a transformer go to negative? If so under what
condition?
Yes. If the load has leading power factor.
14. What is meant by turns ratio in transformer?
Turns ratio in transformers,K is the ratio of number of turns in the secondary winding T 2
to number of turns in the primary winding T1
K = T2/T1
15. Why are cooling tubes provided in transformer tanks?
By providing cooling tubes, oil circulation and hence heat dissipation can further be
improved by providing cooling tubes in two or all four walls of the transformer tanks
EE6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I-UNIT 2
Page 2 of 6
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH, VIRUDHUNAGAR QUESTION BANK
16.When will a Bucholz relay operate in a transformer?
Bucholz rely is a protective device in a transformer. If the temperature of the coil
exceeds its limit, Bucholz relay operates and gives an alarm.
17. List out general application of transformers.
1) Stepping-up of voltage
2) Stepping-down of voltage
3) Instrument extension
4) Electrical isolation
5) Impedance matching
7) Link between AC and DC systems
18. What is the purpose of conducting open circuit and short circuit tests in
transformers?
Open circuit Test:
i) To find out the equivalent circuit parameters R0 & X0 or no load resistance and reactance.
ii) To find out the Iron loss of the transformer.
Short circuit Test:
i) To find out the equivalent circuit parameters R01 & X01 or esistance and reactance of
the transformer referred to primary or secondary
iii) To find out the copper loss of the transformer
By using these two tests we can find out the efficiency and regulation of the transformer.
19. What do you understand by ideal transformer?
If the properties of transformer be idealized in that the winding resistances are negligible
and assume that all the flux is conferred to the core and links both windings core losses are
negligible, and permeability of core is so higher that only a negligible exciting MMF in required
to establish the flux. these properties are closely approached but never actually attained in
practical transformers. A hypothetical transformer having these properties is called an “ideal
transformer”
20. If a transformer is operated at a frequency other than the designed one, what will
happen to its performance?
Iron loss increases with a decrease in frequency. For example if a 60 HZ transformer is
allowed to work at 50Hz supply. the iron loss will increase by 11% so heating will be more and
the efficiency will decrease when worked on lower frequency.
21. Can you apply D.C supply in a single phase transformer? Give reason for your
answer.
Transformer should not be connected to a D.C Source. If the primary of a transformer is
connected to D.C supply mains, the flux produced will not vary but remain constant in
magnitude and therefore no EMF will be induced in the secondary winding. Also there will be no
back EMF induced in the primary winding and therefore a heavy current will be drawn from the
supply which may result in the burning out of the winding.
EE6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I-UNIT 2
Page 3 of 6
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH, VIRUDHUNAGAR QUESTION BANK
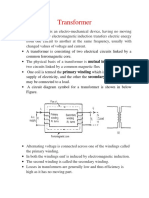
22. State the principle of operation of a transformer.
Transformer operates on the principle of mutual induction between inductively coupled
coils. When A.C source is connected to one coil flux is produced in the core which links both the
coils. As per the Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction EMF is induced in the secondary
coil also. if the external circuit is closed power is supplied.
23. A single phase transformer designed for 50 Hz operation is connected to a supply of
60 HZ. What will happen?
The iron loss will be reduced, less heating and the efficiency will increase.
24. Why is the rating of transformer given in KVA?
Copper loss of a transformer depends on current and iron loss on voltage. Hence, total
transformer loss depends on volt ampere (VA) and not on phase angle between voltage and
current i.e, it is independent of load power factor. That is why rating of transformer is in KVA
and not in KW.
25. How do you reduce hysteresis loss in a transformer?
Hysteresis loss can be reduced by selecting suitable core material silicon steel is having less stein
metz hysteresis co-efficient.
26. In O.C test in single phase transformer why do you use low power factor watt
meter to measure the power?
The power factor of the circuit at no-load is very low. So if a low power factor watt meter is
used, the reading will be very accurate.
27. The efficiency of a transformer is always higher than that of rotating electric
machines, why?
In rotating electric machines there is mechanical losses (frictional and wind age losses) due to
the rotating parts. As there is no rotating part in transformer, efficiency of transformer is always
higher than rotating electric machines.
28. Explain why only low voltage is applied to the transformer during short circuit test?
In this test the terminals of the secondary winding are short- circuited, therefore transformer
becomes equivalent to a coil having an impedance equal to impedance of both the windings. The
value of impedance is also very low. Therefore low voltage is sufficient for the circulation of full
load, current to find the copper loss, resistance and reactance.
29. State why the open circuit test on a transformer is conducted at rated voltage?
The purpose of this test is to determine coreloss and no-load current I0 which is helpful in
winding X0 and R0 Only with normal voltage applied to the primary, normal flux will be set up
in the core, hence normal iron losses will occur.
EE6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I-UNIT 2
Page 4 of 6
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH, VIRUDHUNAGAR QUESTION BANK
30. What are the conditions for parallel operation of 3-phase transformers?
i. Should have equal voltage ratio.
ii. The phase sequence must be the same.
iii. The percentage impedance of the transformers should be equal
iv. The transformers to be connected in parallel should belong to the same vector group.
31. State some advantages of shell type transformer
Advantages of shell -type transformer:
i. Better cooling
ii. Less leakage reactance
iii. Greater mechanical strength
iv. Less magnetising current.
32. The no-load ratio required in a single phase 50 Hz transformer is 6600/300V. If the
maximum value of flux in the core is to be about 0.09 weber. Find the number of turns in each
winding.
33. The no load current of a transformer is 15A at a power factor of 0.2 when connected to a
460V, 50 Hz supply. If the primary winding has 550 turns Calculate.
i) The magnetizing component (I).
ii) Iron loss (Wo)
34. Find (i) active component and reactive components of no-load current and (ii) no-load
current of a 230V/ 115V single-phase transformer if the power input on no-load to the high
voltage winding is 70 Kl and power factor of no-load current is 0.25 lagging.
PART – B
1. What are the tests required to draw the equivalent circuit of a Single phase Transformer? How
they are conducted? (Nov – 02)
2. Draw phasor diagram to represent conditions in a single-phase transformer-supplying load at1.
Unity p.f , 2.Lagging p.f 3. Leading p.f (Nov-02)
3. Explain the Back to back method of testing of two identical single phase transformers (May03)
4. Explain the construction and principle of operation of single phase transformer (A 97)
5. Deduce the equivalent circuit of a Transformer (Oct – 97)
6. Derive the emf equation of the Transformer (April – 99)
7. List the losses, which occur in a loaded transformer. Deduce the relationship between losses
for maximum efficiency (Oct –97)
8. Derive the condition for maximum efficiency of a Transformer (Oct–98)
9. Explain the types of testing of transformer
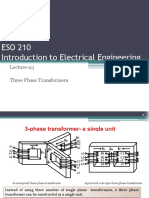
10. Explain the Construction of 3 phase Transformer (Apr- 99)
EE6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I-UNIT 2
Page 5 of 6
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH, VIRUDHUNAGAR QUESTION BANK
11. Describe the various three phase transformer connections. (Apr - 99)
12. State and explain the necessary conditions for parallel operation of three phase
transformers.
13. Explain about auto transformer and drive an expression between the weight of winding
material of auto and ordinary transformer.
14. What is Scott connection and explain how phase conversion is carried out?
15. A 6600/440V Single phase 600 KVA transformer has 1200 primary turns. Find (i)
Transformation ratio (ii) Secondary turns (iii) Voltage / turn (iv) Secondary current when it
supplies a load of 400 kW at 0.8 p.f. lagging.
16. A 50 KVA, 4400/220 V, transformer has R1 = 3.45 Ω; R2 = 0.009Ω. The values of
reactances are X1 = 5.2Ω and X2 = 0.015Ω. Calculate for the transformer.
(i) Equivalent resistance referred to primary
(ii) Equivalent reactance reference to primary
(iii) Equivalent impedance reference to primary
(iv) Equivalent resistance, reactance and impedance referred to secondary.
EE6401 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I-UNIT 2
Page 6 of 6
You might also like
- A2 UNIT 4 Test Answer Key HigherDocument2 pagesA2 UNIT 4 Test Answer Key HigherMaxi Comas60% (5)
- (English) MEGACITIES of The World (Season 1 - Complete)Document58 pages(English) MEGACITIES of The World (Season 1 - Complete)Sveta EnglishNo ratings yet
- Transformer Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesTransformer Interview QuestionsAnonymous sAmJfcV50% (4)
- Automation Studio User ManualDocument152 pagesAutomation Studio User ManualS Rao Cheepuri100% (1)
- Transformer QuestionsDocument48 pagesTransformer QuestionsPraveen Chandran100% (1)
- Abc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesFrom EverandAbc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesWürth ElektronikNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 1 PDFDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines 1 PDFThangam MaheshNo ratings yet
- II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IDocument6 pagesII yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IanunilaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument45 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineeringsurya892No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 2 MARKSDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines 2 MARKSdtselvanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine QueationsDocument22 pagesElectrical Machine QueationsAtharva DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines EE1211Document15 pagesElectrical Machines EE1211Atchutharam EceNo ratings yet
- 2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2Document5 pages2marks and 3 Marks Questions From Unit-2soumya vollalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Two Marks Noorul Islam Colleege of Engineering KumaracoilDocument6 pagesElectrical Machines Two Marks Noorul Islam Colleege of Engineering KumaracoilSuresh DulamNo ratings yet
- EM1 - Unit 2 - 2marksDocument5 pagesEM1 - Unit 2 - 2marksAmarabalan NarasingamNo ratings yet
- Bee Voltage Regulation EfficiencyDocument8 pagesBee Voltage Regulation EfficiencyrasoolNo ratings yet
- EfficiencyDocument21 pagesEfficiency4zfq8g84rkNo ratings yet
- BEE Module 4 TransformerDocument9 pagesBEE Module 4 TransformerMintu MinjNo ratings yet
- Transformers - Three Phase TransformersDocument25 pagesTransformers - Three Phase TransformersDeepakDeep100% (1)
- Chapter 3 MSDocument42 pagesChapter 3 MSRounak ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, Transformer FinalDocument37 pagesChapter 2, Transformer Finaltemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, TransformerDocument28 pagesChapter 2, Transformertemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamDocument52 pagesElectrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamMy EverythingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Transformer: Electrical MachineDocument39 pagesChapter 3: Transformer: Electrical MachineThe zeroNo ratings yet
- Two Marks Question With Answer Magnetic Circuits and Magnetic MaterialDocument9 pagesTwo Marks Question With Answer Magnetic Circuits and Magnetic MaterialChandra SekarNo ratings yet
- Transformers: 1 K Hinds - 2012Document5 pagesTransformers: 1 K Hinds - 2012Jelani GreerNo ratings yet
- Eee PDFDocument19 pagesEee PDFRanchuNo ratings yet
- Dav Public SchoolDocument14 pagesDav Public Schools sundararajan100% (1)
- TransformerDocument22 pagesTransformerIF21 Minit ChitrodaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 MCQDocument20 pagesUnit 2 MCQanand anithaNo ratings yet
- Capacitance:: Armature Windings Lap and Wave Windings (Year - 2) - YoutubeDocument6 pagesCapacitance:: Armature Windings Lap and Wave Windings (Year - 2) - YoutubeMukeshKumarMahtoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine I-3140913Document44 pagesElectrical Machine I-3140913Patel KashyapNo ratings yet
- Transformer & MotorDocument92 pagesTransformer & MotorAshutosh Rai100% (1)
- Transformers: Basic Electrical Engineering ECE-133Document23 pagesTransformers: Basic Electrical Engineering ECE-133Pulkit SethiNo ratings yet
- EEE Unit 4Document7 pagesEEE Unit 4pradeepkumarsa980No ratings yet
- Transformer Theory Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesTransformer Theory Questions and AnswersVishal Sawh100% (3)
- Transformer Gec228 2024 2Document26 pagesTransformer Gec228 2024 2eerandomstuff1211No ratings yet
- Electrical TransformerDocument19 pagesElectrical Transformer164ec1f5100% (1)
- Unit IIIDocument11 pagesUnit IIIAshok BNo ratings yet
- Auto Transformer: Auto Transformer Is Kind of Electrical Transformer Where Primary and Secondary Shares SameDocument8 pagesAuto Transformer: Auto Transformer Is Kind of Electrical Transformer Where Primary and Secondary Shares SameAbhishek PareekNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument20 pagesTransformerAjayNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Single Phase Transformers - LA Teacher Guide - ENGDocument15 pagesGrade 11 Single Phase Transformers - LA Teacher Guide - ENGnolotshiaNo ratings yet
- EE8301 Electrical Machines-I Transformers Ms.J.Sumithra, Asp/EeeDocument39 pagesEE8301 Electrical Machines-I Transformers Ms.J.Sumithra, Asp/Eeedaniel alejandro chaparro zipaNo ratings yet
- Autotransformer Connection ExplaineDocument6 pagesAutotransformer Connection ExplaineNepoliyanNo ratings yet
- Kskcet Ee6352-Electrical Engg & Instrm. Year/Sem:Iv/ViiDocument15 pagesKskcet Ee6352-Electrical Engg & Instrm. Year/Sem:Iv/ViimanikandanNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMER (Levinesh)Document16 pagesTRANSFORMER (Levinesh)livinesh05rNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 1Document2 pagesAssignment Unit 1DHANUSH SHIVANANDNo ratings yet
- Electricalprep Com Transformers More 5Document16 pagesElectricalprep Com Transformers More 5gokulchandruNo ratings yet
- UNIT-II Transformers & Alternator-2marksDocument5 pagesUNIT-II Transformers & Alternator-2marksashwen30No ratings yet
- Viva EM LabDocument4 pagesViva EM LabcoolrajeeeNo ratings yet
- Module-1 TransformersDocument27 pagesModule-1 TransformersSuraj Gowda BHNo ratings yet
- Module4 TransformerDocument47 pagesModule4 Transformeranvay.shirsatNo ratings yet
- Transformers 22-02-2023Document25 pagesTransformers 22-02-2023Youth Empowerment and Talent RecognitionNo ratings yet
- Transformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument32 pagesTransformer - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaParvezKhanNo ratings yet
- Regent Education & Research FoundationDocument28 pagesRegent Education & Research FoundationSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment No3 Beae-EDocument3 pagesAssignment No3 Beae-EAR KhokharNo ratings yet
- Auto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenFrom EverandAuto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Summer Intership ProjectDocument68 pagesSummer Intership ProjectDaksha Milind Patil100% (2)
- Real Time Detection of Human Stress Using Sensors and Machine Learning TechniquesDocument12 pagesReal Time Detection of Human Stress Using Sensors and Machine Learning TechniquesA M WamiqueNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/33Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/33Saleha ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- GPS Tracker Communication ProtocolDocument39 pagesGPS Tracker Communication ProtocolMuhammed EmamNo ratings yet
- Government Engineering College Dahod: Dadhichi HostelDocument5 pagesGovernment Engineering College Dahod: Dadhichi HostelSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Psychology and AdvertisingDocument59 pagesPsychology and AdvertisingEMMA SHAFFU EL CHACARNo ratings yet
- Cathay Pacific Research PaperDocument4 pagesCathay Pacific Research Paperafeawfxlb100% (1)
- EMMVEE - On-Grid PV Modules - DatasheetDocument2 pagesEMMVEE - On-Grid PV Modules - Datasheetmk gandhiNo ratings yet
- Small-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutionDocument81 pagesSmall-Angle Scattering: A View On The Properties, Structures and Structural Changes of Biological Macromolecules in SolutiondibudkNo ratings yet
- Bettin Bots - False FavouritesDocument41 pagesBettin Bots - False Favouriteskaalingaa starNo ratings yet
- ACK NAK EnhancementDocument15 pagesACK NAK Enhancementbasit_engineerNo ratings yet
- TST2601 - Minor Test 1 - Memo - 2022Document8 pagesTST2601 - Minor Test 1 - Memo - 2022Johan PienaarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Perspective in PsychologyDocument74 pagesCognitive Perspective in PsychologyrubinaNo ratings yet
- Manual - HSIDocument23 pagesManual - HSIrichardfloyd100% (2)
- Chapter 4.5 SC f5Document7 pagesChapter 4.5 SC f5kwongyawNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders:: Identification and ManagementDocument45 pagesMood Disorders:: Identification and ManagementFikatu HugoronNo ratings yet
- 07363769410070872Document15 pages07363769410070872Palak AgarwalNo ratings yet
- HP ProLiant ML370 G6 ServerDocument4 pagesHP ProLiant ML370 G6 ServerTrenell Steffan IsraelNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading 1Document17 pagesDevelopmental Reading 1api-310357012100% (1)
- Instruction Manual For Barber-Colman Series EA Electric High Torque ActuatorsDocument12 pagesInstruction Manual For Barber-Colman Series EA Electric High Torque ActuatorsMaximiliano SanchezNo ratings yet
- Commercial Book ListDocument6 pagesCommercial Book Listoto saviourNo ratings yet
- Funda Finals ReviewerDocument23 pagesFunda Finals Reviewerchloepaxton030No ratings yet
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSAmanda100% (1)
- Tentative Awards ListDocument121 pagesTentative Awards ListA.R MaheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Project Scheduling Lagging, Crashing and Activity NetworksDocument26 pagesChapter 6 Project Scheduling Lagging, Crashing and Activity NetworksMỹ Mộc LinhNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering ObservationDocument2 pagesCollege of Engineering ObservationFrenz VillasisNo ratings yet
- LearnEnglish Listening B1 Meeting An Old FriendDocument4 pagesLearnEnglish Listening B1 Meeting An Old FriendTr RoseNo ratings yet