Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre-Cal Infographics PT
Pre-Cal Infographics PT
Uploaded by
Daphne Ezra F. OlegarioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-Cal Infographics PT
Pre-Cal Infographics PT
Uploaded by
Daphne Ezra F. OlegarioCopyright:
Available Formats
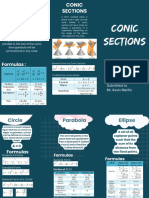
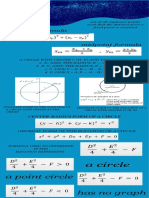
PRE-CALCULUS
Conic sections, also known as
cone sections, are curves
formed when a plane and a cone
intersects. Parabola, hyperbola,
and ellipse (the circle is a
specific type of ellipse) are the
three main sections that make
up a cone or conic section. To
create the conic sections, a
cone with two nappes that are
the same is used.
Conic section knowledge may be dated back to Ancient Greece. Menaechmus is
credited with discovering conic sections between 360 and 350 B.C., and it is said
that he employed them in his two answers to the issue of "doubling the cube."
llipse hyper
TYPE OF DEGENERATED
e
CONIC SECTIONS
POINT – the degenerated form of circle or ellipse
bola
LINE – the degenerated form of parabola.
TWO INTERSECCTING LINES - the
p
degenerate form of a hyperbola.
c ir c l e ara b ola e W
Lif
hee
-
Real
EQUATION OF CIRCLE CIR
Exam
ple CLE
As a conic section, the circle is the intersection
of a plane perpendicular to the cone's axis.
ELLIPSE The distance from the center to any
An ellipse is an important The ellipse is defined by two point on the circle is constant and is
conic section created by points, each called a focus. 𝑎>𝑏 called the radius of the circle.
intersecting a cone with a
plane that does not pass
From any point on the ellipse,
the sum of the distances to
𝑐=√𝑎2-𝑏2 Real-life
E xample
through a cone's vertex. the focus points is constant. 𝑎, 𝑏 and 𝑐 are related
P AR ABOL A
S A
A parabola is the set of all points in the plane equidistant
T E L LI T
from a fixed point F and a fixed line l not containing F.
Parts of a Parabola E
vertex latus rectum focus DIS H
axis of symmetry directrix
A hyperbola is an open curve with two branches formed by
the intersection of a plane and both parts of a double HYPERBOLA
cone. The plane does not have to be parallel to the axis of
the cone; the hyperbola will be symmetrical regardless. HYPERBOLA
GUITAR
(REAL LIFE EXAMPLE)
Hyperbola can be defined as the difference of distances
between a set of points, which are present in a plane to
two fixed points, is a positive constant.
REFERENCES: https://unacademy.com/content/jee/study-material/mathematics/a-brief-analysis-of-circles-conic-sections/
https://sites.math.rutgers.edu/~cherlin/History/Papers1999/schmarge.html#:~:text=The%20knowledge%20of%20conic%20sections,of%20%22doubling%20the%20cube%22.
https://www.snow.edu/academics/science_math/math/resources/Cindy_Alder/pdf_lecture_notes/chapter11/11.2%20Circles%20and%20Ellipses%20Conic%20Sections.pdf
https://www.brightstorm.com/math/precalculus/conic-sections/the-ellipse/#:~:text=An%20ellipse%20is%20an%20important,the%20focus%20points%20is%20constant.
https://byjus.com/question-answer/what-is-a-real-life-example-of-a-parabola/
https://math.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Algebra/Algebra_and_Trigonometry_1e_(OpenStax)/12%3A_Analytic_Geometry/12.02%3A_The_Hyperbola#:~:text=In%20analytic%20g
eometry%2C%20a%20hyperbola,of%20each%20other%20
https://www.cuemath.com/learn/mathematics/conics-in-real-life/
Daphne Ezra F. Olegario
11 - Lovelace
You might also like
- Imagining the Nation in Nature: Landscape Preservation and German Identity, 1885–1945From EverandImagining the Nation in Nature: Landscape Preservation and German Identity, 1885–1945No ratings yet
- THIRD PERIODIC TEST IN MATHEMATICS WITH TosDocument5 pagesTHIRD PERIODIC TEST IN MATHEMATICS WITH Tosaljem tubigon100% (1)
- Parabola PDF SK GOYAL - CompressedDocument97 pagesParabola PDF SK GOYAL - CompressedDarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Parabola ArigantDocument97 pagesParabola ArigantVarun JishnuNo ratings yet
- Conics and CurvesDocument58 pagesConics and Curvesrishi21211835No ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument71 pagesParabolaShubhamWaghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document1 pageChapter 11DarkstalkerNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERINGCURVESppt 2019 11 06 20 32 10Document17 pagesENGINEERINGCURVESppt 2019 11 06 20 32 10Parth KaravadraNo ratings yet
- Engineering CurvesDocument23 pagesEngineering CurvesAshok PallothuNo ratings yet
- Polar Coordinates Conics And: Learning OutcomesDocument43 pagesPolar Coordinates Conics And: Learning OutcomesAnkur GuptaNo ratings yet
- STM NotesDocument3 pagesSTM NotesDiako Unknown 12No ratings yet
- Design Folio 1c - Geo Forms Handout - Curvilinear.2023Document2 pagesDesign Folio 1c - Geo Forms Handout - Curvilinear.2023Champ PlayerNo ratings yet
- Engineering Curves: Part-I (Conic Sections)Document19 pagesEngineering Curves: Part-I (Conic Sections)Ivan JosephNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections - The Curves of Intersection That The Plane Makes With The Doubl e Right Circular ConeDocument1 pageConic Sections - The Curves of Intersection That The Plane Makes With The Doubl e Right Circular Conebonifacio gianga jrNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Mendoza, Jillea RDocument4 pagesAssignment - Mendoza, Jillea Rjillea mendozaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections and CurvesDocument18 pagesConic Sections and CurvesRechintalapavankumar Reddy100% (1)
- Ellipse: Universitas Negeri MakassarDocument6 pagesEllipse: Universitas Negeri MakassarNur Rahmah SariNo ratings yet
- ConicsDocument18 pagesConicsDr. Arun Kumar SriranganNo ratings yet
- Pre CalDocument5 pagesPre CalCristina Astrero BisqueraNo ratings yet
- Parabola: Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument10 pagesParabola: Introduction To Conic SectionsGURUMARUTHI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Engineering CurvesDocument39 pagesEngineering Curves20bt04047No ratings yet
- The Descriptive Geometry of Nose ConeDocument15 pagesThe Descriptive Geometry of Nose ConeAhmad Nur ShofaNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11Document5 pagesCONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11ha hakdogNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document36 pagesLecture 4Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4-5 Curve-1Document28 pagesLecture-4-5 Curve-1nameNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Calculus I With Anaylytic GeometryDocument6 pagesModule 1 - Calculus I With Anaylytic GeometryMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- Each Point of A Parabola Is Equally Distant From A Fixed Point (Focus) and A Fixed Line (Directrix)Document7 pagesEach Point of A Parabola Is Equally Distant From A Fixed Point (Focus) and A Fixed Line (Directrix)GilbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter ViDocument23 pagesChapter Vilj6244866No ratings yet
- Conic Sections NotesDocument7 pagesConic Sections Notesbavithaprasanthi27No ratings yet
- Blue White Geometric Modern Sea Travel BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue White Geometric Modern Sea Travel Brochurenightmarehappy142No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 2Document27 pagesAnalytic Geometry 2Ian Arnold FamiNo ratings yet
- 11 ConicsDocument9 pages11 Conicsshubhamdalal.anmNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument23 pagesConic SectionsRohit Kumar AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Conic Section - WikipediaDocument24 pagesConic Section - WikipediaAustin ZilkerNo ratings yet
- Theory HyperbolaDocument13 pagesTheory HyperbolaAlfiya ManzarNo ratings yet
- EllipseDocument2 pagesEllipsetishvill18No ratings yet
- The Elliptic Arc, Azimuth, and Chord of A Normal SectionDocument10 pagesThe Elliptic Arc, Azimuth, and Chord of A Normal SectionKismet100% (2)
- (PreCal 11) Conic Section - Ellipse PDFDocument49 pages(PreCal 11) Conic Section - Ellipse PDFTeacher Len EnoyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Curves: Part-I (Conic Sections)Document21 pagesEngineering Curves: Part-I (Conic Sections)Piyush RamawatNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionJohn Anthony Bersabe ChavezNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionRiza Mae BayoNo ratings yet
- Construction of EllipsesDocument20 pagesConstruction of EllipsesSrinivas Rao Yenda100% (1)
- Pre CalculusDocument5 pagesPre CalculusLahkuz Avril VasayNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project Math ProjectDocument28 pagesInvestigatory Project Math ProjectYesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Midterms ReviewerDocument4 pagesPre Calculus Midterms ReviewerJasmine RavenNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONS and Circles Grade 11Document7 pagesCONIC SECTIONS and Circles Grade 11ha hakdogNo ratings yet
- 03 Curves-IDocument22 pages03 Curves-Iakshath.rk2002No ratings yet
- Unit DDocument36 pagesUnit Dsoundu ranganathNo ratings yet
- 'LLCH A Anks - 2 !L.7 D On Methods of Actuation BaseDocument11 pages'LLCH A Anks - 2 !L.7 D On Methods of Actuation BaseBilal BilalNo ratings yet
- Q3 Geometry Definition Undefined-TermsDocument3 pagesQ3 Geometry Definition Undefined-TermsSteward john Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola PropertiesDocument4 pagesHyperbola PropertiesArsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- GEME 113 Engineering Drawing: W01-C05, C06, C07, C08, C09 W02-C10, C11, C12, C13 G2:U5-U7Document50 pagesGEME 113 Engineering Drawing: W01-C05, C06, C07, C08, C09 W02-C10, C11, C12, C13 G2:U5-U7Venkata Krishnan GangadharanNo ratings yet
- To Conic Sections: Prepared By: Miss Carizza BatacDocument24 pagesTo Conic Sections: Prepared By: Miss Carizza BatacBruceNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Polar CurvesDocument17 pagesDifferent Types of Polar CurvesJade ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- MODULE Conic SectionsDocument18 pagesMODULE Conic SectionsAudie T. MataNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Mar 21 2023Document12 pagesAdobe Scan Mar 21 2023Wilbert MannNo ratings yet
- CIRCLEDocument5 pagesCIRCLEAdduru, Krizzy Avrienne C.No ratings yet
- Port FolioDocument7 pagesPort FolioDaphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- PT Collab in Esci & EtechDocument1 pagePT Collab in Esci & EtechDaphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument1 pageReflectionDaphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document1 pageDocument 1Daphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Pintasan-Pintasan-: y M X Y-Intercept M X-Intercept X X y y XyDocument2 pagesPintasan-Pintasan-: y M X Y-Intercept M X-Intercept X X y y Xykalai2725100% (1)
- 7.2 Integral Calculus 02 SolutionsDocument6 pages7.2 Integral Calculus 02 SolutionsKurt Marfil100% (4)
- 1.the Property of The Perpendicular Drawn From The Centre To The Chord of A CircleDocument8 pages1.the Property of The Perpendicular Drawn From The Centre To The Chord of A CircleNarendra JadhavNo ratings yet
- REF 3 Plain and Solid MensurationDocument2 pagesREF 3 Plain and Solid MensurationJacobi LaplaceNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument2 pagesMathematics in Modern WorldYzza BiblaniasNo ratings yet
- Plane GeometryDocument135 pagesPlane GeometryRameshKumarMuraliNo ratings yet
- Lesson Code 1.1Document6 pagesLesson Code 1.1Eriel MagramoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration II (Important Results)Document13 pagesMensuration II (Important Results)Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- List of SPM Modern Mathematics FormulasDocument0 pagesList of SPM Modern Mathematics FormulasNur'Alya Nasuha80% (10)
- Circle Practice Barron's SAT, 29th EditionDocument3 pagesCircle Practice Barron's SAT, 29th EditionKellNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Euclidean and Non Euclidean GeometryDocument2 pagesDifference Between Euclidean and Non Euclidean GeometryBelle OleNo ratings yet
- 2013 Vatankhah Semiregular Polygon Best Hydraulic SectionDocument6 pages2013 Vatankhah Semiregular Polygon Best Hydraulic SectionMelissa CueroNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface Area AnswersDocument5 pagesVolume and Surface Area AnswersArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sharon Hampton 100 Word Vocabulary List GeometryDocument3 pagesSharon Hampton 100 Word Vocabulary List Geometryhodgeheg999123450% (2)
- Math6 ST4 Q3Document3 pagesMath6 ST4 Q3michelle milleondagaNo ratings yet
- Triangles - Equilateral, Isosceles and ScaleneDocument3 pagesTriangles - Equilateral, Isosceles and ScaleneReddysreekanth BhumaNo ratings yet
- Iemh 113Document30 pagesIemh 113Younus JalilNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document18 pagesUnit 1cooooool1927No ratings yet
- Punjab Patwari MensurationDocument7 pagesPunjab Patwari Mensurationmrafridi44No ratings yet
- PaperMath EnglishDocument79 pagesPaperMath EnglishpalamramyaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections FormulasDocument2 pagesConic Sections FormulasMulti talented IndiaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan1Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan1Joseph Nobleza33% (3)
- WCi 0 FPB VW B2 ELdue Piw 2Document24 pagesWCi 0 FPB VW B2 ELdue Piw 2Murtaza YousufNo ratings yet
- TNM Teaching Aids For Mathematics - LaPINE 1969 20171108 0001 PDFDocument82 pagesTNM Teaching Aids For Mathematics - LaPINE 1969 20171108 0001 PDFNaranLoganNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives: Class Xii E-Mail: Sangram3007@yahoo - Co.in Sangram Singh: 9810926815Document10 pagesApplications of Derivatives: Class Xii E-Mail: Sangram3007@yahoo - Co.in Sangram Singh: 9810926815Reena JainNo ratings yet
- CircleterminologyDocument84 pagesCircleterminologyJepoy OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formula and Questions For 2D and 3D Shapes KolaatDocument13 pagesMensuration Formula and Questions For 2D and 3D Shapes KolaatmonnakeyoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Geometric FiguresDocument11 pagesLesson 1 Geometric FiguresAllan PachecoNo ratings yet
- MATH 4 Q3 W6 Visualizes, Measures and Finds The Perimeter of Any Given Plane FigureDocument18 pagesMATH 4 Q3 W6 Visualizes, Measures and Finds The Perimeter of Any Given Plane FigureJuvi EspejonNo ratings yet