Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Econ7010 Midterm Ans
Econ7010 Midterm Ans
Uploaded by
shadowman22788Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Econ7010 Midterm Ans
Econ7010 Midterm Ans
Uploaded by
shadowman22788Copyright:
Available Formats
Econ7010, Macroeconomics Midterm Exam, 18 October 2010
1. (20 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether it is true, false or uncertain and explain your choice. No points will be given for an answer without an explanation. (a) In measuring gross domestic product, consumption in the expenditure approach equals to the market value of newly produced nal goods minus the unsold goods in the product approach. False. The consumption of the expenditure approach counts only purchases by the households. The newly produced nal goods also include goods purchased by the government and nal goods used as capital and therefore counted as investment. (b) A negative current account balance means that investment must be higher than saving. True. S = I + CA. When saving is lower than investment, the dierence is made up by borrowing from abroad. (c) Negative slope of the labor demand curve is a direct consequence of the diminishing marginal product of capital. False. Negative slope of the labor demand is the consequence of the diminishing marginal product of labor. Labor demand curve is given by the marginal product of labor, which equals to the slope of the production function when capital is held constant. The slope of the production function is atter for higher values of L, which means that the real wage will be lower for higher values of L. Thus the negative slope of the labor demand. (d) According to the permanent income hypothesis, a prevalent economic model of consumption, an increase in the current income will cause an equal increase in consumption. Uncertain. According to the PIH, consumption depends only on the permanent income. So, if the increase in current income is permanent, then consumption will rise by the same amount. Otherwise, it will rise by a fraction of that amount. (e) A rise in productivity causes labor demand curve to shift up and right. True. A rise in productivity shifts the production function up. This also means that for every value of labor the slope of the production function will be steeper, which, in turn, means that the real wage will be higher for every quantity of labor. 1
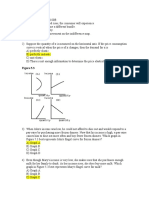
2. (20 points) Dene each of the following terms and write relevant equations if any: (a) Real interest rate. Return of an asset in real (or purchasing power) terms. It is calculated by eliminating the eect of change in price level from the nominal interest rate: r = i . (b) Expected ination. The rate of ination in the future; normally, in the next time period. (c) Structural unemployment. Unemployment due to mismatch in labor skills. Mostly in case of low-skilled labor, shrinking industry, depressed regions, etc. (d) GDP deator. A price index that measures overall price level of goods and services included in GDP. (e) Marginal propensity of consumption. The fraction of additional income that is consumed. 3. (20 points) Suppose that an economy has a production function Y = AK .25 N .75 , where Y is total output, A productivity, K capital stock and N labor. Marginal productivity of labor equals to M P N = Y /N = .75A(K/N ).25 . Assume that A = 1 and K = 4096. Labor supply for the economy is given by w = .005N . (a) Draw labor demand and supply on the same graph and label them accordingly. See the graph below. There three labor demand curves for dierent values of A and K, and the labor supply curve. (b) Assuming that the labor market is in the equilibrium, calculate the amount of labor employed, real wage and the amount of output. In equilibrium, labor supply equals labor demand: .75(4096/N ).25 = .005N . From this, we get N = 12001/1.25 = 290.6. Real wage: w = M P N = .75(4096/290.6).25 = .005N = 1.45. Output: Y = 4096.25 290.6.75 = 563.1 (c) Suppose that productivity increases by 20%. Describe what happens in the economy and calculate new values of the variables that change, if any. Indicate this change on the graph. There are two eects of the increase in the productivity. First, it directly increases output through the production function. Second, the increase in productivity shifts the labor demand up. Labor supply remains the same. This moves the labor market to a new equilibrium with higher real wage and labor. This increase in labor additional increase in output. New labor market equilibrium: 1.2 .75(4096/N ). 25 = .005N N = 336.3 Real wage: w = M P N = 1.2 .75(4096/336.3).25 = .005N = 1.68. Output:Y = 4096.25 336.3.75 = 753.9 2
(d) What would have happened if, instead of productivity, capital increased by 20%? New labor market equilibrium: .75(1.2 4096/N ). 25 = .005N N = 301.4 Real wage: w = M P N = 1.2 .75(4096/301.4).25 = .005N = 1.51. Output:Y = (1.2 4096).25 301.4.75 = 605.7 (e) What can you say about the eect on output of changes in capital and productivity? Changes in both capital and productivity have similar eect on output. Both aect it directly, through the production function, and indirectly, through the labor market. The two eects, however, are stronger in the case of a productivity change.
You might also like
- Tuning Guide Peug. 206 2.0L HDI EDC15C2 90cv - 120HP by J-SkyDocument6 pagesTuning Guide Peug. 206 2.0L HDI EDC15C2 90cv - 120HP by J-Skyzo68No ratings yet
- Mcroeconomics Chapter 3 Pratice QuestionsDocument12 pagesMcroeconomics Chapter 3 Pratice QuestionsClaire ZhengNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Saqib Tariq0% (1)
- Econ 212 Final Exam PracticeDocument9 pagesEcon 212 Final Exam PracticecodsocNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Summer 2018Document4 pagesHomework 1 Summer 2018Amirhosein AbediniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 For StudentsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 For Studentsdesada testNo ratings yet
- Peb 2024Document10 pagesPeb 2024Karunambika ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Assignment 2 (Fall 2018)Document3 pagesMacroeconomics Assignment 2 (Fall 2018)Raahim Najmi100% (1)
- Macro EconomicsDocument40 pagesMacro EconomicsSharangdhar DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- (Ii) National Wealth Is The Total Wealth of The Residents of A CountryDocument5 pages(Ii) National Wealth Is The Total Wealth of The Residents of A CountryOasama BatlaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Macroeconomics IIDocument48 pagesAdvanced Macroeconomics IIZemichael SeltanNo ratings yet
- Classical TheorDocument7 pagesClassical TheorRaghaNo ratings yet
- PS1 Answers Macroeconomic TheoryDocument2 pagesPS1 Answers Macroeconomic TheorymiguealsilvaruizNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics and Public Policy, 252H: Problem Set 1Document6 pagesMacroeconomics and Public Policy, 252H: Problem Set 1UdayNo ratings yet
- Economics MSDocument9 pagesEconomics MSKanak RaiNo ratings yet
- Simple Keynesian Model of Income DeterminationDocument60 pagesSimple Keynesian Model of Income DeterminationRakesh Seela100% (2)
- Wage SettingDocument3 pagesWage SettingMohit RakyanNo ratings yet
- Ned University of Engineering & Technology: Principles of Economics - MT-153Document2 pagesNed University of Engineering & Technology: Principles of Economics - MT-153Syed AliainNo ratings yet
- Macro Finals: Key Section A: 1 of 2 PagesDocument3 pagesMacro Finals: Key Section A: 1 of 2 PagesAnkur GoelNo ratings yet
- Ps1 101 YonseiDocument4 pagesPs1 101 Yonseihoobigo3No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument66 pagesNational IncomeMaugahn Muff-WheelerNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 HoursDocument13 pagesSample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 Hourstheunsung taleNo ratings yet
- Advanced Macroeconomics ProblemsDocument1 pageAdvanced Macroeconomics ProblemsAdriano_Axel_9404No ratings yet
- Classical Approach of Macroeconomics: After Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Conversant WithDocument14 pagesClassical Approach of Macroeconomics: After Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Conversant Withutreja12No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics & The Global Economy: Session 2: National Income-Where It Comes and Where It Goes?Document43 pagesMacroeconomics & The Global Economy: Session 2: National Income-Where It Comes and Where It Goes?Susmriti ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Exam 1Document7 pagesSample Questions Exam 1Mindy Tweet NogNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microeconomics II Q & ADocument34 pagesAdvanced Microeconomics II Q & AZemichael SeltanNo ratings yet
- Economics Set II (2015-16) Answer Key Section-ADocument6 pagesEconomics Set II (2015-16) Answer Key Section-Aabhishek sharmaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Macroeconomics (Ecn 2215)Document35 pagesIntermediate Macroeconomics (Ecn 2215)Yande ZuluNo ratings yet
- Cournot Model With Entry NewDocument8 pagesCournot Model With Entry NewhashimNo ratings yet
- Questions: Download More at WWW - Ebookskenya.co - KeDocument38 pagesQuestions: Download More at WWW - Ebookskenya.co - KeSamielMuhamedOmarNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument17 pagesEconomicschiaraghezNo ratings yet
- Summary Moneter CH 5Document10 pagesSummary Moneter CH 5Kadek Indah Dwi CahyaniNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument5 pagesFormulasraj_mishra_17No ratings yet
- 20201221203332YWLEE003Perfect Compyp SolutionDocument19 pages20201221203332YWLEE003Perfect Compyp SolutionDương DươngNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Mankiw Chapter 3Document68 pagesMacroeconomics Mankiw Chapter 3SajidahPutri0% (1)
- ECN 2215 - Topic - 2 PDFDocument54 pagesECN 2215 - Topic - 2 PDFKalenga AlexNo ratings yet
- Practice: + 10Q and FC ($) 200, Where Q Is inDocument2 pagesPractice: + 10Q and FC ($) 200, Where Q Is insơn trầnNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam 2Document7 pagesSample Exam 2Kateryna TernovaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument13 pagesUnit 1 NotesLluisGuillemBoludaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Open Economic SystemDocument65 pagesChapter 4 Open Economic Systemtigabuyeshiber034No ratings yet
- CHAP03 Teori GrowthDocument64 pagesCHAP03 Teori GrowthFirman DariyansyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Theory-ProductionDocument25 pagesChapter 3-Theory-ProductionKumar SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Theory-Production PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 3-Theory-Production PDFKumar SiddharthNo ratings yet
- M Kim Section001 Leontief IO ModelDocument8 pagesM Kim Section001 Leontief IO Modelsomeone that you used to knowNo ratings yet
- Topic D STD VerDocument49 pagesTopic D STD Verwgg5774No ratings yet
- Classical Theory of Employment-2Document13 pagesClassical Theory of Employment-2pphiriemmanuel888No ratings yet
- PS3 Ch10&Ch04&Ch05Document3 pagesPS3 Ch10&Ch04&Ch05品未No ratings yet
- Answers To Text Questions and Problems in Chapter 8Document12 pagesAnswers To Text Questions and Problems in Chapter 8carynesssNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 HoursDocument4 pagesSample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 HoursGaurav VermaNo ratings yet
- Chap10 (Agg Demand I) 0Document41 pagesChap10 (Agg Demand I) 0Hisham JawharNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Introductory Macroeconomics Chapter 3Document28 pagesLecture Notes in Introductory Macroeconomics Chapter 3ArrianeNo ratings yet
- The Keynesian Cross: A Simple Closed Economy Model in Which Income Is Determined by ExpenditureDocument39 pagesThe Keynesian Cross: A Simple Closed Economy Model in Which Income Is Determined by ExpenditureHimanshu KshatriyaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Homework Macro QuestionsDocument38 pagesAnswers To Homework Macro QuestionsAmna ShahNo ratings yet
- Theory of Production and Cost Analysis: Unit - IiDocument17 pagesTheory of Production and Cost Analysis: Unit - IisantoshvimsNo ratings yet
- PDTN FXNDocument9 pagesPDTN FXNrachmmmNo ratings yet
- Aggregate OutputDocument25 pagesAggregate OutputPrince AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Labor in A Economically Competitive StructureDocument7 pagesDistribution of Labor in A Economically Competitive StructureLalakisNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Modeling of Cavitation ErosionDocument11 pagesExperimental and Numerical Modeling of Cavitation ErosionКонстантин ФинниковNo ratings yet
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDocument12 pagesHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNo ratings yet
- DLL Mother TongueDocument41 pagesDLL Mother TongueMarxPascualBlancoNo ratings yet
- Onco, TSG & CancerDocument8 pagesOnco, TSG & Cancersumera120488No ratings yet
- Ozone Therapy Is Safest Known TherapyDocument35 pagesOzone Therapy Is Safest Known Therapyherdin2008100% (1)
- 8DIO Claire Oboe Virtuoso ManualDocument10 pages8DIO Claire Oboe Virtuoso ManualNiskaNo ratings yet
- HS-PS201: Simple ManualDocument6 pagesHS-PS201: Simple ManualCambiando CaminosNo ratings yet
- Characterising Roof Ventilators: P 2 A Q CDocument4 pagesCharacterising Roof Ventilators: P 2 A Q CDhirendra Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Tic EbookDocument215 pagesTic EbookTaju Deen100% (1)
- Statement of PurposeDocument3 pagesStatement of PurposeehsanNo ratings yet
- Laboratorium Pengujian Teknik Sipil Universitas Bandar LampungDocument1 pageLaboratorium Pengujian Teknik Sipil Universitas Bandar LampungPanji OctaWirawanNo ratings yet
- 21CC 4 U6Document10 pages21CC 4 U6Adrian Spanu100% (1)
- PR m1Document15 pagesPR m1Jazmyn BulusanNo ratings yet
- File Handling in JavaDocument8 pagesFile Handling in JavaDipendra KmNo ratings yet
- William Gann Method PDFDocument1 pageWilliam Gann Method PDFchandra widjajaNo ratings yet
- Communication CaseDocument3 pagesCommunication CasemirzaNo ratings yet
- SPECALOG Hitachi Ex2600-6Document7 pagesSPECALOG Hitachi Ex2600-6andrefilthNo ratings yet
- ERRF (Authentication Certification)Document3 pagesERRF (Authentication Certification)Aboi HubertNo ratings yet
- Ent Secretory Otitis MediaDocument3 pagesEnt Secretory Otitis MediaIrena DayehNo ratings yet
- Soc TB 25 May 2017Document37 pagesSoc TB 25 May 2017Ipie BsaNo ratings yet
- OrganoLithium ReagentDocument6 pagesOrganoLithium ReagentizaowsikNo ratings yet
- Multi-Component FTIR Emission Monitoring System: Abb Measurement & Analytics - Data SheetDocument16 pagesMulti-Component FTIR Emission Monitoring System: Abb Measurement & Analytics - Data SheetRonaldo JuniorNo ratings yet
- 5054 s16 Ms 41 PDFDocument3 pages5054 s16 Ms 41 PDFKritish RamnauthNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Battery Life of Your Galaxy Note 10 and Note 10Document18 pagesHow To Improve Battery Life of Your Galaxy Note 10 and Note 10rainpcruzNo ratings yet
- Protocols For Public-Key CryptosystemsDocument13 pagesProtocols For Public-Key CryptosystemsIvo LemosNo ratings yet
- Explosion Protection - E PDFDocument7 pagesExplosion Protection - E PDFAPCANo ratings yet
- Oliveira Et Al 2010Document8 pagesOliveira Et Al 2010Rômulo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Particle Filter TutorialDocument8 pagesParticle Filter TutorialTanmay NathNo ratings yet
- MTCNA Lab Guide INTRA 1st Edition - Id.en PDFDocument87 pagesMTCNA Lab Guide INTRA 1st Edition - Id.en PDFreyandyNo ratings yet