Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Specific Latent Heat-1
Specific Latent Heat-1
Uploaded by
Ejaz YusuffCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- KKS Code DescriptionDocument31 pagesKKS Code DescriptionAmal Chinthaka100% (3)
- MSDS New BERKO SAFE 106 NSFDocument5 pagesMSDS New BERKO SAFE 106 NSFAlves EdattukaranNo ratings yet
- E 107Document15 pagesE 107Thomas MelgarNo ratings yet
- Phys101l Report3 SaludDocument11 pagesPhys101l Report3 Saludyyuan ssaludNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationDocument5 pagesExperiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationMae Joy PalmaNo ratings yet
- Heat of Fusion of IceDocument2 pagesHeat of Fusion of IceReyna Federo100% (1)
- Experiment 6 Formal Report PDF FreeDocument9 pagesExperiment 6 Formal Report PDF FreeAliNo ratings yet
- Heat Fusion of Ice ReportDocument8 pagesHeat Fusion of Ice Reporthasifah abdazizNo ratings yet
- PAIR Report TemplateDocument2 pagesPAIR Report TemplateMharianne MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Physics: Heat TransferDocument18 pagesPhysics: Heat TransferDuncan KingNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Methods of MixturesDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - Methods of MixturesAngelica UyNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat of A LiquidDocument9 pagesSpecific Heat of A LiquidSai Swetha KVNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 (Formal Report)Document9 pagesExperiment 6 (Formal Report)Thea IbarraNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics Expt. 8. Latent HeatDocument3 pagesCSEC Physics Expt. 8. Latent HeatWHITTINHGAM RAYANNANo ratings yet
- HeatDocument7 pagesHeatkrushnakadam0029No ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument3 pagesLatent HeatJessicaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Matter - 23-24Document9 pagesThermal Properties of Matter - 23-24smodi6545No ratings yet
- Heat of Fusion of Ice: ScientificDocument4 pagesHeat of Fusion of Ice: ScientificSubha ShankareeNo ratings yet
- HW Chemistry 3may2024Document3 pagesHW Chemistry 3may2024rabiotadrien068No ratings yet
- Heat: A Measurable Form of Energy: CalorimetryDocument8 pagesHeat: A Measurable Form of Energy: CalorimetryAman LilaniNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Phys LabDocument3 pagesWeek 9 Phys LabJacob JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Edicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionDocument2 pagesEdicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionEdicto, Beatrice CarolineNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 Thermal EquilibriumDocument5 pagesExpt 2 Thermal EquilibriumchelcieariendeleonNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Heat of Fusion-Melting IceDocument7 pagesExp 4 Heat of Fusion-Melting IceEngelbert AddonganNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Document20 pagesThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument45 pagesThermal PhysicsChristine MalibiranNo ratings yet
- Rhys and Lazar of Heat Transfer ExperimentDocument6 pagesRhys and Lazar of Heat Transfer Experiment25.lazar.mNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat Fizik F4 Heat Notes SignedDocument17 pagesNota Padat Fizik F4 Heat Notes SignedkwNo ratings yet
- Thermody Lab Wa Na PerformDocument2 pagesThermody Lab Wa Na PerformGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 4: Heat: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocument10 pagesForm 4 Chapter 4: Heat: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumbatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Exp6Document7 pagesFormal Report Exp6Rachel CajilesNo ratings yet
- Experimental Determination of Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice: July 2022Document5 pagesExperimental Determination of Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice: July 2022Eric IradukundaNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument3 pagesHEATCrystal Blue Sapphire Silver Ace FleminixNo ratings yet
- Name: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeDocument11 pagesName: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeChrise RajNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Phy SyllabusDocument3 pagesSection 1 Phy SyllabusSHarves AUdiNo ratings yet
- Practical Work No 4Document2 pagesPractical Work No 4atd8950No ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document9 pagesExperiment 8Lj VillenaNo ratings yet
- Physics 223 Experiment 3: Latent Heat of Fusion: March 24, 2009Document1 pagePhysics 223 Experiment 3: Latent Heat of Fusion: March 24, 2009Tom WatsonNo ratings yet
- The Molecular Basis of Specific HeatDocument7 pagesThe Molecular Basis of Specific HeatJACOB SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 Specific Heat of SubstancesDocument5 pagesExperiment 10 Specific Heat of SubstancesAlexandra LynnNo ratings yet
- What We Have Already LearntDocument13 pagesWhat We Have Already Learnt'Shyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument30 pagesChapter 4 HeatSIP190004 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity and Calorimetry StudentDocument4 pagesHeat Capacity and Calorimetry StudentAmal JaberNo ratings yet
- Heat of FusionDocument3 pagesHeat of FusionDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- 6 Heat of Combust and Phase W PictureDocument4 pages6 Heat of Combust and Phase W Pictureaeliaeli29No ratings yet
- Thermal EnergyDocument48 pagesThermal EnergyDuncan StanleyNo ratings yet
- LATENT HEAT NotesDocument4 pagesLATENT HEAT NotesSowndaryaNo ratings yet
- Practice IV: Specific Heat of The MetalDocument6 pagesPractice IV: Specific Heat of The MetalMaria Jose CruzNo ratings yet
- Quantity of HeatDocument20 pagesQuantity of HeatabeeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Latent HeatDocument11 pagesExperiment 7 Latent HeatThomas MelgarNo ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of WaterDocument3 pagesSpecific Latent Heat of Fusion of WaterDon Donatus PhedsonNo ratings yet
- PHY210 CHAPTER 5 - THERMAL PHYSICS Students PDFDocument34 pagesPHY210 CHAPTER 5 - THERMAL PHYSICS Students PDFNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- Molar Enthalpy of SolutionDocument3 pagesMolar Enthalpy of SolutionKefentse Hinckson100% (1)
- To Find The Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of IceDocument4 pagesTo Find The Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of IcelalNo ratings yet
- 13 14 15 Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat GGDocument36 pages13 14 15 Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat GGNauman QureshyNo ratings yet
- 1 Secondary - Homework Sheet: H Oh Academy For ChemistryDocument7 pages1 Secondary - Homework Sheet: H Oh Academy For ChemistryMark FahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 IGCSE - ActualDocument7 pagesChapter 2 IGCSE - ActualNajia UmarNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatDocument6 pages4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- POB LogisticsDocument9 pagesPOB LogisticsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- May 2024 P2 SolutionsDocument23 pagesMay 2024 P2 SolutionsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of A BusinessDocument6 pagesLegal Aspects of A BusinessEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Pob Topic 8 - Business FinanceDocument13 pagesPob Topic 8 - Business FinanceEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry by Group PeaceDocument41 pagesCoordinate Geometry by Group PeaceEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- CSEC Agri Science P2s SolutionsDocument34 pagesCSEC Agri Science P2s SolutionsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Farm Financing and Support Services - 2020-12-09 - 1-21Document17 pages2.2 Farm Financing and Support Services - 2020-12-09 - 1-21Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Circle Thereoms2Document2 pagesCircle Thereoms2Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Reactivitty of Metals-1Document3 pagesReactivitty of Metals-1Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Lipids Presentation Group 1Document44 pagesLipids Presentation Group 1Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Group Success - Equation of LinesDocument35 pagesGroup Success - Equation of LinesEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Definition and The Functions of An EntrepreneurDocument2 pagesDefinition and The Functions of An EntrepreneurEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Ejaz Yusuff Grade 11scienceDocument1 pageEjaz Yusuff Grade 11scienceEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- NameDocument1 pageNameEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pagesQuadratic EquationsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Biology Long PaperDocument10 pagesBiology Long PaperEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Group Honesty Presentation On VariationDocument57 pagesGroup Honesty Presentation On VariationEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Sirpaul - Math Group Faith Simultaneous Equations Substitution Method PresentationDocument30 pagesSirpaul - Math Group Faith Simultaneous Equations Substitution Method PresentationEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Royal Purple MSDSDocument4 pagesRoyal Purple MSDSEugene MelamedNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet Class IX PDFDocument4 pagesScience Worksheet Class IX PDFsundar rajNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Geothermal EnergyDocument5 pagesCH 10 Geothermal EnergyscharichNo ratings yet
- Vildagliptin Using Metabolite Data To Develop Patient Centric SDocument10 pagesVildagliptin Using Metabolite Data To Develop Patient Centric SВасилина ДмитеркоNo ratings yet
- Ch 1 上課教材 PDFDocument12 pagesCh 1 上課教材 PDFTai-Yuan HsuNo ratings yet
- GlossaireDocument21 pagesGlossaireDenis SuntovNo ratings yet
- Astm A999 A999m 13Document11 pagesAstm A999 A999m 13islamakthamNo ratings yet
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Torque Rheometry: A Viable Combination For Determining Processing Parameters of Thermosetting PlasticsDocument7 pagesDifferential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Torque Rheometry: A Viable Combination For Determining Processing Parameters of Thermosetting Plasticsgunawan refiadiNo ratings yet
- ICH 361 Polymer RheologyDocument9 pagesICH 361 Polymer RheologyOkolo GloryNo ratings yet
- H 55.25 Mev (Bragg Peak Used As "Range") : Let (In Water) 1.162 Kev/ MDocument12 pagesH 55.25 Mev (Bragg Peak Used As "Range") : Let (In Water) 1.162 Kev/ MdimbillNo ratings yet
- Geostats Pty LTD: Base Metal AnalysesDocument1 pageGeostats Pty LTD: Base Metal AnalysesJhony Enrique Morales LauraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical SealsDocument2 pagesMechanical Sealscuraaj100% (1)
- Mgti - MSDS Granulated CharcoalDocument4 pagesMgti - MSDS Granulated CharcoalRyan NufableNo ratings yet
- Chapter01 PDFDocument16 pagesChapter01 PDFnirattisaikulNo ratings yet
- Gastro Retentive DELIVERY SYSTEMSDocument77 pagesGastro Retentive DELIVERY SYSTEMSAnirudh Jain ChampawatNo ratings yet
- Sikafloor Duochem 6001 (A B) EDocument10 pagesSikafloor Duochem 6001 (A B) EYesi SaputriNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: XDocument8 pagesFood Chemistry: XGuisela Carbajal RomeroNo ratings yet
- 5.lecture For Microbial Nutrition and GrowthDocument89 pages5.lecture For Microbial Nutrition and GrowthTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Terpenes and Terpenoids: Principles of Biochemistry BIOC-301 Dr. Gull-E-FaranDocument10 pagesTerpenes and Terpenoids: Principles of Biochemistry BIOC-301 Dr. Gull-E-FaranFahad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Table of Content of Printouts:: Externally Bonded FRP Reinforcement For RC Structures: Post StrengtheningDocument50 pagesTable of Content of Printouts:: Externally Bonded FRP Reinforcement For RC Structures: Post StrengtheningacribdingNo ratings yet
- Pmwasabi cx43Document4 pagesPmwasabi cx43AlleleBiotechNo ratings yet
- Basics in Mineral Processing-Wear in OperationDocument12 pagesBasics in Mineral Processing-Wear in Operationmakedo33100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Chemistry Sample Qp-2023-1Document207 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Chemistry Sample Qp-2023-1jklementeenaNo ratings yet
- Alkali Sulphur RatioDocument3 pagesAlkali Sulphur RatioSiddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Refractory and High Temperature Ceramic Coatings and CementsDocument2 pagesRefractory and High Temperature Ceramic Coatings and CementsAnderman Ceramics LtNo ratings yet
- 1 SDS Econat LASDocument5 pages1 SDS Econat LASandriNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure PDFMiaMiaNo ratings yet
- CFBT GlossaryDocument93 pagesCFBT GlossaryShan RaffelNo ratings yet
Specific Latent Heat-1
Specific Latent Heat-1
Uploaded by
Ejaz YusuffOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Specific Latent Heat-1
Specific Latent Heat-1
Uploaded by
Ejaz YusuffCopyright:
Available Formats
Title: Specific latent heat of fusion of ice
Aim: To determine the specific latent heat of fusion
Theory : Specific latent heat of fusion of a substance is the heat energy needed to change unit mass of
the substance from solid to liquid without a change in temperature. Heat is the form of energy that is
transferred between systems or objects with different temperatures.
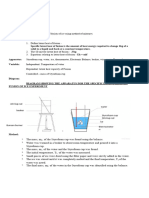
The mass of the Styrofoam cup will be determined, water will be heated to 35 degrees Celsius and
transferred into the cup, temperature will be recorded, mass of the water will be determined, ice will be
added, stirred until completely melted, and the final temperature will be recorded.
Apparatus:
1. Thermometer
2. Electronic scale
Material :
1. Styrofoam cup
2. Ice
3. Tissue
4. Heater
5. Water
Method:
1. The mass of the Styrofoam cup was determined
2. The water was heated to 35 degrees Celsius and transferred into the Styrofoam cup
3. Temperature was then recorded
4. The mass of the water was determined
5. Small pieces of ice were dried with tissue and added to the water in the Styrofoam cup.
6. It was then stirred with the thermometer until the ice was completely melted.
7. The final temperature was recorded.
Results and calculations:
Discussion:
In this experiment the aim was to find the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. In the solid state,
exemplified by the ice molecules are held together by intermolecular forces. When heat energy is
supplied to the ice, these molecules gain internal energy, eventually surpassing the forces that hold them
in place. At the melting point, usually 0 degrees Celsius for ice, thus energy is utilized to weaken the
intermolecular bonds allowing the molecules to transition into the liquid state. This transition occurs
without a change in temperature due to the absorbed energy being used solely for breaking these bond
representing the specific latent heat of fusion.
The initial temperature of the water was when it was transferred to the Styrofoam cup, which was
36.5 degrees Celsius, and when the ice was added, the final temperature was 24 degrees Celsius.The ice
had cooled the water. The mass of the water was 0.11930kg and the mass of the ice was 0.0185kg. The
heat loss of the water is equal to the heat gain of the ice. To find for the specific latent heat of fusion of
ice the formula:
mcΔt= Lfm + mcΔt
will be used. Where, M is be the mass,c is the specific heat capacity, and Δt is the change in temperature.
Limitations:
1. Evaporation can occur causing the experiments results and calculations.
Sources of error:
1. Incomplete melting of ice
2. Incorrect reading of electronic scale.
Precautions :
1. Read electronic scale accurately
2. Make sure all the ice was fully melted.
3. Be sensible when handling apparatus.
Conclusion:
It can be concluded that the specific latent heat of fusion of 0.0185kg of ice is 2.3 * 10^5 j kg^-1.
You might also like
- KKS Code DescriptionDocument31 pagesKKS Code DescriptionAmal Chinthaka100% (3)
- MSDS New BERKO SAFE 106 NSFDocument5 pagesMSDS New BERKO SAFE 106 NSFAlves EdattukaranNo ratings yet
- E 107Document15 pagesE 107Thomas MelgarNo ratings yet
- Phys101l Report3 SaludDocument11 pagesPhys101l Report3 Saludyyuan ssaludNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationDocument5 pagesExperiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationMae Joy PalmaNo ratings yet
- Heat of Fusion of IceDocument2 pagesHeat of Fusion of IceReyna Federo100% (1)
- Experiment 6 Formal Report PDF FreeDocument9 pagesExperiment 6 Formal Report PDF FreeAliNo ratings yet
- Heat Fusion of Ice ReportDocument8 pagesHeat Fusion of Ice Reporthasifah abdazizNo ratings yet
- PAIR Report TemplateDocument2 pagesPAIR Report TemplateMharianne MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Physics: Heat TransferDocument18 pagesPhysics: Heat TransferDuncan KingNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Methods of MixturesDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - Methods of MixturesAngelica UyNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat of A LiquidDocument9 pagesSpecific Heat of A LiquidSai Swetha KVNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 (Formal Report)Document9 pagesExperiment 6 (Formal Report)Thea IbarraNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics Expt. 8. Latent HeatDocument3 pagesCSEC Physics Expt. 8. Latent HeatWHITTINHGAM RAYANNANo ratings yet
- HeatDocument7 pagesHeatkrushnakadam0029No ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument3 pagesLatent HeatJessicaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Matter - 23-24Document9 pagesThermal Properties of Matter - 23-24smodi6545No ratings yet
- Heat of Fusion of Ice: ScientificDocument4 pagesHeat of Fusion of Ice: ScientificSubha ShankareeNo ratings yet
- HW Chemistry 3may2024Document3 pagesHW Chemistry 3may2024rabiotadrien068No ratings yet
- Heat: A Measurable Form of Energy: CalorimetryDocument8 pagesHeat: A Measurable Form of Energy: CalorimetryAman LilaniNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Phys LabDocument3 pagesWeek 9 Phys LabJacob JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Edicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionDocument2 pagesEdicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionEdicto, Beatrice CarolineNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 Thermal EquilibriumDocument5 pagesExpt 2 Thermal EquilibriumchelcieariendeleonNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Heat of Fusion-Melting IceDocument7 pagesExp 4 Heat of Fusion-Melting IceEngelbert AddonganNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Document20 pagesThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument45 pagesThermal PhysicsChristine MalibiranNo ratings yet
- Rhys and Lazar of Heat Transfer ExperimentDocument6 pagesRhys and Lazar of Heat Transfer Experiment25.lazar.mNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat Fizik F4 Heat Notes SignedDocument17 pagesNota Padat Fizik F4 Heat Notes SignedkwNo ratings yet
- Thermody Lab Wa Na PerformDocument2 pagesThermody Lab Wa Na PerformGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chapter 4: Heat: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumDocument10 pagesForm 4 Chapter 4: Heat: Understanding Thermal EquilibriumbatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Exp6Document7 pagesFormal Report Exp6Rachel CajilesNo ratings yet
- Experimental Determination of Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice: July 2022Document5 pagesExperimental Determination of Latent Heat of Fusion of Ice: July 2022Eric IradukundaNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument3 pagesHEATCrystal Blue Sapphire Silver Ace FleminixNo ratings yet
- Name: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeDocument11 pagesName: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeChrise RajNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Phy SyllabusDocument3 pagesSection 1 Phy SyllabusSHarves AUdiNo ratings yet
- Practical Work No 4Document2 pagesPractical Work No 4atd8950No ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document9 pagesExperiment 8Lj VillenaNo ratings yet
- Physics 223 Experiment 3: Latent Heat of Fusion: March 24, 2009Document1 pagePhysics 223 Experiment 3: Latent Heat of Fusion: March 24, 2009Tom WatsonNo ratings yet
- The Molecular Basis of Specific HeatDocument7 pagesThe Molecular Basis of Specific HeatJACOB SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 Specific Heat of SubstancesDocument5 pagesExperiment 10 Specific Heat of SubstancesAlexandra LynnNo ratings yet
- What We Have Already LearntDocument13 pagesWhat We Have Already Learnt'Shyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument30 pagesChapter 4 HeatSIP190004 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity and Calorimetry StudentDocument4 pagesHeat Capacity and Calorimetry StudentAmal JaberNo ratings yet
- Heat of FusionDocument3 pagesHeat of FusionDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- 6 Heat of Combust and Phase W PictureDocument4 pages6 Heat of Combust and Phase W Pictureaeliaeli29No ratings yet
- Thermal EnergyDocument48 pagesThermal EnergyDuncan StanleyNo ratings yet
- LATENT HEAT NotesDocument4 pagesLATENT HEAT NotesSowndaryaNo ratings yet
- Practice IV: Specific Heat of The MetalDocument6 pagesPractice IV: Specific Heat of The MetalMaria Jose CruzNo ratings yet
- Quantity of HeatDocument20 pagesQuantity of HeatabeeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Latent HeatDocument11 pagesExperiment 7 Latent HeatThomas MelgarNo ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Heating Substances COMPLETEDocument13 pagesHeating Substances COMPLETEMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of WaterDocument3 pagesSpecific Latent Heat of Fusion of WaterDon Donatus PhedsonNo ratings yet
- PHY210 CHAPTER 5 - THERMAL PHYSICS Students PDFDocument34 pagesPHY210 CHAPTER 5 - THERMAL PHYSICS Students PDFNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- Molar Enthalpy of SolutionDocument3 pagesMolar Enthalpy of SolutionKefentse Hinckson100% (1)
- To Find The Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of IceDocument4 pagesTo Find The Specific Latent Heat of Fusion of IcelalNo ratings yet
- 13 14 15 Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat GGDocument36 pages13 14 15 Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat GGNauman QureshyNo ratings yet
- 1 Secondary - Homework Sheet: H Oh Academy For ChemistryDocument7 pages1 Secondary - Homework Sheet: H Oh Academy For ChemistryMark FahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 IGCSE - ActualDocument7 pagesChapter 2 IGCSE - ActualNajia UmarNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatDocument6 pages4.1 Understanding Thermal Equilibrium: Chapter Summary / Chap. 4/ HeatkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- POB LogisticsDocument9 pagesPOB LogisticsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- May 2024 P2 SolutionsDocument23 pagesMay 2024 P2 SolutionsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of A BusinessDocument6 pagesLegal Aspects of A BusinessEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Pob Topic 8 - Business FinanceDocument13 pagesPob Topic 8 - Business FinanceEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry by Group PeaceDocument41 pagesCoordinate Geometry by Group PeaceEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- CSEC Agri Science P2s SolutionsDocument34 pagesCSEC Agri Science P2s SolutionsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Farm Financing and Support Services - 2020-12-09 - 1-21Document17 pages2.2 Farm Financing and Support Services - 2020-12-09 - 1-21Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Circle Thereoms2Document2 pagesCircle Thereoms2Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Reactivitty of Metals-1Document3 pagesReactivitty of Metals-1Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Lipids Presentation Group 1Document44 pagesLipids Presentation Group 1Ejaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Group Success - Equation of LinesDocument35 pagesGroup Success - Equation of LinesEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Definition and The Functions of An EntrepreneurDocument2 pagesDefinition and The Functions of An EntrepreneurEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Ejaz Yusuff Grade 11scienceDocument1 pageEjaz Yusuff Grade 11scienceEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- NameDocument1 pageNameEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument28 pagesQuadratic EquationsEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Biology Long PaperDocument10 pagesBiology Long PaperEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Group Honesty Presentation On VariationDocument57 pagesGroup Honesty Presentation On VariationEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Sirpaul - Math Group Faith Simultaneous Equations Substitution Method PresentationDocument30 pagesSirpaul - Math Group Faith Simultaneous Equations Substitution Method PresentationEjaz YusuffNo ratings yet
- Royal Purple MSDSDocument4 pagesRoyal Purple MSDSEugene MelamedNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet Class IX PDFDocument4 pagesScience Worksheet Class IX PDFsundar rajNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Geothermal EnergyDocument5 pagesCH 10 Geothermal EnergyscharichNo ratings yet
- Vildagliptin Using Metabolite Data To Develop Patient Centric SDocument10 pagesVildagliptin Using Metabolite Data To Develop Patient Centric SВасилина ДмитеркоNo ratings yet
- Ch 1 上課教材 PDFDocument12 pagesCh 1 上課教材 PDFTai-Yuan HsuNo ratings yet
- GlossaireDocument21 pagesGlossaireDenis SuntovNo ratings yet
- Astm A999 A999m 13Document11 pagesAstm A999 A999m 13islamakthamNo ratings yet
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Torque Rheometry: A Viable Combination For Determining Processing Parameters of Thermosetting PlasticsDocument7 pagesDifferential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Torque Rheometry: A Viable Combination For Determining Processing Parameters of Thermosetting Plasticsgunawan refiadiNo ratings yet
- ICH 361 Polymer RheologyDocument9 pagesICH 361 Polymer RheologyOkolo GloryNo ratings yet
- H 55.25 Mev (Bragg Peak Used As "Range") : Let (In Water) 1.162 Kev/ MDocument12 pagesH 55.25 Mev (Bragg Peak Used As "Range") : Let (In Water) 1.162 Kev/ MdimbillNo ratings yet
- Geostats Pty LTD: Base Metal AnalysesDocument1 pageGeostats Pty LTD: Base Metal AnalysesJhony Enrique Morales LauraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical SealsDocument2 pagesMechanical Sealscuraaj100% (1)
- Mgti - MSDS Granulated CharcoalDocument4 pagesMgti - MSDS Granulated CharcoalRyan NufableNo ratings yet
- Chapter01 PDFDocument16 pagesChapter01 PDFnirattisaikulNo ratings yet
- Gastro Retentive DELIVERY SYSTEMSDocument77 pagesGastro Retentive DELIVERY SYSTEMSAnirudh Jain ChampawatNo ratings yet
- Sikafloor Duochem 6001 (A B) EDocument10 pagesSikafloor Duochem 6001 (A B) EYesi SaputriNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: XDocument8 pagesFood Chemistry: XGuisela Carbajal RomeroNo ratings yet
- 5.lecture For Microbial Nutrition and GrowthDocument89 pages5.lecture For Microbial Nutrition and GrowthTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Terpenes and Terpenoids: Principles of Biochemistry BIOC-301 Dr. Gull-E-FaranDocument10 pagesTerpenes and Terpenoids: Principles of Biochemistry BIOC-301 Dr. Gull-E-FaranFahad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Table of Content of Printouts:: Externally Bonded FRP Reinforcement For RC Structures: Post StrengtheningDocument50 pagesTable of Content of Printouts:: Externally Bonded FRP Reinforcement For RC Structures: Post StrengtheningacribdingNo ratings yet
- Pmwasabi cx43Document4 pagesPmwasabi cx43AlleleBiotechNo ratings yet
- Basics in Mineral Processing-Wear in OperationDocument12 pagesBasics in Mineral Processing-Wear in Operationmakedo33100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Chemistry Sample Qp-2023-1Document207 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Chemistry Sample Qp-2023-1jklementeenaNo ratings yet
- Alkali Sulphur RatioDocument3 pagesAlkali Sulphur RatioSiddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Refractory and High Temperature Ceramic Coatings and CementsDocument2 pagesRefractory and High Temperature Ceramic Coatings and CementsAnderman Ceramics LtNo ratings yet
- 1 SDS Econat LASDocument5 pages1 SDS Econat LASandriNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure PDFMiaMiaNo ratings yet
- CFBT GlossaryDocument93 pagesCFBT GlossaryShan RaffelNo ratings yet