Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsAlgebra
Algebra
Uploaded by
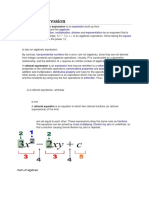
salomon.pupoAlgebra deals with mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating them. It focuses on representing quantities and solving equations. Key concepts in algebra include variables and expressions, equations and inequalities, polynomials, factoring, functions, systems of equations and inequalities, matrices and determinants, graphs and coordinate geometry, exponents and radicals, and quadratic equations. Algebra provides a framework for problem-solving, modeling real-world situations, and understanding mathematical relationships that serves as a foundation for more advanced mathematics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Calculus 1 By: Grace Carticiano & Francheska Cuison Quizzes Quiz 3Document17 pagesCalculus 1 By: Grace Carticiano & Francheska Cuison Quizzes Quiz 3Jas John50% (8)
- Dixmier - C AlgebrasDocument493 pagesDixmier - C AlgebrasgalileoNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 (Direct and Inverse Variations)Document1 pageSummative Test 1 (Direct and Inverse Variations)Kresel Dioneda83% (6)
- Algebra 2 Curriculum AlignmentDocument43 pagesAlgebra 2 Curriculum Alignmentapi-254765842No ratings yet
- It's A Request As Your Teacher and Elder Brother To All of You Guys To Please Please Do It by YourselfDocument8 pagesIt's A Request As Your Teacher and Elder Brother To All of You Guys To Please Please Do It by YourselfAbeer Zahid0% (1)
- AlgebraDocument1 pageAlgebrahl69962731No ratings yet
- Mathq Prelim ReviewerDocument4 pagesMathq Prelim Reviewerfujiko galboNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3rteNo ratings yet
- Basic Algebra NotesDocument2 pagesBasic Algebra NotesCedric MontianoNo ratings yet
- Algebra MasteringDocument2 pagesAlgebra MasteringamisdpcstudentsNo ratings yet
- The Math Test: Overview: Updated From Website On 01 July 2022Document7 pagesThe Math Test: Overview: Updated From Website On 01 July 2022FARRAGONo ratings yet
- Algebra NotesDocument2 pagesAlgebra Notesjanas.neilcarloNo ratings yet
- ALJABARDocument3 pagesALJABARauliyah copyNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1Document2 pagesAlgebra 1dummkopfworkNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument4 pagesAlgebrahellashah5412No ratings yet
- Algebra EssayDocument2 pagesAlgebra Essayritam96799No ratings yet
- TestDocument1 pageTest649f6c4a3bNo ratings yet
- Algebra Math: Algebra Is One Among The Oldest Branches in The History of Mathematics Dealing With The NumberDocument6 pagesAlgebra Math: Algebra Is One Among The Oldest Branches in The History of Mathematics Dealing With The Numbersania2011No ratings yet
- CONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Document17 pagesCONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Jaysa Avila SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- AlzebraDocument3 pagesAlzebrareachudaycNo ratings yet
- ExpressionsDocument9 pagesExpressionsapi-242295647No ratings yet
- CcssDocument5 pagesCcssapi-237229475No ratings yet
- Algebra EssayDocument1 pageAlgebra Essayjohn williamsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document8 pagesLecture 01maryam.abid.vuNo ratings yet
- ECON1003 UNIT 2 Version 1 - Part 1 REV 2Document29 pagesECON1003 UNIT 2 Version 1 - Part 1 REV 2Kyle MerrittNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and ScienceDocument21 pagesMathematics and ScienceTricia BautistaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Reference: Basic IdentitiesDocument18 pagesAlgebra Reference: Basic IdentitiesgowsikhNo ratings yet
- Cau 1 Parentletter 1Document2 pagesCau 1 Parentletter 1api-208514376No ratings yet
- CL 1.4 Quantitative Methods For BusinessDocument145 pagesCL 1.4 Quantitative Methods For BusinessnushathNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematics: Week 1 Review of Basic Arithmetic Operations & AlgebraDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mathematics: Week 1 Review of Basic Arithmetic Operations & AlgebraRafay ShahabNo ratings yet
- 712at2algebrabig IdeasDocument3 pages712at2algebrabig IdeasMarc MatthewsNo ratings yet
- College & Advanced Algebra Course OutlineDocument7 pagesCollege & Advanced Algebra Course OutlinemsavilesnetsecphNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Algebra Arranged by Unit Mathematics Standards Committee March 15, 2005Document9 pagesAlgebra: Algebra Arranged by Unit Mathematics Standards Committee March 15, 2005Masha IwqedweNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Teaching Elementary MathematicsDocument10 pagesStrategies For Teaching Elementary MathematicsRhomalyn ValentonNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview What Is Algebra? History Algebra Is Named in Honor of Mohammed Ibn-e-MusaDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Overview What Is Algebra? History Algebra Is Named in Honor of Mohammed Ibn-e-Musagulfam yasinNo ratings yet
- 06 Maths Ch11 AlgebraDocument2 pages06 Maths Ch11 Algebrakavita.giri47No ratings yet
- Algebraic Expression: 3x 2xy + CDocument1 pageAlgebraic Expression: 3x 2xy + CKennedy BolanteNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry Are Both Branches of MathematicsDocument1 pageAlgebra and Trigonometry Are Both Branches of MathematicsAshly VillaramaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Skills: Number PatternsDocument2 pagesAlgebraic Skills: Number PatternsGeorgeAruNo ratings yet
- Equations and Inequalities: College AlgebraDocument22 pagesEquations and Inequalities: College AlgebraRic NapusNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Student NotesDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra Student NotesJaromír KoflákNo ratings yet
- Syllabus OutlineDocument88 pagesSyllabus OutlineKazi Ayman RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabi 2015-2016Document1 pageCourse Syllabi 2015-2016api-294397535No ratings yet
- Expressions and Formulaes - Understanding DifferencesDocument10 pagesExpressions and Formulaes - Understanding DifferencesAKSHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Mathematics AA HL SyllabusDocument58 pagesMathematics AA HL SyllabusGraciela AudreyNo ratings yet
- Math Class NotesDocument1 pageMath Class Notesainur.seidullaNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Algebra (2ND Sem)Document8 pagesMath 2 Algebra (2ND Sem)jennylynbodota17No ratings yet
- Algebra Class NotesDocument3 pagesAlgebra Class Notesxh7xyn8qsbNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Expressionapi-150539480No ratings yet
- Elementary Algebra: Elementary Algebra Encompasses Some of The Basic Concepts ofDocument17 pagesElementary Algebra: Elementary Algebra Encompasses Some of The Basic Concepts ofNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- GRE Maths Syllabus (Quantitative Reasoning) : ArithmeticDocument4 pagesGRE Maths Syllabus (Quantitative Reasoning) : ArithmeticAhmed Magdy El-SayedNo ratings yet
- Math2056 Lecturenotes Week1Document69 pagesMath2056 Lecturenotes Week1Taha MisirliNo ratings yet
- Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 4 Parent Tip SheetDocument2 pagesEureka Math Grade 6 Module 4 Parent Tip Sheetapi-324380772No ratings yet
- Numerical and Abstract Reasoning: Mathematics GuideDocument17 pagesNumerical and Abstract Reasoning: Mathematics GuideKazi Ayman RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Regional Math Olympaid How To StudyDocument2 pagesRegional Math Olympaid How To StudySudip799No ratings yet
- L4a - Supervised LearningDocument25 pagesL4a - Supervised LearningKinya KageniNo ratings yet
- Day 2 AlgebraDocument2 pagesDay 2 AlgebraCarl Dominic LlavanNo ratings yet
- AA Syllabus Outline 2019Document87 pagesAA Syllabus Outline 2019derrickzptofficialNo ratings yet
- AL3451 - Unit 1Document12 pagesAL3451 - Unit 1jeffrinsb7No ratings yet
- Glossary of Areas of Mathematics - WikipediaDocument123 pagesGlossary of Areas of Mathematics - WikipediaUchechukwu MarizuNo ratings yet
- Ap Calculus Ab - Week of Feb 27 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAp Calculus Ab - Week of Feb 27 Lesson Planapi-282064530100% (1)
- Term 1 - End of Unit Math Topic ListDocument2 pagesTerm 1 - End of Unit Math Topic ListMáxima BrunoNo ratings yet
- The Modulus Function - DefinationsDocument4 pagesThe Modulus Function - DefinationsCompetitive TutorialNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 MAT2002 ETH VL2019201000415 Reference Material II 06-Aug-2019 Half Range SeriesDocument11 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 MAT2002 ETH VL2019201000415 Reference Material II 06-Aug-2019 Half Range SeriesShridhar MahtoNo ratings yet
- OMAT - Lecture 1 Review of Fundamentals - STD PDFDocument76 pagesOMAT - Lecture 1 Review of Fundamentals - STD PDFNguyễn Ngọc PhươngNo ratings yet
- Connection Machine LispDocument19 pagesConnection Machine LispchaitanyaguptaNo ratings yet
- NET Past Paper 5 PlspotDocument29 pagesNET Past Paper 5 PlspotVishal Raj SundraniNo ratings yet
- Math HL Baseline SyllabusDocument9 pagesMath HL Baseline SyllabusNoyonika DeyNo ratings yet
- Infinite Series, Improper Integrals, and Taylor SeriesDocument21 pagesInfinite Series, Improper Integrals, and Taylor SeriesscribddivNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Python Programming: Fission Reactor Physics 1Document56 pagesIntroduction To Python Programming: Fission Reactor Physics 1Leonardo MonacoNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 3Document32 pagesPractice Test 3api-359949059No ratings yet
- Integrales Elipticas y Funciones Elipticas PDFDocument108 pagesIntegrales Elipticas y Funciones Elipticas PDFJhon Edison Bravo BuitragoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Mathematical Languages and SymbolsDocument15 pagesLesson 3 Mathematical Languages and SymbolsMV ANo ratings yet
- Calculator TipsDocument6 pagesCalculator TipsCNo ratings yet
- Compiler DesignDocument186 pagesCompiler DesignsudiptoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Generation of A Software Requirements Specification SRS DocumentDocument6 pagesAutomatic Generation of A Software Requirements Specification SRS DocumentAgain MishraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Embedded ControllersDocument122 pagesLecture Notes For Embedded ControllersJorge PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 2015 Nsucrypto ArticleDocument32 pages2015 Nsucrypto ArticlebayareakingNo ratings yet
- Math SymbolsDocument22 pagesMath SymbolsHoang GiangNo ratings yet
- Diss Week 6Document5 pagesDiss Week 6John Briane CapiliNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Introduction-to-FUNCTIONDocument36 pagesGen Math Introduction-to-FUNCTIONJaena Marie EwenNo ratings yet
- Lagro High SchoolDocument12 pagesLagro High SchoolKarl SiaganNo ratings yet
- 0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDocument2 pages0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDiep NguyenNo ratings yet
- Critical PointsDocument7 pagesCritical PointsjeffconnorsNo ratings yet
- MOdule GRADE 11 Module 1-2Document8 pagesMOdule GRADE 11 Module 1-2Christian CabadonggaNo ratings yet
- Python - Make Your Own Mandelbrot Set PDFDocument8 pagesPython - Make Your Own Mandelbrot Set PDFRicardo_SemogNo ratings yet
- Application of Surface of Revolution in Different Branches of ScienceDocument8 pagesApplication of Surface of Revolution in Different Branches of ScienceThe MukherjeeNo ratings yet
Algebra
Algebra
Uploaded by
salomon.pupo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesAlgebra deals with mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating them. It focuses on representing quantities and solving equations. Key concepts in algebra include variables and expressions, equations and inequalities, polynomials, factoring, functions, systems of equations and inequalities, matrices and determinants, graphs and coordinate geometry, exponents and radicals, and quadratic equations. Algebra provides a framework for problem-solving, modeling real-world situations, and understanding mathematical relationships that serves as a foundation for more advanced mathematics.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlgebra deals with mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating them. It focuses on representing quantities and solving equations. Key concepts in algebra include variables and expressions, equations and inequalities, polynomials, factoring, functions, systems of equations and inequalities, matrices and determinants, graphs and coordinate geometry, exponents and radicals, and quadratic equations. Algebra provides a framework for problem-solving, modeling real-world situations, and understanding mathematical relationships that serves as a foundation for more advanced mathematics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesAlgebra
Algebra
Uploaded by
salomon.pupoAlgebra deals with mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating them. It focuses on representing quantities and solving equations. Key concepts in algebra include variables and expressions, equations and inequalities, polynomials, factoring, functions, systems of equations and inequalities, matrices and determinants, graphs and coordinate geometry, exponents and radicals, and quadratic equations. Algebra provides a framework for problem-solving, modeling real-world situations, and understanding mathematical relationships that serves as a foundation for more advanced mathematics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as rtf, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with mathematical
symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols. It involves the
study of mathematical structures and relationships, focusing on the
representation of quantities and the solution of equations. Algebra is a
fundamental tool in various fields, including science, engineering,
economics, and computer science. Key concepts and topics in algebra
include:
Variables and Expressions:
• Variables are symbols (usually letters) that represent unknown or
varying quantities.
• Expressions are combinations of variables, numbers, and operations.
Equations and Inequalities:
• Equations express a relationship between two expressions and are
typically solved to find the values of the variables.
• Inequalities compare two expressions using symbols like <, >, ≤, or ≥.
Polynomials:
• Polynomials are expressions consisting of variables and coefficients,
combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
• Monomials, binomials, and trinomials are specific types of polynomials.
Factoring:
• Factoring involves expressing a polynomial as a product of its factors.
• Factoring is crucial for solving equations and simplifying expressions.
Functions:
• Functions describe a relationship between input and output values.
• Linear functions, quadratic functions, and exponential functions are
common types.
Systems of Equations and Inequalities:
• Systems involve multiple equations or inequalities that share common
variables.
• Solutions are sets of values that satisfy all equations or inequalities
simultaneously.
Matrices and Determinants:
• Matrices are arrays of numbers, and determinants are specific values
associated with square matrices.
• Matrices are used in solving systems of linear equations and various
applications.
Graphs and Coordinate Geometry:
• Graphs visually represent mathematical relationships on a coordinate
plane.
• Algebraic concepts are often connected to geometric interpretations.
Exponents and Radicals:
• Exponents represent repeated multiplication, while radicals involve
roots.
• Laws of exponents and rules for radicals are essential for simplifying
expressions.
Quadratic Equations:
• Quadratic equations involve second-degree polynomials and can be
solved using methods like factoring, completing the square, or the
quadratic formula.
Algebra provides a powerful framework for problem-solving, modeling
real-world situations, and understanding mathematical relationships. It
serves as a foundation for more advanced mathematical studies and has
widespread applications across various disciplines.
You might also like
- Calculus 1 By: Grace Carticiano & Francheska Cuison Quizzes Quiz 3Document17 pagesCalculus 1 By: Grace Carticiano & Francheska Cuison Quizzes Quiz 3Jas John50% (8)
- Dixmier - C AlgebrasDocument493 pagesDixmier - C AlgebrasgalileoNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 (Direct and Inverse Variations)Document1 pageSummative Test 1 (Direct and Inverse Variations)Kresel Dioneda83% (6)
- Algebra 2 Curriculum AlignmentDocument43 pagesAlgebra 2 Curriculum Alignmentapi-254765842No ratings yet
- It's A Request As Your Teacher and Elder Brother To All of You Guys To Please Please Do It by YourselfDocument8 pagesIt's A Request As Your Teacher and Elder Brother To All of You Guys To Please Please Do It by YourselfAbeer Zahid0% (1)
- AlgebraDocument1 pageAlgebrahl69962731No ratings yet
- Mathq Prelim ReviewerDocument4 pagesMathq Prelim Reviewerfujiko galboNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3rteNo ratings yet
- Basic Algebra NotesDocument2 pagesBasic Algebra NotesCedric MontianoNo ratings yet
- Algebra MasteringDocument2 pagesAlgebra MasteringamisdpcstudentsNo ratings yet
- The Math Test: Overview: Updated From Website On 01 July 2022Document7 pagesThe Math Test: Overview: Updated From Website On 01 July 2022FARRAGONo ratings yet
- Algebra NotesDocument2 pagesAlgebra Notesjanas.neilcarloNo ratings yet
- ALJABARDocument3 pagesALJABARauliyah copyNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1Document2 pagesAlgebra 1dummkopfworkNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument4 pagesAlgebrahellashah5412No ratings yet
- Algebra EssayDocument2 pagesAlgebra Essayritam96799No ratings yet
- TestDocument1 pageTest649f6c4a3bNo ratings yet
- Algebra Math: Algebra Is One Among The Oldest Branches in The History of Mathematics Dealing With The NumberDocument6 pagesAlgebra Math: Algebra Is One Among The Oldest Branches in The History of Mathematics Dealing With The Numbersania2011No ratings yet
- CONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Document17 pagesCONTENT AREA: Mathematics GRADE LEVEL: Grade 10/high School (HS)Jaysa Avila SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- AlzebraDocument3 pagesAlzebrareachudaycNo ratings yet
- ExpressionsDocument9 pagesExpressionsapi-242295647No ratings yet
- CcssDocument5 pagesCcssapi-237229475No ratings yet
- Algebra EssayDocument1 pageAlgebra Essayjohn williamsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document8 pagesLecture 01maryam.abid.vuNo ratings yet
- ECON1003 UNIT 2 Version 1 - Part 1 REV 2Document29 pagesECON1003 UNIT 2 Version 1 - Part 1 REV 2Kyle MerrittNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and ScienceDocument21 pagesMathematics and ScienceTricia BautistaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Reference: Basic IdentitiesDocument18 pagesAlgebra Reference: Basic IdentitiesgowsikhNo ratings yet
- Cau 1 Parentletter 1Document2 pagesCau 1 Parentletter 1api-208514376No ratings yet
- CL 1.4 Quantitative Methods For BusinessDocument145 pagesCL 1.4 Quantitative Methods For BusinessnushathNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematics: Week 1 Review of Basic Arithmetic Operations & AlgebraDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mathematics: Week 1 Review of Basic Arithmetic Operations & AlgebraRafay ShahabNo ratings yet
- 712at2algebrabig IdeasDocument3 pages712at2algebrabig IdeasMarc MatthewsNo ratings yet
- College & Advanced Algebra Course OutlineDocument7 pagesCollege & Advanced Algebra Course OutlinemsavilesnetsecphNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Algebra Arranged by Unit Mathematics Standards Committee March 15, 2005Document9 pagesAlgebra: Algebra Arranged by Unit Mathematics Standards Committee March 15, 2005Masha IwqedweNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Teaching Elementary MathematicsDocument10 pagesStrategies For Teaching Elementary MathematicsRhomalyn ValentonNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview What Is Algebra? History Algebra Is Named in Honor of Mohammed Ibn-e-MusaDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Overview What Is Algebra? History Algebra Is Named in Honor of Mohammed Ibn-e-Musagulfam yasinNo ratings yet
- 06 Maths Ch11 AlgebraDocument2 pages06 Maths Ch11 Algebrakavita.giri47No ratings yet
- Algebraic Expression: 3x 2xy + CDocument1 pageAlgebraic Expression: 3x 2xy + CKennedy BolanteNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry Are Both Branches of MathematicsDocument1 pageAlgebra and Trigonometry Are Both Branches of MathematicsAshly VillaramaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Skills: Number PatternsDocument2 pagesAlgebraic Skills: Number PatternsGeorgeAruNo ratings yet
- Equations and Inequalities: College AlgebraDocument22 pagesEquations and Inequalities: College AlgebraRic NapusNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Student NotesDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra Student NotesJaromír KoflákNo ratings yet
- Syllabus OutlineDocument88 pagesSyllabus OutlineKazi Ayman RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabi 2015-2016Document1 pageCourse Syllabi 2015-2016api-294397535No ratings yet
- Expressions and Formulaes - Understanding DifferencesDocument10 pagesExpressions and Formulaes - Understanding DifferencesAKSHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Mathematics AA HL SyllabusDocument58 pagesMathematics AA HL SyllabusGraciela AudreyNo ratings yet
- Math Class NotesDocument1 pageMath Class Notesainur.seidullaNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Algebra (2ND Sem)Document8 pagesMath 2 Algebra (2ND Sem)jennylynbodota17No ratings yet
- Algebra Class NotesDocument3 pagesAlgebra Class Notesxh7xyn8qsbNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionDocument3 pagesAlgebraic Expressionapi-150539480No ratings yet
- Elementary Algebra: Elementary Algebra Encompasses Some of The Basic Concepts ofDocument17 pagesElementary Algebra: Elementary Algebra Encompasses Some of The Basic Concepts ofNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- GRE Maths Syllabus (Quantitative Reasoning) : ArithmeticDocument4 pagesGRE Maths Syllabus (Quantitative Reasoning) : ArithmeticAhmed Magdy El-SayedNo ratings yet
- Math2056 Lecturenotes Week1Document69 pagesMath2056 Lecturenotes Week1Taha MisirliNo ratings yet
- Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 4 Parent Tip SheetDocument2 pagesEureka Math Grade 6 Module 4 Parent Tip Sheetapi-324380772No ratings yet
- Numerical and Abstract Reasoning: Mathematics GuideDocument17 pagesNumerical and Abstract Reasoning: Mathematics GuideKazi Ayman RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Regional Math Olympaid How To StudyDocument2 pagesRegional Math Olympaid How To StudySudip799No ratings yet
- L4a - Supervised LearningDocument25 pagesL4a - Supervised LearningKinya KageniNo ratings yet
- Day 2 AlgebraDocument2 pagesDay 2 AlgebraCarl Dominic LlavanNo ratings yet
- AA Syllabus Outline 2019Document87 pagesAA Syllabus Outline 2019derrickzptofficialNo ratings yet
- AL3451 - Unit 1Document12 pagesAL3451 - Unit 1jeffrinsb7No ratings yet
- Glossary of Areas of Mathematics - WikipediaDocument123 pagesGlossary of Areas of Mathematics - WikipediaUchechukwu MarizuNo ratings yet
- Ap Calculus Ab - Week of Feb 27 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAp Calculus Ab - Week of Feb 27 Lesson Planapi-282064530100% (1)
- Term 1 - End of Unit Math Topic ListDocument2 pagesTerm 1 - End of Unit Math Topic ListMáxima BrunoNo ratings yet
- The Modulus Function - DefinationsDocument4 pagesThe Modulus Function - DefinationsCompetitive TutorialNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 MAT2002 ETH VL2019201000415 Reference Material II 06-Aug-2019 Half Range SeriesDocument11 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 MAT2002 ETH VL2019201000415 Reference Material II 06-Aug-2019 Half Range SeriesShridhar MahtoNo ratings yet
- OMAT - Lecture 1 Review of Fundamentals - STD PDFDocument76 pagesOMAT - Lecture 1 Review of Fundamentals - STD PDFNguyễn Ngọc PhươngNo ratings yet
- Connection Machine LispDocument19 pagesConnection Machine LispchaitanyaguptaNo ratings yet
- NET Past Paper 5 PlspotDocument29 pagesNET Past Paper 5 PlspotVishal Raj SundraniNo ratings yet
- Math HL Baseline SyllabusDocument9 pagesMath HL Baseline SyllabusNoyonika DeyNo ratings yet
- Infinite Series, Improper Integrals, and Taylor SeriesDocument21 pagesInfinite Series, Improper Integrals, and Taylor SeriesscribddivNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Python Programming: Fission Reactor Physics 1Document56 pagesIntroduction To Python Programming: Fission Reactor Physics 1Leonardo MonacoNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 3Document32 pagesPractice Test 3api-359949059No ratings yet
- Integrales Elipticas y Funciones Elipticas PDFDocument108 pagesIntegrales Elipticas y Funciones Elipticas PDFJhon Edison Bravo BuitragoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Mathematical Languages and SymbolsDocument15 pagesLesson 3 Mathematical Languages and SymbolsMV ANo ratings yet
- Calculator TipsDocument6 pagesCalculator TipsCNo ratings yet
- Compiler DesignDocument186 pagesCompiler DesignsudiptoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Generation of A Software Requirements Specification SRS DocumentDocument6 pagesAutomatic Generation of A Software Requirements Specification SRS DocumentAgain MishraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Embedded ControllersDocument122 pagesLecture Notes For Embedded ControllersJorge PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 2015 Nsucrypto ArticleDocument32 pages2015 Nsucrypto ArticlebayareakingNo ratings yet
- Math SymbolsDocument22 pagesMath SymbolsHoang GiangNo ratings yet
- Diss Week 6Document5 pagesDiss Week 6John Briane CapiliNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Introduction-to-FUNCTIONDocument36 pagesGen Math Introduction-to-FUNCTIONJaena Marie EwenNo ratings yet
- Lagro High SchoolDocument12 pagesLagro High SchoolKarl SiaganNo ratings yet
- 0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDocument2 pages0.2 - Matching Linear Functions WorksheetDiep NguyenNo ratings yet
- Critical PointsDocument7 pagesCritical PointsjeffconnorsNo ratings yet
- MOdule GRADE 11 Module 1-2Document8 pagesMOdule GRADE 11 Module 1-2Christian CabadonggaNo ratings yet
- Python - Make Your Own Mandelbrot Set PDFDocument8 pagesPython - Make Your Own Mandelbrot Set PDFRicardo_SemogNo ratings yet
- Application of Surface of Revolution in Different Branches of ScienceDocument8 pagesApplication of Surface of Revolution in Different Branches of ScienceThe MukherjeeNo ratings yet