Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P119 - Module 8
P119 - Module 8
Uploaded by
Mariella MarianoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Art of Facilitative LeadershipDocument4 pagesThe Art of Facilitative Leadershipolof perssonNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 Lesson 8 Leadership Training and TeamworkDocument5 pagesNSTP 1 Lesson 8 Leadership Training and TeamworkJames Kyle Apa-ap0% (1)
- Coaching and MentoringDocument5 pagesCoaching and MentoringNashwa SaadNo ratings yet
- Technology Enhanced Blended Learning Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTechnology Enhanced Blended Learning Lesson Planapi-334622058No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Using Time Samples To Look at Attention SpanDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Using Time Samples To Look at Attention Spanapi-381559096100% (1)
- P119 - Module 8Document2 pagesP119 - Module 8Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Sample DeckDocument3 pagesSample DeckCris Juev Jonathan RecayoNo ratings yet
- Group DiscussionDocument7 pagesGroup DiscussionRahul ShramaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 PresentationDocument27 pagesGROUP 4 Presentationpvrk123No ratings yet
- Leadership 402 Cont.Document7 pagesLeadership 402 Cont.norlisa sambayonNo ratings yet
- Group DiscussionDocument8 pagesGroup Discussionninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- Psychology in Human Welfare - EditedDocument3 pagesPsychology in Human Welfare - EditedExpert AnswersNo ratings yet
- Leadership Initiative AlignmentDocument3 pagesLeadership Initiative Alignmentguvvalarohith1998No ratings yet
- Diss 11 - Discipline of CounselingDocument7 pagesDiss 11 - Discipline of CounselingRochelle Acala Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Organizational Change PracticeDocument11 pagesOrganizational Change PracticeRio AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- The Skilled Facilitator: Brief Summary of by Roger SchwartzDocument8 pagesThe Skilled Facilitator: Brief Summary of by Roger SchwartzTakunda NohaNo ratings yet
- Submitted byDocument29 pagesSubmitted byDecember CoolNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document4 pagesBook 1Parag VarsHneyNo ratings yet
- DCL Individual Output - Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesDCL Individual Output - Self AssessmentShanNo ratings yet
- CHN-Finals (1) - 1Document18 pagesCHN-Finals (1) - 1M.I Dia Izibelle F. AMENAMENNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 2nd PartDocument30 pagesGROUP 1 2nd PartsitoygysylmNo ratings yet
- Types of Groups and RolesDocument7 pagesTypes of Groups and RolesJelina GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Innovation Plan UpdatesDocument15 pagesInnovation Plan Updatesapi-654160262No ratings yet
- Thomas G. Cummings and Christoper G. Worley - Organization Development and Change (2015, Cengage Learning) (1) - Trang-287-315-Đã NénDocument29 pagesThomas G. Cummings and Christoper G. Worley - Organization Development and Change (2015, Cengage Learning) (1) - Trang-287-315-Đã NénKim Phương PhanNo ratings yet
- Discipline of CounselingDocument2 pagesDiscipline of CounselingAila CastilloNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Project Manager Soft Skill SetDocument4 pages3.0 Project Manager Soft Skill SetSebastián MooreNo ratings yet
- Team Dynamic MGT430Document9 pagesTeam Dynamic MGT430NUR SYAZIRA BAHAROMNo ratings yet
- Facilitation 101: Samantha DaweDocument3 pagesFacilitation 101: Samantha DaweBusiness Expert PressNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Leadership in GroupDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Leadership in GroupMazumder SumanNo ratings yet
- ADMINIS ReviewerDocument7 pagesADMINIS ReviewerJustine angelesNo ratings yet
- Emergent LeadershipDocument6 pagesEmergent Leadershipsaurabhsingh.cambridgeNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module 4 LeadershipDocument3 pagesNSTP Module 4 LeadershipTheo DoreNo ratings yet
- LP (Assignment)Document7 pagesLP (Assignment)Jyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CLFM 2Document6 pagesUnit 1 CLFM 2kristinejoy pacalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 22.frac, RinaDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 22.frac, RinaRina FracNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness and Leadership, Thompson 2017Document3 pagesMindfulness and Leadership, Thompson 2017fernanda gutierrezNo ratings yet
- 02-Definasi Dan Peranan Kepemimpinan PendidikanDocument25 pages02-Definasi Dan Peranan Kepemimpinan Pendidikanمحمد عريفNo ratings yet
- MentoringDocument4 pagesMentoringharmizan2212No ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document6 pagesLesson 4justen camingawanNo ratings yet
- Measure Your Leadership SkillsDocument1 pageMeasure Your Leadership SkillsNeill WhyborneNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2 Leadership and TeambuildingDocument5 pagesNSTP 2 Leadership and TeambuildingJEAN MARRICE DUNTARNo ratings yet
- Final Ledearship StylesDocument24 pagesFinal Ledearship StylesUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- MEDI11004 - Week 2 Study GuideDocument13 pagesMEDI11004 - Week 2 Study GuidesrhNo ratings yet
- The Lafarge Learning & Development NetworkDocument11 pagesThe Lafarge Learning & Development NetworkdebjittNo ratings yet
- Group Development Theory PDFDocument2 pagesGroup Development Theory PDFMark Diyammi100% (1)
- Leadership and The Challenge of IdentityDocument22 pagesLeadership and The Challenge of IdentityRichel FloresNo ratings yet
- Unit 11Document17 pagesUnit 11Muskan KumariNo ratings yet
- Info. Sheet 1.3-1Document4 pagesInfo. Sheet 1.3-1Rubz BulquerinNo ratings yet
- Ri Effective Facilitation GuideDocument22 pagesRi Effective Facilitation GuideRustam KoshelevNo ratings yet
- MAN201 - Class 2 - LeadershipDocument11 pagesMAN201 - Class 2 - LeadershipNgoc Nguyen Thi MinhNo ratings yet
- Coaching and MentoringDocument8 pagesCoaching and MentoringNABEEL AHMED KHANNo ratings yet
- Leadership StyleDocument16 pagesLeadership StyleJohanz PacrisNo ratings yet
- Facilitation: Train The FacilitatorDocument93 pagesFacilitation: Train The Facilitatorphilip_kockNo ratings yet
- Knowledge & Organisation Development in IFADDocument1 pageKnowledge & Organisation Development in IFADEM NjorogeNo ratings yet
- DIASS Rousseau Week2Document4 pagesDIASS Rousseau Week2Yasui Asian StoreNo ratings yet
- Program SupportDocument4 pagesProgram SupportJoderon NimesNo ratings yet
- Va PG 4Document3 pagesVa PG 4kchkch1No ratings yet
- Guidance and Counseling Notes - 085413Document6 pagesGuidance and Counseling Notes - 085413saisaijason15No ratings yet
- Managing Quality Improvement TeamsDocument25 pagesManaging Quality Improvement TeamsΑυτός είμαι εγώNo ratings yet
- Teamwork - OB Group 3 - FinalDocument24 pagesTeamwork - OB Group 3 - FinalferdialrfNo ratings yet
- GRCC Learning and Development Policy TemplateDocument8 pagesGRCC Learning and Development Policy TemplateSatyen ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- P117 - Module 5Document4 pagesP117 - Module 5Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Motivating LearnersDocument8 pagesLesson 9 - Motivating LearnersMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P117 - Module 3Document8 pagesP117 - Module 3Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P117 - Module 1 Intro To Clinical PsychDocument22 pagesP117 - Module 1 Intro To Clinical PsychMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P119 - MOdule 5 & 6Document6 pagesP119 - MOdule 5 & 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P119 - Module 1Document18 pagesP119 - Module 1Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- ICRC HeheDocument2 pagesICRC HeheMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Techno - Module 7Document4 pagesTechno - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Techno Module 5 and 6Document4 pagesTechno Module 5 and 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P113 - Lesson 6-9Document12 pagesP113 - Lesson 6-9Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Pe M2Document2 pagesPe M2Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- IOP - Module 2Document24 pagesIOP - Module 2Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Act. 9 Proteins IIIDocument3 pagesAct. 9 Proteins IIIMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument2 pagesApplicationMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- United NationsDocument3 pagesUnited NationsMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 10Document4 pagesP110 - Module 10Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- PE - M7 ReflectionDocument2 pagesPE - M7 ReflectionMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Recorded MamayaDocument1 pagePre-Recorded MamayaMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P111 - Module 6Document7 pagesP111 - Module 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesHydrocarbonsMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- FieldDocument1 pageFieldMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 6Document15 pagesP110 - Module 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P111 - Module 7Document6 pagesP111 - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 10Document4 pagesP110 - Module 10Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 7Document9 pagesP110 - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P111 - Module 8Document6 pagesP111 - Module 8Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 9Document7 pagesP110 - Module 9Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 11Document4 pagesP110 - Module 11Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Approach m6.1 m6Document5 pagesHumanistic Approach m6.1 m6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Existential Approach Notes-1Document15 pagesExistential Approach Notes-1Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Sesok (2001)Document4 pagesSesok (2001)yossi.zana100% (1)
- Action Plan in Reading: GOAL: Make Every Child A Reader. Objectives: 1. Develop The Ability To ReadDocument3 pagesAction Plan in Reading: GOAL: Make Every Child A Reader. Objectives: 1. Develop The Ability To ReadCARLOS FERNANDEZ100% (4)
- BalibarDocument22 pagesBalibarHansNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophies of Educationedenfiel100% (1)
- 1002 Impulse Control Strategies Ready Set GoDocument2 pages1002 Impulse Control Strategies Ready Set GoLucijaNo ratings yet
- Henry WiddowsonDocument3 pagesHenry WiddowsonKeila ArandaNo ratings yet
- Wolfsdorf - 2005 in LachesDocument24 pagesWolfsdorf - 2005 in LachesphilodemusNo ratings yet
- Oral Com (Missed Act)Document2 pagesOral Com (Missed Act)Aizel Nova AranezNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Montessori Council: Assignment Module 08Document9 pagesPakistan Montessori Council: Assignment Module 08YasirNo ratings yet
- 4 Peter Newmarks Approach To TranslationDocument9 pages4 Peter Newmarks Approach To TranslationhendrysaragiNo ratings yet
- Communication Pitfalls To Avoid PDFDocument3 pagesCommunication Pitfalls To Avoid PDF565Sarbanshu PanditNo ratings yet
- Strategic Safari - Henry Mintzberg: Presented By-Akriti Gupta Karuna PatelDocument13 pagesStrategic Safari - Henry Mintzberg: Presented By-Akriti Gupta Karuna PatelTung DoNo ratings yet
- Brain Rule For Aging Wells: Principles For Staying Vital, Happy & SharpsDocument30 pagesBrain Rule For Aging Wells: Principles For Staying Vital, Happy & Sharpsgunawan wibisanaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Learning Gamification Strategy To The Grade 5 With Numeracy Difficulty of Macayug Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesEffect of Learning Gamification Strategy To The Grade 5 With Numeracy Difficulty of Macayug Elementary Schoolsana minatozakiNo ratings yet
- Challenges Related To Educational Interpreting For Students Who Are Deaf With DisabilitiesDocument12 pagesChallenges Related To Educational Interpreting For Students Who Are Deaf With DisabilitiesVictor Rivera100% (1)
- QM CH 13 Decision TheoryDocument11 pagesQM CH 13 Decision TheoryChandra MouliNo ratings yet
- 7Cs and Listening SkillsDocument40 pages7Cs and Listening SkillsjhonNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument3 pagesTENSESYareli OrdazNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument29 pagesDecision MakingKoggilavani MunnindyNo ratings yet
- An Analysis Method For Interpretability of CNN Text Classification ModelDocument14 pagesAn Analysis Method For Interpretability of CNN Text Classification ModelMoh SalehNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading AND Thinking: Reporter: Sophia BuiserDocument11 pagesCritical Reading AND Thinking: Reporter: Sophia BuiserYohan BuiserNo ratings yet
- Cognitive-Distortions Charm Dalupang 1MT-L USELF PDFDocument2 pagesCognitive-Distortions Charm Dalupang 1MT-L USELF PDFCharm Angeles100% (1)
- Mil FinalDocument2 pagesMil FinalJoshua SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Using Paragraphs - University of LeicesterDocument2 pagesUsing Paragraphs - University of LeicesterVin BitzNo ratings yet
- A Concise Guide To Neurodiversity: David CyclebackDocument43 pagesA Concise Guide To Neurodiversity: David CyclebackJessica JessicaNo ratings yet
- Noun ClauseDocument2 pagesNoun ClauseLalllaNo ratings yet
- FS4 Episode 2!Document10 pagesFS4 Episode 2!Jesiemel100% (1)
- Class 3 Unit 1 Lesson 1.3 How Do You Spell Your Last Name?Document11 pagesClass 3 Unit 1 Lesson 1.3 How Do You Spell Your Last Name?José SaquinaulaNo ratings yet
P119 - Module 8
P119 - Module 8
Uploaded by
Mariella MarianoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P119 - Module 8
P119 - Module 8
Uploaded by
Mariella MarianoCopyright:
Available Formats
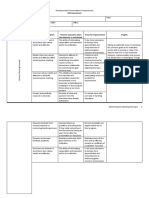
8.
1: Facilitation
O principles and integrating factual strategies that and connects
FACILITATION processes to information. stress conscious historical material
C improve practice thoughts, feelings to the present using
and to foster New information and behavior. interpersonal
… IS DEFINED AS TO MAKE THINGS EASY … making it easier U accomplishments is incorporated assessment /
for people to work together, to get more done, in less time, creating of identified through the use of Uses interactive diagnosis, and
creative and practical solutions to the challenges and opportunities a S work goals planned skill feedback and interpretation
group faces building exercises support methods
in a here-and now
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LEADING AND time frame
FACILITATING
Leadership is something you do to a group, while facilitation is L Helps the group Aim in providing Structure activities Helps individual
something you do with a group. enhance or members with of the group; group members
E correct their increased remediate in depth
performance; awareness of - to see that a psychological
Although many leaders can (and should) be effective facilitators, the
A develop skill in some life climate favorable problems;
facilitator differs from a leader in that the former is cognizant about organizational problems and the to productive work
the use of power, authority, or control and places limitations on the D assessment, tolls to better is maintained; - helping member’s
use of it. training program cope with it - to facilitate develop a new
E development, member’s perspective on
A facilitator should be "a neutral mediator whose job is to provide and program interactions; ‘unfinished
information and accommodate the exchange of dialogue among ... R evaluation - to provide business’ with
participants" (from Catalyst). information that significant others
F will help members
Facilitators assist groups as they work together toward achieving see alternatives to
U their modes of
group goals, and in most instances do not interject their own personal
behavior
opinions or agenda. By expressing their opinions to the group, N - to encourage
facilitators risk discouraging others with differing opinions from members to
speaking. They remain alert to group dynamics and encourage C translate their
challenging reflection while maintaining respect and safety within the insights into
group. Although facilitators may help guide a discussion, they also T concrete action
recognize and foster the group's own ability to lead itself. Thus unlike plans
I
authoritative leaders, good facilitators relinquish control to the group
and promote open, democratic dialogue among group members. O
CORE VALUES OF FACILITATION (by Roger Schwartz) N
1. VALID INFORMATION means that everyone involved shares
all information relevant to an issue. It also means that people A Facilitation Managing stress, Career / Re-experience
understand the information and its implications. involves course learning assertion educational traumatic situations
P work in the broad training, eating /personal / social so that catharsis can
area of disorders; and developmental occur, alleviate
2. FREE AND INFORMED CHOICE means that participants P organizational learning coping concerns (support specific symptoms /
have the ability to define their own goals and ways of achieving development, skills; managing groups) psychological
them. A facilitator can help the parties determine or alter their L consultation and relationships and problems
goals, and assess whether a particular option or decision meets management ending
those goals. But the ultimate decisions are up to the parties I relationships;
themselves. supporting
C survivors of
physical and
3. INTERNAL COMMITMENT TO THE CHOICE means that A sexual abuse
people feel personally responsible for the choices they make.
This type of commitment results because people are happy with T
the decision and their involvement in it, not because there is any
I
possibility of reward or punishment for supporting it -- other
than the benefits inherent in the agreement itself. O
8.2: Facilitator
TYPES OF FACILITATION
FACILITATOR
TASK PSYCHO COUNSELING PSYCHOTHERAP
FACILITATION EDUCATTIONA Y By definition, a facilitator is “a person…that makes an action or
L process easy or easier.”
A facilitator is a person who helps a group of people to work
F The application Deal with Interpersonal Explores
of group imparting, processes and antecedents to
together better, understand their common objectives, and plan how to
dynamics discussing and problem-solving current behavior achieve these objectives, during meetings or discussions. In doing so,
the facilitator remains "neutral", meaning they do not take a particular Types of Facilitators:
position in the discussion. Some facilitator tools will try to assist the
1. Business Facilitators. The facilitator's role is to make it easier for
group in achieving a consensus on any disagreements that preexist or
emerge in the meeting so that it has a solid basis for future action. the group to arrive at its own answer, decision, or deliverable.
2. Conflict Resolution Facilitators. are used in peace and
A facilitator is someone who reconciliation processes both during and after a conflict. Conflict
resolution facilitators must be impartial to the conflicting groups and
helps a group of people to understand their common objectives must adhere to the rules of the democratic dialogue. They may not
and assists them to plan how to achieve these objectives; in take sides or express personal opinions. Their role is to support
doing so, the facilitator remains "neutral", meaning he/she does groups develop a shared vision for the future, learn to listen to each
not take a particular position in the discussion other, and understand and appreciate the feelings, experiences, and
assists the group in achieving a consensus on any disagreements positions of the opposing side.
that preexist or emerge in the meeting so that it has a strong
3. Educational Facilitators. Educators in dialogic learning and
basis for future action
other peer instruction approaches often serve as facilitators. Effective
provides information and accommodate the exchange of
facilitation requires self-monitoring and careful attention to the
dialogue among participants
details of interaction as well as the content of the material.
assist groups as they work together toward achieving group
goals, and in most instances do not interject their own personal 4. Small Group Facilitators. The facilitator is often appointed in
opinions or agenda. place of what would once have been a chairperson's role. Along with
other officers, the facilitator is appointed at the group's annual general
To put it another way, facilitating actually means: meeting to fill the role for the year ahead.
5. Training Facilitators. Training facilitators are used in adult
Understanding the goals of the meeting and the organization education. These facilitators are not always subject experts, and
Keeping the group on the agenda and moving forward attempt to draw on the existing knowledge of the participant(s), and
Involving everyone in the meeting, including drawing out the to then facilitate access to training where gaps in knowledge are
quiet participants and controlling the domineering ones identified and agreed on.
Making sure that decisions are made democratically 6. Wraparound Facilitators. Wraparound facilitators are facilitators
in the social services community. They originally served disabled
The 8 Roles of a Facilitator teens who were transitioning into adulthood. Now they include
facilitators serving children between the ages of 0–3 years who are in
1. Motivator: ignites a fire within the group, establishes momentum, need of services. Outside the meetings, the facilitator organizes
and keeps the pace. meetings, engages team members, and conducts follow-through.
2. Guide: knows the steps of the process the group will execute from During meetings, the facilitator leads and manages the team by
beginning to end and carefully guide the participants through each keeping the participants on track and encouraging a strength-based
step in turn. discussion addressing the child's needs. The facilitator encourages
3. Questioner: listens carefully to the discussion and quickly equal participation among team members.
analyzes comments to formulate questions that help guide a
productive group discussion and challenge the group when
appropriate.
4. Bridge Builder: creates and maintains a safe and open
environment for sharing ideas.
5. Clairvoyant: attuned to signs of strain, weariness, aggravation,
and disempowerment, and respond in advance to prevent
dysfunctional behavior.
6. Peacemaker: steps in quickly to reestablish order and direct the
group toward a constructive resolution.
7. Taskmaster: keeping the session on track.
8. Praiser: praise participants for good effort, progress, and results –
praise well, praise often, praise specifically.
You might also like
- The Art of Facilitative LeadershipDocument4 pagesThe Art of Facilitative Leadershipolof perssonNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 Lesson 8 Leadership Training and TeamworkDocument5 pagesNSTP 1 Lesson 8 Leadership Training and TeamworkJames Kyle Apa-ap0% (1)
- Coaching and MentoringDocument5 pagesCoaching and MentoringNashwa SaadNo ratings yet
- Technology Enhanced Blended Learning Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesTechnology Enhanced Blended Learning Lesson Planapi-334622058No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Using Time Samples To Look at Attention SpanDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Using Time Samples To Look at Attention Spanapi-381559096100% (1)
- P119 - Module 8Document2 pagesP119 - Module 8Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Sample DeckDocument3 pagesSample DeckCris Juev Jonathan RecayoNo ratings yet
- Group DiscussionDocument7 pagesGroup DiscussionRahul ShramaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 PresentationDocument27 pagesGROUP 4 Presentationpvrk123No ratings yet
- Leadership 402 Cont.Document7 pagesLeadership 402 Cont.norlisa sambayonNo ratings yet
- Group DiscussionDocument8 pagesGroup Discussionninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- Psychology in Human Welfare - EditedDocument3 pagesPsychology in Human Welfare - EditedExpert AnswersNo ratings yet
- Leadership Initiative AlignmentDocument3 pagesLeadership Initiative Alignmentguvvalarohith1998No ratings yet
- Diss 11 - Discipline of CounselingDocument7 pagesDiss 11 - Discipline of CounselingRochelle Acala Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Organizational Change PracticeDocument11 pagesOrganizational Change PracticeRio AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- The Skilled Facilitator: Brief Summary of by Roger SchwartzDocument8 pagesThe Skilled Facilitator: Brief Summary of by Roger SchwartzTakunda NohaNo ratings yet
- Submitted byDocument29 pagesSubmitted byDecember CoolNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document4 pagesBook 1Parag VarsHneyNo ratings yet
- DCL Individual Output - Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesDCL Individual Output - Self AssessmentShanNo ratings yet
- CHN-Finals (1) - 1Document18 pagesCHN-Finals (1) - 1M.I Dia Izibelle F. AMENAMENNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 2nd PartDocument30 pagesGROUP 1 2nd PartsitoygysylmNo ratings yet
- Types of Groups and RolesDocument7 pagesTypes of Groups and RolesJelina GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Innovation Plan UpdatesDocument15 pagesInnovation Plan Updatesapi-654160262No ratings yet
- Thomas G. Cummings and Christoper G. Worley - Organization Development and Change (2015, Cengage Learning) (1) - Trang-287-315-Đã NénDocument29 pagesThomas G. Cummings and Christoper G. Worley - Organization Development and Change (2015, Cengage Learning) (1) - Trang-287-315-Đã NénKim Phương PhanNo ratings yet
- Discipline of CounselingDocument2 pagesDiscipline of CounselingAila CastilloNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Project Manager Soft Skill SetDocument4 pages3.0 Project Manager Soft Skill SetSebastián MooreNo ratings yet
- Team Dynamic MGT430Document9 pagesTeam Dynamic MGT430NUR SYAZIRA BAHAROMNo ratings yet
- Facilitation 101: Samantha DaweDocument3 pagesFacilitation 101: Samantha DaweBusiness Expert PressNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Leadership in GroupDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Leadership in GroupMazumder SumanNo ratings yet
- ADMINIS ReviewerDocument7 pagesADMINIS ReviewerJustine angelesNo ratings yet
- Emergent LeadershipDocument6 pagesEmergent Leadershipsaurabhsingh.cambridgeNo ratings yet
- NSTP Module 4 LeadershipDocument3 pagesNSTP Module 4 LeadershipTheo DoreNo ratings yet
- LP (Assignment)Document7 pagesLP (Assignment)Jyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CLFM 2Document6 pagesUnit 1 CLFM 2kristinejoy pacalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 22.frac, RinaDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 22.frac, RinaRina FracNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness and Leadership, Thompson 2017Document3 pagesMindfulness and Leadership, Thompson 2017fernanda gutierrezNo ratings yet
- 02-Definasi Dan Peranan Kepemimpinan PendidikanDocument25 pages02-Definasi Dan Peranan Kepemimpinan Pendidikanمحمد عريفNo ratings yet
- MentoringDocument4 pagesMentoringharmizan2212No ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document6 pagesLesson 4justen camingawanNo ratings yet
- Measure Your Leadership SkillsDocument1 pageMeasure Your Leadership SkillsNeill WhyborneNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2 Leadership and TeambuildingDocument5 pagesNSTP 2 Leadership and TeambuildingJEAN MARRICE DUNTARNo ratings yet
- Final Ledearship StylesDocument24 pagesFinal Ledearship StylesUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- MEDI11004 - Week 2 Study GuideDocument13 pagesMEDI11004 - Week 2 Study GuidesrhNo ratings yet
- The Lafarge Learning & Development NetworkDocument11 pagesThe Lafarge Learning & Development NetworkdebjittNo ratings yet
- Group Development Theory PDFDocument2 pagesGroup Development Theory PDFMark Diyammi100% (1)
- Leadership and The Challenge of IdentityDocument22 pagesLeadership and The Challenge of IdentityRichel FloresNo ratings yet
- Unit 11Document17 pagesUnit 11Muskan KumariNo ratings yet
- Info. Sheet 1.3-1Document4 pagesInfo. Sheet 1.3-1Rubz BulquerinNo ratings yet
- Ri Effective Facilitation GuideDocument22 pagesRi Effective Facilitation GuideRustam KoshelevNo ratings yet
- MAN201 - Class 2 - LeadershipDocument11 pagesMAN201 - Class 2 - LeadershipNgoc Nguyen Thi MinhNo ratings yet
- Coaching and MentoringDocument8 pagesCoaching and MentoringNABEEL AHMED KHANNo ratings yet
- Leadership StyleDocument16 pagesLeadership StyleJohanz PacrisNo ratings yet
- Facilitation: Train The FacilitatorDocument93 pagesFacilitation: Train The Facilitatorphilip_kockNo ratings yet
- Knowledge & Organisation Development in IFADDocument1 pageKnowledge & Organisation Development in IFADEM NjorogeNo ratings yet
- DIASS Rousseau Week2Document4 pagesDIASS Rousseau Week2Yasui Asian StoreNo ratings yet
- Program SupportDocument4 pagesProgram SupportJoderon NimesNo ratings yet
- Va PG 4Document3 pagesVa PG 4kchkch1No ratings yet
- Guidance and Counseling Notes - 085413Document6 pagesGuidance and Counseling Notes - 085413saisaijason15No ratings yet
- Managing Quality Improvement TeamsDocument25 pagesManaging Quality Improvement TeamsΑυτός είμαι εγώNo ratings yet
- Teamwork - OB Group 3 - FinalDocument24 pagesTeamwork - OB Group 3 - FinalferdialrfNo ratings yet
- GRCC Learning and Development Policy TemplateDocument8 pagesGRCC Learning and Development Policy TemplateSatyen ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- P117 - Module 5Document4 pagesP117 - Module 5Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Motivating LearnersDocument8 pagesLesson 9 - Motivating LearnersMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P117 - Module 3Document8 pagesP117 - Module 3Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P117 - Module 1 Intro To Clinical PsychDocument22 pagesP117 - Module 1 Intro To Clinical PsychMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P119 - MOdule 5 & 6Document6 pagesP119 - MOdule 5 & 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P119 - Module 1Document18 pagesP119 - Module 1Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- ICRC HeheDocument2 pagesICRC HeheMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Techno - Module 7Document4 pagesTechno - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Techno Module 5 and 6Document4 pagesTechno Module 5 and 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P113 - Lesson 6-9Document12 pagesP113 - Lesson 6-9Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Pe M2Document2 pagesPe M2Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- IOP - Module 2Document24 pagesIOP - Module 2Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Act. 9 Proteins IIIDocument3 pagesAct. 9 Proteins IIIMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument2 pagesApplicationMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- United NationsDocument3 pagesUnited NationsMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 10Document4 pagesP110 - Module 10Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- PE - M7 ReflectionDocument2 pagesPE - M7 ReflectionMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Recorded MamayaDocument1 pagePre-Recorded MamayaMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P111 - Module 6Document7 pagesP111 - Module 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesHydrocarbonsMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- FieldDocument1 pageFieldMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 6Document15 pagesP110 - Module 6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P111 - Module 7Document6 pagesP111 - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 10Document4 pagesP110 - Module 10Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 7Document9 pagesP110 - Module 7Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P111 - Module 8Document6 pagesP111 - Module 8Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 9Document7 pagesP110 - Module 9Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P110 - Module 11Document4 pagesP110 - Module 11Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Approach m6.1 m6Document5 pagesHumanistic Approach m6.1 m6Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Existential Approach Notes-1Document15 pagesExistential Approach Notes-1Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Sesok (2001)Document4 pagesSesok (2001)yossi.zana100% (1)
- Action Plan in Reading: GOAL: Make Every Child A Reader. Objectives: 1. Develop The Ability To ReadDocument3 pagesAction Plan in Reading: GOAL: Make Every Child A Reader. Objectives: 1. Develop The Ability To ReadCARLOS FERNANDEZ100% (4)
- BalibarDocument22 pagesBalibarHansNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophies of Educationedenfiel100% (1)
- 1002 Impulse Control Strategies Ready Set GoDocument2 pages1002 Impulse Control Strategies Ready Set GoLucijaNo ratings yet
- Henry WiddowsonDocument3 pagesHenry WiddowsonKeila ArandaNo ratings yet
- Wolfsdorf - 2005 in LachesDocument24 pagesWolfsdorf - 2005 in LachesphilodemusNo ratings yet
- Oral Com (Missed Act)Document2 pagesOral Com (Missed Act)Aizel Nova AranezNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Montessori Council: Assignment Module 08Document9 pagesPakistan Montessori Council: Assignment Module 08YasirNo ratings yet
- 4 Peter Newmarks Approach To TranslationDocument9 pages4 Peter Newmarks Approach To TranslationhendrysaragiNo ratings yet
- Communication Pitfalls To Avoid PDFDocument3 pagesCommunication Pitfalls To Avoid PDF565Sarbanshu PanditNo ratings yet
- Strategic Safari - Henry Mintzberg: Presented By-Akriti Gupta Karuna PatelDocument13 pagesStrategic Safari - Henry Mintzberg: Presented By-Akriti Gupta Karuna PatelTung DoNo ratings yet
- Brain Rule For Aging Wells: Principles For Staying Vital, Happy & SharpsDocument30 pagesBrain Rule For Aging Wells: Principles For Staying Vital, Happy & Sharpsgunawan wibisanaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Learning Gamification Strategy To The Grade 5 With Numeracy Difficulty of Macayug Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesEffect of Learning Gamification Strategy To The Grade 5 With Numeracy Difficulty of Macayug Elementary Schoolsana minatozakiNo ratings yet
- Challenges Related To Educational Interpreting For Students Who Are Deaf With DisabilitiesDocument12 pagesChallenges Related To Educational Interpreting For Students Who Are Deaf With DisabilitiesVictor Rivera100% (1)
- QM CH 13 Decision TheoryDocument11 pagesQM CH 13 Decision TheoryChandra MouliNo ratings yet
- 7Cs and Listening SkillsDocument40 pages7Cs and Listening SkillsjhonNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument3 pagesTENSESYareli OrdazNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument29 pagesDecision MakingKoggilavani MunnindyNo ratings yet
- An Analysis Method For Interpretability of CNN Text Classification ModelDocument14 pagesAn Analysis Method For Interpretability of CNN Text Classification ModelMoh SalehNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading AND Thinking: Reporter: Sophia BuiserDocument11 pagesCritical Reading AND Thinking: Reporter: Sophia BuiserYohan BuiserNo ratings yet
- Cognitive-Distortions Charm Dalupang 1MT-L USELF PDFDocument2 pagesCognitive-Distortions Charm Dalupang 1MT-L USELF PDFCharm Angeles100% (1)
- Mil FinalDocument2 pagesMil FinalJoshua SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Using Paragraphs - University of LeicesterDocument2 pagesUsing Paragraphs - University of LeicesterVin BitzNo ratings yet
- A Concise Guide To Neurodiversity: David CyclebackDocument43 pagesA Concise Guide To Neurodiversity: David CyclebackJessica JessicaNo ratings yet
- Noun ClauseDocument2 pagesNoun ClauseLalllaNo ratings yet
- FS4 Episode 2!Document10 pagesFS4 Episode 2!Jesiemel100% (1)
- Class 3 Unit 1 Lesson 1.3 How Do You Spell Your Last Name?Document11 pagesClass 3 Unit 1 Lesson 1.3 How Do You Spell Your Last Name?José SaquinaulaNo ratings yet