Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phasese of Matter - Science (4thquarter)
Phasese of Matter - Science (4thquarter)
Uploaded by
geecyjane Yguinto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThis document defines matter and describes the three phases of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. It outlines the fundamental properties of gases, including pressure, temperature, amount of gas, and kinetic molecular theory. Pressure is defined as the force exerted by gas per unit area. Temperature depends on the kinetic energy of the gas. Amount of gas relates the mass of gas to the number of moles. Kinetic molecular theory explains gas behavior in terms of tiny particles with mass that travel randomly and collide without losing kinetic energy.
Original Description:
Original Title
PHASESE OF MATTER- SCIENCE(4THQUARTER)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines matter and describes the three phases of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. It outlines the fundamental properties of gases, including pressure, temperature, amount of gas, and kinetic molecular theory. Pressure is defined as the force exerted by gas per unit area. Temperature depends on the kinetic energy of the gas. Amount of gas relates the mass of gas to the number of moles. Kinetic molecular theory explains gas behavior in terms of tiny particles with mass that travel randomly and collide without losing kinetic energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagePhasese of Matter - Science (4thquarter)
Phasese of Matter - Science (4thquarter)
Uploaded by
geecyjane YguintoThis document defines matter and describes the three phases of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. It outlines the fundamental properties of gases, including pressure, temperature, amount of gas, and kinetic molecular theory. Pressure is defined as the force exerted by gas per unit area. Temperature depends on the kinetic energy of the gas. Amount of gas relates the mass of gas to the number of moles. Kinetic molecular theory explains gas behavior in terms of tiny particles with mass that travel randomly and collide without losing kinetic energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
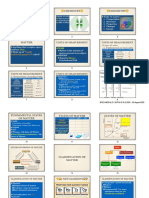
PHASESE OF MATTER PRESSURE - Force exerted by the gas per unit area.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Formula: P=F/A
1) Define matter. Conversion: 1 atm = 760mmHg = 760 torr = 1.01325 bar =
101.325 kPa
2) Differentiate solid, liquid, and gas.
SI Unit: Pa, atm, mmHg, torr, bar, kPa
3) Describe gases
TEMPERATURE - Depends on the kinetic energy of the gas.
MATTER
Formulae: K = °C + 273.15
Anything that takes up space and can be weighed.
°C = (°F – 32) 5/9
PHASES OF MATTER
SI Unit: °F, °C, K
1. SOLID - Particles are tightly packed together.
AMOUNT OF GAS - Mass of the gas is related to the
2. LIQUID - Particles have more movement. number of moles of the gas.
3. GAS - Particles are spread out. Formula: n = mass of the gas
4. PLASMA - Superheated matter. molar mass of the gas
SI Unit: kg or g
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY - Explain
the behavior of gases.
CHARACYERISTICS OF GASES
- Consists of very tiny particles, each of which has
mass.
- Gas particles travel constantly and in random
directions.
- Gases diffuse very rapidly.
FUNDAMENTAL PROPERTIES OF GASES - The forces of attraction are negligible.
- Gas particles collide but does not lose their kinetic
VOLUME - How much space a substance takes up.
energy.
Conversions: 1 L = 10dm³ = 10m³ = 1000 mL = 1000 cm³ - All gases have the same average kinetic energy at a
given temperature of gas.
SI Unit: L, mL, cm³, m³, dm³
You might also like
- THERMODYNAMICSDocument66 pagesTHERMODYNAMICSReyno D. Paca-anas33% (3)
- exercise1 2 63 solution-2311-16147698251550-ผสานDocument27 pagesexercise1 2 63 solution-2311-16147698251550-ผสานMaytawee Juntorn100% (1)
- Object of The Game Winning Object of The GameDocument1 pageObject of The Game Winning Object of The GameScience HouseNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument9 pagesGASES2100428No ratings yet
- SCIENCE Q4 NotesDocument2 pagesSCIENCE Q4 NotesKyshley VargasNo ratings yet
- Me 313 Thermodynamics 11Document68 pagesMe 313 Thermodynamics 11ICT AKO100% (2)
- 4TH SciDocument2 pages4TH ScijjjjjNo ratings yet
- G10 Science ReviewerDocument6 pagesG10 Science ReviewereupphyyyyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 GasesDocument41 pagesUnit 2 GasesSai TendoNo ratings yet
- Macroscopic vs. Microscopic Representation: Gases and The Kinetic - Molecular TheoryDocument16 pagesMacroscopic vs. Microscopic Representation: Gases and The Kinetic - Molecular TheoryMochamad RizalNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesThermodynamicsjudith matienzoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SatDocument17 pagesChemistry SatAriana GameroNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AiimsVikash Rao khatodiyaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Prelims ReviewerDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Prelims ReviewerSophia BrionesNo ratings yet
- CLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFDocument57 pagesCLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFSarah RashidNo ratings yet
- Chem4engr Lesson 1 - ReviewerDocument5 pagesChem4engr Lesson 1 - Reviewerchloemagsalin619No ratings yet
- G12 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument21 pagesG12 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryThea NavarezNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws - Boyles LawDocument10 pagesGas Laws - Boyles LawParth JainNo ratings yet
- Gases and Atmospheric ChemistryDocument10 pagesGases and Atmospheric ChemistryKatheeja MusatheekNo ratings yet
- THERMO 1 (Intro Elements Units Common Properties)Document3 pagesTHERMO 1 (Intro Elements Units Common Properties)Beaw GtNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic PressureDocument22 pagesHydrostatic PressureScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Science10 - 4th Periodical ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience10 - 4th Periodical ReviewerJewel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gr11chem - 2ND Sem - Lesson 1 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument4 pagesGr11chem - 2ND Sem - Lesson 1 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryJerome HizonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 9 t3Document2 pagesReviewer in Science 9 t3Nicos BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q4 Module 1Document4 pagesScience10 Q4 Module 1bongatomarieveroniqueNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 05Document48 pagesNotes Chapter 05Biruk BtNo ratings yet
- Behavior ofDocument19 pagesBehavior ofFayeNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument12 pagesProperties of Gasesshasagail100% (1)
- CHM122 1Document25 pagesCHM122 1COLLINS MUENo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument3 pagesREVIEWERLoren Atasha YaptangcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Study of ChangeDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Study of ChangeMark Julius Felix PagudNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument13 pagesGASESJUAN MENDOZANo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument11 pagesChemistryBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- Sat Chemistry Notes: Matter Mass Inertia Density Activation EnergyDocument11 pagesSat Chemistry Notes: Matter Mass Inertia Density Activation Energy김나연No ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical PharmacyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Physical PharmacyKaren GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument19 pagesThermal PhysicsMaya SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CH 4Document20 pagesChemistry CH 4husnainraza0403No ratings yet
- Gases: Grade 12 Rutherford - ThomsonDocument36 pagesGases: Grade 12 Rutherford - ThomsonLennie ManaloNo ratings yet
- Thermo DyDocument18 pagesThermo Dykeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasesDocument61 pagesProperties of GasesHye Rin KangNo ratings yet
- CT - Gaseous State - Module Gaseous State - 10112021 - 7. Xi - Gaseous State ModuleDocument80 pagesCT - Gaseous State - Module Gaseous State - 10112021 - 7. Xi - Gaseous State ModuleAnita Akhilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- General Physics g12 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeneral Physics g12 ReviewerJASMINE AUBREY GENERATONo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument5 pagesStates of MatterSai SawantNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3rd GradingDocument7 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd GradingSean Irvin MirandaNo ratings yet
- FsdfvsdfvsDocument9 pagesFsdfvsdfvsmwah mwahNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Units ASDocument79 pagesPhysical Quantities and Units ASAng Wei LunNo ratings yet
- G10 LAP 4.1 Properties of GasesDocument5 pagesG10 LAP 4.1 Properties of GasesAzria SolanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-Gas PropertiesDocument16 pagesLesson 4-Gas PropertiesLouise Yvonne ManaloNo ratings yet
- Matter Exercises2Document6 pagesMatter Exercises2Camila PrzNo ratings yet
- Prelims ThermoDocument96 pagesPrelims ThermoJoshua BarteNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesDocument24 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory of GasesmaximofwwandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17,18 Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument88 pagesLecture 17,18 Kinetic Theory of GasesHuraira AbidNo ratings yet
- Theory of Combustion - YIN-ChungenDocument35 pagesTheory of Combustion - YIN-Chungenapi-3830481100% (1)
- Properties of Gas - de LinaDocument1 pageProperties of Gas - de LinaJana De LiñaNo ratings yet
- CHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1Document74 pagesCHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1meamatafarms KennethNo ratings yet
- KMT TheoryDocument15 pagesKMT TheoryDandy VictaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics (Kinetic Particle Model of Matter) - Particle ModelDocument1 pageThermal Physics (Kinetic Particle Model of Matter) - Particle ModelTamilore AdegbonmireNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties and CorrelationsDocument18 pagesGas Properties and CorrelationsNurudeen YekiniNo ratings yet
- Brex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 9 SlidesDocument153 pagesBrex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 9 SlidesNEIL RYAN LAGARDENo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document19 pagesLesson 1Kassandra PaculanNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- OR ModuleDocument186 pagesOR Moduletame kibruNo ratings yet
- Final Report TEDocument29 pagesFinal Report TESonali PawarNo ratings yet
- Configuring Multiple Archive Locations GridProtectionAlliance - Openhistorian Wiki GitHubDocument3 pagesConfiguring Multiple Archive Locations GridProtectionAlliance - Openhistorian Wiki GitHubaaaaNo ratings yet
- XC ZXC ZXZXC ZX ZCXDocument14 pagesXC ZXC ZXZXC ZX ZCXDeepanshu JoshiNo ratings yet
- Bar Swing ChartDocument62 pagesBar Swing Chartsujanreddy100% (2)
- RRE, 8FBRE: Supplement To The Repair Manual: Service Message/BSM: 0915Document3 pagesRRE, 8FBRE: Supplement To The Repair Manual: Service Message/BSM: 0915candra pmNo ratings yet
- HMG 2500Document4 pagesHMG 2500tarobaclashNo ratings yet
- PROJECT: Door Lock Using Microcontroller: Group MembersDocument11 pagesPROJECT: Door Lock Using Microcontroller: Group MembersNitin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lubrication Chart - HP800 (1) Shougang 2020Document1 pageLubrication Chart - HP800 (1) Shougang 2020carlos trilloNo ratings yet
- Designing For Earthquakes A Manual For Architects PDFDocument392 pagesDesigning For Earthquakes A Manual For Architects PDFPatrick Creek100% (2)
- Review of Development The Application Alkaline Surfactant and Polymer in EOR TechnologyDocument15 pagesReview of Development The Application Alkaline Surfactant and Polymer in EOR TechnologyALVE DINO RUMANDANo ratings yet
- LS-804 - Rev 34 - May 2020Document5 pagesLS-804 - Rev 34 - May 2020ming_zhu10No ratings yet
- SMOPS Mock 2Document17 pagesSMOPS Mock 2Marilyn CitadelNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Due To CurrentDocument21 pagesMagnetic Field Due To Currentthinkiit100% (2)
- Markup Pricing Versus Marginalism PDFDocument26 pagesMarkup Pricing Versus Marginalism PDFDNo ratings yet
- Whittle D. - Vassiliev P. - apcOM97 - Construction Economic Ore Body ModelsDocument6 pagesWhittle D. - Vassiliev P. - apcOM97 - Construction Economic Ore Body ModelsJuan Leiva FuentesNo ratings yet
- Hukum Hooke ExperimentDocument11 pagesHukum Hooke ExperimentCitra MarsidiNo ratings yet
- 1-Phase IM-2Document8 pages1-Phase IM-2abcdNo ratings yet
- ISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRDocument6 pagesISRO3 WWW Matterhere Com NRRParth PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 - Coroutines 基本概念与极简模型Document14 pages1 - Coroutines 基本概念与极简模型张奎No ratings yet
- Carcassi Op 59 PDFDocument152 pagesCarcassi Op 59 PDFCarlos del Río Silván100% (6)
- Lenovo Wrokstation Product PresentationDocument19 pagesLenovo Wrokstation Product PresentationchethanNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet For Prilepin's MesocycleDocument4 pagesSpreadsheet For Prilepin's MesocycleGiuliano IsoardiNo ratings yet
- Bayley DevelopmentMotorAbilities 1936Document29 pagesBayley DevelopmentMotorAbilities 1936Ave BellowsNo ratings yet
- NC 1Document10 pagesNC 1razauuuuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Comprehensive Exam Review QuestionsDocument22 pagesAnatomy Comprehensive Exam Review QuestionsKlean Jee Teo-TrazoNo ratings yet
- Region Based SegmentationDocument2 pagesRegion Based SegmentationSakshi AgarwalNo ratings yet