Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finacc 6 A3 1
Finacc 6 A3 1
Uploaded by
200617Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Study On Buying Behaviour of Consumer For Different Brands of Chocolates Project Report New 2021Document67 pagesStudy On Buying Behaviour of Consumer For Different Brands of Chocolates Project Report New 2021Sarika RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Assessment 4 Tax 1Document3 pagesAssessment 4 Tax 1Judy Ann Gaceta0% (1)
- DocxDocument21 pagesDocxDhiananda zhuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Chapter 22Document30 pagesPrinciples of Economics Chapter 22Lu CheNo ratings yet
- TAXATION ON INDIVIDUALS Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesTAXATION ON INDIVIDUALS Lecture NotesLucille Rose MamburaoNo ratings yet
- Past MA Exams by Lecture Topic - Solutions PDFDocument59 pagesPast MA Exams by Lecture Topic - Solutions PDFbooks_sumiNo ratings yet
- Uses of National Income DataDocument2 pagesUses of National Income Dataarchitjain7080% (5)
- Toaz - Info 89bf91d5 1612761367237 PRDocument7 pagesToaz - Info 89bf91d5 1612761367237 PRAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap - IAS 12 - Tu LuanDocument14 pagesBai Tap - IAS 12 - Tu LuanTrần Nguyễn Tuệ MinhNo ratings yet
- Income Tax AccountingDocument3 pagesIncome Tax Accountinghae1234No ratings yet
- Lobrigas Unit6 AssessmentDocument4 pagesLobrigas Unit6 AssessmentClaudine LobrigasNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument5 pagesDocxJohn Vincent CruzNo ratings yet
- ACT150 Assignment DIMAAMPAODocument4 pagesACT150 Assignment DIMAAMPAOJeromeNo ratings yet
- Special Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureDocument5 pagesSpecial Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureClarisse AlimotNo ratings yet
- Solution - Accounting For Income TaxesDocument12 pagesSolution - Accounting For Income TaxesKlarissemay MontallanaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument3 pagesAccounting For Income TaxDaniel Kahn GillamacNo ratings yet
- LAGRIMAS, Sarah Nicole S. - Income Taxes 2Document4 pagesLAGRIMAS, Sarah Nicole S. - Income Taxes 2saturdaysunbaeNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 3A Assignment 2Document10 pagesFinancial Accounting 3A Assignment 2Mikaeel MohamedNo ratings yet
- VOL 2 16. Accounting For Income TaxationDocument15 pagesVOL 2 16. Accounting For Income TaxationdmangiginNo ratings yet
- Class Activities (Millan, 2019) : Requirements: A. How Much Is The Income Tax Expense For 2003? SolutionDocument6 pagesClass Activities (Millan, 2019) : Requirements: A. How Much Is The Income Tax Expense For 2003? SolutionPrincess TaizeNo ratings yet
- Special Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureDocument4 pagesSpecial Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureNoorodden50% (2)
- Income TaxesDocument3 pagesIncome TaxesCENTENO, JOAN R.No ratings yet
- Sample Test (Extract)Document6 pagesSample Test (Extract)Julie KimNo ratings yet
- Ege, Kenneth M. Bsa22A1Document3 pagesEge, Kenneth M. Bsa22A1Kenneth Marcial Ege IINo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Tax Comprehensive Problem 1: Additional InformationDocument1 pageAccounting For Income Tax Comprehensive Problem 1: Additional InformationAngel Keith MercadoNo ratings yet
- FA2-08 Income TaxesDocument3 pagesFA2-08 Income Taxeskrisha millo0% (1)
- Tutorial 2: Exercise 12.2 Calculation of Current TaxDocument13 pagesTutorial 2: Exercise 12.2 Calculation of Current TaxKim FloresNo ratings yet
- Lamagan, Kyla T. BSA 401 Intermediate Acct. 2 Final Output Problem 16-13 (IAA)Document14 pagesLamagan, Kyla T. BSA 401 Intermediate Acct. 2 Final Output Problem 16-13 (IAA)lana del reyNo ratings yet
- Insurance Expense Allocated To The Quarter: SolutionDocument4 pagesInsurance Expense Allocated To The Quarter: Solutionasdfghjkl zxcvbnmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Accounting For Income Tax Problem 19-1Document5 pagesChapter 19 Accounting For Income Tax Problem 19-1nicole bancoroNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Accounting Rules and Tax RulesDocument18 pagesDifference Between Accounting Rules and Tax RulesCezar Rishane Mae SaligueNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Chapter 16Document8 pagesGroup 1 - Chapter 16Cherie Soriano AnanayoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Calculations Using The Tax-Payable MethodDocument10 pagesActivity 1 Calculations Using The Tax-Payable MethodJohn TomNo ratings yet
- He Is Not Subject To Basic Income Tax. However, His 13th Month Pay Exceeds 90,000. ThereforeDocument15 pagesHe Is Not Subject To Basic Income Tax. However, His 13th Month Pay Exceeds 90,000. ThereforeEarl Daniel RemorozaNo ratings yet
- CPAT Reviewer - TRAIN (Tax Reform) #1Document8 pagesCPAT Reviewer - TRAIN (Tax Reform) #1Zaaavnn VannnnnNo ratings yet
- 30 - Aathifah Teta Fitranti - 195020307111072 - AKM 3Document2 pages30 - Aathifah Teta Fitranti - 195020307111072 - AKM 3Aathifah Teta FitrantiNo ratings yet
- AFA IIP.L III SolutionJune 2016Document4 pagesAFA IIP.L III SolutionJune 2016HossainNo ratings yet
- 2542 - Tut1Document14 pages2542 - Tut1(Alumna 2018-6A07) CHUCK LONG YAU 卓朗悠No ratings yet
- Topic 1: Accounting For Income TaxesDocument13 pagesTopic 1: Accounting For Income TaxesPillos Jr., ElimarNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Tax Valix StudentDocument4 pagesAccounting For Income Tax Valix Studentvee viajeroNo ratings yet
- R2. TAX (M.L) Solution CMA May-2023 ExamDocument5 pagesR2. TAX (M.L) Solution CMA May-2023 ExamSharif MahmudNo ratings yet
- ACW2491 Lecture 4 Handout SolutionS22016Document4 pagesACW2491 Lecture 4 Handout SolutionS22016林志成No ratings yet
- BAFACR16 01 Problem IllustrationsDocument2 pagesBAFACR16 01 Problem Illustrationsmisssunshine112No ratings yet
- TAÑOTE Daisy AEC7 MEPIIDocument9 pagesTAÑOTE Daisy AEC7 MEPIIDaisy TañoteNo ratings yet
- R2. TAX ML Solution CMA January 2022 ExaminationDocument6 pagesR2. TAX ML Solution CMA January 2022 ExaminationPavel DhakaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Seatwork - Answers Ver 2 PartialDocument3 pagesIncome Tax Seatwork - Answers Ver 2 PartialgillianNo ratings yet
- Manny Company: Required: Compute For The Balances of The Following On December 31, 2X14Document4 pagesManny Company: Required: Compute For The Balances of The Following On December 31, 2X14MauiNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: Subject ProfessorDocument6 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines: Subject ProfessorMarie Lyne AlanoNo ratings yet
- Income Tax - Corporations Sample Problems: SolutionsDocument12 pagesIncome Tax - Corporations Sample Problems: SolutionsYellow BelleNo ratings yet
- Income Taxes: Problem 1: True or FalseDocument17 pagesIncome Taxes: Problem 1: True or FalseJean Mira AribalNo ratings yet
- Interim Financial Reporting and Operating Segment Discussion Problems and Answer KeyDocument4 pagesInterim Financial Reporting and Operating Segment Discussion Problems and Answer Keyprincess QNo ratings yet
- Problem & Solution_June 2019_FDocument3 pagesProblem & Solution_June 2019_FMohammed Shihab UddinNo ratings yet
- Fa ReportDocument1 pageFa ReportAlfonso Miguel BuenoNo ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 9 - Income Taxes - 2021Document18 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 9 - Income Taxes - 2021Ventilacion, Jayson M.No ratings yet
- Problems Accouting For Deferred Taxes Webinar ReoDocument7 pagesProblems Accouting For Deferred Taxes Webinar ReocrookshanksNo ratings yet
- 01 Audit of Income Tax Exercise SetDocument2 pages01 Audit of Income Tax Exercise SetBecky GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Finals Take No 2Document2 pagesFinals Take No 2Wally AranasNo ratings yet
- Gross Reportable Compensation Income 285,000Document3 pagesGross Reportable Compensation Income 285,000WenjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 and 26Document10 pagesChapter 25 and 26Sittie Aisah AmpatuaNo ratings yet
- Use The Following Information To Answer Items 1 To 3:: FARQ 218 Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesUse The Following Information To Answer Items 1 To 3:: FARQ 218 Page 1 of 3Irvin LevieNo ratings yet
- Ventura, Mary Mickaella R. - p.49 - Statement of Financial PositionDocument5 pagesVentura, Mary Mickaella R. - p.49 - Statement of Financial PositionMary VenturaNo ratings yet
- J.K. Lasser's Small Business Taxes 2021: Your Complete Guide to a Better Bottom LineFrom EverandJ.K. Lasser's Small Business Taxes 2021: Your Complete Guide to a Better Bottom LineNo ratings yet
- PGBP Book NotesDocument41 pagesPGBP Book NoteskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Budget: Budgeting ProcessDocument23 pagesBudget: Budgeting Processgkmishra2001 at gmail.com100% (3)
- Dwnload Full Essentials of Economics 10th Edition Schiller Solutions Manual PDFDocument20 pagesDwnload Full Essentials of Economics 10th Edition Schiller Solutions Manual PDFcryer.westing.44mwoe100% (15)
- Exercises: Method. Under This Form Expenses Are Aggregated According To Their Nature and NotDocument15 pagesExercises: Method. Under This Form Expenses Are Aggregated According To Their Nature and NotCherry Doong CuantiosoNo ratings yet
- An Empirical Study of Road Accidents: Influence of The Costs of LivingDocument9 pagesAn Empirical Study of Road Accidents: Influence of The Costs of Livingncarab15No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Basics of AnalysisDocument76 pagesChapter 5 - Basics of AnalysisNguyễn Yến NhiNo ratings yet
- 1.3 REA Formula From William Ventolo JRDocument20 pages1.3 REA Formula From William Ventolo JRbhobot riveraNo ratings yet
- Bagan Akun Ud BuanaDocument2 pagesBagan Akun Ud BuanaYose SuprapmanNo ratings yet
- Sales Exclusive Tax Rate &Document3 pagesSales Exclusive Tax Rate &HaripriyaNo ratings yet
- T R S A: HE Eview Chool of CcountancyDocument12 pagesT R S A: HE Eview Chool of CcountancyNamnam KimNo ratings yet
- FSA - Tutorial 4 - Fall 2021Document3 pagesFSA - Tutorial 4 - Fall 2021Ging freexNo ratings yet
- Blu Containers Worksheet - IntermediateDocument13 pagesBlu Containers Worksheet - Intermediateahmedmostafaibrahim22No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document79 pagesUnit 2Carlos Abadía MorenoNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument22 pagesDemandSerenity Kerr100% (1)
- Earning For The Month - April 2023: Jubilant Foodworks LTDDocument1 pageEarning For The Month - April 2023: Jubilant Foodworks LTDnishankithkumarNo ratings yet
- Bea Vert Fooddict For The Month Ended March 2019: Income StatementDocument4 pagesBea Vert Fooddict For The Month Ended March 2019: Income StatementRhea May BaluteNo ratings yet
- AFST Short Quiz 02 Partnership OperationsDocument2 pagesAFST Short Quiz 02 Partnership Operationssad gurlNo ratings yet
- Partnership Operations Lecture Problem and QuizzerPDFDocument6 pagesPartnership Operations Lecture Problem and QuizzerPDFjanefern49No ratings yet
- Economics PYQ'sDocument43 pagesEconomics PYQ'sWERNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Caselette - Accounting CycleDocument51 pagesCHAPTER 1 Caselette - Accounting CycleKaren MagsayoNo ratings yet
- Magic Dominique Julius Julius TotalDocument4 pagesMagic Dominique Julius Julius TotalPaupauNo ratings yet
- Audit of Revenue and Receipts Cycle BA 123 Exercise Set 1: Problem 1: ABC COMPANY (Sales Cutoff Test)Document3 pagesAudit of Revenue and Receipts Cycle BA 123 Exercise Set 1: Problem 1: ABC COMPANY (Sales Cutoff Test)Becky GonzagaNo ratings yet
- First Quiz Financial Statement Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesFirst Quiz Financial Statement Analysis PDFRandy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- MADM In-Class QuizDocument11 pagesMADM In-Class QuizPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 To 30Document24 pagesLecture 28 To 30Pankaj MahantaNo ratings yet
- Solved Question Paper 2019-Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesSolved Question Paper 2019-Managerial EconomicsSheetal ShettyNo ratings yet
Finacc 6 A3 1
Finacc 6 A3 1
Uploaded by
200617Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finacc 6 A3 1
Finacc 6 A3 1
Uploaded by
200617Copyright:
Available Formats
Sample Problem #1
Animo Company leased a facility and received Php 600,000 annual rental payment on June 16, 2020. The beginning of the
lease was July 1, 2020. Rental income is taxable when received. The income tax rate 32%. Animo had no other permanent
or temporary difference.
1. Using the income statement liability method, what amount of deferred tax asset should Animo report on December
31, 2020 balance sheet?
Answer:
Accounting Income < Taxable Income
Accounting income (600,000 x 6 / 12) 300,000
Add: DTD 300,000
Taxable Income 600,000
Deferred Tax Asset = DTD x Tr
Deferred Tax Asset = 300,000 x 32%
Deferred Tax Asset = 96,000
2. Using the balance sheet liability method, what amount of deferred tax asset should Animo report on December 31,
2020 balance sheet?
Answer:
Carrying Amount of liability > Tax Base
Carrying amount of Unearned Rent 12/31 300,000
Less: Tax Base 0
Deductible Temporary Difference 300,000
Tax rate 32%
Deferred tax asset 96,000
Sample Problem #2
An entity reported the following information during the first year of operations:
Pretax financial income 9,000,000
Nontaxable interest received 1,000,000
Long-term loss accrual in excess of deductible amount 1,500,000
Tax depreciation in excess of financial depreciation 2,000,000
Income tax rate 30%
1. What is the current tax expense?
Answer: 2,250,000
2. What is the total tax expense?
Answer: 8M x 30% = 2,400,000
3. What is the deferred tax liability at year-end?
Answer: 2M x 30% = 600,000
4. What is the deferred tax asset at year-end?
Answer: 1,500,000 x 30% = 450,000
Accounting Income 9,000,000
Permanent difference: Nontaxable interest 1,000,000
Income subject to tax 8,000,000
Long-term loss accrual in excess of deductible amount 1,500,000
Excess depreciation (2,000,000)
Taxable Income 7,500,000
Tax rate 30%
Current Tax Expense 2,250,000
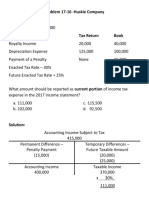
Problem 1
Viking Company reported pretax income of P1,000,000 in the income statement for the current year.
Tax return Accounting record
Rent income 70,000 120,000
Depreciation 280,000 220,000
Premiums on officers’ life insurance 90,000
Income tax rate 30%
1. What is the current provision for income tax for the current year?
Answer:
Pretax accounting income 1,000,000
Premium on officers’ life insurance – nondeductible 90,000
Accounting income subject to tax 1,090,000
Rent income – temporary difference (70k – 120k) - 50,000
Depreciation – temporary difference (280k – 220k) - 60,000
Taxable income 980,000
Current provision for income tax (980,000 x 30%) 294,000
2. What is the total tax expense?
Answer: Total tax expense (1,090,000 x 30%) 327,000
Problem 2
Huskie Company reported in the income statement for the current year pretax accounting income of P400,000.
The following items are treated differently per tax return and per book:
Tax return Book
Royalty income 20,000 40,000
Depreciation expense 125,000 100,000
Payment of a penalty None 15,000
Income tax rate 30%
1. What amount should be reported as current portion of income tax expense?
Answer:
Pretax accounting income 400,000
Payment of penalty – nondeductible 15,000
Accounting income subject to tax 415,000
Royalty income in excess of taxable amount (20,000)
Excess tax depreciation (25,000)
Taxable income 370,000
2. What is the total tax expense?
Answer:
Current tax expense (370,000 x 30%) 111,000
Total tax expense (415,000 x 30%) 124,500
Problem 3
Jasco Company is in the first year of operations and reported pretax accounting income of P4,000,000. The entity provided
the following information for the first year:
Premium on life insurance of key officer 100,000
Depreciation on tax return in excess of book depreciation 200,000
Interest on municipal bonds 50,000
Warranty expense 40,000
Actual warranty repairs 30,000
Bad debt expense 60,000
Beginning balance in allowance for bad debts 0
Ending balance in allowance for bad debts 40,000
Rent received in advance that will be recognized evenly
over the next three years 300,000
What is the taxable income for the first year?
Answer:
Pretax accounting income 4,000,000
Premium on life insurance 100,000
Excess tax depreciation (200,000)
Interest on municipal bonds (50,000)
Excess warranty expense (40,000 – 30,000) 10,000
Excess of bad debt expense over write-off (60,000 – 20,000) 40,000
Rent received in advance 300,000
Taxable income 4,200,000
Beginning allowance for bad debts 0
Bad debts expense 60,000
Total 60,000
Write-off (squeeze) (20,000)
Ending allowance for bad debts 40,000
II. CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING
1. In its December 31, 20x0 balance sheet, Quinn Co. reported a deferred tax asset of ₱9,000 and no deferred tax
liability. For 20x1, Quinn reported pretax financial statement income of ₱300,000. Temporary differences of
₱100,000 resulted in taxable income of ₱200,000 for 20x1. At December 31, 20x1, Quinn had cumulative taxable
differences of ₱70,000. Quinn's effective income tax rate is 30%. In its December 31, 20x1, income statement, what
should Quinn report as deferred income tax expense?
Answer:
Decrease in DTA (the beginning balance) P9,000
Increase in DTL (70k TTD x 30%) 21,000
Deferred tax expense P30,000
2. Dunn, Inc. uses the accrual method of accounting for financial reporting purposes and appropriately uses the
installment method of accounting for income tax purposes. Installment income of $1,500,000 will be collected in the
following years when the enacted tax rates are:
Collection of Income Enacted Tax Rates
2020 150,000 35%
2021 300,000 30%
2022 450,000 30%
2023 600,000 25%
The installment income is Dunn's only temporary difference. What amount should be included in the deferred income tax
liability in Dunn's December 31, 2020 balance sheet?
Answer:
DTL = CI x ETR
Collection of Income Enacted Tax Rates Deferred tax liability
2020 P150,000 35% P52,500 (not included)
2021 P300,000 30% P90,000
2022 P450,000 30% P135,000
2023 P600,000 25% P150,000
P375,000
PROBLEM 1
The records for Siemens Inc. show this data for 2020:
• Gross profit on installment sales recorded on the books was Php 360,000. Gross profit from collections of
installment receivables was Php 240,000.
• Non-deductible premium on life insurance was Php 3,800.
• Machinery was acquired in January for Php 300,000. Straight-line depreciation over a ten-year life (no salvage
value) is used. For tax purposes, Siemens may deduct 14% for 2020.
• Interest received on tax exempt government bonds was Php 9,000.
• The estimated warranty liability related to 2020 sales was Php 21,600. Repair costs under warranties during 2020
were Php 13,600. The remainder will be incurred in 2021. Pretax financial income is Php 600,000. The tax rate is
30%.
Requirements:
Accounting Tax
360,000 240,000 120,000 TTD
3,800 PD
30,000 42,000 12,000 TTD
-9,000 PD
21,600 13,600 8,000 DTD
Accounting Income 600,000
Add: Non-deductible expense 3,800
Less: Non-taxable income (9,000)
Accounting profit subject to tax 594,800 30% 178,440
Less: Taxable temporary difference (120,000 +
12,000) (132,000) 30% (39,600)
Add: Deductible temporary difference (21,600 +
13,600) 8,000 30% 2,400
Taxable Income 470,800 30% 141,240
a. What is the income tax expense to be recognized?
Answer:
Tax Expense P178,440
b. How much is the deferred tax liability and deferred tax asset?
Answer:
Deferred Tax Liability P(39,600)
Deferred Tax Asset P2,400
c. Provide the journal entry to record the income taxes for 2020.
Answer:
Income Tax Expense P178,440
Deferred Tax Asset 2,400
Deferred Tax Liability P39,600
Income Tax Payable 141,240
PROBLEM 2
Bee Corp. prepared the following reconciliation between book income and taxable income for the year ended December
31, 20x0:
Pretax accounting income 500,000
Taxable income 300,000
Difference 200,000
Interest on municipal bonds 50,000
Lower depreciation per financial statements 150,000
Total differences 200,000
Bee's effective income tax rate for 20x0 is 30%. The depreciation difference will reverse equally over the next three years
at enacted tax rates as follows:
Years Tax rates
20x1 30%
20x2 25%
20x3 25%
Requirements:
a. In Bee's 20x0 income statement, the current portion of its provision for income taxes should be
Answer:
Taxable income P300,000 x Tax Rates 30% = P90,000 Current Tax Expense
b. In Bee's 20x0 financial statements, the deferred portion of its provision for income taxes should be
Answer:
Year *Reversals Tax rate Deferred tax
20x1 P50,000 30% P15,000
20x2 P50,000 25% P12,500
20x3 P50,000 25% P12,500
P40,000
Solution:
*Lower depreciation per financial statements P150,000
Divided by: 3 years
Equal amounts of reversals P50,000
PROBLEM 3
In 2020, its first year of operations, SEA Corp. has a Php 1,000,000 net operating loss when the tax rate is 30%. The
Bureau of Internal Revenue has extended to five years the carry-over period for net operating losses incurred by businesses
in 2020 and 2021 due to the impact of the coronavirus pandemic.
2020 2021
Accounting Income (Loss) P(1,000,000) P400,000
Allowable deduction (400,000)
0
a. What is the entry in 2020 to record the tax loss carryforward?
Answer:
*-1M x 30% x -1
Deferred Tax Asset *P300,000
Income Tax Benefit P300,000
b. In 2021, SEA Corp has Php 400,000 taxable income and tax rate remains to be 30%. What entry would be
made in 2021 to recognize the loss carryforward?
Answer:
*-400k x 30% x -1
Income Tax Expense *P120,000
Deferred Tax Asset P120,000
You might also like
- Study On Buying Behaviour of Consumer For Different Brands of Chocolates Project Report New 2021Document67 pagesStudy On Buying Behaviour of Consumer For Different Brands of Chocolates Project Report New 2021Sarika RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Assessment 4 Tax 1Document3 pagesAssessment 4 Tax 1Judy Ann Gaceta0% (1)
- DocxDocument21 pagesDocxDhiananda zhuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Chapter 22Document30 pagesPrinciples of Economics Chapter 22Lu CheNo ratings yet
- TAXATION ON INDIVIDUALS Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesTAXATION ON INDIVIDUALS Lecture NotesLucille Rose MamburaoNo ratings yet
- Past MA Exams by Lecture Topic - Solutions PDFDocument59 pagesPast MA Exams by Lecture Topic - Solutions PDFbooks_sumiNo ratings yet
- Uses of National Income DataDocument2 pagesUses of National Income Dataarchitjain7080% (5)
- Toaz - Info 89bf91d5 1612761367237 PRDocument7 pagesToaz - Info 89bf91d5 1612761367237 PRAEHYUN YENVYNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap - IAS 12 - Tu LuanDocument14 pagesBai Tap - IAS 12 - Tu LuanTrần Nguyễn Tuệ MinhNo ratings yet
- Income Tax AccountingDocument3 pagesIncome Tax Accountinghae1234No ratings yet
- Lobrigas Unit6 AssessmentDocument4 pagesLobrigas Unit6 AssessmentClaudine LobrigasNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument5 pagesDocxJohn Vincent CruzNo ratings yet
- ACT150 Assignment DIMAAMPAODocument4 pagesACT150 Assignment DIMAAMPAOJeromeNo ratings yet
- Special Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureDocument5 pagesSpecial Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureClarisse AlimotNo ratings yet
- Solution - Accounting For Income TaxesDocument12 pagesSolution - Accounting For Income TaxesKlarissemay MontallanaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income TaxDocument3 pagesAccounting For Income TaxDaniel Kahn GillamacNo ratings yet
- LAGRIMAS, Sarah Nicole S. - Income Taxes 2Document4 pagesLAGRIMAS, Sarah Nicole S. - Income Taxes 2saturdaysunbaeNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 3A Assignment 2Document10 pagesFinancial Accounting 3A Assignment 2Mikaeel MohamedNo ratings yet
- VOL 2 16. Accounting For Income TaxationDocument15 pagesVOL 2 16. Accounting For Income TaxationdmangiginNo ratings yet
- Class Activities (Millan, 2019) : Requirements: A. How Much Is The Income Tax Expense For 2003? SolutionDocument6 pagesClass Activities (Millan, 2019) : Requirements: A. How Much Is The Income Tax Expense For 2003? SolutionPrincess TaizeNo ratings yet
- Special Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureDocument4 pagesSpecial Liabilities - Income Taxes: Income Tax Rate Is 40% and Is Not Expected To Change in The FutureNoorodden50% (2)
- Income TaxesDocument3 pagesIncome TaxesCENTENO, JOAN R.No ratings yet
- Sample Test (Extract)Document6 pagesSample Test (Extract)Julie KimNo ratings yet
- Ege, Kenneth M. Bsa22A1Document3 pagesEge, Kenneth M. Bsa22A1Kenneth Marcial Ege IINo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Tax Comprehensive Problem 1: Additional InformationDocument1 pageAccounting For Income Tax Comprehensive Problem 1: Additional InformationAngel Keith MercadoNo ratings yet
- FA2-08 Income TaxesDocument3 pagesFA2-08 Income Taxeskrisha millo0% (1)
- Tutorial 2: Exercise 12.2 Calculation of Current TaxDocument13 pagesTutorial 2: Exercise 12.2 Calculation of Current TaxKim FloresNo ratings yet
- Lamagan, Kyla T. BSA 401 Intermediate Acct. 2 Final Output Problem 16-13 (IAA)Document14 pagesLamagan, Kyla T. BSA 401 Intermediate Acct. 2 Final Output Problem 16-13 (IAA)lana del reyNo ratings yet
- Insurance Expense Allocated To The Quarter: SolutionDocument4 pagesInsurance Expense Allocated To The Quarter: Solutionasdfghjkl zxcvbnmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Accounting For Income Tax Problem 19-1Document5 pagesChapter 19 Accounting For Income Tax Problem 19-1nicole bancoroNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Accounting Rules and Tax RulesDocument18 pagesDifference Between Accounting Rules and Tax RulesCezar Rishane Mae SaligueNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Chapter 16Document8 pagesGroup 1 - Chapter 16Cherie Soriano AnanayoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Calculations Using The Tax-Payable MethodDocument10 pagesActivity 1 Calculations Using The Tax-Payable MethodJohn TomNo ratings yet
- He Is Not Subject To Basic Income Tax. However, His 13th Month Pay Exceeds 90,000. ThereforeDocument15 pagesHe Is Not Subject To Basic Income Tax. However, His 13th Month Pay Exceeds 90,000. ThereforeEarl Daniel RemorozaNo ratings yet
- CPAT Reviewer - TRAIN (Tax Reform) #1Document8 pagesCPAT Reviewer - TRAIN (Tax Reform) #1Zaaavnn VannnnnNo ratings yet
- 30 - Aathifah Teta Fitranti - 195020307111072 - AKM 3Document2 pages30 - Aathifah Teta Fitranti - 195020307111072 - AKM 3Aathifah Teta FitrantiNo ratings yet
- AFA IIP.L III SolutionJune 2016Document4 pagesAFA IIP.L III SolutionJune 2016HossainNo ratings yet
- 2542 - Tut1Document14 pages2542 - Tut1(Alumna 2018-6A07) CHUCK LONG YAU 卓朗悠No ratings yet
- Topic 1: Accounting For Income TaxesDocument13 pagesTopic 1: Accounting For Income TaxesPillos Jr., ElimarNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Income Tax Valix StudentDocument4 pagesAccounting For Income Tax Valix Studentvee viajeroNo ratings yet
- R2. TAX (M.L) Solution CMA May-2023 ExamDocument5 pagesR2. TAX (M.L) Solution CMA May-2023 ExamSharif MahmudNo ratings yet
- ACW2491 Lecture 4 Handout SolutionS22016Document4 pagesACW2491 Lecture 4 Handout SolutionS22016林志成No ratings yet
- BAFACR16 01 Problem IllustrationsDocument2 pagesBAFACR16 01 Problem Illustrationsmisssunshine112No ratings yet
- TAÑOTE Daisy AEC7 MEPIIDocument9 pagesTAÑOTE Daisy AEC7 MEPIIDaisy TañoteNo ratings yet
- R2. TAX ML Solution CMA January 2022 ExaminationDocument6 pagesR2. TAX ML Solution CMA January 2022 ExaminationPavel DhakaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Seatwork - Answers Ver 2 PartialDocument3 pagesIncome Tax Seatwork - Answers Ver 2 PartialgillianNo ratings yet
- Manny Company: Required: Compute For The Balances of The Following On December 31, 2X14Document4 pagesManny Company: Required: Compute For The Balances of The Following On December 31, 2X14MauiNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: Subject ProfessorDocument6 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines: Subject ProfessorMarie Lyne AlanoNo ratings yet
- Income Tax - Corporations Sample Problems: SolutionsDocument12 pagesIncome Tax - Corporations Sample Problems: SolutionsYellow BelleNo ratings yet
- Income Taxes: Problem 1: True or FalseDocument17 pagesIncome Taxes: Problem 1: True or FalseJean Mira AribalNo ratings yet
- Interim Financial Reporting and Operating Segment Discussion Problems and Answer KeyDocument4 pagesInterim Financial Reporting and Operating Segment Discussion Problems and Answer Keyprincess QNo ratings yet
- Problem & Solution_June 2019_FDocument3 pagesProblem & Solution_June 2019_FMohammed Shihab UddinNo ratings yet
- Fa ReportDocument1 pageFa ReportAlfonso Miguel BuenoNo ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 9 - Income Taxes - 2021Document18 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 9 - Income Taxes - 2021Ventilacion, Jayson M.No ratings yet
- Problems Accouting For Deferred Taxes Webinar ReoDocument7 pagesProblems Accouting For Deferred Taxes Webinar ReocrookshanksNo ratings yet
- 01 Audit of Income Tax Exercise SetDocument2 pages01 Audit of Income Tax Exercise SetBecky GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Finals Take No 2Document2 pagesFinals Take No 2Wally AranasNo ratings yet
- Gross Reportable Compensation Income 285,000Document3 pagesGross Reportable Compensation Income 285,000WenjunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 and 26Document10 pagesChapter 25 and 26Sittie Aisah AmpatuaNo ratings yet
- Use The Following Information To Answer Items 1 To 3:: FARQ 218 Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesUse The Following Information To Answer Items 1 To 3:: FARQ 218 Page 1 of 3Irvin LevieNo ratings yet
- Ventura, Mary Mickaella R. - p.49 - Statement of Financial PositionDocument5 pagesVentura, Mary Mickaella R. - p.49 - Statement of Financial PositionMary VenturaNo ratings yet
- J.K. Lasser's Small Business Taxes 2021: Your Complete Guide to a Better Bottom LineFrom EverandJ.K. Lasser's Small Business Taxes 2021: Your Complete Guide to a Better Bottom LineNo ratings yet
- PGBP Book NotesDocument41 pagesPGBP Book NoteskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Budget: Budgeting ProcessDocument23 pagesBudget: Budgeting Processgkmishra2001 at gmail.com100% (3)
- Dwnload Full Essentials of Economics 10th Edition Schiller Solutions Manual PDFDocument20 pagesDwnload Full Essentials of Economics 10th Edition Schiller Solutions Manual PDFcryer.westing.44mwoe100% (15)
- Exercises: Method. Under This Form Expenses Are Aggregated According To Their Nature and NotDocument15 pagesExercises: Method. Under This Form Expenses Are Aggregated According To Their Nature and NotCherry Doong CuantiosoNo ratings yet
- An Empirical Study of Road Accidents: Influence of The Costs of LivingDocument9 pagesAn Empirical Study of Road Accidents: Influence of The Costs of Livingncarab15No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Basics of AnalysisDocument76 pagesChapter 5 - Basics of AnalysisNguyễn Yến NhiNo ratings yet
- 1.3 REA Formula From William Ventolo JRDocument20 pages1.3 REA Formula From William Ventolo JRbhobot riveraNo ratings yet
- Bagan Akun Ud BuanaDocument2 pagesBagan Akun Ud BuanaYose SuprapmanNo ratings yet
- Sales Exclusive Tax Rate &Document3 pagesSales Exclusive Tax Rate &HaripriyaNo ratings yet
- T R S A: HE Eview Chool of CcountancyDocument12 pagesT R S A: HE Eview Chool of CcountancyNamnam KimNo ratings yet
- FSA - Tutorial 4 - Fall 2021Document3 pagesFSA - Tutorial 4 - Fall 2021Ging freexNo ratings yet
- Blu Containers Worksheet - IntermediateDocument13 pagesBlu Containers Worksheet - Intermediateahmedmostafaibrahim22No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document79 pagesUnit 2Carlos Abadía MorenoNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument22 pagesDemandSerenity Kerr100% (1)
- Earning For The Month - April 2023: Jubilant Foodworks LTDDocument1 pageEarning For The Month - April 2023: Jubilant Foodworks LTDnishankithkumarNo ratings yet
- Bea Vert Fooddict For The Month Ended March 2019: Income StatementDocument4 pagesBea Vert Fooddict For The Month Ended March 2019: Income StatementRhea May BaluteNo ratings yet
- AFST Short Quiz 02 Partnership OperationsDocument2 pagesAFST Short Quiz 02 Partnership Operationssad gurlNo ratings yet
- Partnership Operations Lecture Problem and QuizzerPDFDocument6 pagesPartnership Operations Lecture Problem and QuizzerPDFjanefern49No ratings yet
- Economics PYQ'sDocument43 pagesEconomics PYQ'sWERNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Caselette - Accounting CycleDocument51 pagesCHAPTER 1 Caselette - Accounting CycleKaren MagsayoNo ratings yet
- Magic Dominique Julius Julius TotalDocument4 pagesMagic Dominique Julius Julius TotalPaupauNo ratings yet
- Audit of Revenue and Receipts Cycle BA 123 Exercise Set 1: Problem 1: ABC COMPANY (Sales Cutoff Test)Document3 pagesAudit of Revenue and Receipts Cycle BA 123 Exercise Set 1: Problem 1: ABC COMPANY (Sales Cutoff Test)Becky GonzagaNo ratings yet
- First Quiz Financial Statement Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesFirst Quiz Financial Statement Analysis PDFRandy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- MADM In-Class QuizDocument11 pagesMADM In-Class QuizPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 To 30Document24 pagesLecture 28 To 30Pankaj MahantaNo ratings yet
- Solved Question Paper 2019-Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesSolved Question Paper 2019-Managerial EconomicsSheetal ShettyNo ratings yet