Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsLPB V Unit
LPB V Unit
Uploaded by
Tony StarkThe document discusses recent trends in banking in India, including the development of electronic payment services like e-cheques and the increasing use of digital banking technologies. Some of the key banking technologies and services covered are real-time gross settlement (RTGS), electronic funds transfer (EFT), national electronic funds transfer (NEFT), electronic clearing service (ECS), automatic teller machines (ATMs), point of sale terminals, telebanking, internet banking, and anywhere banking. These electronic banking innovations allow customers to perform basic transactions remotely and transfer funds between accounts in real-time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Easy Drive GT20manualV1.1Document102 pagesEasy Drive GT20manualV1.1Musa inverter HouseNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Hospital PlanningDocument7 pagesOrthopedic Hospital Planningሀይደር ዶ.ርNo ratings yet
- List of Filipino ArchitectsDocument12 pagesList of Filipino ArchitectsSussybelle Bandoy100% (2)
- Case Digest - Peralta vs. Civil Service Commission 212 SCRA 425, G.R. No. 95832, Aug. 10, 1992Document2 pagesCase Digest - Peralta vs. Civil Service Commission 212 SCRA 425, G.R. No. 95832, Aug. 10, 1992Lu Cas100% (3)
- Banking in 21st CenturyDocument4 pagesBanking in 21st CenturyDr. Ashish Kumar ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in Banking Services - Trends, Issues and ChallengesDocument9 pagesInformation Technology in Banking Services - Trends, Issues and ChallengesSneha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Commercial Banks: DefinitionDocument2 pagesCommercial Banks: DefinitionKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Banking 5Document29 pagesBanking 5Rakshitha. A GedamNo ratings yet
- Fmbo CH 5Document17 pagesFmbo CH 5sumedh narwadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. L3.2. Kinds of Trends in BankingDocument4 pagesChapter 3. L3.2. Kinds of Trends in BankingvibhuNo ratings yet
- E BankingDocument3 pagesE BankingSumedhaa Srivastava 34 Sem-1,CNo ratings yet
- E-Banking or Online BankingDocument35 pagesE-Banking or Online BankingMohan kumar K.SNo ratings yet
- E-Payment SystemDocument13 pagesE-Payment SystemDr. Azhar Ahmed SheikhNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends and Development of Banking SystemDocument5 pagesRecent Trends and Development of Banking Systemvishnu priya v 149No ratings yet
- E PaymentDocument15 pagesE PaymentRohan KirpekarNo ratings yet
- CA Project On Internet BankingDocument18 pagesCA Project On Internet BankingTejal KirpekarNo ratings yet
- Shubham Kumar Chachan CIA - 1Document12 pagesShubham Kumar Chachan CIA - 1AYUSH TREHAN 20215023No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction To BankingDocument14 pagesChapter-1 Introduction To BankingAnonymous 22GBLsme1No ratings yet
- UNIT 1 E Payment SystemDocument76 pagesUNIT 1 E Payment SystemRahul DesuNo ratings yet
- Banking Notes Part 2. E BankingDocument22 pagesBanking Notes Part 2. E Bankingnichumon319No ratings yet
- Electronic Fund TransferDocument19 pagesElectronic Fund Transfersandhya kumarNo ratings yet
- 3RD SemDocument34 pages3RD SemMohan kumar K.SNo ratings yet
- Computer Banking: E - BankingDocument14 pagesComputer Banking: E - BankingMALKANI DISHA DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- E-Business Unit4Document29 pagesE-Business Unit4vkr DiariesNo ratings yet
- Institute of Managment Studies, Davv, Indore Finance and Administration - Semester Iv Credit Management and Retail BankingDocument5 pagesInstitute of Managment Studies, Davv, Indore Finance and Administration - Semester Iv Credit Management and Retail BankingSNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank ProjectDocument85 pagesAxis Bank Projectsv net100% (1)
- Kalenzi WorkDocument6 pagesKalenzi WorkhassankitwangoNo ratings yet
- Technology in BankingDocument7 pagesTechnology in BankingBinshaNo ratings yet
- Tabish AssignmentDocument10 pagesTabish AssignmenttabishalizahidNo ratings yet
- Antony Kolanchery Faculty of Management: E-BankingDocument19 pagesAntony Kolanchery Faculty of Management: E-BankingRoshniNo ratings yet
- National Law Institute University, Bhopal: Basics of E-BankingDocument21 pagesNational Law Institute University, Bhopal: Basics of E-BankingDikshaNo ratings yet
- Recent in BankingDocument25 pagesRecent in BankingSrividya SNo ratings yet
- Epayment SeminarDocument5 pagesEpayment Seminardheeraj_ddNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument15 pagesContractsNnNo ratings yet
- Banking ServicesDocument40 pagesBanking ServicesrishiomkumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Banking LawDocument16 pagesUnit 5 Banking LawRoy Stephen RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in BankingDocument2 pagesRecent Trends in BankingFire BoltNo ratings yet
- Commercial BankingDocument74 pagesCommercial BankingShishir N VNo ratings yet
- Electronic BankingDocument8 pagesElectronic BankingBatch 27No ratings yet
- E-Banking Transactions: Your CustomerDocument6 pagesE-Banking Transactions: Your CustomerJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- E Payment SystemDocument47 pagesE Payment SystemNamrata KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Electronic TransferDocument12 pagesElectronic Transferlavanyasundar7No ratings yet
- Unit Iv (Foit)Document48 pagesUnit Iv (Foit)varsha.j2177No ratings yet
- Banking 3,4&5 NotesDocument38 pagesBanking 3,4&5 NotesSowmya BatchuNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Bank Computerization Payment Systems and Electronic BankingDocument7 pagesEssentials of Bank Computerization Payment Systems and Electronic Bankingvijayadarshini vNo ratings yet
- EftDocument44 pagesEftAparna SamuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CBO BBM 5th SemDocument9 pagesChapter 10 CBO BBM 5th SemNikesh GhimireNo ratings yet
- E Banking and E Payment - IsDocument20 pagesE Banking and E Payment - IsaliiiiNo ratings yet
- Bfs - Unit III Short NotesDocument9 pagesBfs - Unit III Short NotesvelmuruganbNo ratings yet
- Internet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemDocument6 pagesInternet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemRohan Freako RawalNo ratings yet
- Popular Services Under E-Banking in IndiaDocument5 pagesPopular Services Under E-Banking in IndiaPramil AnandNo ratings yet
- Electronic BankingDocument50 pagesElectronic BankingNazlia NadiaNo ratings yet
- Banking Technology 1Document9 pagesBanking Technology 1Pragathi PriyaNo ratings yet
- 202005031242173294rajiv Applied E Banking UpdatedDocument8 pages202005031242173294rajiv Applied E Banking UpdatedKirana KNo ratings yet
- Ict Group Assignment For Grade 12Document9 pagesIct Group Assignment For Grade 12KaddunNo ratings yet
- Banking ProductsDocument9 pagesBanking Productsbeena antuNo ratings yet
- Online Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnDocument9 pagesOnline Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnJamshed AlamNo ratings yet
- Online Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnDocument4 pagesOnline Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnJamshed AlamNo ratings yet
- E Banking e PaymentsDocument7 pagesE Banking e Paymentsgarima424582638No ratings yet
- Ruchi Finance LabDocument35 pagesRuchi Finance LabNitish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CH-6 E MarketingDocument17 pagesCH-6 E Marketingabdelamuzemil8No ratings yet
- Im Mini ProjectDocument10 pagesIm Mini Projectsrividya balajiNo ratings yet
- E BankingDocument19 pagesE BankingramyaNo ratings yet
- Review of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersFrom EverandReview of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersNo ratings yet
- Reactsurf 0092 TDSDocument26 pagesReactsurf 0092 TDSprchnandagawaliNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateNaina Umar VaishyaNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesScheduling Practice ProblemsM ThuNo ratings yet
- Prem NewDocument34 pagesPrem NewShaik RuksanaNo ratings yet
- Caf-8 All Test (Sp-24)Document87 pagesCaf-8 All Test (Sp-24)hashmiabdullah4948No ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Shear Strength of Rock DiscontinuityDocument6 pagesAn Investigation Into The Shear Strength of Rock DiscontinuityAzeNo ratings yet
- Dahua DVR 5104C/5408C/5116C Especificaciones: M Odel DH-DVR5104C-V2 DH-DVR5108C DH-DVR5116C SystemDocument1 pageDahua DVR 5104C/5408C/5116C Especificaciones: M Odel DH-DVR5104C-V2 DH-DVR5108C DH-DVR5116C Systemomar mejiaNo ratings yet
- Wl130v Led20s 840 Psu WHDocument3 pagesWl130v Led20s 840 Psu WHayoubNo ratings yet
- 7 Crystal Reports Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pages7 Crystal Reports Interview Questions and AnswersshyamVENKAT0% (1)
- Mindray BC-2800 - Service ManualDocument108 pagesMindray BC-2800 - Service ManualAvilianaK.Bintari80% (5)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional Slides v2.0Document724 pagesAWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional Slides v2.0John Nguyen100% (1)
- Liquid Resins Additives - EmeaDocument59 pagesLiquid Resins Additives - Emearndsb.aopNo ratings yet
- Strategic Plan For The Dem PartyDocument7 pagesStrategic Plan For The Dem Partyapi-255139145100% (1)
- Media and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFElishaNo ratings yet
- English Ki Tooti Hui TangDocument2 pagesEnglish Ki Tooti Hui TangGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- HR ReportDocument6 pagesHR ReportJulius EdillorNo ratings yet
- MCKEE vs. IACDocument3 pagesMCKEE vs. IACJohnny EnglishNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Disinterested PersonDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Disinterested PersonDexter John SuyatNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Design Principles and Their Impact On Digital DesignsDocument14 pagesFundamental Design Principles and Their Impact On Digital DesignsCARLOS, EPHRAIM O.No ratings yet
- MGT 3110: Exam 3 Study Guide Discussion QuestionsDocument13 pagesMGT 3110: Exam 3 Study Guide Discussion QuestionsSihle GwazelaNo ratings yet
- Save Money. Live BetterDocument1 pageSave Money. Live BetterdopoviNo ratings yet
- M-Class Parts Catalog 92-2505-01 EDocument24 pagesM-Class Parts Catalog 92-2505-01 EjNo ratings yet
- A4 Food Spoilage & PreservationDocument15 pagesA4 Food Spoilage & PreservationRavi kishore KuchiyaNo ratings yet
- Application For ParoleDocument2 pagesApplication For ParoleChristian Rivera100% (3)
- EB 06 LightingDocument45 pagesEB 06 LightingTamNo ratings yet
- Hiệu part3Document4 pagesHiệu part3Đỗ Đại HọcNo ratings yet
LPB V Unit
LPB V Unit
Uploaded by
Tony Stark0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views12 pagesThe document discusses recent trends in banking in India, including the development of electronic payment services like e-cheques and the increasing use of digital banking technologies. Some of the key banking technologies and services covered are real-time gross settlement (RTGS), electronic funds transfer (EFT), national electronic funds transfer (NEFT), electronic clearing service (ECS), automatic teller machines (ATMs), point of sale terminals, telebanking, internet banking, and anywhere banking. These electronic banking innovations allow customers to perform basic transactions remotely and transfer funds between accounts in real-time.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses recent trends in banking in India, including the development of electronic payment services like e-cheques and the increasing use of digital banking technologies. Some of the key banking technologies and services covered are real-time gross settlement (RTGS), electronic funds transfer (EFT), national electronic funds transfer (NEFT), electronic clearing service (ECS), automatic teller machines (ATMs), point of sale terminals, telebanking, internet banking, and anywhere banking. These electronic banking innovations allow customers to perform basic transactions remotely and transfer funds between accounts in real-time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views12 pagesLPB V Unit
LPB V Unit
Uploaded by
Tony StarkThe document discusses recent trends in banking in India, including the development of electronic payment services like e-cheques and the increasing use of digital banking technologies. Some of the key banking technologies and services covered are real-time gross settlement (RTGS), electronic funds transfer (EFT), national electronic funds transfer (NEFT), electronic clearing service (ECS), automatic teller machines (ATMs), point of sale terminals, telebanking, internet banking, and anywhere banking. These electronic banking innovations allow customers to perform basic transactions remotely and transfer funds between accounts in real-time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
Scanned with CamScanner
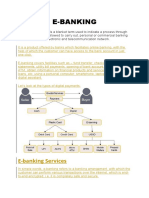
RECENT TRENDS IN BANKING
1. Electronic Payment Services – E Cheques:
Now-a-days we are hearing about e-governance, e-mail, e-commerce, e-tail etc. In the
same manner, a new technology is being developed in US for introduction of e-cheque,
which will eventually replace the conventional paper cheque. India, as harbinger to the
introduction of e-cheque, the Negotiable Instruments Act has already been amended to
include; Truncated cheque and E-cheque instruments.
2. e-Banking:
Electronic Banking is nothing but banking through electronic media. It enables customers
to perform their basic banking transactions around the clock globally
3. Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS):
Real Time Gross Settlement system, introduced in India since March 2004, is a system
through which electronics instructions can be given by banks to transfer funds from their
account to the account of another bank. The RTGS system is maintained and operated by
the RBI and provides a means of efficient and faster funds transfer among banks
facilitating their financial operations. As the name suggests, funds transfer between banks
takes place on a ‘Real Time' basis. Therefore, money can reach the beneficiary
instantaneously and the beneficiary's bank has the responsibility to credit the beneficiary's
account within two hours.
4. Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT):
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is a system whereby anyone who wants to make
payment to another person/company etc. can approach his bank and make cash payment
or give instructions/authorization to transfer funds directly from his own account to
the bank account of the receiver/beneficiary. Complete details such as the receiver's
name, bank account number, account type (savings or current account), bank name, city,
branch name etc. should be furnished to the bank at the time of requesting for such
transfers so that the amount reaches the beneficiaries' account correctly and faster. RBI is
the service provider of EFT.
5. National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT):
NEFT means National Electronic Funds Transfer. It is a mode of money transfer that
enables one-to-one payments within India. NEFT is owned and operated by the Reserve
Bank of India, and through this facility, you can transfer money from one account to
another.
6. Electronic Clearing Service (ECS):
Electronic Clearing Service is a retail payment system that can be used to make bulk
payments/receipts of a similar nature especially where each individual payment is of a
repetitive nature and of relatively smaller amount. This facility is meant for companies
and government departments to make/receive large volumes of payments rather than for
funds transfers by individuals.
7. Automatic Teller Machine (ATM):
Automatic Teller Machine is the most popular devise in India, which enables the
customers to withdraw their money 24 hours a day 7 days a week. It is a devise that
allows customer who has an ATM card to perform routine banking transactions without
interacting with a human teller. In addition to cash withdrawal, ATMs can be used for
payment of utility bills, funds transfer between accounts, deposit of cheques and cash into
accounts, balance enquiry etc.
8. Point of Sale Terminal:
Point of Sale Terminal is a computer terminal that is linked online to the computerized
customer information files in a bank and magnetically encoded plastic transaction card
that identifies the customer to the computer. During a transaction, the customer's account
is debited and the retailer's account is credited by the computer for the amount of
purchase.
9. Tele Banking:
Tele Banking facilitates the customer to do entire non-cash related banking on telephone.
Under this devise Automatic Voice Recorder is used for simpler queries and transactions.
For complicated queries and transactions, manned phone terminals are used.
10. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI):
Electronic Data Interchange is the electronic exchange of business documents like
purchase order, invoices, shipping notices, receiving advices etc. in a standard, computer
processed, universally accepted format between trading partners. EDI can also be used to
transmit financial information and payments in electronic form.
11. Passbook Printing Kiosk:
A Passbook Printing Kiosk is an automated machine that enables the customer to update
their passbook. These machines are primarily available in banks and other financial
institutions that require account updating or bookkeeping. It fetches all the account
transaction details.
12. Internet Banking:
Internet Banking is a part of e-commerce in the field of banking. Internet banking is very
fast and cost effective. It can be operated at any time or anywhere according to the needs
and convenience of the highly demanding customers of today.
13. Anywhere Banking:
With this facility, a customer of a bank can operate his account not only at his own
branch bank but also from other branch of that bank which has the ‘Anywhere banking’
facility.
You might also like
- Easy Drive GT20manualV1.1Document102 pagesEasy Drive GT20manualV1.1Musa inverter HouseNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Hospital PlanningDocument7 pagesOrthopedic Hospital Planningሀይደር ዶ.ርNo ratings yet
- List of Filipino ArchitectsDocument12 pagesList of Filipino ArchitectsSussybelle Bandoy100% (2)
- Case Digest - Peralta vs. Civil Service Commission 212 SCRA 425, G.R. No. 95832, Aug. 10, 1992Document2 pagesCase Digest - Peralta vs. Civil Service Commission 212 SCRA 425, G.R. No. 95832, Aug. 10, 1992Lu Cas100% (3)
- Banking in 21st CenturyDocument4 pagesBanking in 21st CenturyDr. Ashish Kumar ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in Banking Services - Trends, Issues and ChallengesDocument9 pagesInformation Technology in Banking Services - Trends, Issues and ChallengesSneha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Commercial Banks: DefinitionDocument2 pagesCommercial Banks: DefinitionKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Banking 5Document29 pagesBanking 5Rakshitha. A GedamNo ratings yet
- Fmbo CH 5Document17 pagesFmbo CH 5sumedh narwadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. L3.2. Kinds of Trends in BankingDocument4 pagesChapter 3. L3.2. Kinds of Trends in BankingvibhuNo ratings yet
- E BankingDocument3 pagesE BankingSumedhaa Srivastava 34 Sem-1,CNo ratings yet
- E-Banking or Online BankingDocument35 pagesE-Banking or Online BankingMohan kumar K.SNo ratings yet
- E-Payment SystemDocument13 pagesE-Payment SystemDr. Azhar Ahmed SheikhNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends and Development of Banking SystemDocument5 pagesRecent Trends and Development of Banking Systemvishnu priya v 149No ratings yet
- E PaymentDocument15 pagesE PaymentRohan KirpekarNo ratings yet
- CA Project On Internet BankingDocument18 pagesCA Project On Internet BankingTejal KirpekarNo ratings yet
- Shubham Kumar Chachan CIA - 1Document12 pagesShubham Kumar Chachan CIA - 1AYUSH TREHAN 20215023No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction To BankingDocument14 pagesChapter-1 Introduction To BankingAnonymous 22GBLsme1No ratings yet
- UNIT 1 E Payment SystemDocument76 pagesUNIT 1 E Payment SystemRahul DesuNo ratings yet
- Banking Notes Part 2. E BankingDocument22 pagesBanking Notes Part 2. E Bankingnichumon319No ratings yet
- Electronic Fund TransferDocument19 pagesElectronic Fund Transfersandhya kumarNo ratings yet
- 3RD SemDocument34 pages3RD SemMohan kumar K.SNo ratings yet
- Computer Banking: E - BankingDocument14 pagesComputer Banking: E - BankingMALKANI DISHA DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- E-Business Unit4Document29 pagesE-Business Unit4vkr DiariesNo ratings yet
- Institute of Managment Studies, Davv, Indore Finance and Administration - Semester Iv Credit Management and Retail BankingDocument5 pagesInstitute of Managment Studies, Davv, Indore Finance and Administration - Semester Iv Credit Management and Retail BankingSNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank ProjectDocument85 pagesAxis Bank Projectsv net100% (1)
- Kalenzi WorkDocument6 pagesKalenzi WorkhassankitwangoNo ratings yet
- Technology in BankingDocument7 pagesTechnology in BankingBinshaNo ratings yet
- Tabish AssignmentDocument10 pagesTabish AssignmenttabishalizahidNo ratings yet
- Antony Kolanchery Faculty of Management: E-BankingDocument19 pagesAntony Kolanchery Faculty of Management: E-BankingRoshniNo ratings yet
- National Law Institute University, Bhopal: Basics of E-BankingDocument21 pagesNational Law Institute University, Bhopal: Basics of E-BankingDikshaNo ratings yet
- Recent in BankingDocument25 pagesRecent in BankingSrividya SNo ratings yet
- Epayment SeminarDocument5 pagesEpayment Seminardheeraj_ddNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument15 pagesContractsNnNo ratings yet
- Banking ServicesDocument40 pagesBanking ServicesrishiomkumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Banking LawDocument16 pagesUnit 5 Banking LawRoy Stephen RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in BankingDocument2 pagesRecent Trends in BankingFire BoltNo ratings yet
- Commercial BankingDocument74 pagesCommercial BankingShishir N VNo ratings yet
- Electronic BankingDocument8 pagesElectronic BankingBatch 27No ratings yet
- E-Banking Transactions: Your CustomerDocument6 pagesE-Banking Transactions: Your CustomerJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- E Payment SystemDocument47 pagesE Payment SystemNamrata KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Electronic TransferDocument12 pagesElectronic Transferlavanyasundar7No ratings yet
- Unit Iv (Foit)Document48 pagesUnit Iv (Foit)varsha.j2177No ratings yet
- Banking 3,4&5 NotesDocument38 pagesBanking 3,4&5 NotesSowmya BatchuNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Bank Computerization Payment Systems and Electronic BankingDocument7 pagesEssentials of Bank Computerization Payment Systems and Electronic Bankingvijayadarshini vNo ratings yet
- EftDocument44 pagesEftAparna SamuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CBO BBM 5th SemDocument9 pagesChapter 10 CBO BBM 5th SemNikesh GhimireNo ratings yet
- E Banking and E Payment - IsDocument20 pagesE Banking and E Payment - IsaliiiiNo ratings yet
- Bfs - Unit III Short NotesDocument9 pagesBfs - Unit III Short NotesvelmuruganbNo ratings yet
- Internet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemDocument6 pagesInternet Banking in India:) Information Only SystemRohan Freako RawalNo ratings yet
- Popular Services Under E-Banking in IndiaDocument5 pagesPopular Services Under E-Banking in IndiaPramil AnandNo ratings yet
- Electronic BankingDocument50 pagesElectronic BankingNazlia NadiaNo ratings yet
- Banking Technology 1Document9 pagesBanking Technology 1Pragathi PriyaNo ratings yet
- 202005031242173294rajiv Applied E Banking UpdatedDocument8 pages202005031242173294rajiv Applied E Banking UpdatedKirana KNo ratings yet
- Ict Group Assignment For Grade 12Document9 pagesIct Group Assignment For Grade 12KaddunNo ratings yet
- Banking ProductsDocument9 pagesBanking Productsbeena antuNo ratings yet
- Online Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnDocument9 pagesOnline Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnJamshed AlamNo ratings yet
- Online Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnDocument4 pagesOnline Banking (Or Internet Banking) Allows Customers To Conduct Financial Transactions OnJamshed AlamNo ratings yet
- E Banking e PaymentsDocument7 pagesE Banking e Paymentsgarima424582638No ratings yet
- Ruchi Finance LabDocument35 pagesRuchi Finance LabNitish BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CH-6 E MarketingDocument17 pagesCH-6 E Marketingabdelamuzemil8No ratings yet
- Im Mini ProjectDocument10 pagesIm Mini Projectsrividya balajiNo ratings yet
- E BankingDocument19 pagesE BankingramyaNo ratings yet
- Review of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersFrom EverandReview of Some Online Banks and Visa/Master Cards IssuersNo ratings yet
- Reactsurf 0092 TDSDocument26 pagesReactsurf 0092 TDSprchnandagawaliNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateNaina Umar VaishyaNo ratings yet
- Scheduling Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesScheduling Practice ProblemsM ThuNo ratings yet
- Prem NewDocument34 pagesPrem NewShaik RuksanaNo ratings yet
- Caf-8 All Test (Sp-24)Document87 pagesCaf-8 All Test (Sp-24)hashmiabdullah4948No ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Shear Strength of Rock DiscontinuityDocument6 pagesAn Investigation Into The Shear Strength of Rock DiscontinuityAzeNo ratings yet
- Dahua DVR 5104C/5408C/5116C Especificaciones: M Odel DH-DVR5104C-V2 DH-DVR5108C DH-DVR5116C SystemDocument1 pageDahua DVR 5104C/5408C/5116C Especificaciones: M Odel DH-DVR5104C-V2 DH-DVR5108C DH-DVR5116C Systemomar mejiaNo ratings yet
- Wl130v Led20s 840 Psu WHDocument3 pagesWl130v Led20s 840 Psu WHayoubNo ratings yet
- 7 Crystal Reports Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pages7 Crystal Reports Interview Questions and AnswersshyamVENKAT0% (1)
- Mindray BC-2800 - Service ManualDocument108 pagesMindray BC-2800 - Service ManualAvilianaK.Bintari80% (5)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional Slides v2.0Document724 pagesAWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional Slides v2.0John Nguyen100% (1)
- Liquid Resins Additives - EmeaDocument59 pagesLiquid Resins Additives - Emearndsb.aopNo ratings yet
- Strategic Plan For The Dem PartyDocument7 pagesStrategic Plan For The Dem Partyapi-255139145100% (1)
- Media and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFElishaNo ratings yet
- English Ki Tooti Hui TangDocument2 pagesEnglish Ki Tooti Hui TangGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- HR ReportDocument6 pagesHR ReportJulius EdillorNo ratings yet
- MCKEE vs. IACDocument3 pagesMCKEE vs. IACJohnny EnglishNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Disinterested PersonDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Disinterested PersonDexter John SuyatNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Design Principles and Their Impact On Digital DesignsDocument14 pagesFundamental Design Principles and Their Impact On Digital DesignsCARLOS, EPHRAIM O.No ratings yet
- MGT 3110: Exam 3 Study Guide Discussion QuestionsDocument13 pagesMGT 3110: Exam 3 Study Guide Discussion QuestionsSihle GwazelaNo ratings yet
- Save Money. Live BetterDocument1 pageSave Money. Live BetterdopoviNo ratings yet
- M-Class Parts Catalog 92-2505-01 EDocument24 pagesM-Class Parts Catalog 92-2505-01 EjNo ratings yet
- A4 Food Spoilage & PreservationDocument15 pagesA4 Food Spoilage & PreservationRavi kishore KuchiyaNo ratings yet
- Application For ParoleDocument2 pagesApplication For ParoleChristian Rivera100% (3)
- EB 06 LightingDocument45 pagesEB 06 LightingTamNo ratings yet
- Hiệu part3Document4 pagesHiệu part3Đỗ Đại HọcNo ratings yet