Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsBSC 21 Fuel Phase Test Witra Rusli 11nov22
BSC 21 Fuel Phase Test Witra Rusli 11nov22
Uploaded by
witrazuhayli431Aviation fuels include aviation gasoline and kerosene. Kerosene fuels, commonly known as Jet A-1, are clear and colorless. Microbial corrosion from fungi like Cladosporium Resinae is most likely to occur in kerosene fuels where water is present at temperatures between 15 to 35 degrees Celsius. Fuel systems use various pumps like booster pumps, transfer pumps, and jet pumps to move fuel between tanks and to aircraft engines.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- EOOW - Orals Questions & AnswersDocument54 pagesEOOW - Orals Questions & Answersnkosithandile Vuke100% (1)
- Class 4 EoowDocument74 pagesClass 4 EoowRyan Cardoza0% (1)
- Aircraft Fuel SystemDocument63 pagesAircraft Fuel SystemsushantreshmaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Phthalic AnhydrideDocument16 pagesManufacturing of Phthalic AnhydrideAnkit Mistry100% (2)
- PartsDocument9 pagesPartsRosario SisniegasNo ratings yet
- All About Marine Enginnering OralsDocument76 pagesAll About Marine Enginnering OralsUdana Hettiarachchi100% (3)
- Tanker Questions From Ship EducationDocument33 pagesTanker Questions From Ship EducationAshok YNo ratings yet
- General Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersDocument31 pagesGeneral Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- EvapEmission PDFDocument8 pagesEvapEmission PDFpivillamilNo ratings yet
- What Is An Inert Gas or IG System On Ships?Document21 pagesWhat Is An Inert Gas or IG System On Ships?Jeric SorianoNo ratings yet
- VOA Question & AnswersDocument5 pagesVOA Question & AnswersStefanVisNo ratings yet
- AMT Module 1 - PartB-1Document12 pagesAMT Module 1 - PartB-1PrathikNo ratings yet
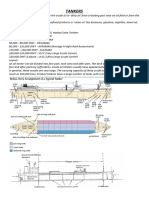
- Oil Tanker Cargo WorkDocument12 pagesOil Tanker Cargo WorkAshutosh Singh100% (4)
- How To Synchronize Generators On A ShipDocument115 pagesHow To Synchronize Generators On A Shipandriea03100% (1)
- (Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic BasicDocument76 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic Basiceng_ebrahim_2000100% (2)
- Aircraft Fuel SystemDocument64 pagesAircraft Fuel SystemAbinashMahapatraNo ratings yet
- Homework #2 - Ethan Archibald - HVAC 103 - 09FEB2021Document4 pagesHomework #2 - Ethan Archibald - HVAC 103 - 09FEB2021Ethan Carlisle Couto ArchibaldNo ratings yet
- Internal Test May 2024 - Set BDocument5 pagesInternal Test May 2024 - Set Bakashdiwaker8034No ratings yet
- MEK Gen BMP KMDocument6 pagesMEK Gen BMP KMRahul NaikNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of HydraulicsDocument101 pagesFundamentals of HydraulicswissamhijaziNo ratings yet
- TankerDocument31 pagesTankerpushkarsidhayeNo ratings yet
- Refinery Definitions - FAQDocument7 pagesRefinery Definitions - FAQbalajiupesNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Inert Gas SystemDocument8 pages1.6 Inert Gas SystemAbcdNo ratings yet
- Inert Gas SystemDocument9 pagesInert Gas Systemchristian popeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Hydralic SystemDocument101 pagesBasics of Hydralic SystemNikhil MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Baburaj Sir Frequently Asked Q A For MEP and MOTOR - AKGDocument10 pagesBaburaj Sir Frequently Asked Q A For MEP and MOTOR - AKGarunengr.mnavyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of HydraulicsDocument101 pagesFundamentals of HydraulicsLuis Nunes100% (1)
- Qdoc - Tips - Class-4 EoowDocument74 pagesQdoc - Tips - Class-4 EoowShamsad alamNo ratings yet
- Ers Possible Questions IIIDocument4 pagesErs Possible Questions IIIIsaacNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Steam TurbinesDocument58 pagesQuestions & Answers On Steam TurbinesVishal JaishankarNo ratings yet
- C 11.C Pumps and CompressorsDocument4 pagesC 11.C Pumps and Compressorsanom7No ratings yet
- Accumulator and BOP Control Unit5 - Aly2Document65 pagesAccumulator and BOP Control Unit5 - Aly2Khaled Yazid100% (1)
- Final Edition of Automotive QBDocument15 pagesFinal Edition of Automotive QByoussef faroukNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPDocument1 pageBest Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPashutosh ambeyNo ratings yet
- 8 Most Common Problems in Hydraulic Operated Remote Valve System On ShipsDocument23 pages8 Most Common Problems in Hydraulic Operated Remote Valve System On ShipsVasileios PantouvakisNo ratings yet
- ExamsDocument15 pagesExamsTarek MassimoNo ratings yet
- Start Air System ProblemsDocument47 pagesStart Air System Problemshpss77100% (5)
- Report AirsystemDocument24 pagesReport Airsystemchristian pagtamaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Week ReviseDocument15 pages2nd Week ReviseCarlo ValdezNo ratings yet
- IC Engine - Chapter 5, 6 & 7 Handout - 2022Document21 pagesIC Engine - Chapter 5, 6 & 7 Handout - 2022nunuNo ratings yet
- Chennai Oral With AnsDocument43 pagesChennai Oral With AnsSahil Mishra100% (5)
- Steam Turbine QuestionsDocument56 pagesSteam Turbine QuestionsNivas Ssv67% (3)
- Ch5 - Anti and DeicingDocument7 pagesCh5 - Anti and DeicingPavan SushantNo ratings yet
- Piping System: Group 3Document25 pagesPiping System: Group 3Aaron NakpilNo ratings yet
- Starting - Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesDocument6 pagesStarting - Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesTarek AzizNo ratings yet
- Starting & Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesDocument6 pagesStarting & Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesUjjwal Singh100% (1)
- Vapour Management ControlDocument22 pagesVapour Management Controlviktor_gligorovNo ratings yet
- Chapter A 09 Fuel Storage, Transfer EtcDocument7 pagesChapter A 09 Fuel Storage, Transfer EtcСергей КороткийNo ratings yet
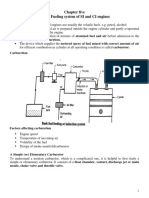
- Fuel SystemDocument7 pagesFuel SystemখালিদহাসানNo ratings yet
- Descripción Del Equipamiento para SLOP OILDocument25 pagesDescripción Del Equipamiento para SLOP OILLilianaNo ratings yet
- Short Note On Oil Tankers Cargo SystemDocument4 pagesShort Note On Oil Tankers Cargo SystemAdmiral_pouria7564100% (9)
- S10 Service ManualDocument53 pagesS10 Service ManualDave M67% (3)
- Airframe Oral & Practical Study Guide: Fuel SystemsDocument3 pagesAirframe Oral & Practical Study Guide: Fuel SystemsEduardo QuinteroNo ratings yet
- AccumulatorDocument5 pagesAccumulatorMohan CharanchathNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument35 pagesSteam Turbinerajan100% (1)
- Question & Answers On Steam Turbines: 1. What Is A Stage in A Steam Turbine?Document114 pagesQuestion & Answers On Steam Turbines: 1. What Is A Stage in A Steam Turbine?tejaswini100% (1)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Naval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsFrom EverandNaval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Communication SystemsDocument31 pagesAircraft Communication SystemsAhmedShah75% (4)
- OptiX Metro WDM Series Equipment Commissioning and Testing Introduction ISSUE1.0Document28 pagesOptiX Metro WDM Series Equipment Commissioning and Testing Introduction ISSUE1.0SeifEldinADelNo ratings yet
- QC RegisterDocument29 pagesQC RegisterBilal Ahmed BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Shape Dental - DigitalDocument52 pages3 Shape Dental - DigitaltashtashNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency Hasdrede KengneDocument4 pagesEnergy Efficiency Hasdrede Kengneapi-342523815No ratings yet
- Undergraduate Studies Calendar - University of WaterlooDocument4 pagesUndergraduate Studies Calendar - University of WaterlooBrandin RoveloNo ratings yet
- Hafen CityDocument7 pagesHafen CityAndree MosqueraNo ratings yet
- ST Mary AxeDocument23 pagesST Mary AxeBharathVenkatachalamNo ratings yet
- GMW 3172 ConnectorDocument3 pagesGMW 3172 ConnectorFreddy Tituaña CadenaNo ratings yet
- Seminarski Rad Fizika RTG Aparata Radioskopija RadiografijaDocument31 pagesSeminarski Rad Fizika RTG Aparata Radioskopija RadiografijaNenadStankovićNo ratings yet
- SG 248055Document566 pagesSG 248055Sofiane HamidNo ratings yet
- Stratus Ftserver System Administrator'S Guide For The Windows Operating SystemDocument144 pagesStratus Ftserver System Administrator'S Guide For The Windows Operating SystemphyosithumgNo ratings yet
- Orcad 16.5 Signal IntegrityDocument37 pagesOrcad 16.5 Signal Integrityhpnx9420No ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Code No. 042) : Besides, The Syllabus Also Attempts ToDocument11 pagesPHYSICS (Code No. 042) : Besides, The Syllabus Also Attempts ToRanit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database 12c R2: Administration Workshop Ed 3: DurationDocument6 pagesOracle Database 12c R2: Administration Workshop Ed 3: Durationjackomito100% (1)
- Marine Smart Trash (New)Document5 pagesMarine Smart Trash (New)king syNo ratings yet
- ATS 4 Accelerating AdmixturesDocument4 pagesATS 4 Accelerating AdmixturescuibaprauNo ratings yet
- October Week Equations of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesOctober Week Equations of Motion Worksheetmatthewlaw107No ratings yet
- Wavistrong Supplemental Installation InstructionsDocument13 pagesWavistrong Supplemental Installation Instructionsmg4myNo ratings yet
- Richard Clem Over-Unity Engine - 1992Document11 pagesRichard Clem Over-Unity Engine - 19921357531100% (1)
- Conveying Equipment - Mpi Magnetic ProductsDocument4 pagesConveying Equipment - Mpi Magnetic ProductsMpi ServicesNo ratings yet
- Buku G.S. Manku Chapter 8Document5 pagesBuku G.S. Manku Chapter 8Taro PurpleNo ratings yet
- Cyanogen Mod 7.2 para U20a UnlockbootloaderDocument5 pagesCyanogen Mod 7.2 para U20a UnlockbootloaderarcontetetricoNo ratings yet
- DS 2AF1 516 DatasheetDocument1 pageDS 2AF1 516 DatasheetTas DtNo ratings yet
- As NZS 4763-2011 Safety of Portable InvertersDocument8 pagesAs NZS 4763-2011 Safety of Portable InvertersSAI Global - APAC0% (2)
- Danfoss TL5GDocument2 pagesDanfoss TL5GAnonymous uxZ5FYLP3jNo ratings yet
- Top Gun 200i MSTDocument15 pagesTop Gun 200i MSTTom PleysierNo ratings yet
- Fig. 910 - Swivel Sway Brace FittingDocument1 pageFig. 910 - Swivel Sway Brace FittingANTONIO GUTIERREZ MIRANDANo ratings yet
BSC 21 Fuel Phase Test Witra Rusli 11nov22
BSC 21 Fuel Phase Test Witra Rusli 11nov22
Uploaded by
witrazuhayli4310 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesAviation fuels include aviation gasoline and kerosene. Kerosene fuels, commonly known as Jet A-1, are clear and colorless. Microbial corrosion from fungi like Cladosporium Resinae is most likely to occur in kerosene fuels where water is present at temperatures between 15 to 35 degrees Celsius. Fuel systems use various pumps like booster pumps, transfer pumps, and jet pumps to move fuel between tanks and to aircraft engines.
Original Description:
Original Title
BSc 21 Fuel Phase Test Witra Rusli 11Nov22
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAviation fuels include aviation gasoline and kerosene. Kerosene fuels, commonly known as Jet A-1, are clear and colorless. Microbial corrosion from fungi like Cladosporium Resinae is most likely to occur in kerosene fuels where water is present at temperatures between 15 to 35 degrees Celsius. Fuel systems use various pumps like booster pumps, transfer pumps, and jet pumps to move fuel between tanks and to aircraft engines.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesBSC 21 Fuel Phase Test Witra Rusli 11nov22
BSC 21 Fuel Phase Test Witra Rusli 11nov22
Uploaded by
witrazuhayli431Aviation fuels include aviation gasoline and kerosene. Kerosene fuels, commonly known as Jet A-1, are clear and colorless. Microbial corrosion from fungi like Cladosporium Resinae is most likely to occur in kerosene fuels where water is present at temperatures between 15 to 35 degrees Celsius. Fuel systems use various pumps like booster pumps, transfer pumps, and jet pumps to move fuel between tanks and to aircraft engines.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
BSc 21 Fuel System Phase Test
1. What are the two types of fuel in general use
- Aviation gasoline and kerosene.
2. How are they identified
- For AVGAS, it is a single blue band followed by a red
rectangle with AVGAS 100LL written in white. However, for
AVTUR, it is two black bands followed by a black rectangle
with JET A-1 written in white.
3. What colour is Jet A1
- Clear or colourless.
4. What additive can be put into fuel to prevent freezing
- Fuel system icing inhibitor
5. What is the name of fuel tank microbial corrosion
- Cladosporium Resinae
6. How is it identified
- Fungus is of a slimy nature and may appear in various
colours from white to brown to near black. Also, it possesses
an offensive odour.
7. Where is it most likely to occur
- Kerosene fuels, where water is present and temperature is
between 15 and 35 degrees celcius. These conditions can
be found in between latitudes 30 degrees north to 30
degrees south.
8. What are the design minimum fuel flow requirements
- Full power at sea level with an almost empty tank.
9. What are the three main types of fuel tank
- Rigid, flexible and integral fuel tanks.
10. What is a booster pump
- Pumps situated in fuel tanks and used to supply fuel under
low pressure to engines.
11. What is a transfer pump
- Transfer fuel between tanks.
12. What is a jet pump
- These pumps use a supply of fuel from the booster pump to
induce a flow of fuel through a venture connected to a
pipeline. It has no moving parts relying on the motive flow
from the booster pump to move the fuel within the tank
preventing stagnation.
13. What is the advantage of a 3 phase pump
- High flow rates from relatively small pumps.
14. How is vapour removed during pumping
- Centrifugal action causes swirl at impeller eye, which
separates the air and vapour from the fuel resulting in a
vapour free delivery of fuel to the engine.
15. What are float valves used for
- Used as cross-feed valves and inter-engine valves.
16. What are float switches used for
- Isolates the electrical mechanism from the fuel tank for
safety reasons.
17. What is an LP cock
- They are usually ball-type, full-flow type having a range of
movement of 90 from closed to fully open.
18. How can we tell valve position on a fuel system
- A ‘detent’ at each selected position ensures that the correct
selection has been made.
19. What is a Suction Valve for
- Permit fuel to be drawn from the tanks in the event of a
booster pump failure.
20. What is an Interference Spider
- It is fitted to the inlet side in order to prevent the valve from
being fitted the wrong way round.
21. What is the International symbol for fuel
- Four-sided star
22. How can fuel system contamination be identified
- Through the drain valve, a small quantity of fuel drained into
a glass jar and checked for the presence of water, sediment
and microbiological contamination.
23. What is the purpose of a cascade device
- Prevents damage to the tank interior especially the sealant,
which would be the result if a pressurised jet of fuel entered
the tank.
24. What is ground refuelling pressure
- 50 lbs. psi
25. What is ground de-fuelling pressure
- 11 lbs psi
26. What is a Dip Stick
- A rod with a screwed fitting at the top, which screws into a
mating fitting in the top skin of the tank. Protrudes into the
tank and is calibrated to indicate the contents of the tank
between certain limits.
27. What is a Drip Stick
- Short outer tube, which is attached to an adaptor in the lower
wing skin and protrudes upwards into the tank, and a long
inner tube(calibrated in gallons or inches), which slides in the
outer tube, and is secured to the adaptor by a bayonet fitting.
28. How does a Mag Level Indicator work
- Similar to a drip stick but the top of the outer tube is sealed.
A magnet is mounted on a float which surrounds the outer
tube rises and falls with the fuel level.
29. How does a Wax Charge Fuel Heater work
- An automatically controlled fuel heating system consists of a
thermostatically controlled air inlet valve on the heat
exchanger, which progressively opens and closes to
maintain fuel outlet temperature within pre-set limits above 0
degrees celcius.
30. Where are Sliding Couplings used
- Where only air or vapour passes through a pipe.
31. What is Specific Gravity
- It refers to the weight of a liquid, in comparison with that of
water, the SG of water is taken as 1.
You might also like
- EOOW - Orals Questions & AnswersDocument54 pagesEOOW - Orals Questions & Answersnkosithandile Vuke100% (1)
- Class 4 EoowDocument74 pagesClass 4 EoowRyan Cardoza0% (1)
- Aircraft Fuel SystemDocument63 pagesAircraft Fuel SystemsushantreshmaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Phthalic AnhydrideDocument16 pagesManufacturing of Phthalic AnhydrideAnkit Mistry100% (2)
- PartsDocument9 pagesPartsRosario SisniegasNo ratings yet
- All About Marine Enginnering OralsDocument76 pagesAll About Marine Enginnering OralsUdana Hettiarachchi100% (3)
- Tanker Questions From Ship EducationDocument33 pagesTanker Questions From Ship EducationAshok YNo ratings yet
- General Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersDocument31 pagesGeneral Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- EvapEmission PDFDocument8 pagesEvapEmission PDFpivillamilNo ratings yet
- What Is An Inert Gas or IG System On Ships?Document21 pagesWhat Is An Inert Gas or IG System On Ships?Jeric SorianoNo ratings yet
- VOA Question & AnswersDocument5 pagesVOA Question & AnswersStefanVisNo ratings yet
- AMT Module 1 - PartB-1Document12 pagesAMT Module 1 - PartB-1PrathikNo ratings yet
- Oil Tanker Cargo WorkDocument12 pagesOil Tanker Cargo WorkAshutosh Singh100% (4)
- How To Synchronize Generators On A ShipDocument115 pagesHow To Synchronize Generators On A Shipandriea03100% (1)
- (Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic BasicDocument76 pages(Oto-Hui - Com) Doosan Hydraulic Basiceng_ebrahim_2000100% (2)
- Aircraft Fuel SystemDocument64 pagesAircraft Fuel SystemAbinashMahapatraNo ratings yet
- Homework #2 - Ethan Archibald - HVAC 103 - 09FEB2021Document4 pagesHomework #2 - Ethan Archibald - HVAC 103 - 09FEB2021Ethan Carlisle Couto ArchibaldNo ratings yet
- Internal Test May 2024 - Set BDocument5 pagesInternal Test May 2024 - Set Bakashdiwaker8034No ratings yet
- MEK Gen BMP KMDocument6 pagesMEK Gen BMP KMRahul NaikNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of HydraulicsDocument101 pagesFundamentals of HydraulicswissamhijaziNo ratings yet
- TankerDocument31 pagesTankerpushkarsidhayeNo ratings yet
- Refinery Definitions - FAQDocument7 pagesRefinery Definitions - FAQbalajiupesNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Inert Gas SystemDocument8 pages1.6 Inert Gas SystemAbcdNo ratings yet
- Inert Gas SystemDocument9 pagesInert Gas Systemchristian popeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Hydralic SystemDocument101 pagesBasics of Hydralic SystemNikhil MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Baburaj Sir Frequently Asked Q A For MEP and MOTOR - AKGDocument10 pagesBaburaj Sir Frequently Asked Q A For MEP and MOTOR - AKGarunengr.mnavyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of HydraulicsDocument101 pagesFundamentals of HydraulicsLuis Nunes100% (1)
- Qdoc - Tips - Class-4 EoowDocument74 pagesQdoc - Tips - Class-4 EoowShamsad alamNo ratings yet
- Ers Possible Questions IIIDocument4 pagesErs Possible Questions IIIIsaacNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Steam TurbinesDocument58 pagesQuestions & Answers On Steam TurbinesVishal JaishankarNo ratings yet
- C 11.C Pumps and CompressorsDocument4 pagesC 11.C Pumps and Compressorsanom7No ratings yet
- Accumulator and BOP Control Unit5 - Aly2Document65 pagesAccumulator and BOP Control Unit5 - Aly2Khaled Yazid100% (1)
- Final Edition of Automotive QBDocument15 pagesFinal Edition of Automotive QByoussef faroukNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPDocument1 pageBest Practice Guide For Power Transformer Maintenance EEPashutosh ambeyNo ratings yet
- 8 Most Common Problems in Hydraulic Operated Remote Valve System On ShipsDocument23 pages8 Most Common Problems in Hydraulic Operated Remote Valve System On ShipsVasileios PantouvakisNo ratings yet
- ExamsDocument15 pagesExamsTarek MassimoNo ratings yet
- Start Air System ProblemsDocument47 pagesStart Air System Problemshpss77100% (5)
- Report AirsystemDocument24 pagesReport Airsystemchristian pagtamaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Week ReviseDocument15 pages2nd Week ReviseCarlo ValdezNo ratings yet
- IC Engine - Chapter 5, 6 & 7 Handout - 2022Document21 pagesIC Engine - Chapter 5, 6 & 7 Handout - 2022nunuNo ratings yet
- Chennai Oral With AnsDocument43 pagesChennai Oral With AnsSahil Mishra100% (5)
- Steam Turbine QuestionsDocument56 pagesSteam Turbine QuestionsNivas Ssv67% (3)
- Ch5 - Anti and DeicingDocument7 pagesCh5 - Anti and DeicingPavan SushantNo ratings yet
- Piping System: Group 3Document25 pagesPiping System: Group 3Aaron NakpilNo ratings yet
- Starting - Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesDocument6 pagesStarting - Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesTarek AzizNo ratings yet
- Starting & Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesDocument6 pagesStarting & Reversing Problems in Marine EnginesUjjwal Singh100% (1)
- Vapour Management ControlDocument22 pagesVapour Management Controlviktor_gligorovNo ratings yet
- Chapter A 09 Fuel Storage, Transfer EtcDocument7 pagesChapter A 09 Fuel Storage, Transfer EtcСергей КороткийNo ratings yet
- Fuel SystemDocument7 pagesFuel SystemখালিদহাসানNo ratings yet
- Descripción Del Equipamiento para SLOP OILDocument25 pagesDescripción Del Equipamiento para SLOP OILLilianaNo ratings yet
- Short Note On Oil Tankers Cargo SystemDocument4 pagesShort Note On Oil Tankers Cargo SystemAdmiral_pouria7564100% (9)
- S10 Service ManualDocument53 pagesS10 Service ManualDave M67% (3)
- Airframe Oral & Practical Study Guide: Fuel SystemsDocument3 pagesAirframe Oral & Practical Study Guide: Fuel SystemsEduardo QuinteroNo ratings yet
- AccumulatorDocument5 pagesAccumulatorMohan CharanchathNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument35 pagesSteam Turbinerajan100% (1)
- Question & Answers On Steam Turbines: 1. What Is A Stage in A Steam Turbine?Document114 pagesQuestion & Answers On Steam Turbines: 1. What Is A Stage in A Steam Turbine?tejaswini100% (1)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Naval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsFrom EverandNaval Mechanical Engineering: Gas Turbine Propulsion, Auxiliary, and Engineering Support SystemsNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Communication SystemsDocument31 pagesAircraft Communication SystemsAhmedShah75% (4)
- OptiX Metro WDM Series Equipment Commissioning and Testing Introduction ISSUE1.0Document28 pagesOptiX Metro WDM Series Equipment Commissioning and Testing Introduction ISSUE1.0SeifEldinADelNo ratings yet
- QC RegisterDocument29 pagesQC RegisterBilal Ahmed BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Shape Dental - DigitalDocument52 pages3 Shape Dental - DigitaltashtashNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency Hasdrede KengneDocument4 pagesEnergy Efficiency Hasdrede Kengneapi-342523815No ratings yet
- Undergraduate Studies Calendar - University of WaterlooDocument4 pagesUndergraduate Studies Calendar - University of WaterlooBrandin RoveloNo ratings yet
- Hafen CityDocument7 pagesHafen CityAndree MosqueraNo ratings yet
- ST Mary AxeDocument23 pagesST Mary AxeBharathVenkatachalamNo ratings yet
- GMW 3172 ConnectorDocument3 pagesGMW 3172 ConnectorFreddy Tituaña CadenaNo ratings yet
- Seminarski Rad Fizika RTG Aparata Radioskopija RadiografijaDocument31 pagesSeminarski Rad Fizika RTG Aparata Radioskopija RadiografijaNenadStankovićNo ratings yet
- SG 248055Document566 pagesSG 248055Sofiane HamidNo ratings yet
- Stratus Ftserver System Administrator'S Guide For The Windows Operating SystemDocument144 pagesStratus Ftserver System Administrator'S Guide For The Windows Operating SystemphyosithumgNo ratings yet
- Orcad 16.5 Signal IntegrityDocument37 pagesOrcad 16.5 Signal Integrityhpnx9420No ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Code No. 042) : Besides, The Syllabus Also Attempts ToDocument11 pagesPHYSICS (Code No. 042) : Besides, The Syllabus Also Attempts ToRanit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database 12c R2: Administration Workshop Ed 3: DurationDocument6 pagesOracle Database 12c R2: Administration Workshop Ed 3: Durationjackomito100% (1)
- Marine Smart Trash (New)Document5 pagesMarine Smart Trash (New)king syNo ratings yet
- ATS 4 Accelerating AdmixturesDocument4 pagesATS 4 Accelerating AdmixturescuibaprauNo ratings yet
- October Week Equations of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesOctober Week Equations of Motion Worksheetmatthewlaw107No ratings yet
- Wavistrong Supplemental Installation InstructionsDocument13 pagesWavistrong Supplemental Installation Instructionsmg4myNo ratings yet
- Richard Clem Over-Unity Engine - 1992Document11 pagesRichard Clem Over-Unity Engine - 19921357531100% (1)
- Conveying Equipment - Mpi Magnetic ProductsDocument4 pagesConveying Equipment - Mpi Magnetic ProductsMpi ServicesNo ratings yet
- Buku G.S. Manku Chapter 8Document5 pagesBuku G.S. Manku Chapter 8Taro PurpleNo ratings yet
- Cyanogen Mod 7.2 para U20a UnlockbootloaderDocument5 pagesCyanogen Mod 7.2 para U20a UnlockbootloaderarcontetetricoNo ratings yet
- DS 2AF1 516 DatasheetDocument1 pageDS 2AF1 516 DatasheetTas DtNo ratings yet
- As NZS 4763-2011 Safety of Portable InvertersDocument8 pagesAs NZS 4763-2011 Safety of Portable InvertersSAI Global - APAC0% (2)
- Danfoss TL5GDocument2 pagesDanfoss TL5GAnonymous uxZ5FYLP3jNo ratings yet
- Top Gun 200i MSTDocument15 pagesTop Gun 200i MSTTom PleysierNo ratings yet
- Fig. 910 - Swivel Sway Brace FittingDocument1 pageFig. 910 - Swivel Sway Brace FittingANTONIO GUTIERREZ MIRANDANo ratings yet