Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsTHBHDK 26
THBHDK 26
Uploaded by
RGNitinDevaAccurate measurements are close to the true value, while precise measurements are consistent when repeated. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision refers to the reproducibility of measurements. There are two types of errors in measurements - systematic errors, which make all measurements incorrect by the same amount and reduce accuracy, and random errors, which produce slightly different values each time and reduce precision.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- DLL PR2Document4 pagesDLL PR2jrtlim100% (1)
- Joseph W. McMoneagle - The Adventures of A Remote Viewer: Psychic HackingDocument4 pagesJoseph W. McMoneagle - The Adventures of A Remote Viewer: Psychic HackingAndross580100% (1)
- C2S3Document14 pagesC2S3John Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- 3 Measuring in ScienceDocument4 pages3 Measuring in ScienceChis KutiNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson 2Document1 pagePhysics Lesson 2shenNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Week 1 (Phy11)Document11 pagesStudy Guide For Week 1 (Phy11)Jezzel Ren AuxteroNo ratings yet
- Precision Vs Accuracy PDFDocument9 pagesPrecision Vs Accuracy PDFSabeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Precision and Accuracy-1Document14 pagesPrecision and Accuracy-1yousaf khanNo ratings yet
- Errors and Uncertainty in Experimental DataDocument12 pagesErrors and Uncertainty in Experimental DataKengkoy PascualNo ratings yet
- BRM Accuracy Vs PrecisionDocument7 pagesBRM Accuracy Vs PrecisionYuga NayakNo ratings yet
- Errors 11Document3 pagesErrors 11Tushar RajNo ratings yet
- 15 01 - 20 00 LeyDocument1 page15 01 - 20 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 3130 - 2 - Ketakpastian Dalam Pengukuran NiniDocument36 pages3130 - 2 - Ketakpastian Dalam Pengukuran NiniIrene KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 DatahandlingDocument42 pagesChapter12 Datahandlingsyaz lianaNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision Are Two Important Concepts in ScienceDocument3 pagesAccuracy and Precision Are Two Important Concepts in ScienceCrystel Joy CamasisNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 BiologyDocument120 pagesActivate 1 BiologyMarina Belloni100% (1)
- ME8501 MM - Accuracy Vs PrecisionDocument1 pageME8501 MM - Accuracy Vs PrecisionKarthick NNo ratings yet
- Accuracy Vs PrecisionDocument2 pagesAccuracy Vs PrecisionJoshua Bature SamboNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and PrecisionDocument3 pagesAccuracy and PrecisionRaghuveerprasad IppiliNo ratings yet
- GetIT Practical Key Words 1 PowerPoint SlidesDocument11 pagesGetIT Practical Key Words 1 PowerPoint SlidesAdam TanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 1 ReviewerabadarthusNo ratings yet
- Biology of How Science Works (As & A2)Document117 pagesBiology of How Science Works (As & A2)Chris Corey-PhiloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Week 4 ReviewerDocument6 pagesWeek 1 - Week 4 Reviewerronanmorales93No ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of Validity and ReliabilityDocument1 pageFundamental Principles of Validity and ReliabilityVIPLAV SRIVASTAVNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Properties of Sea Water PDFDocument6 pagesLecture 01 Properties of Sea Water PDFClow NNo ratings yet
- AH Uncertainties 2012 SSERC BookletDocument20 pagesAH Uncertainties 2012 SSERC BookletLNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Understanding MeasurementsDocument27 pages1.4 Understanding MeasurementsMakcikHajarNo ratings yet
- 02 Accuracy vs. Precision NotesDocument16 pages02 Accuracy vs. Precision NotessharmilaNo ratings yet
- Q3w1d2 - Accuracy and Precision PresentationDocument16 pagesQ3w1d2 - Accuracy and Precision PresentationGelo VeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Precision and Accuracy: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Precision and Accuracy: ObjectivesRuby Cocal0% (1)
- Some Discussions On Unit - 1Document11 pagesSome Discussions On Unit - 1kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- Accuracy PrecisionDocument1 pageAccuracy PrecisionspmothukuriNo ratings yet
- Language of Measurement in Context ChemistryDocument6 pagesLanguage of Measurement in Context ChemistryVictor BabsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Metrology Terminology Accuracy Precision ResolutionDocument2 pagesMetrology Terminology Accuracy Precision ResolutionQuality controllerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- MEASUREMENT AND DATA QUALITY LabordsDocument6 pagesMEASUREMENT AND DATA QUALITY LabordsMarimiel PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Topic 11: Measurement & Data ProcessingDocument17 pagesTopic 11: Measurement & Data ProcessingkatNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision PDFDocument1 pageAccuracy and Precision PDFthryeeNo ratings yet
- ERRORS in Measurements - 26april2021Document13 pagesERRORS in Measurements - 26april2021Julianne DimaguilaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Understanding Measurements Using Measuring Intruments 1.metre Rule 2.stopwatch 3.thermometer 4.measuring Cylinder 5.protractor 6.measuring TapeDocument26 pages1.4 Understanding Measurements Using Measuring Intruments 1.metre Rule 2.stopwatch 3.thermometer 4.measuring Cylinder 5.protractor 6.measuring TapeE-one Saw-dNo ratings yet
- Errors & Measurements (Interated) VPR Garu (40-54)Document15 pagesErrors & Measurements (Interated) VPR Garu (40-54)PHYSICS LSNo ratings yet
- 614 Lab - Error in MeasurementsDocument3 pages614 Lab - Error in Measurementsjilldlrs06No ratings yet
- Accuracy Is How Close Your ObservedDocument1 pageAccuracy Is How Close Your ObservedJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Business Research Levels of Measurement Nominal, Ordial, RatioDocument19 pagesBusiness Research Levels of Measurement Nominal, Ordial, RatioAashna jainNo ratings yet
- Why We Need Statistics? Scales of Measurement: FIRST SEMESTER - A.Y. 2022-2023 A Statistics RefresherDocument6 pagesWhy We Need Statistics? Scales of Measurement: FIRST SEMESTER - A.Y. 2022-2023 A Statistics RefresherANGELA FAYE MARIE BAWALANNo ratings yet
- Topic: Measurement: Meadowbrook High School Physics Lesson 1 Grade 10 Teacher: Ms. S. FindleyDocument14 pagesTopic: Measurement: Meadowbrook High School Physics Lesson 1 Grade 10 Teacher: Ms. S. Findleychristopher chanNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsDocument20 pagesMeasurements and Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsHassan Ali BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Te Chapter 03 - 1Document10 pagesTe Chapter 03 - 1stephensreenivasulutNo ratings yet
- CHEMOMETRICSDocument45 pagesCHEMOMETRICSApheleleNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - Lesson 2Document26 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Lesson 2Christian Karl GarciaNo ratings yet
- Measurement, Accuracy and Precision PDFDocument19 pagesMeasurement, Accuracy and Precision PDFAyush ZalaNo ratings yet
- Error Analysis ManualDocument13 pagesError Analysis ManualBrian Keston SubitNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1. Measurements and Uncertainty: Every Measurement Is Associated With A Certain UncertaintyDocument7 pagesExperiment 1. Measurements and Uncertainty: Every Measurement Is Associated With A Certain UncertaintyBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- 8602 Assignment No 2Document24 pages8602 Assignment No 2Fatima YousafNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1st MQADocument4 pagesPhysics - 1st MQALance LirioNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision - Definition, ExamplesDocument3 pagesAccuracy and Precision - Definition, ExamplescesarinigillasNo ratings yet
- Nr2 PrelimsDocument5 pagesNr2 PrelimsCarl Angelo MahaitNo ratings yet
- Objectives: General Physics 1Document8 pagesObjectives: General Physics 1Raymond De AsisNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 27Document1 pageTHBHDK 27RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- GaugesDocument24 pagesGaugesRGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 33Document1 pageTHBHDK 33RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- Permanent WayDocument18 pagesPermanent WayRGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- Airport, Harbour - NOTES-2Document1 pageAirport, Harbour - NOTES-2RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 41Document1 pageTHBHDK 41RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 35Document1 pageTHBHDK 35RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 37Document1 pageTHBHDK 37RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 48Document1 pageTHBHDK 48RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 39Document1 pageTHBHDK 39RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 23Document1 pageTHBHDK 23RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 34Document1 pageTHBHDK 34RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 9Document1 pageTHBHDK 9RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 27Document1 pageTHBHDK 27RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 14Document1 pageTHBHDK 14RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 12Document1 pageTHBHDK 12RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 68Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 68RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 6Document1 pageTHBHDK 6RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 44Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 44RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 40Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 40RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 48Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 48RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 42Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 42RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 41Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 41RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 19Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 19RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 34Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 34RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 22Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 22RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 33Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 33RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 30Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 30RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 27Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 27RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 10Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 10RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 14Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 14RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- Lesbian and Gays StudiesDocument31 pagesLesbian and Gays StudiesJoaquín Edgardo Reyes RomeroNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The Evaluation of Uncertainties Associated With RecoveryDocument10 pagesApproaches To The Evaluation of Uncertainties Associated With RecoveryAnonymous 3OFvtiNo ratings yet
- Ieee Format ThesisDocument4 pagesIeee Format ThesisAllan Añavisa Ostique Jr.No ratings yet
- Training Program Laboratories Accreditation ISO 17025 2017 13012021Document4 pagesTraining Program Laboratories Accreditation ISO 17025 2017 13012021kim phaNo ratings yet
- Robots 15 December 2011: BBC Learning English 6 Minute EnglishDocument5 pagesRobots 15 December 2011: BBC Learning English 6 Minute EnglishwiltorNo ratings yet
- Literature Matrix FullDocument31 pagesLiterature Matrix Fullapi-583156298No ratings yet
- PR2 - D e 4Document26 pagesPR2 - D e 4Susan T. Laxamana100% (1)
- Cdsco Stem CellDocument84 pagesCdsco Stem CellKIITAA FANINo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Utilization of Library Resources AmongDocument14 pagesFactors Affecting The Utilization of Library Resources AmongOlive Therese100% (1)
- Natalia JasiakDocument1 pageNatalia Jasiakapi-693801600No ratings yet
- Psych Test in SchoolsDocument6 pagesPsych Test in SchoolsDenilyn CortezNo ratings yet
- State of The Art Review Proposal GuidelinesDocument1 pageState of The Art Review Proposal Guidelineshesam khorramiNo ratings yet
- Rerp2018 8146819Document10 pagesRerp2018 8146819Dwi NilamsariNo ratings yet
- Afflux & Loss of Flood Plain at BridgesDocument19 pagesAfflux & Loss of Flood Plain at BridgesannelcarrollNo ratings yet
- KM Mat KMMM EhmsDocument8 pagesKM Mat KMMM EhmsiedaNo ratings yet
- Persistence of Health Habits and Their Relationship To Mortality'Document15 pagesPersistence of Health Habits and Their Relationship To Mortality'Par DoNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Machine-Learning Techniques in PDFDocument24 pagesA Survey On Machine-Learning Techniques in PDFArthiNo ratings yet
- Tsa Policy BriefDocument17 pagesTsa Policy BriefBongani SaidiNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument9 pagesStem CellsMaria Del Mar RoblesNo ratings yet
- 3.1-3.3 EegiiDocument18 pages3.1-3.3 EegiiEegii EgNo ratings yet
- Action VerbsDocument1 pageAction VerbsSheetanshuNo ratings yet
- Aivazian, Ge and Qiu - 2005Document15 pagesAivazian, Ge and Qiu - 2005bildyNo ratings yet
- An Internship Project Report On Customer Preference and Satisfaction Level Towards Their Expectation With Special Reference ToDocument50 pagesAn Internship Project Report On Customer Preference and Satisfaction Level Towards Their Expectation With Special Reference ToDhiraj Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan 11ACP PR1 Week 3 4Document5 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan 11ACP PR1 Week 3 4Jealf Zenia CastroNo ratings yet
- Introducing and Using The Dialogic Reading Method: Pearson Family Book NightsDocument3 pagesIntroducing and Using The Dialogic Reading Method: Pearson Family Book NightsMyraChNo ratings yet
- SDS-Sodium Nitrite Solution 40 CHE-2021SDocument9 pagesSDS-Sodium Nitrite Solution 40 CHE-2021SpibemauNo ratings yet
- RP 140109021328 Phpapp01Document29 pagesRP 140109021328 Phpapp01enam professorNo ratings yet
- Unit IV 7.: M. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2017Document2 pagesUnit IV 7.: M. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2017Mohit NaraNo ratings yet
THBHDK 26
THBHDK 26
Uploaded by
RGNitinDeva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageAccurate measurements are close to the true value, while precise measurements are consistent when repeated. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision refers to the reproducibility of measurements. There are two types of errors in measurements - systematic errors, which make all measurements incorrect by the same amount and reduce accuracy, and random errors, which produce slightly different values each time and reduce precision.
Original Description:
Original Title
thbhdk-26
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAccurate measurements are close to the true value, while precise measurements are consistent when repeated. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision refers to the reproducibility of measurements. There are two types of errors in measurements - systematic errors, which make all measurements incorrect by the same amount and reduce accuracy, and random errors, which produce slightly different values each time and reduce precision.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageTHBHDK 26
THBHDK 26
Uploaded by
RGNitinDevaAccurate measurements are close to the true value, while precise measurements are consistent when repeated. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision refers to the reproducibility of measurements. There are two types of errors in measurements - systematic errors, which make all measurements incorrect by the same amount and reduce accuracy, and random errors, which produce slightly different values each time and reduce precision.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
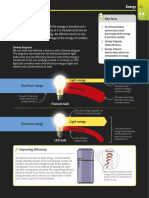
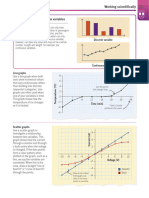
26 Working scientifically
Accuracy and Key facts
precision ✓ Accurate measurements are ones
that are close to the true value
being measured.
When planning and evaluating an experiment, you
✓ Precise measurements are those that
need to think about the accuracy and precision
give the same (or similar) values when
of your measurements. The words accurate and the measurement is repeated.
precise have specific meanings in science.
✓ Errors in measurements can be
random or systematic.
Accurate or precise?
A measurement is considered more accurate if it is closer
than other measurements to the true value being measured.
It is precise if repeating the measurement several times
produces values that are the same or very close to each The center of the target
other. To understand the difference, it helps to think of represents the true
measurements as trying to hit a target. value being measured.
Inaccurate and imprecise Precise but inaccurate Accurate but imprecise Accurate and precise
The measurements are These measurements are These are close to the center These measurements are both
inaccurate, as they are not precise because they are all but not to each other, so they accurate and precise.
near the center of the target, nearly the same value, but are accurate but imprecise.
and imprecise, as they are they are inaccurate because
not close to each other. they aren’t close to the center.
Types of error
Systematic errors Random errors
The accuracy of some instruments Random errors are different
depends on how they’re used. Balances for every reading. For example,
should be set to zero with a container on if you take the temperature
them so you only measure the mass of of water in a beaker, the
the contents. If a balance is not zeroed thermometer might return a
properly, all the measurements will be slightly different reading each
incorrect by the same amount. This is time it dips into a different part
a systematic error and reduces the of the water. This reduces the
accuracy of the measurements. precision of your measurements.
0.5
This should be zero when the
beaker is empty.
You might also like
- DLL PR2Document4 pagesDLL PR2jrtlim100% (1)
- Joseph W. McMoneagle - The Adventures of A Remote Viewer: Psychic HackingDocument4 pagesJoseph W. McMoneagle - The Adventures of A Remote Viewer: Psychic HackingAndross580100% (1)
- C2S3Document14 pagesC2S3John Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- 3 Measuring in ScienceDocument4 pages3 Measuring in ScienceChis KutiNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson 2Document1 pagePhysics Lesson 2shenNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Week 1 (Phy11)Document11 pagesStudy Guide For Week 1 (Phy11)Jezzel Ren AuxteroNo ratings yet
- Precision Vs Accuracy PDFDocument9 pagesPrecision Vs Accuracy PDFSabeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Precision and Accuracy-1Document14 pagesPrecision and Accuracy-1yousaf khanNo ratings yet
- Errors and Uncertainty in Experimental DataDocument12 pagesErrors and Uncertainty in Experimental DataKengkoy PascualNo ratings yet
- BRM Accuracy Vs PrecisionDocument7 pagesBRM Accuracy Vs PrecisionYuga NayakNo ratings yet
- Errors 11Document3 pagesErrors 11Tushar RajNo ratings yet
- 15 01 - 20 00 LeyDocument1 page15 01 - 20 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 3130 - 2 - Ketakpastian Dalam Pengukuran NiniDocument36 pages3130 - 2 - Ketakpastian Dalam Pengukuran NiniIrene KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 DatahandlingDocument42 pagesChapter12 Datahandlingsyaz lianaNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision Are Two Important Concepts in ScienceDocument3 pagesAccuracy and Precision Are Two Important Concepts in ScienceCrystel Joy CamasisNo ratings yet
- Activate 1 BiologyDocument120 pagesActivate 1 BiologyMarina Belloni100% (1)
- ME8501 MM - Accuracy Vs PrecisionDocument1 pageME8501 MM - Accuracy Vs PrecisionKarthick NNo ratings yet
- Accuracy Vs PrecisionDocument2 pagesAccuracy Vs PrecisionJoshua Bature SamboNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and PrecisionDocument3 pagesAccuracy and PrecisionRaghuveerprasad IppiliNo ratings yet
- GetIT Practical Key Words 1 PowerPoint SlidesDocument11 pagesGetIT Practical Key Words 1 PowerPoint SlidesAdam TanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 1 ReviewerabadarthusNo ratings yet
- Biology of How Science Works (As & A2)Document117 pagesBiology of How Science Works (As & A2)Chris Corey-PhiloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Week 4 ReviewerDocument6 pagesWeek 1 - Week 4 Reviewerronanmorales93No ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of Validity and ReliabilityDocument1 pageFundamental Principles of Validity and ReliabilityVIPLAV SRIVASTAVNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Properties of Sea Water PDFDocument6 pagesLecture 01 Properties of Sea Water PDFClow NNo ratings yet
- AH Uncertainties 2012 SSERC BookletDocument20 pagesAH Uncertainties 2012 SSERC BookletLNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Understanding MeasurementsDocument27 pages1.4 Understanding MeasurementsMakcikHajarNo ratings yet
- 02 Accuracy vs. Precision NotesDocument16 pages02 Accuracy vs. Precision NotessharmilaNo ratings yet
- Q3w1d2 - Accuracy and Precision PresentationDocument16 pagesQ3w1d2 - Accuracy and Precision PresentationGelo VeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Precision and Accuracy: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Precision and Accuracy: ObjectivesRuby Cocal0% (1)
- Some Discussions On Unit - 1Document11 pagesSome Discussions On Unit - 1kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- Accuracy PrecisionDocument1 pageAccuracy PrecisionspmothukuriNo ratings yet
- Language of Measurement in Context ChemistryDocument6 pagesLanguage of Measurement in Context ChemistryVictor BabsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- Metrology Terminology Accuracy Precision ResolutionDocument2 pagesMetrology Terminology Accuracy Precision ResolutionQuality controllerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Measurements & Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- MEASUREMENT AND DATA QUALITY LabordsDocument6 pagesMEASUREMENT AND DATA QUALITY LabordsMarimiel PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Topic 11: Measurement & Data ProcessingDocument17 pagesTopic 11: Measurement & Data ProcessingkatNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision PDFDocument1 pageAccuracy and Precision PDFthryeeNo ratings yet
- ERRORS in Measurements - 26april2021Document13 pagesERRORS in Measurements - 26april2021Julianne DimaguilaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Understanding Measurements Using Measuring Intruments 1.metre Rule 2.stopwatch 3.thermometer 4.measuring Cylinder 5.protractor 6.measuring TapeDocument26 pages1.4 Understanding Measurements Using Measuring Intruments 1.metre Rule 2.stopwatch 3.thermometer 4.measuring Cylinder 5.protractor 6.measuring TapeE-one Saw-dNo ratings yet
- Errors & Measurements (Interated) VPR Garu (40-54)Document15 pagesErrors & Measurements (Interated) VPR Garu (40-54)PHYSICS LSNo ratings yet
- 614 Lab - Error in MeasurementsDocument3 pages614 Lab - Error in Measurementsjilldlrs06No ratings yet
- Accuracy Is How Close Your ObservedDocument1 pageAccuracy Is How Close Your ObservedJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- Business Research Levels of Measurement Nominal, Ordial, RatioDocument19 pagesBusiness Research Levels of Measurement Nominal, Ordial, RatioAashna jainNo ratings yet
- Why We Need Statistics? Scales of Measurement: FIRST SEMESTER - A.Y. 2022-2023 A Statistics RefresherDocument6 pagesWhy We Need Statistics? Scales of Measurement: FIRST SEMESTER - A.Y. 2022-2023 A Statistics RefresherANGELA FAYE MARIE BAWALANNo ratings yet
- Topic: Measurement: Meadowbrook High School Physics Lesson 1 Grade 10 Teacher: Ms. S. FindleyDocument14 pagesTopic: Measurement: Meadowbrook High School Physics Lesson 1 Grade 10 Teacher: Ms. S. Findleychristopher chanNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsDocument20 pagesMeasurements and Error Analysis: The Uncertainty of MeasurementsHassan Ali BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Te Chapter 03 - 1Document10 pagesTe Chapter 03 - 1stephensreenivasulutNo ratings yet
- CHEMOMETRICSDocument45 pagesCHEMOMETRICSApheleleNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 - Lesson 2Document26 pagesGeneral Physics 1 - Lesson 2Christian Karl GarciaNo ratings yet
- Measurement, Accuracy and Precision PDFDocument19 pagesMeasurement, Accuracy and Precision PDFAyush ZalaNo ratings yet
- Error Analysis ManualDocument13 pagesError Analysis ManualBrian Keston SubitNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1. Measurements and Uncertainty: Every Measurement Is Associated With A Certain UncertaintyDocument7 pagesExperiment 1. Measurements and Uncertainty: Every Measurement Is Associated With A Certain UncertaintyBianca Chellyne AguilarNo ratings yet
- 8602 Assignment No 2Document24 pages8602 Assignment No 2Fatima YousafNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1st MQADocument4 pagesPhysics - 1st MQALance LirioNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Precision - Definition, ExamplesDocument3 pagesAccuracy and Precision - Definition, ExamplescesarinigillasNo ratings yet
- Nr2 PrelimsDocument5 pagesNr2 PrelimsCarl Angelo MahaitNo ratings yet
- Objectives: General Physics 1Document8 pagesObjectives: General Physics 1Raymond De AsisNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 27Document1 pageTHBHDK 27RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- GaugesDocument24 pagesGaugesRGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 33Document1 pageTHBHDK 33RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- Permanent WayDocument18 pagesPermanent WayRGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- Airport, Harbour - NOTES-2Document1 pageAirport, Harbour - NOTES-2RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 41Document1 pageTHBHDK 41RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 35Document1 pageTHBHDK 35RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 37Document1 pageTHBHDK 37RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 48Document1 pageTHBHDK 48RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 39Document1 pageTHBHDK 39RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 23Document1 pageTHBHDK 23RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 34Document1 pageTHBHDK 34RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 9Document1 pageTHBHDK 9RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 27Document1 pageTHBHDK 27RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 14Document1 pageTHBHDK 14RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 12Document1 pageTHBHDK 12RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 68Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 68RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- THBHDK 6Document1 pageTHBHDK 6RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 44Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 44RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 40Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 40RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 48Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 48RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 42Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 42RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 41Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 41RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 19Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 19RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 34Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 34RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 22Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 22RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 33Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 33RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 30Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 30RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 27Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 27RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 10Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 10RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- The Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 14Document1 pageThe Great Atlas of Discovery DK History Books PDF 14RGNitinDevaNo ratings yet
- Lesbian and Gays StudiesDocument31 pagesLesbian and Gays StudiesJoaquín Edgardo Reyes RomeroNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The Evaluation of Uncertainties Associated With RecoveryDocument10 pagesApproaches To The Evaluation of Uncertainties Associated With RecoveryAnonymous 3OFvtiNo ratings yet
- Ieee Format ThesisDocument4 pagesIeee Format ThesisAllan Añavisa Ostique Jr.No ratings yet
- Training Program Laboratories Accreditation ISO 17025 2017 13012021Document4 pagesTraining Program Laboratories Accreditation ISO 17025 2017 13012021kim phaNo ratings yet
- Robots 15 December 2011: BBC Learning English 6 Minute EnglishDocument5 pagesRobots 15 December 2011: BBC Learning English 6 Minute EnglishwiltorNo ratings yet
- Literature Matrix FullDocument31 pagesLiterature Matrix Fullapi-583156298No ratings yet
- PR2 - D e 4Document26 pagesPR2 - D e 4Susan T. Laxamana100% (1)
- Cdsco Stem CellDocument84 pagesCdsco Stem CellKIITAA FANINo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Utilization of Library Resources AmongDocument14 pagesFactors Affecting The Utilization of Library Resources AmongOlive Therese100% (1)
- Natalia JasiakDocument1 pageNatalia Jasiakapi-693801600No ratings yet
- Psych Test in SchoolsDocument6 pagesPsych Test in SchoolsDenilyn CortezNo ratings yet
- State of The Art Review Proposal GuidelinesDocument1 pageState of The Art Review Proposal Guidelineshesam khorramiNo ratings yet
- Rerp2018 8146819Document10 pagesRerp2018 8146819Dwi NilamsariNo ratings yet
- Afflux & Loss of Flood Plain at BridgesDocument19 pagesAfflux & Loss of Flood Plain at BridgesannelcarrollNo ratings yet
- KM Mat KMMM EhmsDocument8 pagesKM Mat KMMM EhmsiedaNo ratings yet
- Persistence of Health Habits and Their Relationship To Mortality'Document15 pagesPersistence of Health Habits and Their Relationship To Mortality'Par DoNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Machine-Learning Techniques in PDFDocument24 pagesA Survey On Machine-Learning Techniques in PDFArthiNo ratings yet
- Tsa Policy BriefDocument17 pagesTsa Policy BriefBongani SaidiNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument9 pagesStem CellsMaria Del Mar RoblesNo ratings yet
- 3.1-3.3 EegiiDocument18 pages3.1-3.3 EegiiEegii EgNo ratings yet
- Action VerbsDocument1 pageAction VerbsSheetanshuNo ratings yet
- Aivazian, Ge and Qiu - 2005Document15 pagesAivazian, Ge and Qiu - 2005bildyNo ratings yet
- An Internship Project Report On Customer Preference and Satisfaction Level Towards Their Expectation With Special Reference ToDocument50 pagesAn Internship Project Report On Customer Preference and Satisfaction Level Towards Their Expectation With Special Reference ToDhiraj Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan 11ACP PR1 Week 3 4Document5 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan 11ACP PR1 Week 3 4Jealf Zenia CastroNo ratings yet
- Introducing and Using The Dialogic Reading Method: Pearson Family Book NightsDocument3 pagesIntroducing and Using The Dialogic Reading Method: Pearson Family Book NightsMyraChNo ratings yet
- SDS-Sodium Nitrite Solution 40 CHE-2021SDocument9 pagesSDS-Sodium Nitrite Solution 40 CHE-2021SpibemauNo ratings yet
- RP 140109021328 Phpapp01Document29 pagesRP 140109021328 Phpapp01enam professorNo ratings yet
- Unit IV 7.: M. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2017Document2 pagesUnit IV 7.: M. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2017Mohit NaraNo ratings yet