Professional Documents
Culture Documents
History American Revolution
History American Revolution
Uploaded by
asmigujar31050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
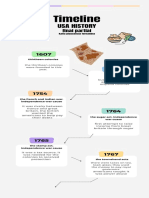
5 views3 pagesThe document outlines key events from the French and Indian War in 1754 to the signing of the US Constitution in 1787, including several acts passed by the British Parliament to tax the American colonies that increased tensions and led to the American Revolutionary War, such as the Stamp Act, Townshend Acts, Intolerable Acts, and the Boston Tea Party. Major events of the Revolutionary War include the 'shot heard round the world' at Lexington and Concord, the adoption of the Declaration of Independence, and the Treaty of Paris that recognized American independence.
Original Description:
timeline and small summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines key events from the French and Indian War in 1754 to the signing of the US Constitution in 1787, including several acts passed by the British Parliament to tax the American colonies that increased tensions and led to the American Revolutionary War, such as the Stamp Act, Townshend Acts, Intolerable Acts, and the Boston Tea Party. Major events of the Revolutionary War include the 'shot heard round the world' at Lexington and Concord, the adoption of the Declaration of Independence, and the Treaty of Paris that recognized American independence.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesHistory American Revolution
History American Revolution
Uploaded by
asmigujar3105The document outlines key events from the French and Indian War in 1754 to the signing of the US Constitution in 1787, including several acts passed by the British Parliament to tax the American colonies that increased tensions and led to the American Revolutionary War, such as the Stamp Act, Townshend Acts, Intolerable Acts, and the Boston Tea Party. Major events of the Revolutionary War include the 'shot heard round the world' at Lexington and Concord, the adoption of the Declaration of Independence, and the Treaty of Paris that recognized American independence.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Event Date Description
French and Indian War 28 May 1754 – 10 February The French and Indian
1763 War granted Britain
important North
American territories,
but disputes over
frontier policy and
expenses led to
discontent among
colonists.
Proclamation of 1763 7 October 1763 The Proclamation, a
British-made boundary
in the Appalachian
Mountains, prohibited
Anglo-American
colonists from settling
on French territory
after the French and
Indian War.
Sugar Act 5 April 1764 The Sugar Act was
established to prevent
the smuggling of sugar
and molasses from the
French and Dutch West
Indies and to boost
revenue for the British
Empire.
Stamp Act 22 March 1765 The stamp act imposed a
tax on all papers and
official documents in
the American colonies,
though not in England,
to raise money for
Britain.
Quartering act of 1765 24 March 1765 The Quartering Act
mandated Great Britain
to house its soldiers in
American barracks and
public houses, and if
colonial housing was
insufficient, they would
be quartered in various
buildings.
Townshend Act 29 June 1767 The Townshend Acts were
enacted by Parliament,
introducing taxes on
various goods such as
glass, lead, paint, paper,
and tea.
Boston Massacre 5 March 1770 The Boston Massacre
happened due to
colonists' resentment
towards British troops,
resulting in the
shooting of a mob and
several deaths.
Boston Tea Party 16 December 1773 In the Boston Tea Party, a
group of 60 American
colonists protested
against a tea tax and the
perceived East India
Company monopoly by
throwing 342 chests of
tea into Boston Harbor.
Intolerable Acts 20 May 1774 The British Parliament
passed four ‘Intolerable
Acts’ to punish
Massachusetts Bay for the
Boston Tea Party.
First Continental 5 September 1774 - 26 The first continental
Congress October 1774 congress was a gathering
of delegates from twelve
of Britain's thirteen
American colonies to
discuss America's future
amid increasing British
aggression.
‘Shot was heard’ 19 April 1775 The phrase 'shot was
heard' refers to the
opening shot during the
battles of Lexington and
Concord which sparked
the American
Revolutionary War.
Congress adopted 4 July 1776 The Declaration of
Declaration of Independence, adopted by
Independence the Continental
Congress, marked the 13
American colonies' break
from Britain and
outlined their reasons
for independence.
Treaty of Paris 3 September 1783 The treaty between the
American colonies and
Great Britain ended the
American Revolution and
officially recognized
the United States as an
independent nation.
United States 17 September 1887 The Constitution of the
Constitution signed United States, signed by
delegates at the
Constitutional
Convention in
Philadelphia,
established the national
government, fundamental
laws, and guaranteed
basic rights for its
citizens.
You might also like
- Colonist ReactionsDocument5 pagesColonist Reactionsapi-224225781No ratings yet
- The Americans 2.1 - pg46 - 57Document12 pagesThe Americans 2.1 - pg46 - 57Joe BradleyNo ratings yet
- Matching GameDocument2 pagesMatching Gameapi-478806676No ratings yet
- Causes of The RevolutionDocument3 pagesCauses of The RevolutionFrancisco Solis AilonNo ratings yet
- Revoltionary War NewsletterDocument2 pagesRevoltionary War Newsletterapi-733702132No ratings yet
- American RevolutionDocument25 pagesAmerican RevolutionMbaka RitaNo ratings yet
- American RevolutionpptDocument109 pagesAmerican RevolutionpptHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- A Timeline of The American Revolution From 1763Document3 pagesA Timeline of The American Revolution From 1763api-305014058No ratings yet
- Boston Tea Party G3Document13 pagesBoston Tea Party G3patrickNo ratings yet
- Excel Portfolio AssignmentDocument10 pagesExcel Portfolio Assignmentapi-706734090No ratings yet
- Revolution 2Document20 pagesRevolution 2api-256560022No ratings yet
- American Colonies - 5Document30 pagesAmerican Colonies - 5Lily lolaNo ratings yet
- 1763 To 1781Document9 pages1763 To 1781api-323269525No ratings yet
- Timeline USA History FinalDocument4 pagesTimeline USA History FinalDANIEL ESCOBAR ROJASNo ratings yet
- Annotated-Edu 20labDocument1 pageAnnotated-Edu 20labapi-652213613No ratings yet
- Causes of The American War of IndependenceDocument5 pagesCauses of The American War of Independenceemilythansin26No ratings yet
- The American RevolutionDocument7 pagesThe American RevolutionTaaboNo ratings yet
- Timeling RevolutionaryDocument12 pagesTimeling RevolutionaryAubrie WilcoxNo ratings yet
- Causes of The American Revolutionary WarDocument5 pagesCauses of The American Revolutionary Warvernon whiteNo ratings yet
- WK 4 Lab 2 EduDocument2 pagesWK 4 Lab 2 Eduapi-659439430No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Sections 1, 2, and 3Document16 pagesChapter 3 Sections 1, 2, and 3Christian JonesNo ratings yet
- War of Independence: A. Attitude of AmericansDocument5 pagesWar of Independence: A. Attitude of AmericanswaqarNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: Causes of The American RevolutionDocument2 pagesClass Notes: Causes of The American RevolutionCurtis J. SmothersNo ratings yet
- American RevDocument27 pagesAmerican RevNeena QuicksandNo ratings yet
- The Royal Proclamation (1763)Document8 pagesThe Royal Proclamation (1763)api-240746852No ratings yet
- Newsletter For Events That Led To The American RevolutionDocument1 pageNewsletter For Events That Led To The American Revolutionapi-521509439No ratings yet
- Pages 78-88Document45 pagesPages 78-88KatelinwarnockNo ratings yet
- American Revolution PresentationDocument10 pagesAmerican Revolution PresentationHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- American Revolt Reading TCIDocument43 pagesAmerican Revolt Reading TCItianrun.guNo ratings yet
- 9 - Causes of The American Revolution Student NotesDocument20 pages9 - Causes of The American Revolution Student Notesapi-327777794100% (2)
- Economic Causes of American Revolution 3Document10 pagesEconomic Causes of American Revolution 3Diksha BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Imperial Reforms and Colonial ProtestsDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Imperial Reforms and Colonial ProtestsJonathan NunesNo ratings yet
- American Revolution 3Document16 pagesAmerican Revolution 3Rhia May OrtigaNo ratings yet
- Colonial UnrestDocument9 pagesColonial UnrestThien TranNo ratings yet
- Movement of Peoples: Depth Study y OptionDocument46 pagesMovement of Peoples: Depth Study y OptionClaudia Patricia FernándezNo ratings yet
- The Road To Revolution TimelineDocument10 pagesThe Road To Revolution TimelineLa' Mi EslingerNo ratings yet
- Acts and Legislation 1763-1774Document12 pagesActs and Legislation 1763-1774Doan Chan PhongNo ratings yet
- APUSH French and Indian War and The End of Salutory NeglectDocument20 pagesAPUSH French and Indian War and The End of Salutory NeglectPeter Dunham100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 03-Mar-2023Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 03-Mar-2023Aashi SinghNo ratings yet
- Events Leading To American IndependenceDocument3 pagesEvents Leading To American Independenceapi-336248135No ratings yet
- Chronology Cards 1Document5 pagesChronology Cards 1api-341625144No ratings yet
- Revolution ChartDocument5 pagesRevolution Chartapi-236323575No ratings yet
- Building Colonial Unity: Chapter 5, Section 2Document13 pagesBuilding Colonial Unity: Chapter 5, Section 2patrickcermenoNo ratings yet
- Period Three Key Concept Framework Filled inDocument15 pagesPeriod Three Key Concept Framework Filled inCharlie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Causes of American RevolutionDocument31 pagesCauses of American RevolutionAlfredNo ratings yet
- The American Revolution OR War For Independence: 13 Colonies of United States of America Vs Great BritainDocument24 pagesThe American Revolution OR War For Independence: 13 Colonies of United States of America Vs Great BritainDhawan Gupta100% (1)
- Edu American RevolutionDocument2 pagesEdu American Revolutionapi-734006465No ratings yet
- Ece 133 4Document2 pagesEce 133 4api-734006633No ratings yet
- American Revolution Timeline (1763 - 1790)Document20 pagesAmerican Revolution Timeline (1763 - 1790)vernon whiteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Independence Lecture UpdatedDocument6 pagesLecture 3 Independence Lecture UpdatedQamar SohailNo ratings yet
- USA Assignment 1Document7 pagesUSA Assignment 1Diksha BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Battle for a New Nation: Causes and Effects of the Revolutionary WarFrom EverandBattle for a New Nation: Causes and Effects of the Revolutionary WarNo ratings yet
- Events Leading To The American RevolutionDocument9 pagesEvents Leading To The American Revolutionapi-524592800No ratings yet
- 5 Unit 2 RoadToRevolutionDocument37 pages5 Unit 2 RoadToRevolutionmancalleduncle57No ratings yet
- 4.1 The Stirrings of RebellionDocument7 pages4.1 The Stirrings of RebellionPatrick ThorntonNo ratings yet
- History of UsaDocument13 pagesHistory of UsaSyeda hudaibiyaNo ratings yet
- RevwarDocument6 pagesRevwarapi-142630794No ratings yet
- Ho HupDocument25 pagesHo Hupcacamarba20036236No ratings yet
- Estanislao, Jr. vs. Court of Appeals, 160 SCRA 830Document6 pagesEstanislao, Jr. vs. Court of Appeals, 160 SCRA 830Santiago TiongcoNo ratings yet
- Drug and Cosmetic Act 1940 - IIDocument59 pagesDrug and Cosmetic Act 1940 - IIDevendra VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Most Corrupt 2011: Rep. Joe Walsh (R-IL)Document6 pagesMost Corrupt 2011: Rep. Joe Walsh (R-IL)CREWNo ratings yet
- United States v. Mulero-Diaz, 1st Cir. (2016)Document12 pagesUnited States v. Mulero-Diaz, 1st Cir. (2016)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- 2011 Ylr 888Document4 pages2011 Ylr 888mahnoor tariqNo ratings yet
- Meeting, ResolutionDocument21 pagesMeeting, ResolutionMonica BBANo ratings yet
- Corp Prac PonziDocument39 pagesCorp Prac PonziChad Daniel MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Compromise AgreementDocument2 pagesCompromise AgreementKyll Micabalo NavarroNo ratings yet
- Presidential Decree 1221Document8 pagesPresidential Decree 1221fire_ice888No ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report Conducted at Tis Hazari District CourtDocument38 pagesSummer Internship Report Conducted at Tis Hazari District CourtjahanwiNo ratings yet
- Labor Relations Box Questions - Azucena - FinalDocument27 pagesLabor Relations Box Questions - Azucena - Finalkmaxest487100% (2)
- Greece-Distortions From Special Labor Regimes and Legacy ProblemsDocument7 pagesGreece-Distortions From Special Labor Regimes and Legacy ProblemsΣΠΥΡΟΣ ΠΑΠΑΚΩΣΤΟΠΟΥΛΟΣNo ratings yet
- Philippine Telegraph Telephone Co V NLRCDocument1 pagePhilippine Telegraph Telephone Co V NLRCAsru RojamNo ratings yet
- Format Form For Claim of Balance in The Savings Bank Account ofDocument6 pagesFormat Form For Claim of Balance in The Savings Bank Account ofGoutham Kumar Teella0% (2)
- Bangladesh University of Professionals: Mirpur Cantonment, Dhaka-1216, BangladeshDocument2 pagesBangladesh University of Professionals: Mirpur Cantonment, Dhaka-1216, BangladeshImtiaz JamilNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE VI - Other Acts of Abuse Acts Penalties Other NotesDocument1 pageARTICLE VI - Other Acts of Abuse Acts Penalties Other NotesAlfred Bryan AspirasNo ratings yet
- Rousseau (Notes)Document1 pageRousseau (Notes)pasensyaNo ratings yet
- Liability Without Reliance - Solicitors andDocument8 pagesLiability Without Reliance - Solicitors andDheebak KumaranNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 70748Document52 pagesG.R. No. 70748Ran NgiNo ratings yet
- Must Read Cases in Remedial Law As of March 31, 2015Document57 pagesMust Read Cases in Remedial Law As of March 31, 2015Dorothy ParkerNo ratings yet
- Extinguishment of ObligationsDocument10 pagesExtinguishment of ObligationsNimfa SabanalNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM Reviewer Consti 1 Sy 09-10 Sem1Document5 pagesMIDTERM Reviewer Consti 1 Sy 09-10 Sem1leiben173938100% (1)
- 45 CIR vs. Liquigaz Philippines CorporationDocument3 pages45 CIR vs. Liquigaz Philippines CorporationOzacNo ratings yet
- Louisiana Bar PrepDocument2 pagesLouisiana Bar PrepBrandonNo ratings yet
- SPA - Sample OnlyDocument2 pagesSPA - Sample OnlyYsabelleNo ratings yet
- The Law On Common Carrier and The Air Passenger Bill of RightsDocument1 pageThe Law On Common Carrier and The Air Passenger Bill of RightsNathalia BautistaNo ratings yet
- Article 22 23 &24Document7 pagesArticle 22 23 &24ShreyaNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs For VaoDocument105 pagesCurrent Affairs For VaoMadhumitha RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Multan Electric Power Company: Say No To CorruptionDocument1 pageMultan Electric Power Company: Say No To CorruptionAllah dittaNo ratings yet