Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kali Linux
Kali Linux
Uploaded by
Siddhesh Karekar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThe document discusses basic operating system architecture and components of various command line interfaces. It provides information on:
1) The basic components of an OS including hardware, kernel, shell, and applications.
2) Features and purposes of command shells in Windows and Linux including interacting with the OS kernel and accessing files.
3) Common file systems like FAT, NTFS, and Ext4 and their characteristics.
4) Linux user administration concepts such as file ownership, permissions, and changing permissions.
5) Examples of common commands in Windows DOS and Linux shells.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses basic operating system architecture and components of various command line interfaces. It provides information on:
1) The basic components of an OS including hardware, kernel, shell, and applications.
2) Features and purposes of command shells in Windows and Linux including interacting with the OS kernel and accessing files.
3) Common file systems like FAT, NTFS, and Ext4 and their characteristics.
4) Linux user administration concepts such as file ownership, permissions, and changing permissions.
5) Examples of common commands in Windows DOS and Linux shells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesKali Linux
Kali Linux
Uploaded by
Siddhesh KarekarThe document discusses basic operating system architecture and components of various command line interfaces. It provides information on:
1) The basic components of an OS including hardware, kernel, shell, and applications.
2) Features and purposes of command shells in Windows and Linux including interacting with the OS kernel and accessing files.
3) Common file systems like FAT, NTFS, and Ext4 and their characteristics.
4) Linux user administration concepts such as file ownership, permissions, and changing permissions.
5) Examples of common commands in Windows DOS and Linux shells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as txt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
# Basic OS Architecture:
1. Hardware
2. Kernel
3. Shell
4. Applications /Utilities
# Command Shell Basics:
→Text based application for viewing, handling and manipulating, files on your
computer.
→Other names: cmd, CLI, prompt, console, terminal
→Use to Kernel interface
→Interface to use operating system services
→Read from input devices such as kyboards or from files
→The shell gets tarted when the user logs in or start the terminal
# Windows Commnad Line:
→Windows has two command shells: The Command Shell and PowerShell
→Officially called Windows Command Processor, but also sometimes referred to as
the the commnd shell or cmd prompt or cmd.exe
→Sometimes called DOS prompt incorrectly
→Powershell was designed to extend the capabilities of the command shell to run
Powershell command called cmdlets
→You can run windows Commands and powershell cmdlets in powershell, but the
command shell can only run windows commands and not Powershell cmdlets.
# Linux Command Line:
→Kali Linuc uses the Bourne Again or Bash Shell, created for use in the GNU, as a
successor to the Bourne Shell
→Bash can also read and execute commands from afile, called a shell script.
→Bash command syntax includes ideas drawn from the Korn shell (ksh) and C shell
such as command line editing, command history
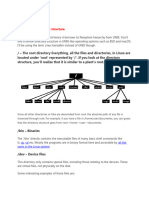
#Linux File System:
/bin: contains user executable files.
/boot: contains the static bootloader and kernel executable
/dev: contains the device files for every hardware device attached to the system
/etc: contains the local system configuration files for the host computer
/home: Home directory storage for user files. Each user has a subdirectory in/home
/lib: Contains shared library files that required to boot the system.
/media: A place to mount external removable media devices such as USB thumb drives
that may be connected to the host.
/mnt: A temporary mountpoint for regular file system
/root: It is home directory for the root user.
/tmp: Used by the operating system and many programs to store temporary files.
/usr: Sherable, read-only files, including executables binaries and libraries,
man files and other types of documentation.
# NTFS, FAT, EXT
1. FAT 32 (File Allocation Table):
→Increases the number of bits used to address clusters and reduces the size of each
cluster.
→Supports larger disks (up to 2 terabytes) and better storage efficiency, 4 GB max
file size
2. NTFS (New Technology File System):
→Windows NT operating system uses for storing and retrieving files on a Hard Disk
→Linux and BSD have a free and Open source NTFS driver
→macOS comes with read only support for NTFS
→16TB max file size, 4KB cluster size
3. Ext4 (Extended File System 4)
→Ext4 support file-based encryption
→File content, filenames, and symbolic link targets are all encrypted
→Being used bt Linux Kernel
# Linux User Administration
A. Ownership of Files:
1. User:
→A user is the owner of the file
→the person who created the file
2. Group:
→A user group can contain multiple users
→All users belonging to a group will have the same access permission to the file
3. Others:
→Everybody else
→Neither created the file, nor the belongs to a usergroup who could own the file
B. Permission of Files
1. Read
2. Write
3.Execute
C. Changing File Permissions
1. Absolute (Numeric) mode
→ 0 for no permission
→ 1 for execute
→ 2 for write
→ 4 for read
2. Symbolic Mode(for all 3 User types)
→ + for adding permission
→ - for removing permission
→ = sets and overrides permissions
→ u user /owner
→ g group
→ o other
→ a all
### Windows DOS shell Command ###
Run CMD as administrator
1. cd = Change directory
for example: step1: cd D:
step2: D:
2. dir = Directory
3. mkdir = make directory
4. rddir = removed directory
5. echo = to write a file with making file (Redirect)
for example
→ echo Prasad Karekar > sample.txt
and you want to write on same file and you don't want overwrite on it then
→ echo Hello World >> sample.txt
6. type <file name with extension> = to view what is inside file
7. copy = to copy file
8. <command>/? = help of any command
9. move = to move file
10.help = to find all command
11.systeminfo = to view system information
12.ping = to check target is available or not (use ICMP)
13.ipconfig = to check all network information
14.arp -a = to display ARP table
15.getmac = to find mac address
16.tracert = to check path from machine to destinaton (use ICMP)
17.netstat = to check working network process
18telnet =
19.ftp<ip address> = file transfer protocol
### Linux Command ###
You might also like
- Linux Commands - Mithun Technologies-1Document21 pagesLinux Commands - Mithun Technologies-1Viswa Teja100% (1)
- Blue Prism DeveloperDocument19 pagesBlue Prism DeveloperSonal PawarNo ratings yet
- Linux and Shell CommandsDocument23 pagesLinux and Shell CommandsMANOJ100% (5)
- What Is Linux?: OS X and WindowsDocument8 pagesWhat Is Linux?: OS X and WindowsTroyFerrerNo ratings yet
- 3.1 LinuxFilesystemHierarchyDocument31 pages3.1 LinuxFilesystemHierarchyHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Linux Filesystem Hierarchy: The Linux Documentation ProjectDocument29 pagesLinux Filesystem Hierarchy: The Linux Documentation ProjectthewhiteeyeNo ratings yet
- Linux Filesystem Hierarchy: The Linux Documentation ProjectDocument29 pagesLinux Filesystem Hierarchy: The Linux Documentation Projectkarant1No ratings yet
- Beginners' Guide To LinuxDocument9 pagesBeginners' Guide To Linuxlight66No ratings yet
- What Is O.S.: Hardware, Memory, Processes and Applications. AnDocument18 pagesWhat Is O.S.: Hardware, Memory, Processes and Applications. AnAnkit BhutwalaNo ratings yet
- Linux Basics: Ansh BhawnaniDocument32 pagesLinux Basics: Ansh BhawnaniMamertopendNo ratings yet
- Linux Basic CommandsDocument40 pagesLinux Basic CommandsPardeep JogNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 UNIX / Linux - File System Basics: Directory StructureDocument41 pagesUnit - 5 UNIX / Linux - File System Basics: Directory StructureAnshuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Linux Notes For FinalDocument65 pagesLinux Notes For Finalabdullahprofessor0No ratings yet
- (Backup) ITEC3116-SNAL-Lecture 08 - File System HierarchyDocument21 pages(Backup) ITEC3116-SNAL-Lecture 08 - File System HierarchyHassnain IjazNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 PDFDocument6 pagesLab 1 PDFMuddassir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Shell Navigation - Team GiganticDocument15 pagesShell Navigation - Team GiganticIsreal UuuNo ratings yet
- Certified Linux Practitioner - CyberTalentsDocument16 pagesCertified Linux Practitioner - CyberTalentsmostafa omarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linux and Its Command Line Interface: Operating SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Linux and Its Command Line Interface: Operating SystemAnmolNo ratings yet
- Operating System DA-3Document9 pagesOperating System DA-3Varun TejNo ratings yet
- 1.presentation Command Line and Shell ProgrammingDocument48 pages1.presentation Command Line and Shell Programmingyogeshwari bahiramNo ratings yet
- Linux Lab ManuelDocument23 pagesLinux Lab ManuelNikhil MaliNo ratings yet
- Linux Administrator Guide1Document31 pagesLinux Administrator Guide1Moe Thet HninNo ratings yet
- Kernal Shell: 1. / (Root) : 2. 1bin: 3. 1sbin: 4. /etc:-5. /usrDocument7 pagesKernal Shell: 1. / (Root) : 2. 1bin: 3. 1sbin: 4. /etc:-5. /usrCharith Nilanga WeerasekaraNo ratings yet
- Intro To LinuxDocument34 pagesIntro To LinuxNiklaus MichaelsonNo ratings yet
- Rishabh Linux FileDocument26 pagesRishabh Linux Filerish212004No ratings yet
- Rhce NotesDocument40 pagesRhce NotescoolzabNo ratings yet
- Hostinger Linux CommandsDocument21 pagesHostinger Linux Commandsmeister ederNo ratings yet
- Principle of Programming LanguageDocument5 pagesPrinciple of Programming LanguageRudraksh MittalNo ratings yet
- Confidence With LinuxDocument26 pagesConfidence With LinuxrupeshNo ratings yet
- LSP LabDocument7 pagesLSP LabJat SarkarNo ratings yet
- Basic Linux Commands and InstallationDocument27 pagesBasic Linux Commands and InstallationAdarsh100% (13)
- Cyber Security Pr1Document11 pagesCyber Security Pr1muskan24bandariaNo ratings yet
- Linux SeminarDocument26 pagesLinux SeminarPiyuSh JainNo ratings yet
- Unix - File System Basics: Directory StructureDocument5 pagesUnix - File System Basics: Directory StructureIngiaNo ratings yet
- Day 1Document8 pagesDay 1poorvaja.rNo ratings yet
- Linux CommandsDocument21 pagesLinux Commandsskmahancs1No ratings yet
- M Hassan Bin AdeelDocument5 pagesM Hassan Bin AdeelHassan AdeelNo ratings yet
- Operating System: Lab Session # 6 BS (CS) - 2020Document8 pagesOperating System: Lab Session # 6 BS (CS) - 2020taz araishNo ratings yet
- OS - Lab#2 - LinuxDocument5 pagesOS - Lab#2 - LinuxRaja Shaban Qamer MukhlisNo ratings yet
- RHCE NotesDocument58 pagesRHCE NotesmyoaunglattNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Linux Overview: Official Mascot of Linux KernelDocument66 pagesPart 1: Linux Overview: Official Mascot of Linux KernelHamdanNo ratings yet
- Os Expt 1Document9 pagesOs Expt 1mayanksanjay007No ratings yet
- Rhcsa 1 PDFDocument152 pagesRhcsa 1 PDFdwarez100% (1)
- Unixnew 2Document12 pagesUnixnew 2KeerthanAradhya SNo ratings yet
- OS Practical FileDocument25 pagesOS Practical Filekanika MittalNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 Study of Linux Shell CommandsDocument4 pagesExpt 2 Study of Linux Shell Commandsdojeka9685No ratings yet
- Introduction To LinuxDocument30 pagesIntroduction To LinuxtrilokbsnlNo ratings yet
- Linux PPSXDocument58 pagesLinux PPSXNama SivayamNo ratings yet
- Command Linux Fast CutDocument5 pagesCommand Linux Fast CutWan BaharudinNo ratings yet
- Basic Directory Navigation CommandsDocument9 pagesBasic Directory Navigation CommandsManmeet Kaur100% (1)
- ASSIGENMENTDocument13 pagesASSIGENMENTR.N. PatelNo ratings yet
- Linux and (Bash) Shell BasicsDocument26 pagesLinux and (Bash) Shell BasicsJazzer Ora100% (1)
- Linux Directory Structure and Important Files Paths ExplainedDocument4 pagesLinux Directory Structure and Important Files Paths ExplainedmanikandanNo ratings yet
- Linux Interview QuestionsDocument64 pagesLinux Interview QuestionsRZ BNo ratings yet
- Free Open Source Linux OS For Data Recovery & Data Rescue Bilingual Version UltimateFrom EverandFree Open Source Linux OS For Data Recovery & Data Rescue Bilingual Version UltimateNo ratings yet
- Linux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemFrom EverandLinux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Unix and Linux System Administration: Mastering the Command Line. A Comprehensive Guide to Unix and Linux System AdministrationFrom EverandUnix and Linux System Administration: Mastering the Command Line. A Comprehensive Guide to Unix and Linux System AdministrationNo ratings yet
- Admin GuideDocument231 pagesAdmin Guidesunil1287No ratings yet
- Onkyo HT-R330 Manual TécnicoDocument76 pagesOnkyo HT-R330 Manual TécnicoYagoNo ratings yet
- 08 - DME 415-435 Vol 2 Ing Sect 07 DPR Thales March 03Document20 pages08 - DME 415-435 Vol 2 Ing Sect 07 DPR Thales March 03Vagner AndréNo ratings yet
- Free Primavera p6 Training PDFDocument2 pagesFree Primavera p6 Training PDFChad0% (3)
- Manual FBs Parte IIDocument307 pagesManual FBs Parte IIcalangogoianoNo ratings yet
- PS2 KBC 8042Document6 pagesPS2 KBC 8042John SmithNo ratings yet
- Cyberark - Cau201.V2022-04-19.Q108: Show AnswerDocument28 pagesCyberark - Cau201.V2022-04-19.Q108: Show AnswerHakanNo ratings yet
- Sam4s ER-380 Service ManualDocument110 pagesSam4s ER-380 Service Manualsupport-43No ratings yet
- LG 42LH50Document77 pagesLG 42LH50Francisco AntonioNo ratings yet
- Xtreemstore - : A Scalable Storage Management Software Without LimitsDocument30 pagesXtreemstore - : A Scalable Storage Management Software Without LimitsharindramehtaNo ratings yet
- Urm-00Document5 pagesUrm-00haha2012No ratings yet
- Openocd Preliminary 20060102Document46 pagesOpenocd Preliminary 20060102aaabbbccc111222No ratings yet
- AMP2 S8 MDA - DDocument4 pagesAMP2 S8 MDA - DaboediartoNo ratings yet
- ALLIANCE Multi-Operator DAS: Product Specifications / Parts ListDocument5 pagesALLIANCE Multi-Operator DAS: Product Specifications / Parts ListLuisNo ratings yet
- Fusion DCRDocument2 pagesFusion DCRMikal SmithNo ratings yet
- 2023 Contoh Soalan Computer Architecture and OrganizationDocument7 pages2023 Contoh Soalan Computer Architecture and OrganizationHarith HiewNo ratings yet
- COAL Theory Outline Fall 2022Document4 pagesCOAL Theory Outline Fall 2022Mohammad HumayunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1avi kumarNo ratings yet
- SG 010 Contrail Networking Arch GuideDocument53 pagesSG 010 Contrail Networking Arch GuidedhkhtnNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Sensor BasicsDocument41 pages3.1 Sensor BasicsAnonn NymousNo ratings yet
- BTM200 Unit 2 Definitions 2Document3 pagesBTM200 Unit 2 Definitions 2Sainz MNo ratings yet
- Salesforce Apex Trigger ScenariosDocument11 pagesSalesforce Apex Trigger ScenariosAditya Tiwari100% (1)
- Ter 7Document5 pagesTer 7raitoyusaNo ratings yet
- User Exit Enhancement AIST0002 Step by StepDocument10 pagesUser Exit Enhancement AIST0002 Step by StepGilberto FolgosoNo ratings yet
- PLSQL s06 l02 TryDocument3 pagesPLSQL s06 l02 TryMuhammad ChoymnsNo ratings yet
- Assignment # (02) : Abasyn University Peshawar Department of Computer ScienceDocument4 pagesAssignment # (02) : Abasyn University Peshawar Department of Computer ScienceAndroid 360No ratings yet
- Silicon Chip-1995 12Document98 pagesSilicon Chip-1995 12Jorge AgarieNo ratings yet
- 8th Sem Final ReportDocument56 pages8th Sem Final Reportsachin prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Shahid Hussain ResumeDocument2 pagesShahid Hussain ResumeShahid HussainNo ratings yet