Professional Documents
Culture Documents
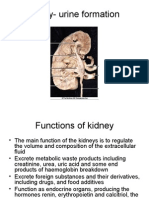
Urine Formation
Urine Formation
Uploaded by
Angelina SoyalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
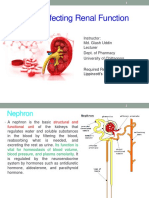
Urine Formation
Urine Formation
Uploaded by
Angelina SoyalCopyright:
Available Formats
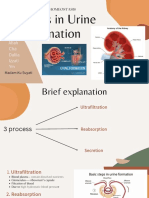
Stages in urine formation
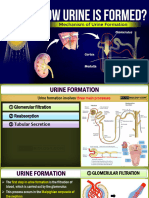
(a) Glomerular Filtration:
● The walls of glomerular capillaries and Bowman’s capsule are very thin and they allow
water and small molecules in the blood to pass across the capillary wall through tiny
spaces between the cells of the Bowman’s capsule.
● The blood pressure is high in the glomerular capillaries because the efferent arteriole,
which drains them, is narrower than the afferent arteriole, which supplies them.
● Filtration of fluid under pressure is termed ultrafiltration. The filtered-out fluid is known
as glomerular filtrate.
● The filtrate contains sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium ions, glucose, amino
acids, and some other useful materials such as vitamins along with urea, uric acid;
ammonia, and some other wastes such as creatinine and ketone bodies and a large
amount of water.
(b) Tubular Reabsorption:
● It takes place mainly at the PCT but some substances are also reabsorbed at the loop of
Henle and DCT.
● Substances such as glucose, almost all amino acids, most of the inorganic ions (Na+,
K+, Cl-), much of the water, some urea, uric acid, and creatinine from the filtrate are
reabsorbed into the blood capillaries around the tubule.
● The movement of these substances takes place either by active transport or by
diffusion.
Tubular Secretion:
● Cells of the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of the nephron excrete
additional waste from the bloodstream into the filtrate by active transport.
● This process of tubular secretion adds urea, creatinine, potassium and hydrogen ions,
ammonia, and a little uric acid.
(c) Osmoregulation at the collecting duct:
● The collecting duct regulates the water content and solute concentration in the surrounding
blood by either becoming permeable or impermeable to the water flow.
● When the solute concentration of blood is high, the collecting duct becomes permeable to
water and allows the movement of water into the surrounding blood capillaries. This
function is due to the secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) from the pituitary gland.
● When the solute concentration of blood is low, ADH secretion is stopped which will then
make the collecting duct become impermeable to water.
You might also like
- Excretion IDocument27 pagesExcretion Ierinjoy77No ratings yet
- APARATUL RenalDocument38 pagesAPARATUL RenalElena SosuNo ratings yet
- What Are AntibioticsDocument29 pagesWhat Are AntibioticsLouie BruanNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Function of The Urinary System-AnswersDocument16 pagesPractice Questions For Function of The Urinary System-AnswersDebra Gan100% (1)
- Function of KidneyDocument66 pagesFunction of KidneyNilesh100% (4)
- Urine Formation and Its CompositionDocument22 pagesUrine Formation and Its CompositionZahidKhanNo ratings yet
- Role of The KIDNEYS in Homeostasis by D SiwaleDocument84 pagesRole of The KIDNEYS in Homeostasis by D Siwalenoahngoma41No ratings yet
- The Urinary System: DR RNGT Amin Samiasih, SKP - Msi.MedDocument36 pagesThe Urinary System: DR RNGT Amin Samiasih, SKP - Msi.MedSura MaduNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System 2013Document52 pagesThe Urinary System 2013adystiNo ratings yet
- Share Mszo113 - Animal-Wps OfficeDocument29 pagesShare Mszo113 - Animal-Wps OfficeRoopa Ram MundhanNo ratings yet
- 09 - CLS 382 - 443 - Renal - FINALDocument19 pages09 - CLS 382 - 443 - Renal - FINALamalNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument87 pagesUrinaryJohn Paolo Dalida SalazarNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract PhysiologykulDocument72 pagesUrinary Tract PhysiologykulAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Group 10 Urine FormationDocument27 pagesGroup 10 Urine FormationgracechamdimbaNo ratings yet
- PHS RenalDocument44 pagesPHS Renaltewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renal FunctionDocument52 pagesDrugs Affecting Renal Functionliakot prantoNo ratings yet
- Excretory Organs in Different Organisms: Excretory Products and Their ElimnationDocument7 pagesExcretory Organs in Different Organisms: Excretory Products and Their ElimnationSreeyansu RajNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument2 pagesExcretionGyunho KimNo ratings yet
- 9.3 NephronDocument15 pages9.3 NephronShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument55 pagesExcretory SystemBhargavi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Process in Urine Formation: Chapter: 9 HomeostasisDocument14 pagesProcess in Urine Formation: Chapter: 9 HomeostasisC.W.DalilaNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation - Human Excretory SystemDocument13 pagesUrine Formation - Human Excretory SystemRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Introducton Renal Physiolgy: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Methodist IndonesiaDocument47 pagesIntroducton Renal Physiolgy: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Methodist IndonesiaHachi Nini Shop II100% (1)
- Mechanism of Urine FormationsDocument20 pagesMechanism of Urine FormationsGAURAVNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System: - Functions of Urinary System - Anatomy of Kidney - Urine FormationDocument49 pagesThe Urinary System: - Functions of Urinary System - Anatomy of Kidney - Urine FormationJasonS.FlavianoNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument25 pagesKidneytiba.qasem2000No ratings yet
- 19.3.2 KidneyDocument77 pages19.3.2 KidneyDak AnneNo ratings yet
- Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarDocument49 pagesTubular Reabsorption and Secretion: by Dr. Rukhsana AnwarZia PhotostateNo ratings yet
- Kidney and OsmoregulationDocument25 pagesKidney and Osmoregulationsoyoung jinNo ratings yet
- Urine Ingredient Analysis: Name: Yunita Punarisma Class: XI IA 3/ 15Document21 pagesUrine Ingredient Analysis: Name: Yunita Punarisma Class: XI IA 3/ 15ladylomoNo ratings yet
- Answers Homeostasis Structured Questions: SMK Sultan Ibrahim Kulai, JohorDocument8 pagesAnswers Homeostasis Structured Questions: SMK Sultan Ibrahim Kulai, JohorKhang Ni 康妮 FooNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Renal FunctionDocument47 pagesUrinary System: Renal Function:)No ratings yet
- BBT221 Lec 18 - Urinary SystemDocument22 pagesBBT221 Lec 18 - Urinary Systemiamraiyan123No ratings yet
- +1 Kite Class 36 ExcretionDocument5 pages+1 Kite Class 36 Excretionsolamanmathew127No ratings yet
- The Urine Production - TabanoDocument16 pagesThe Urine Production - TabanoKenneth TabanoNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their ElimnationDocument5 pagesExcretory Products and Their ElimnationSanskriti VermaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument42 pagesExcretory Systemadedayoadeboye0107No ratings yet
- DCT and Collecting DuctDocument29 pagesDCT and Collecting DuctayeshaNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Fisiologi Sistem Kemih ManusiaDocument104 pagesRangkuman Fisiologi Sistem Kemih ManusiaPAP BungsuNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument95 pagesUrinary SystemCloud D. LuffyNo ratings yet
- DR DedyDocument61 pagesDR DedyFerry PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis in HumansDocument39 pagesHomeostasis in HumansyunzulhasNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesThe Urinary SystemKatelyn PagatpatanNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Functions of Renal SystemDocument28 pagesUrinary System: Functions of Renal SystemAubrey Cissé MwakayeNo ratings yet
- Urine FormationDocument76 pagesUrine FormationPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- A2 Ultrafiltration and Selective ReabsorptionDocument22 pagesA2 Ultrafiltration and Selective ReabsorptionPouyaNonubisNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Urinary SystemDocument19 pagesDrugs Affecting Urinary SystemdionyessNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Excretory System 2021Document49 pagesTopic 6 - Excretory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Concentration of Urine: Maj DR Shavana R.L RanaDocument22 pagesConcentration of Urine: Maj DR Shavana R.L RanaChandan Sah100% (1)
- Tubular Reabsorption & SecretionDocument25 pagesTubular Reabsorption & SecretionRishabh DangiNo ratings yet
- Reabsorption (Excretion Physiology)Document28 pagesReabsorption (Excretion Physiology)Ayesha IqbalNo ratings yet
- Do Can at ExcretionDocument3 pagesDo Can at ExcretionTakashi Schiffer CreXentNo ratings yet
- Topik 3Document29 pagesTopik 3AnnisNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument6 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationkanth3012No ratings yet
- Chapter-19 Excretory Products and Their Elimnation: Forms of Nitrogen ExcretionsDocument8 pagesChapter-19 Excretory Products and Their Elimnation: Forms of Nitrogen Excretionsmaryak3050No ratings yet
- Renal Physiology LatestDocument63 pagesRenal Physiology LatestRaudzah RamliNo ratings yet
- Filtration at Rest: Retention of WaterDocument19 pagesFiltration at Rest: Retention of WaterkoushiksarkerNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument99 pagesUrinary SystemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- After Studying This Chapter, Students Should Be Able To - .Document59 pagesAfter Studying This Chapter, Students Should Be Able To - .Deepika MahajanNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsFrom EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNo ratings yet