Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ChemistryReview26 3 Poster
ChemistryReview26 3 Poster
Uploaded by
ShruthiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ChemistryReview26 3 Poster
ChemistryReview26 3 Poster
Uploaded by
ShruthiCopyright:
Available Formats
in pictures
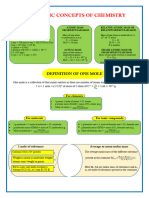
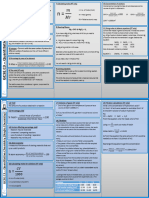
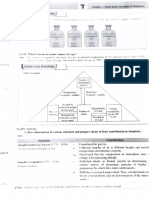
Mass, moles and gas equations
Key definitions you need to remember for your exam calculations
Standard temperature Avogadro’s law
Ideal gas equation and pressure (stp)
Equal volumes of any gases at the
Pressure (Pa) Temperature = 0°C (273 K) same temperature and pressure
Temperature (K) Pressure = 1 atmosphere contain an equal number of
pV = nRT
(101.3 kPa) molecules.
0°C = 273 K
Relative atomic mass (Ar)
Gas constant
Mass of one atom of an element
Volume (m3) 8.31 J K mol
–1 –1 Ar =
1 mass of one atom of 12C
12
Amount of substance (mol)
n= m Relative molecular mass (Mr)
M
Mass (g) The mole Mass of one molecule of a compound
Amount of substance (mol) = Mr =
Molar mass (g mol–1) Amount of substance is 1 mass of one atom of 12C
measured in moles (mol) 12
One mole of a substance
Molar mass (M) contains as many formula units Molar volume
(atoms, molecules etc.) as there
The mass of 1 mole of any entity At standard temperature and
are atoms in 12 g of 12C
Units: g mol–1 pressure (stp) the volume occupied
Avogadro constant (NA or L)
by 1 mole of a gas is 22.4 dm3
= 6.022 × 1023 mol–1
ChemistryReviewExtras
Download this poster at
www.hoddereducation.co.uk/chemistryreviewextras
16 Chemistry Review February 2017 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/chemistryreview 17
You might also like
- Tdi Advanced Nitrox Final ExamDocument8 pagesTdi Advanced Nitrox Final ExamMelissa LaCroce50% (2)
- Physical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirDocument112 pagesPhysical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirKritika Singh100% (1)
- Nanyang JC Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry PDFDocument26 pagesNanyang JC Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry PDFVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equations. Useful.Document1 pageChemistry Equations. Useful.sageriw517No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - MoleDocument2 pagesChapter 9 - MoleKayla WNo ratings yet
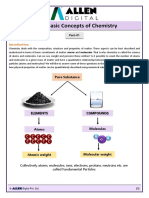
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument2 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistrydeepakjeengar2008No ratings yet
- AmsDocument13 pagesAmsMsMalik_XDNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument19 pagesMole Concept: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryNaman AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument10 pagesIdeal GasОлжас ТыныштыкNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3:chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument7 pagesChapter 3:chemical Formulae and EquationsirisNo ratings yet
- C3 Quantitative ChemistryDocument2 pagesC3 Quantitative ChemistrydeltaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - June 2015Document1 pageChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Chemistrylopa39018No ratings yet
- l7 Berzelius and Avogadro HypothesisDocument20 pagesl7 Berzelius and Avogadro Hypothesisdevendra singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument10 pagesChapter 1atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryMia Hilda AmandaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative ChemistryDocument1 pageQuantitative ChemistryBsbsbaNo ratings yet
- C15 Notes CH2 StoichiometryDocument5 pagesC15 Notes CH2 StoichiometryArnieNo ratings yet
- Aspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)Document44 pagesAspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)sourav gargNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic: Paper - 1Document12 pagesAtoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic: Paper - 1Rezin ChNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: 1 Mol of Entities CDocument9 pagesStoichiometry: 1 Mol of Entities CAnaliza AlcazarenNo ratings yet
- Concept Map 1Document1 pageConcept Map 1Divanshu KapoorNo ratings yet
- Img 20230504 0003Document11 pagesImg 20230504 0003Geetan JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Chemistry Some Basic Concept of Chemistry: Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument9 pagesBasic Concept of Chemistry Some Basic Concept of Chemistry: Dalton's Atomic TheoryAYUSH GOSWAMINo ratings yet
- 02.stoichiometry TheoryDocument27 pages02.stoichiometry Theoryshreyas bulbuleNo ratings yet
- Complete Book 2022Document666 pagesComplete Book 2022kashyapabhinav62No ratings yet
- Topic 15 A2 Ideal Gases NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 15 A2 Ideal Gases NotesIffahNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV Lecture-11 Publishers OverleadsDocument5 pagesUnit-IV Lecture-11 Publishers OverleadsRevilla Marco Robles RatillaNo ratings yet
- IMP Last Minute Revision Formulae Physical ChemistryDocument22 pagesIMP Last Minute Revision Formulae Physical Chemistrydubeyramsagar431100% (1)
- Mole Concept Stoichiometry (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)Document5 pagesMole Concept Stoichiometry (SUMMARY CHEMISTRY CHAPTER)the lillyNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Document18 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Shaista SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- JEE - Chemistry - Atoms, Molecules & Chemical Arithmetic - Atomic, Molecular and Equivalent MassesDocument6 pagesJEE - Chemistry - Atoms, Molecules & Chemical Arithmetic - Atomic, Molecular and Equivalent Massesssatechies62No ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids, and Gases Differ in The Movement of Particles, The Attractive Forces Between Particles, and Inter-Particle SpacingDocument16 pagesSolids, Liquids, and Gases Differ in The Movement of Particles, The Attractive Forces Between Particles, and Inter-Particle SpacingRahul RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Handouts Introduction To Chemistry Theory 2016 eDocument4 pagesHandouts Introduction To Chemistry Theory 2016 eIshhdNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument2 pagesIlovepdf Mergedjawhar impressionNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024shraddha2572sharmaNo ratings yet
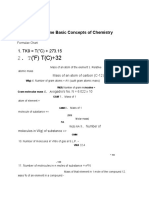
- T ('F) T (C) +32: ShikshaDocument27 pagesT ('F) T (C) +32: ShikshaElbert EinsteinNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept 1Document6 pagesMole Concept 1vinitjadhav727No ratings yet
- 01 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages01 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Formula Sheets QuizrrInertiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 States of Matter 2021Document24 pagesChapter 4 States of Matter 2021suh mey chongNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 31 Jul 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 31 Jul 2022Aayush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3HING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation: Relative Atomic Mass, RAMDocument6 pagesThe Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation: Relative Atomic Mass, RAMWan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Atomic MassDocument8 pagesAtomic MassJennifer SchultzNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument50 pagesIdeal GasesggregresourcesNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument151 pagesChem NotesdashpblvfaidxctaqfNo ratings yet
- VMC Modules PDFDocument1,387 pagesVMC Modules PDFParvathiDevi Paluri86% (7)
- Chapter - 13 Kinetic TheoryDocument20 pagesChapter - 13 Kinetic TheorySiddharth Singh JadonNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument52 pagesRedox ReactionChauhan DharmendraNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument31 pagesBasic Concepts of ChemistryMohammadHussainKhan100% (1)
- Neet ChemistryDocument81 pagesNeet ChemistryPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Edited Mole ConceptDocument22 pagesEdited Mole Conceptd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)BaaM TVNo ratings yet
- 02 Chap 2 ChemF4 Bil 2018 (CSY3p) PDFDocument27 pages02 Chap 2 ChemF4 Bil 2018 (CSY3p) PDFalanislnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument50 pagesChapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistrysumit100% (1)
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument5 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryPandit JiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 StiochiometryDocument64 pagesChapter 5 StiochiometryLo Tin Long 盧天朗 [2020 Graduate]No ratings yet
- Q2 Week7 Mole ConceptDocument48 pagesQ2 Week7 Mole ConceptLance SalotNo ratings yet
- Academy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument4 pagesAcademy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryYash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryReview27 2 PosterDocument1 pageChemistryReview27 2 PosterShruthiNo ratings yet
- Ee PresentationDocument40 pagesEe PresentationShruthiNo ratings yet
- The SciencesDocument5 pagesThe SciencesShruthiNo ratings yet
- Correlation IAs PearsonsDocument11 pagesCorrelation IAs PearsonsShruthiNo ratings yet
- IA New CriteriaDocument4 pagesIA New CriteriaShruthiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The TOK Essay Assessment InstrumentDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The TOK Essay Assessment InstrumentShruthiNo ratings yet
- IA - Draft Check ListDocument5 pagesIA - Draft Check ListShruthiNo ratings yet
- Errors 2Document38 pagesErrors 2ShruthiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Alcohol On Membrane Permeability IrDocument2 pagesEffect of Alcohol On Membrane Permeability IrShruthiNo ratings yet
- Bhargav Kannan's Element Synthesis Model RubricDocument2 pagesBhargav Kannan's Element Synthesis Model RubricShruthiNo ratings yet
- Success Criteria TemplateDocument4 pagesSuccess Criteria TemplateShruthiNo ratings yet
- Trends in Oxide Behaviour - IBDP Chemistry HL FE2016 - KognityDocument5 pagesTrends in Oxide Behaviour - IBDP Chemistry HL FE2016 - KognityShruthiNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Nutrition and Digestion ProjectDocument4 pagesRubric For Nutrition and Digestion ProjectShruthiNo ratings yet
- Independent ThinkkingDocument2 pagesIndependent ThinkkingShruthiNo ratings yet
- The FE Toolkit:: A Magazine For Grade 1 TeachersDocument12 pagesThe FE Toolkit:: A Magazine For Grade 1 TeachersShruthiNo ratings yet
- Differentiation by Task DesignDocument8 pagesDifferentiation by Task DesignShruthiNo ratings yet
- The FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE ToolkitDocument8 pagesThe FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE ToolkitShruthiNo ratings yet
- The FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE ToolkitDocument8 pagesThe FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE Toolkit: The FE ToolkitShruthiNo ratings yet
- Pause-Pose-Pounce-Bounce: What Are The Implications For Teachers?Document1 pagePause-Pose-Pounce-Bounce: What Are The Implications For Teachers?ShruthiNo ratings yet
- Transcript Exemplar T&L M2 Evidence of LearningDocument2 pagesTranscript Exemplar T&L M2 Evidence of LearningShruthiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Worksheet PDFDocument70 pagesGenetics Worksheet PDFShruthiNo ratings yet
- Transcript Exemplar T&L M2 Evidence of ReflectionDocument2 pagesTranscript Exemplar T&L M2 Evidence of ReflectionShruthiNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression, RNA, Transcription and Translation: Higher Human BiologyDocument58 pagesGene Expression, RNA, Transcription and Translation: Higher Human BiologyShruthiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes SL Quiz: The Part of The Enzyme Where The Substrate Binds Is Known As The ....Document2 pagesEnzymes SL Quiz: The Part of The Enzyme Where The Substrate Binds Is Known As The ....ShruthiNo ratings yet
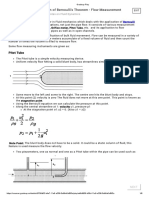
- Application of Bernoulli's TheoremDocument8 pagesApplication of Bernoulli's Theoremram kumarNo ratings yet
- Bhs. Inggris Xii AccDocument8 pagesBhs. Inggris Xii AccnupushaulaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Concentrator Generator: Mayank Kumar Singh (2018016104) Aman Prakash (2019007968) Hamid Siddiqui (2019006342)Document6 pagesOxygen Concentrator Generator: Mayank Kumar Singh (2018016104) Aman Prakash (2019007968) Hamid Siddiqui (2019006342)Rahul SaiNo ratings yet
- LECTURASDocument117 pagesLECTURASBRUCE DARWIN PACHAS TALLANo ratings yet
- What Is Matter?Document39 pagesWhat Is Matter?Mt. CarmelNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument14 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- 0000 20221010 Weekly Report 01 ZAWIA GT 11 C-Inspection Project - Rev 01Document11 pages0000 20221010 Weekly Report 01 ZAWIA GT 11 C-Inspection Project - Rev 01Mohamed JalilNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Water Resources Eng'gDocument3 pagesMidterm Exam Water Resources Eng'gMyrandjes Jailani MagugNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics: Chapter 2 - FluidsDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics: Chapter 2 - FluidsCool DouglasNo ratings yet
- Onshore Oil and Gas EHS Guideline - Comparison Between Draft Revised and 2007 VersionsDocument52 pagesOnshore Oil and Gas EHS Guideline - Comparison Between Draft Revised and 2007 VersionsIFC SustainabilityNo ratings yet
- Thrust BalanceDocument11 pagesThrust BalanceAdán Esteban AguilarNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Gas Charging Kits Brochure PDFDocument12 pagesNitrogen Gas Charging Kits Brochure PDFluisedonossaNo ratings yet
- Heat Pipe, Selection of Working FluidDocument7 pagesHeat Pipe, Selection of Working FluidUmesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Methods of Rainwater HarvestingDocument10 pagesMethods of Rainwater HarvestingChelsea EspirituNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics-Based Study of An Oilfield Separator - Part I: A Realistic SimulationDocument12 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics-Based Study of An Oilfield Separator - Part I: A Realistic SimulationMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Ch.E. 202)Document3 pagesAssignment 1 (Ch.E. 202)Hassaan NaeemNo ratings yet
- Bouwer Rice Slug Test Hydraulic Conductivity WRR1976Document6 pagesBouwer Rice Slug Test Hydraulic Conductivity WRR1976Simson MuliaNo ratings yet
- Building Services Unit 1Document8 pagesBuilding Services Unit 1Payal Yadav100% (1)
- Effect of Liquid Viscosity On Flow Patterns of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase FlowDocument5 pagesEffect of Liquid Viscosity On Flow Patterns of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flowyoupof83No ratings yet
- Cap. 13Document284 pagesCap. 13Ent Qa NepalNo ratings yet
- Annex 3.2 Industrial Processes Sector-Ammonia Production-Kellog Process Detailed Description PDFDocument5 pagesAnnex 3.2 Industrial Processes Sector-Ammonia Production-Kellog Process Detailed Description PDFErol DAĞNo ratings yet
- Distillation ColumnDocument5 pagesDistillation ColumnaimanjamelNo ratings yet
- What Is HCDPDocument5 pagesWhat Is HCDPfumerojr5164100% (1)
- NPSH - Net Positive Suction HeadDocument7 pagesNPSH - Net Positive Suction Headpryor.lamarioNo ratings yet
- WATER Supply NetworkDocument17 pagesWATER Supply NetworkRinpal100% (3)
- Useful Information On NPSH, NPSHA and NPSHRDocument8 pagesUseful Information On NPSH, NPSHA and NPSHRpietroNo ratings yet
- Gas Flow CalculationDocument59 pagesGas Flow CalculationOmprakaash MokideNo ratings yet
- MSOCHA3 - Tutorial 3 - LU 2 - Gas Absorption & Liquid StrippingDocument4 pagesMSOCHA3 - Tutorial 3 - LU 2 - Gas Absorption & Liquid StrippingTshwarelo MahlakoaneNo ratings yet
- PS 3Document9 pagesPS 3naverfallNo ratings yet