Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ob Case Press
Ob Case Press
Uploaded by
Hannah Jane PadernalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ob Case Press
Ob Case Press
Uploaded by
Hannah Jane PadernalCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
The Female Reproductive System is what?
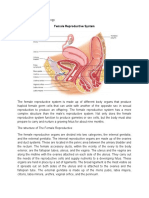
- The organs in the female reproductive system include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes,
cervix, and vagina. The uterus has a muscular outer layer called the myometrium and an inner
lining called the endometrium. The female reproductive system is a group of organs that work
together to enable reproduction, pregnancy, and childbirth. It also produces female sex hormones,
including oestrogen and progesterone.
What does the Female reproductive system do?
Its functions include:
- producing gametes called eggs, which can potentially be fertilized by sperm.
- secreting sex hormones (such as oestrogen and progesterone).
- providing an environment for a fertilized egg to develop during pregnancy.
-gestating a fetus if fertilization occurs.
- facilitating labor and childbirth.
What are the parts of the Female Reproductive system?
The organs of the female reproductive system are found both inside and outside of the female body. The organs inside the body are in the pelvis,
which is the lowest part of the body cavity above the legs.
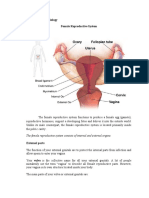
The internal female reproductive organs include:
• Vagina - the area between the lower part of the womb (the cervix) and the outside of the body. The vagina receives the penis during sexual
intercourse and is a passageway for childbirth.
• Womb (uterus) - a hollow, pear-shaped organ that is the home to a developing fetus. The uterus is divided into two parts: the cervix, which
is the lower part that opens into the vagina, and the main body of the uterus, called the corpus. The corpus can easily expand to hold a
developing baby. A channel through the cervix allows sperm to enter and menstrual blood to exit.
• Ovaries - small, oval-shaped glands that are located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries produce eggs (ova - an ovum is one egg, ova
means multiple eggs.) The ovaries also produce the main female sex hormones which are released into the bloodstream.
• Uterine (Fallopian) tubes - narrow tubes that are attached to the upper part of the uterus. They serve as tunnels for the ova to travel from
the ovaries to the uterus. The fertilisation of an egg by a sperm (conception) normally occurs in the uterine tubes. The fertilised egg then
moves to the uterus, where it implants into the lining of the uterine wall.
OVULATION AND FERTILIZATION
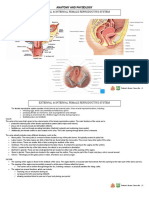
The outside (external) structures of the female reproductive system are grouped together in an area called the vulva. They are located just outside
the opening of the vagina. This includes structures such as the labia, the clitoris and a number of glands. The breasts can also be considered part of
the female reproductive system and are located on the chest.
The vulva consists of:
The labia - skin flaps or folds on either side of the opening of the vagina. There are two layers
of these skin folds. The outer ones are called the labia majora and are covered with pubic hair
after puberty. The inner folds do not have hair and are called the labia minora.
The mons pubis - the fatty bulge above the labia which is covered with hair after puberty.
The vaginal opening (meatus) - the entrance to the vagina.
The urethral opening (meatus) - the end of the tube which carries urine from the bladder to
the outside (urethra).
The clitoris - a lump of tissue at the top of the labia. This becomes full of blood during sexual
excitement (like the penis in the man but much smaller). The clitoris is very sensitive and is
the main source of female sexual pleasure.
The Bartholin's glands (or vestibular glands) - glands on either side of the opening of the
vagina. These produce a sticky substance to moisten (lubricate) the vagina for sexual
intercourse.
Skene’s glands: These glands are located in the vagina near the urethra. They may be part of
the G-spot, and play a role in sexual arousal.
You might also like
- Castor Oil Packs For Abdominal Adhesions ScarringDocument10 pagesCastor Oil Packs For Abdominal Adhesions ScarringWandarh Rh100% (1)
- Maternal & Newborn Nursing ExamDocument3 pagesMaternal & Newborn Nursing ExamPaul Jhon Vergara88% (25)
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDocument41 pagesNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- 16 Prolapse SomaliDocument5 pages16 Prolapse SomaliMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReportDocument18 pagesReproductive System ReportminnieNo ratings yet
- Reproductive sy-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesReproductive sy-WPS OfficeAngelo NolealNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Reproduction: Female Reproduction Male ReproductionDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Reproduction: Female Reproduction Male ReproductionMhiahLine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument34 pagesReproductive Systemsyifa alawiyahNo ratings yet
- Reparoductive SystemDocument4 pagesReparoductive SystemAhmed Mohammed omarNo ratings yet
- GEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Document9 pagesGEC SELF Lesson 5-Activity 5Hannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Organism Hormones Organ Systems FitnessDocument10 pagesOrganism Hormones Organ Systems FitnessAnonymous 0iY2p9FdNo ratings yet
- Bio InfoDocument5 pagesBio InfoSoham MultaniNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemJOSH ELORDENo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive SystemThảo NgânNo ratings yet
- Task 4Document20 pagesTask 4maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- Kuliah Sem4 2008-2Document16 pagesKuliah Sem4 2008-2cathencloxNo ratings yet
- Document (17) XXDocument45 pagesDocument (17) XXShafiq SaweraNo ratings yet
- 10FRSDocument27 pages10FRSWakanda ForeverNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument71 pagesMCN NotesAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Biomedical Perspective in Gender Sexuality 2Document28 pagesLesson 4 Biomedical Perspective in Gender Sexuality 2Nikka GoenettNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive Systems: Ms. Vernon Administrative and Clinical ProceduresDocument26 pagesThe Reproductive Systems: Ms. Vernon Administrative and Clinical ProceduresJustin MilliganNo ratings yet
- Unit XDocument18 pagesUnit XPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- What Constitutes SexDocument9 pagesWhat Constitutes SexAlex GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesReproductive SystemJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- Pandapatan Paler AnaPhyDocument3 pagesPandapatan Paler AnaPhyShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Presented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONDocument67 pagesPresented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONPaul AndersonNo ratings yet
- 1 TransDocument10 pages1 TranssenecabheNo ratings yet
- Female and Male Reproduvtive SytemDocument4 pagesFemale and Male Reproduvtive SytemAndreiNo ratings yet
- FemrepnotesDocument38 pagesFemrepnotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemHoney MalabuteNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJohn Paulo Morales50% (2)
- The Female Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesThe Female Reproductive SystemAnisatul Khabibah ZaenNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemamielle azamingNo ratings yet
- 8reproductive SystemDocument31 pages8reproductive SystemViola ChepletingNo ratings yet
- Sex Organs of The Human FemaleDocument17 pagesSex Organs of The Human FemaleTaniya DwiputriNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Stem 11Document9 pagesHuman Reproductive System Stem 11Ivy Ann P. VillarinNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyIkea Balhon100% (3)
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDocument16 pagesThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMDocument127 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-28 at 10.17.47 PMqdvvqvxn7gNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology OvaryDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OvaryFretchell Aripal MontesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System LessonDocument3 pagesReproductive System LessonmargemunozNo ratings yet
- Dana AssignmentDocument10 pagesDana AssignmentDana khalidNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument25 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemJay PornelaNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument17 pagesHuman Reproductionmyisha dailyNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3Document12 pagesAssignment # 3usaeed00000No ratings yet
- Biomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument29 pagesBiomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionBrian CastañedaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesThe Reproductive SystemRye ManosNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument11 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemArianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemLiangkiuwiliuNo ratings yet
- Hormones in Human ReproductionDocument93 pagesHormones in Human ReproductionKevin Roi RomeroNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Document12 pagesUNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous ActivityDocument8 pagesAsynchronous ActivityMarie PotayreNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument67 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannu panchalNo ratings yet
- External Genital of Female and Internal Sex OrgnsDocument6 pagesExternal Genital of Female and Internal Sex OrgnsChristian BeninNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System HUMANDocument25 pagesReproductive System HUMANGrendel EscultorNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction SystemDocument3 pagesFemale Reproduction SystemAnonymous mKrNwlyNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAlyanna L. ArquillanoNo ratings yet
- MCHDocument3 pagesMCHReniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive SystemShekinah AsebuqueNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemAltheaNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System: Niegas, Eunice Ida Marie A. BSN 1-ADocument3 pagesThe Female Reproductive System: Niegas, Eunice Ida Marie A. BSN 1-AEunice Ida Marie NiegasNo ratings yet
- Female OrganDocument7 pagesFemale OrganMd. Minhazul IslamNo ratings yet
- OXYTOCIN-drug StudyDocument4 pagesOXYTOCIN-drug StudyCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Oncoward 5 April 2021Document140 pagesOncoward 5 April 2021MegaSariDewiNo ratings yet
- Caesarean SectionDocument16 pagesCaesarean SectionA B Siddique RiponNo ratings yet
- (Anatomy & Physiology Lecture) REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESDocument21 pages(Anatomy & Physiology Lecture) REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NOTESNez TraehNo ratings yet
- Bovine Dystocia - An Overview: September 2019Document6 pagesBovine Dystocia - An Overview: September 2019pramiswariNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 16 - Reproduction in HumansDocument17 pages(BIO) Chapter 16 - Reproduction in HumansMahi NoorNo ratings yet
- MCN Notes 2Document26 pagesMCN Notes 2Rogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Libro de Endocrino y FertilidadDocument684 pagesLibro de Endocrino y FertilidadClaudia Mercedes Alonso Cuevas100% (1)
- 17 11 16 Puerperial SepsisDocument15 pages17 11 16 Puerperial SepsisJerry MwandoroNo ratings yet
- Maternal Injuries During Vaginal Delivery and Its ManagementDocument51 pagesMaternal Injuries During Vaginal Delivery and Its ManagementJay Seetohul100% (1)
- Hysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 6 Issue 3 EnglishDocument21 pagesHysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 6 Issue 3 EnglishHisteroscopia.esNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildDocument10 pagesNursing Care of The Family Having Difficulty Conceiving A ChildAndrei Borata100% (2)
- Fibroids PowerpointDocument27 pagesFibroids Powerpointteritohaha100% (3)
- Overview Agenesis VaginaDocument8 pagesOverview Agenesis VaginaArum DwiNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Uterine MyomaDocument39 pagesA Case Study On Uterine MyomaAj GoNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Apana Vayu in Modern Perspective: August 2018Document8 pagesA Critical Review of Apana Vayu in Modern Perspective: August 2018BrucleeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Cancer)Document8 pagesAssignment 1 (Cancer)Leo Aurelio MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Midterms ObDocument29 pagesMidterms ObMary Grace Bañes100% (1)
- DR WriteUpDocument40 pagesDR WriteUpDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery: By: Ma. Kizianne Krystel ManioDocument43 pagesLabor and Delivery: By: Ma. Kizianne Krystel ManioJohn Christian LasalitaNo ratings yet
- Childs World 13Th Edition Martorell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesChilds World 13Th Edition Martorell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFesther.hecker462100% (17)
- Family Clinic Inc Colleges Manila Nursing ProgramDocument21 pagesFamily Clinic Inc Colleges Manila Nursing Programkian5No ratings yet
- Prosedur Tindakan Yang Sering Dilakukan Sesuai ICD9CMDocument8 pagesProsedur Tindakan Yang Sering Dilakukan Sesuai ICD9CMnovi rista anandaNo ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument50 pagesUts Reviewerwoobie spiceNo ratings yet
- Done Uterine RuptureDocument3 pagesDone Uterine RupturejnapalaNo ratings yet