Professional Documents
Culture Documents
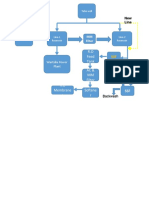
Mass Energy Balance
Mass Energy Balance
Uploaded by
AMIROriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mass Energy Balance
Mass Energy Balance
Uploaded by
AMIRCopyright:
Available Formats
The mass and energy balance of a cement plant is an important aspect of its operations.
The
balance involves accounting for the input and output of materials and energy throughout the
entire production process. Here are some key considerations:
Mass Balance:
1. Raw Materials: The mass of raw materials, such as limestone, clay, and iron ore, entering the
plant needs to be accounted for.
2. Fuel: The mass of different fuels, like coal, natural gas, or alternative fuels, used for heating the
kiln and other processes, must be measured.
3. Additives: Any additional materials, like gypsum or fly ash, that are added to enhance cement
properties should be included in the mass balance.
4. Clinker Production: The mass of clinker produced in the kiln, which is the primary product of
cement manufacturing, needs to be determined.
Energy Balance:
1. Fuel Consumption: The energy content of the fuels used, such as calorific values of coal or
natural gas, should be considered to calculate the total energy input.
2. Heat Losses: Energy losses due to radiation, convection, and other factors need to be
estimated and minimized to improve energy efficiency.
3. Power Consumption: Electrical energy used for running various equipment, such as crushers,
mills, and conveyors, should be accounted for.
4. Waste Heat Recovery: Efforts to recover waste heat from different processes, such as the
preheater and cooler, should be considered to improve energy efficiency.
By maintaining a detailed mass and energy balance, cement plants can monitor and optimize
their processes to improve efficiency, reduce resource consumption, and minimize environmental
impact.
You might also like
- Literature ReviewDocument19 pagesLiterature ReviewManjari Jha0% (1)
- Unit 1,2,3..hotel Engineering NotesDocument4 pagesUnit 1,2,3..hotel Engineering Notespoornima1268100% (2)
- V3i5 Ijertv3is051014 PDFDocument5 pagesV3i5 Ijertv3is051014 PDFRaja ShannmugamNo ratings yet
- Production of Energy From Biomass ResiduesDocument4 pagesProduction of Energy From Biomass ResiduesSalman LabiadhNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources in Chemical IndustryDocument29 pagesEnergy Sources in Chemical Industryadi makayasa maha putraNo ratings yet
- 68 Ijaet Vol III Issue I 2012Document6 pages68 Ijaet Vol III Issue I 2012Ssheshan PugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- Heat BalanceDocument11 pagesHeat BalanceB V S Kumar100% (1)
- Mid Term Mechanical-1Document21 pagesMid Term Mechanical-1Proshenjit BaruaNo ratings yet
- TSEE NoteDocument12 pagesTSEE NoteYogesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NotesDocument15 pagesUnit 4 Notesरितेश हरोडेNo ratings yet
- Fuel, Furnance and RefactoriesDocument50 pagesFuel, Furnance and RefactoriesKISHORE CHANDRA PATRANo ratings yet
- Recoverable Quantity of Waste Heat From Kiln and Preheater Systems and Economic Analysis (Case of Messebo Cement Factory)Document13 pagesRecoverable Quantity of Waste Heat From Kiln and Preheater Systems and Economic Analysis (Case of Messebo Cement Factory)abdulfetahNo ratings yet
- A Thorough Examination of The Many Types 1 1 1Document23 pagesA Thorough Examination of The Many Types 1 1 1Haid AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Coal As A Fuel in Cement IndustryDocument3 pagesCoal As A Fuel in Cement IndustryMohamed GamalNo ratings yet
- Energy ManagementDocument9 pagesEnergy Managementhasan_jafri_2No ratings yet
- Coal Combustion TechnologiesDocument31 pagesCoal Combustion TechnologiesFawad MushtaqNo ratings yet
- CokemakingTechnologies ComparisonDocument9 pagesCokemakingTechnologies Comparisonkselvan_1100% (1)
- Screenshot 2023-05-15 at 10.03.33 AMDocument70 pagesScreenshot 2023-05-15 at 10.03.33 AMPreethi PawarNo ratings yet
- Testing of Solid FuelsDocument8 pagesTesting of Solid FuelsJaaa ReeedNo ratings yet
- Muffle FurnaceDocument31 pagesMuffle FurnaceVignesh NayakNo ratings yet
- Energy Performance Assesment of FurnaceDocument16 pagesEnergy Performance Assesment of FurnacePranoy Barua100% (2)
- 18me81 Energy Engineeringe Module1Document74 pages18me81 Energy Engineeringe Module1Aishwarya SGNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Energy SourcesDocument9 pagesGroup 3 Energy SourcesZeiin ShionNo ratings yet
- The Most Efficient Waste Heat Recovery Device: A Gamma Type Stirling EngineDocument7 pagesThe Most Efficient Waste Heat Recovery Device: A Gamma Type Stirling EngineSutarmoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Working - Indian Power SectorDocument21 pagesThermal Power Plant Working - Indian Power Sectorrohanknh150% (1)
- Cement Plant Thermal EnergyDocument7 pagesCement Plant Thermal Energytsrinivasan5083No ratings yet
- Cement BrochureDocument20 pagesCement BrochureBrunoNo ratings yet
- Energy StatisticsDocument85 pagesEnergy StatisticsBa NyaNo ratings yet
- Material and Energy Balance: Basic PrinciplesDocument17 pagesMaterial and Energy Balance: Basic PrinciplesArjun Trehan100% (1)
- IJME Energyaudit A.RAMESHDocument13 pagesIJME Energyaudit A.RAMESHmanohar1005No ratings yet
- Mme 425 L1Document52 pagesMme 425 L1olanrewajuhbernardNo ratings yet
- Important Factors Affecting Efficiency of Power PlantDocument7 pagesImportant Factors Affecting Efficiency of Power PlantAhmad Ansari100% (1)
- Static Heat Energy Balance Mathematical Model For An Iron Blast FurnaceDocument12 pagesStatic Heat Energy Balance Mathematical Model For An Iron Blast FurnaceShatrughna SamalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Heat Loss in Kiln in Cement Industry-A Review: April 2016Document5 pagesAnalysis of Heat Loss in Kiln in Cement Industry-A Review: April 2016akbar davoodiNo ratings yet
- ECONOMIZER DESIGN FOR 2013 - Sayı 3 - 4 - Selçuk Selimli PDFDocument6 pagesECONOMIZER DESIGN FOR 2013 - Sayı 3 - 4 - Selçuk Selimli PDFNITINNo ratings yet
- WWW - Beeindia.in Energy Managers Auditors Documents Guide Books 2Ch4Document31 pagesWWW - Beeindia.in Energy Managers Auditors Documents Guide Books 2Ch4samcat2009No ratings yet
- A Review On Waste Heat Recovery in IndustriesDocument4 pagesA Review On Waste Heat Recovery in IndustriesBharat ShirsathNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Energy Production Technologies: StructureDocument19 pagesUnit 3 Energy Production Technologies: StructureBaladhamodaran BalajaganathanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Efficiency and Heat Balance of Reheating Furnace of Rolling MillsDocument15 pagesThermal Efficiency and Heat Balance of Reheating Furnace of Rolling MillsGidNo ratings yet
- CFD Modeling of Waste Heat Recovery On The Rotary Kiln System in The Cement IndustryDocument17 pagesCFD Modeling of Waste Heat Recovery On The Rotary Kiln System in The Cement Industryghada ghoudiNo ratings yet
- Aluminium CalculationsDocument2 pagesAluminium CalculationshahikajhNo ratings yet
- Static Heat Energy Balance Mathematical Model For An Iron Blast FurnaceDocument12 pagesStatic Heat Energy Balance Mathematical Model For An Iron Blast FurnaceLokesh BiddikaNo ratings yet
- Igc Power Plant For Biomass UtilizationDocument7 pagesIgc Power Plant For Biomass UtilizationPelita HidupNo ratings yet
- Ppe Unit 1Document18 pagesPpe Unit 1Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- GronliDocument5 pagesGronlijtreiber6627No ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument8 pagesThermal Power PlantGg ezNo ratings yet
- Low Energy Consumption Ammonia Production 2011 Paper PDFDocument14 pagesLow Energy Consumption Ammonia Production 2011 Paper PDFKailash NarainNo ratings yet
- Rehan Hpe ReportDocument9 pagesRehan Hpe ReportPrathamesh GothankarNo ratings yet
- Coal Industry PDFDocument10 pagesCoal Industry PDFVineet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Steam Boiler Technology 2003 PDFDocument218 pagesSteam Boiler Technology 2003 PDFŞeref Aksoy100% (4)
- JK Paper LTD SongadhDocument9 pagesJK Paper LTD SongadhlokririNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementFrom EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementNo ratings yet
- Renewable solutions in end-uses: Heat pump costs and marketsFrom EverandRenewable solutions in end-uses: Heat pump costs and marketsNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Storage: The Legal Landscape of Climate Change Mitigation TechnologyFrom EverandCarbon Capture and Storage: The Legal Landscape of Climate Change Mitigation TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Sat VocabDocument70 pagesSat VocabAMIRNo ratings yet
- Electricity 912-DDocument1 pageElectricity 912-DAMIRNo ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Guideline For Parents (Junior Level)Document9 pagesSummer Vacation Guideline For Parents (Junior Level)AMIRNo ratings yet
- Summer Fitness ProgramDocument10 pagesSummer Fitness ProgramAMIRNo ratings yet
- WHR Blowdo WN: Wartsila Power PlantDocument1 pageWHR Blowdo WN: Wartsila Power PlantAMIRNo ratings yet
- Brochure Velocity Sensors EN2Document12 pagesBrochure Velocity Sensors EN2AMIRNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery Power Generation: Eagle Group S.A.EDocument16 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Power Generation: Eagle Group S.A.EAMIRNo ratings yet
- Comparison of R1S25M1Document5 pagesComparison of R1S25M1AMIRNo ratings yet
- Forbearance and Gratitude ExerciseDocument3 pagesForbearance and Gratitude ExerciseAMIRNo ratings yet
- Basic Difference Between SMPS and T/RDocument1 pageBasic Difference Between SMPS and T/RAMIRNo ratings yet
- A01 Repaired Crad DetailDocument6 pagesA01 Repaired Crad DetailAMIRNo ratings yet
- RestaurantDocument1 pageRestaurantAMIRNo ratings yet
- Special Chemistry: Final ReportDocument1 pageSpecial Chemistry: Final ReportAMIRNo ratings yet
- Special Chemistry: Final ReportDocument1 pageSpecial Chemistry: Final ReportAMIRNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Lipid Levels & Risk of Heart DiseaseDocument1 pageChemistry: Lipid Levels & Risk of Heart DiseaseAMIRNo ratings yet
- Sample BOQDocument4 pagesSample BOQAMIRNo ratings yet
- Solar Car Parks: A Guide For Owners and DevelopersDocument28 pagesSolar Car Parks: A Guide For Owners and DevelopersAMIR100% (1)
- RPT ViewerDocument1 pageRPT ViewerAMIRNo ratings yet