Professional Documents
Culture Documents
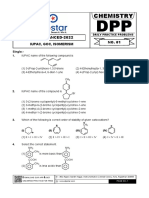
Isomerism DPP-01
Isomerism DPP-01
Uploaded by
pranali.xdfCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Amulet Innovality Operation ManualDocument88 pagesAmulet Innovality Operation ManualSara Bustillos Buenaño100% (2)
- Manual 140120 Fully Automatic Flow Wrapping MachineDocument33 pagesManual 140120 Fully Automatic Flow Wrapping MachineEMRE KAAN USTA100% (1)
- Method 18.0WDocument3 pagesMethod 18.0WVeronika RengganisNo ratings yet
- BD2F BS3F Service Manual OCRDocument340 pagesBD2F BS3F Service Manual OCRWere Wolf100% (2)
- ISOMERISMDocument16 pagesISOMERISMsabhi KeliyeNo ratings yet
- .Archivetemp2. OPTICAL ISOMERISM DPPDocument20 pages.Archivetemp2. OPTICAL ISOMERISM DPPchandalh789No ratings yet
- Isomerism Review 2Document10 pagesIsomerism Review 2ayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- IUPAC 1 To 6Document18 pagesIUPAC 1 To 6bashtaj3456No ratings yet
- JR & ER - Eng. PC PDFDocument33 pagesJR & ER - Eng. PC PDFmarmaduke32No ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP 02Document2 pagesIsomerism DPP 02pranali.xdfNo ratings yet
- SKC Sir Organic Chemistry Exercise-1 (Conceptual Questions) : CH - CH - CH - CH CHDocument22 pagesSKC Sir Organic Chemistry Exercise-1 (Conceptual Questions) : CH - CH - CH - CH CHमंगलेश पाण्डेयNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-08) - OYM - ChemistryDocument6 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-08) - OYM - ChemistryishitaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic DPP PDFDocument3 pagesInorganic DPP PDFashutosh99878No ratings yet
- DPP1 Iupac Goc Iso-20220705164702999094Document6 pagesDPP1 Iupac Goc Iso-20220705164702999094Anshu JayanthiNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-4 SET-2 Chapter-12 PDFDocument42 pagesCLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-4 SET-2 Chapter-12 PDFRitik RajNo ratings yet
- BT HHC Đ I Cuong 10H 2021 Dap AnDocument21 pagesBT HHC Đ I Cuong 10H 2021 Dap An21 01 15 Tường LâmNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature - DPP 04 (Of Lec 06) - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 pagesNomenclature - DPP 04 (Of Lec 06) - Arjuna JEE 2024armughank708No ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP 05Document2 pagesIsomerism DPP 05pranali.xdfNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument20 pagesIsomerismMantavya MeghaniNo ratings yet
- AIPMT SOLUTIONS 2011 (English)Document35 pagesAIPMT SOLUTIONS 2011 (English)Resonance KotaNo ratings yet
- 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques: SolutionsDocument40 pages12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques: SolutionssharmilaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-19 PDFDocument28 pagesCLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-19 PDFÀàkàrsh YàduvàñshiNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Document4 pagesCoordination Chemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Vedant JainNo ratings yet
- Isomerism - NEET TSC Problem Solving PDFDocument13 pagesIsomerism - NEET TSC Problem Solving PDFRishikesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On CST-01 & 02 - ChemistryDocument4 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On CST-01 & 02 - ChemistryUdithyaNo ratings yet
- Questions in TEST BOOKLET: 100 MAX MARKS: 400 (+4/-1) : Minor 9Document8 pagesQuestions in TEST BOOKLET: 100 MAX MARKS: 400 (+4/-1) : Minor 9Sanskar SahuNo ratings yet
- Neet Weekend Test: ChemistryDocument21 pagesNeet Weekend Test: ChemistryTHARUN THANGELLANo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry All DPPDocument61 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry All DPPOm SolankiNo ratings yet
- DPMT 2007 ChemistryDocument5 pagesDPMT 2007 ChemistryRahulNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompundsDocument30 pagesCoordination CompundsAnurag KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Che Study-Package-4 Level-2 Chapter-9 PDFDocument22 pagesCLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Che Study-Package-4 Level-2 Chapter-9 PDFpragyaNo ratings yet
- AITS - 02 - Chemistry Practice SheetDocument4 pagesAITS - 02 - Chemistry Practice Sheetanvitabhardwaj24No ratings yet
- Iupac Nomenclature & Structural Isomerism: Section (A) : Fundamental of Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesIupac Nomenclature & Structural Isomerism: Section (A) : Fundamental of Organic ChemistrynandiniNo ratings yet
- Upload 2Document5 pagesUpload 2k.prarthu0909No ratings yet
- Institute Test PDF ReportDocument8 pagesInstitute Test PDF ReportIshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Chemical Bonding Jee MainDocument5 pagesPages From Chemical Bonding Jee MainYuvarajNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-27: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Document5 pagesM-Caps-27: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 2 MergeDocument30 pagesExercise 1 2 MergesmpopadeNo ratings yet
- Grade 13 SBC 2019 Novemebr Term TestDocument25 pagesGrade 13 SBC 2019 Novemebr Term TestPiyumi ObeyesekeraNo ratings yet
- Core Organic Assessed Homework - 2Document3 pagesCore Organic Assessed Homework - 2Bintou CoulibalyNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XIII Che Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 20Document44 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XIII Che Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 20sanika ///No ratings yet
- Aakash Chemistry Study Package 6 SolutionsDocument103 pagesAakash Chemistry Study Package 6 SolutionsSamuel Moris Mandanakka100% (1)
- 11th-Old 22-23 Assignment-5 Structural Isomerism Dt. 21-07-22 - 986171 - 2022 - 07 - 20 - 12 - 26Document2 pages11th-Old 22-23 Assignment-5 Structural Isomerism Dt. 21-07-22 - 986171 - 2022 - 07 - 20 - 12 - 26Ravindra PatilNo ratings yet
- 659d28b7d925b30018265333 ## Isomerism Practice SheetDocument8 pages659d28b7d925b30018265333 ## Isomerism Practice Sheetabhishekrabidas94No ratings yet
- JEE Main Online Test 12-04-19 EveningDocument26 pagesJEE Main Online Test 12-04-19 EveningKRISHAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- CHE 321 Tutorial 2 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesCHE 321 Tutorial 2 - Solutionsletlhogonolomogakabe58No ratings yet
- Date Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet-6 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level-2 Exact DurationDocument1 pageDate Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet-6 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level-2 Exact DurationVIDYA SRI GANESHNo ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP 03Document2 pagesIsomerism DPP 03pranali.xdfNo ratings yet
- IUPAC ExerciseDocument27 pagesIUPAC ExerciseDhritismita Kalita100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Jee MainDocument22 pagesChemical Bonding Jee MainYuvarajNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-29: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Document3 pagesM-Caps-29: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry SQP 4Document7 pages12 Chemistry SQP 4Prashanth 070No ratings yet
- Goc-I Apsp e Almr63yDocument17 pagesGoc-I Apsp e Almr63yompatil1710.opNo ratings yet
- Goc-I Apsp e Almr63yDocument17 pagesGoc-I Apsp e Almr63yKushal RathoreNo ratings yet
- DPP NomenclatureDocument7 pagesDPP Nomenclaturegamishtag18No ratings yet
- Blue Print, QP (Pre-Board) - Xii (Chem) With Marking Scheme - 19gr5Document11 pagesBlue Print, QP (Pre-Board) - Xii (Chem) With Marking Scheme - 19gr5Sourya AichNo ratings yet
- Stereo ChemDocument12 pagesStereo ChemVanessa AbboudNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNDocument3 pagesPRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNABD 17No ratings yet
- 17CheE 2Document30 pages17CheE 2Amasha SilvaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules DPPDocument8 pagesBiomolecules DPPMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Metallabenzenes: An Expert ViewFrom EverandMetallabenzenes: An Expert ViewL. James WrightNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesFrom EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (Physics-II)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank (Physics-II)Arslan RiazNo ratings yet
- Lifetime Testing of Metallized Thin Film Capacitors For Inverter ApplicationsDocument3 pagesLifetime Testing of Metallized Thin Film Capacitors For Inverter ApplicationsMohammed Al gobariNo ratings yet
- FORM U-5 MANUFACTURERS DATA REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SHEET SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS 2021 EditionDocument1 pageFORM U-5 MANUFACTURERS DATA REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SHEET SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS 2021 EditionjuliocarroregueiroNo ratings yet
- 1.relativity 1 2 Spring 22-23Document31 pages1.relativity 1 2 Spring 22-23arthey FriendNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Manufacturing ProcessDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Manufacturing Processgw21tcyd100% (1)
- Working Principle of Arc Quenching in HVDC: RABINO, Bruce Jerard SDocument14 pagesWorking Principle of Arc Quenching in HVDC: RABINO, Bruce Jerard Srare machineNo ratings yet
- KICE INDUSTRIES Spout ManualDocument48 pagesKICE INDUSTRIES Spout ManualcharlesmpsNo ratings yet
- CSC Spring School 2018: Orca 4.0 & GabeditDocument59 pagesCSC Spring School 2018: Orca 4.0 & GabeditFerzz MontejoNo ratings yet
- Due 11:59 PM, Wednesday, 9/23: Homework Assignment #1 (Total 100 Possible Points)Document11 pagesDue 11:59 PM, Wednesday, 9/23: Homework Assignment #1 (Total 100 Possible Points)Abdu KaziNo ratings yet
- Millimeter Wave Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G MoDocument6 pagesMillimeter Wave Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G MoOwaisKhanNo ratings yet
- Karrykrimp 2 Modular Technical Manual Jan 2011Document22 pagesKarrykrimp 2 Modular Technical Manual Jan 2011Sebastian Molina BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Free Standing Masonry Wall Design Based On TMS 402-16/13 & ACI 318-19Document6 pagesFree Standing Masonry Wall Design Based On TMS 402-16/13 & ACI 318-19biceli samet1No ratings yet
- Mechanical Analysis of Extracted Aggregate: Standard Method of Test ForDocument6 pagesMechanical Analysis of Extracted Aggregate: Standard Method of Test Forclint silNo ratings yet
- DD Cen TS 15534-3-2007Document14 pagesDD Cen TS 15534-3-2007MladenMarkovicNo ratings yet
- Harbor Freight Cable TrackerDocument8 pagesHarbor Freight Cable TrackerUglyoldmanNo ratings yet
- M30 Knig2461 04 Ism C30Document34 pagesM30 Knig2461 04 Ism C30Hanzala TahirNo ratings yet
- A Novel Method To Eliminate The Symmetry Dependence of Fiber Coils For Shupe MitigationDocument8 pagesA Novel Method To Eliminate The Symmetry Dependence of Fiber Coils For Shupe MitigationNormanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- MV Solution Up To 3825 kVA at 1000 VDC: Medium Voltage Inverter Station, Customized Up To 3.83 MvaDocument2 pagesMV Solution Up To 3825 kVA at 1000 VDC: Medium Voltage Inverter Station, Customized Up To 3.83 MvaDeepak GehlotNo ratings yet
- Compendium: Solutions To Selected Exercises From John David Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Edition)Document46 pagesCompendium: Solutions To Selected Exercises From John David Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Edition)Bryan Jesus RANo ratings yet
- Optical Encoder For Motion Control Through ArduinoDocument4 pagesOptical Encoder For Motion Control Through ArduinoMary LongNo ratings yet
- CE8311 - Construction Materials Laboratory Manual - by LearnEngineering - in PDFDocument50 pagesCE8311 - Construction Materials Laboratory Manual - by LearnEngineering - in PDFGayu100% (1)
- Nuclear Heat Transfer and Passive CoolingDocument108 pagesNuclear Heat Transfer and Passive CoolingsadNo ratings yet
- What Is A Final Drive?: Presentation by Howard BellabyDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Final Drive?: Presentation by Howard BellabyHoward BellabyNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction-Composite WallDocument3 pagesHeat Conduction-Composite WallJady chess24No ratings yet
- Material Balance Calculations of VLE SystemsDocument9 pagesMaterial Balance Calculations of VLE SystemsAcademicBMNo ratings yet
Isomerism DPP-01
Isomerism DPP-01
Uploaded by
pranali.xdfOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Isomerism DPP-01
Isomerism DPP-01
Uploaded by
pranali.xdfCopyright:
Available Formats
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Isomerism Part-02
Isomerism DPP-01
1. Structures CH3—CH2—CH=CH2 and are
(1) Chain isomers
(2) Position isomers
(3) Both chain & position isomers
(4) Not isomers
2. How many minimum carbons required for Chain isomerism and Position isomerism in alkanes ?
(1) 4, 5
(2) 3, 5
(3) 4, 6
(4) 4, 4
3. Which molecular formula does not exhibit position isomerism ?
(1) C5H12
(2) C4H8
(3) C6H14
(4) C5H10
4. Isomers are essentially identical with
(1) Structural formula
(2) Chemical properties
(3) Molecular formula
(4) Physical properties
5. Find the value of degree of unsaturation of the following structure
CH2
(1) 4
(2) 3
(3) 2
(4) 5
6. What is the D.U. of Benzene?
(1) 4
(2) 5
(3) 2
(4) 3
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [1]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Isomerism Part-02
7. Degree of unsaturation is also known as
(1) Index of carbon deficiency
(2) Index of hydrogen deficiency
(3) both (1) and (2)
(4) none of these
8. Find the correct match in the following table
Compounds D.U.
(i) C5H10 1
(ii) C4H6 2
(iii) C6H14 1
(1) (i) & (ii)
(2) (ii) & (iii)
(3) (i), (ii) & (iii)
(4) (i) & (iii)
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [2]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Isomerism Part-02
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Answer 1 3 1 3 2 1 2 1
SOLUTIONS DPP-01
1. CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2
P·C·C = 4
and
CH3 – C = CH2
CH3
P.C.C = 3
They are chain isomers
2. Minimum carbons required for chain isomerism in alkanes are 4
Example: CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
P·C·C = 4
and
CH3 – CH – CH3
CH3
P·C·C =3
Minimum carbons required for position isomerism in Alkanes are 6.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5
CH3 – CH–CH2–CH2–CH3
CH3
and
1 2 3 4 5
CH3 – CH2–CH–CH2–CH3
CH3
3. C5H12 can never exhibit position isomerism as minimum number of carbon atoms required by alkane to show
position isomerism is 6.
4. For two compounds to be isomers of each other, the essential condition is that they must have same
molecular formula.
5. D.U. = No. of rings + No. of bonds
D.U. = 1 + 2
=3
6. D.U. = no. of rings + No. of bonds
D.U. = 1 + 3
=4
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [3]
You might also like
- Amulet Innovality Operation ManualDocument88 pagesAmulet Innovality Operation ManualSara Bustillos Buenaño100% (2)
- Manual 140120 Fully Automatic Flow Wrapping MachineDocument33 pagesManual 140120 Fully Automatic Flow Wrapping MachineEMRE KAAN USTA100% (1)
- Method 18.0WDocument3 pagesMethod 18.0WVeronika RengganisNo ratings yet
- BD2F BS3F Service Manual OCRDocument340 pagesBD2F BS3F Service Manual OCRWere Wolf100% (2)
- ISOMERISMDocument16 pagesISOMERISMsabhi KeliyeNo ratings yet
- .Archivetemp2. OPTICAL ISOMERISM DPPDocument20 pages.Archivetemp2. OPTICAL ISOMERISM DPPchandalh789No ratings yet
- Isomerism Review 2Document10 pagesIsomerism Review 2ayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- IUPAC 1 To 6Document18 pagesIUPAC 1 To 6bashtaj3456No ratings yet
- JR & ER - Eng. PC PDFDocument33 pagesJR & ER - Eng. PC PDFmarmaduke32No ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP 02Document2 pagesIsomerism DPP 02pranali.xdfNo ratings yet
- SKC Sir Organic Chemistry Exercise-1 (Conceptual Questions) : CH - CH - CH - CH CHDocument22 pagesSKC Sir Organic Chemistry Exercise-1 (Conceptual Questions) : CH - CH - CH - CH CHमंगलेश पाण्डेयNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-08) - OYM - ChemistryDocument6 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-08) - OYM - ChemistryishitaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic DPP PDFDocument3 pagesInorganic DPP PDFashutosh99878No ratings yet
- DPP1 Iupac Goc Iso-20220705164702999094Document6 pagesDPP1 Iupac Goc Iso-20220705164702999094Anshu JayanthiNo ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-4 SET-2 Chapter-12 PDFDocument42 pagesCLS JEEAD-18-19 XI Che Target-4 SET-2 Chapter-12 PDFRitik RajNo ratings yet
- BT HHC Đ I Cuong 10H 2021 Dap AnDocument21 pagesBT HHC Đ I Cuong 10H 2021 Dap An21 01 15 Tường LâmNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature - DPP 04 (Of Lec 06) - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 pagesNomenclature - DPP 04 (Of Lec 06) - Arjuna JEE 2024armughank708No ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP 05Document2 pagesIsomerism DPP 05pranali.xdfNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument20 pagesIsomerismMantavya MeghaniNo ratings yet
- AIPMT SOLUTIONS 2011 (English)Document35 pagesAIPMT SOLUTIONS 2011 (English)Resonance KotaNo ratings yet
- 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques: SolutionsDocument40 pages12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques: SolutionssharmilaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-19 PDFDocument28 pagesCLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-19 PDFÀàkàrsh YàduvàñshiNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Document4 pagesCoordination Chemistry - Practice Sheet - Lakshya JEE 2024Vedant JainNo ratings yet
- Isomerism - NEET TSC Problem Solving PDFDocument13 pagesIsomerism - NEET TSC Problem Solving PDFRishikesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On CST-01 & 02 - ChemistryDocument4 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On CST-01 & 02 - ChemistryUdithyaNo ratings yet
- Questions in TEST BOOKLET: 100 MAX MARKS: 400 (+4/-1) : Minor 9Document8 pagesQuestions in TEST BOOKLET: 100 MAX MARKS: 400 (+4/-1) : Minor 9Sanskar SahuNo ratings yet
- Neet Weekend Test: ChemistryDocument21 pagesNeet Weekend Test: ChemistryTHARUN THANGELLANo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry All DPPDocument61 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry All DPPOm SolankiNo ratings yet
- DPMT 2007 ChemistryDocument5 pagesDPMT 2007 ChemistryRahulNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompundsDocument30 pagesCoordination CompundsAnurag KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Che Study-Package-4 Level-2 Chapter-9 PDFDocument22 pagesCLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Che Study-Package-4 Level-2 Chapter-9 PDFpragyaNo ratings yet
- AITS - 02 - Chemistry Practice SheetDocument4 pagesAITS - 02 - Chemistry Practice Sheetanvitabhardwaj24No ratings yet
- Iupac Nomenclature & Structural Isomerism: Section (A) : Fundamental of Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesIupac Nomenclature & Structural Isomerism: Section (A) : Fundamental of Organic ChemistrynandiniNo ratings yet
- Upload 2Document5 pagesUpload 2k.prarthu0909No ratings yet
- Institute Test PDF ReportDocument8 pagesInstitute Test PDF ReportIshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Chemical Bonding Jee MainDocument5 pagesPages From Chemical Bonding Jee MainYuvarajNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-27: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Document5 pagesM-Caps-27: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 2 MergeDocument30 pagesExercise 1 2 MergesmpopadeNo ratings yet
- Grade 13 SBC 2019 Novemebr Term TestDocument25 pagesGrade 13 SBC 2019 Novemebr Term TestPiyumi ObeyesekeraNo ratings yet
- Core Organic Assessed Homework - 2Document3 pagesCore Organic Assessed Homework - 2Bintou CoulibalyNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XIII Che Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 20Document44 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XIII Che Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 20sanika ///No ratings yet
- Aakash Chemistry Study Package 6 SolutionsDocument103 pagesAakash Chemistry Study Package 6 SolutionsSamuel Moris Mandanakka100% (1)
- 11th-Old 22-23 Assignment-5 Structural Isomerism Dt. 21-07-22 - 986171 - 2022 - 07 - 20 - 12 - 26Document2 pages11th-Old 22-23 Assignment-5 Structural Isomerism Dt. 21-07-22 - 986171 - 2022 - 07 - 20 - 12 - 26Ravindra PatilNo ratings yet
- 659d28b7d925b30018265333 ## Isomerism Practice SheetDocument8 pages659d28b7d925b30018265333 ## Isomerism Practice Sheetabhishekrabidas94No ratings yet
- JEE Main Online Test 12-04-19 EveningDocument26 pagesJEE Main Online Test 12-04-19 EveningKRISHAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- CHE 321 Tutorial 2 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesCHE 321 Tutorial 2 - Solutionsletlhogonolomogakabe58No ratings yet
- Date Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet-6 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level-2 Exact DurationDocument1 pageDate Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet-6 Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level-2 Exact DurationVIDYA SRI GANESHNo ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP 03Document2 pagesIsomerism DPP 03pranali.xdfNo ratings yet
- IUPAC ExerciseDocument27 pagesIUPAC ExerciseDhritismita Kalita100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Jee MainDocument22 pagesChemical Bonding Jee MainYuvarajNo ratings yet
- M-Caps-29: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Document3 pagesM-Caps-29: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Vishal SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry SQP 4Document7 pages12 Chemistry SQP 4Prashanth 070No ratings yet
- Goc-I Apsp e Almr63yDocument17 pagesGoc-I Apsp e Almr63yompatil1710.opNo ratings yet
- Goc-I Apsp e Almr63yDocument17 pagesGoc-I Apsp e Almr63yKushal RathoreNo ratings yet
- DPP NomenclatureDocument7 pagesDPP Nomenclaturegamishtag18No ratings yet
- Blue Print, QP (Pre-Board) - Xii (Chem) With Marking Scheme - 19gr5Document11 pagesBlue Print, QP (Pre-Board) - Xii (Chem) With Marking Scheme - 19gr5Sourya AichNo ratings yet
- Stereo ChemDocument12 pagesStereo ChemVanessa AbboudNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNDocument3 pagesPRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNABD 17No ratings yet
- 17CheE 2Document30 pages17CheE 2Amasha SilvaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules DPPDocument8 pagesBiomolecules DPPMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Metallabenzenes: An Expert ViewFrom EverandMetallabenzenes: An Expert ViewL. James WrightNo ratings yet
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesFrom EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (Physics-II)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank (Physics-II)Arslan RiazNo ratings yet
- Lifetime Testing of Metallized Thin Film Capacitors For Inverter ApplicationsDocument3 pagesLifetime Testing of Metallized Thin Film Capacitors For Inverter ApplicationsMohammed Al gobariNo ratings yet
- FORM U-5 MANUFACTURERS DATA REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SHEET SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS 2021 EditionDocument1 pageFORM U-5 MANUFACTURERS DATA REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SHEET SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS 2021 EditionjuliocarroregueiroNo ratings yet
- 1.relativity 1 2 Spring 22-23Document31 pages1.relativity 1 2 Spring 22-23arthey FriendNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Manufacturing ProcessDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Manufacturing Processgw21tcyd100% (1)
- Working Principle of Arc Quenching in HVDC: RABINO, Bruce Jerard SDocument14 pagesWorking Principle of Arc Quenching in HVDC: RABINO, Bruce Jerard Srare machineNo ratings yet
- KICE INDUSTRIES Spout ManualDocument48 pagesKICE INDUSTRIES Spout ManualcharlesmpsNo ratings yet
- CSC Spring School 2018: Orca 4.0 & GabeditDocument59 pagesCSC Spring School 2018: Orca 4.0 & GabeditFerzz MontejoNo ratings yet
- Due 11:59 PM, Wednesday, 9/23: Homework Assignment #1 (Total 100 Possible Points)Document11 pagesDue 11:59 PM, Wednesday, 9/23: Homework Assignment #1 (Total 100 Possible Points)Abdu KaziNo ratings yet
- Millimeter Wave Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G MoDocument6 pagesMillimeter Wave Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G MoOwaisKhanNo ratings yet
- Karrykrimp 2 Modular Technical Manual Jan 2011Document22 pagesKarrykrimp 2 Modular Technical Manual Jan 2011Sebastian Molina BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Free Standing Masonry Wall Design Based On TMS 402-16/13 & ACI 318-19Document6 pagesFree Standing Masonry Wall Design Based On TMS 402-16/13 & ACI 318-19biceli samet1No ratings yet
- Mechanical Analysis of Extracted Aggregate: Standard Method of Test ForDocument6 pagesMechanical Analysis of Extracted Aggregate: Standard Method of Test Forclint silNo ratings yet
- DD Cen TS 15534-3-2007Document14 pagesDD Cen TS 15534-3-2007MladenMarkovicNo ratings yet
- Harbor Freight Cable TrackerDocument8 pagesHarbor Freight Cable TrackerUglyoldmanNo ratings yet
- M30 Knig2461 04 Ism C30Document34 pagesM30 Knig2461 04 Ism C30Hanzala TahirNo ratings yet
- A Novel Method To Eliminate The Symmetry Dependence of Fiber Coils For Shupe MitigationDocument8 pagesA Novel Method To Eliminate The Symmetry Dependence of Fiber Coils For Shupe MitigationNormanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- MV Solution Up To 3825 kVA at 1000 VDC: Medium Voltage Inverter Station, Customized Up To 3.83 MvaDocument2 pagesMV Solution Up To 3825 kVA at 1000 VDC: Medium Voltage Inverter Station, Customized Up To 3.83 MvaDeepak GehlotNo ratings yet
- Compendium: Solutions To Selected Exercises From John David Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Edition)Document46 pagesCompendium: Solutions To Selected Exercises From John David Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (3rd Edition)Bryan Jesus RANo ratings yet
- Optical Encoder For Motion Control Through ArduinoDocument4 pagesOptical Encoder For Motion Control Through ArduinoMary LongNo ratings yet
- CE8311 - Construction Materials Laboratory Manual - by LearnEngineering - in PDFDocument50 pagesCE8311 - Construction Materials Laboratory Manual - by LearnEngineering - in PDFGayu100% (1)
- Nuclear Heat Transfer and Passive CoolingDocument108 pagesNuclear Heat Transfer and Passive CoolingsadNo ratings yet
- What Is A Final Drive?: Presentation by Howard BellabyDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Final Drive?: Presentation by Howard BellabyHoward BellabyNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction-Composite WallDocument3 pagesHeat Conduction-Composite WallJady chess24No ratings yet
- Material Balance Calculations of VLE SystemsDocument9 pagesMaterial Balance Calculations of VLE SystemsAcademicBMNo ratings yet