Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Notes
Chemistry Notes
Uploaded by
yoonmimikyaw2008Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Notes
Chemistry Notes
Uploaded by
yoonmimikyaw2008Copyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Notes
Terms Descriptions
Sublimation Changes of state from solid to gas
Deposition Change of state from gas to solid
Condensation Change of state from gas to liquid
(Exothermic) (Energy is released to the surroundings
when a substance condenses or freezes)
Freezing (solidifying) Change of state from liquid to solid
(Exothermic)
Evaporation Change of state from liquid to gas but
(Endothermic) occurs only from the surface
(Energy need to be taken in to melt, boil
or evaporate a substance)
Melting Change of state from solid to liquid
(Endothermic)
Boiling Liquid to gas but occurs throughout the
(Endothermic) liquid
Melting point The temperature at which a solid turn to
liquid
Boiling point The temperature at which a liquid turn
into gas
Freezing point The temperature at which a liquid turn
into solid
Solvent A substance which dissolves another
substance
(E.g., water, ethanol, hexane)
Solute A substance which dissolves in a solvent
(Can be solids, liquids or gases) (E.g., salt)
Solution A homogeneous mixture of a solute in a
solvent
Homogeneous mixture A mixture that has been uniformly
combined (E.g., salt & water)
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
Heterogeneous mixture A mixture that contains visually
distinguishable components
(E.g., Cereal in milk)
Aqueous solution Forms when a solute dissolves in water
Saturated solution Contains the maximum concentration of
solute dissolved in a solvent
(At a specified temperature)
Solubility The maximum amount of a substance
that will dissolve in a given amount of
solvent (at a specified temperature)
Anhydrous Does not contain water
Hydrated The crystals have water chemically
combined in their structure
(Water of crystallization)
Diffusion The spreading out of particles from an
area of higher concentration to lower
concentration
Speed of diffusion of a gas depends on
the relative molecular masses M r
(Lighter mass diffuses faster)
Happens faster in warmer temperatures
Atom The smallest particle that cannot be
broken down by chemical means
Molecule An uncharged particle made of two or
more atoms joined together
Ion An atom or group of atoms that carries
positive or negative electrical charge
Protons (nucleons) (In the nucleus) positive charge
Neutrons (nucleons) (In the nucleus) no charge – neutral
Electrons (Outside the nucleus) negative charge
Atomic Number The number of protons in an atom
Mass Number The number of protons and neutrons
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
(Always the largest number among
the two, shown in the periodic table)
Isotopes Atoms of same element which have
same numbers of protons and electrons
but different numbers of neutrons
Has the same chemical properties but
different physical properties
*Uses: Cancer curing, sterilizing the (E.g., density)
medical garments
Elements Substances that cannot be chemically
broken down into simpler substances
Mixtures Contains two or more elements or
(Can be separated physically) compounds that are not chemically
bonded together
Compounds Made up of two or more different
(Cannot be separated physically) elements chemically bonded together
Electronic Configuration
Periods (8) Horizontal rows in the periodic table
Groups (18) Vertical columns in the periodic table;
Electrons in outer shell
Noble Gases Have a full outer shell of electrons,
unreactive and very stable;
Cannot lose or gain electrons easily
(Group 8)
Halogens Five toxic and non-metallic elements
(Left of the noble gases, Group 7)
Reacts with metals to form solid
compounds
Alkali Metals Soft, shiny, low-melting, highly reactive
metals
(Group 1, except for Hydrogen)
Reacts with water forming hydrogen
Monatomic Exist as single atoms, do not combine
with other elements to form
compounds
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
Retention factor R f Comparing how far the spots have
moved from the base line compared
with the solvent front
distance travelled by substance
Rt =
distance travelled by solvent
Locating agent Used to locate colorless spots by
reacting with the chemicals in the
colorless spots and forming colored
compounds
Solvent front A line at the top of the purple drawn by
pencil
Filtrate The solution which passes through the
filter paper
Residue The solid that stays on the filter paper
Volatile Easily evaporated
Immiscible Liquids not forming a homogeneous
mixture when mixed
Miscible Forms a homogeneous mixed when
mixed together
1 decimeter cubed (dm3) 1000 cm3
Stable OCTET of electrons The full outer shell of 8 electrons
Decomposition Type of chemical reaction where a
compound breaks down to form two or
more substances
Synthesis Where the substance is formed by the
combination of two or more other
substances
Ionic Bonding The electrostatic force of attraction
(Metals + Non-metals) between oppositely charged ions
(Transfer electrons)
Covalent Bonding Two non-metal atoms reacting together
(Non-metals + Non-metal) to share pairs of electrons
Metallic Bonding The strong electrostatic attraction
between the giant lattice of positive
ions and the sea of delocalized electrons
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
Cations Positive ions
Anions Negative ions
Intermolecular forces The weak forces between the separate
molecules
Ionic lattice The three-dimensional network of ions
Empirical formula The formula showing the simplest
whole number ratio of the different
atoms or ions in a compound
Reactants The substances that we add at the start
and are changed during the reaction
Products Substances formed by the reaction
Diatomic molecules Two atoms per molecule
Spectator ions The ions that didn’t take part in the
ionic reaction
Ionic equation A symbol equation that shows only
those ions and molecules that react
Relative Atomic mass ( Ar ¿ The mass of an atom by comparing their
mass with the same number of carbon-
12 atoms
Relative Molecular mass ( M r ¿ The sum of the relative atomic masses
of all the atoms shown in the formula of
a molecule
Relative Formula mass The sun of the relative masses of all the
ions shown in the formula of an ionic
compound
Mole The amount of substance that contains
6.02 ×10 atoms, ions or molecules
23
Stoichiometry The ratio of each reactant and product
in a balanced equation
Limiting reactant The reaction stops when the limiting
reactant is used up
Titration The concentration of alkali needed to
completely react with an acid using a
procedure (acid-base titration)
Mobile electrons Free-moving electrons
Electrical conductor Substances which have low resistance to
the passage of electricity
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
Electrical insulator Substances that resist the flow on an
electric current
Electrolysis The decomposition (breaking down) of
an ionic compound when
molten/aqueous solution, by the
passage of an electric current
Electrolyte The molten/aqueous ionic compound
that conducts electricity and
decomposes during electrolysis
Electrodes Rods that carry the electrical current to
and from the electrolyte
Positive electrode Anode
Negative electrode Cathode
Inert Do not react with electrolyte or the
products of electrolysis
Oxidation - A reaction where electrons are
lost
- Gaining oxygen to a substance
- Losing hydrogen from a substance
- Increasing the oxidation numbers
Reduction - A reaction where electrons are
gained
- Losing oxygen from a substance
- Gaining hydrogen to a substance
- Decreasing the oxidation number
Ionic half equation Type of equation which shows what’s
happening at only one of the electrodes
Electroplating Used to put a thin layer of one metal o
top of another metal using electrolysis
Cryolite Improves the conductivity and lowers
melting points of electrolyte, reducing
energy costs
Enthalpy change The thermal energy change which
occurs during chemical reaction
Activation energy ( E a ¿ The minimum energy that colliding
particles must have in order to react
Bond Energy The amount of energy needed to break
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
one mole of a particular bond in one
mole of gaseous molecules
Petroleum (crude oil) A complex mixture of compounds
containing carbon and hydrogen
Combustion An exothermic chemical reaction
between a fuel and an oxidizing agent
Complete combustion Occurs when hydrocarbons or other
fuels burn in excess oxygen
(Products: carbon dioxide & water)
Incomplete combustion Occurs when there is not enough
oxygen to burn the fuel completely
(Products: carbon monoxide & H2O)
Hydrocarbons Compounds which contain only
hydrogen and carbon
Rate of reaction How rapidly the products are formed
from the reactants
Independent variable The variable that is altered during a
scientific experiment
Dependent variable The variable being tested or measured
Control variable The variable that is kept the same
Catalyst A substance that speeds up a chemical
reaction, by lowering the activation
energy so that greater proportion of the
collisions between particles are
successful (E.g., enzymes)
Collision Frequency The number of successful collisions per
second
Redox reaction Where reduction and oxidation take
place at the same time
Oxidizing Agent A substance which oxidizes another
(In a redox reaction) substance, and is itself reduced
Reducing Agent A substance which reduces another
(In a redox reaction) substance and is itself oxidized
Solid, Liquid and Gas
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
State of Arrangement Motion Separation Volume & Shape
Matters
Solid Fixed pattern Only vibrate Very Definite shape & volume
close/packed
together
Liquid Random; no Slides past each Close together Definite volume; take
fixed pattern other the shape of container
Gas Random Move very rapidly Very far apart No definite shape or
volume
Physical Properties of Metals & Non-Metals
Metals Non-Metals
Density High Low
Melting point/ High Low
Boiling point
Hardness Hard Soft
(Except grp 1 metals)
Ductility Ductile Not ductile
Malleability Malleable Not malleable
Sonority Sonorous Not sonorous
Conductivity Electricity & heat Insulators
Chemical Properties of Metals & Non-Metals
Metals Non-metals
Color on litmus paper Red to blue (alkali) Blue to red (acidic)
Reactions with acids Can react with acids Cannot react with acids
Forming of ions Form positive ions; Form negative ions;
Always give their Always accept electrons from
electrons away metals
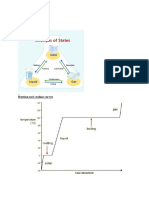
Cooling Curve
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
Heating curve
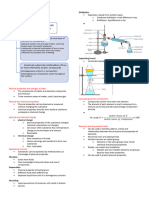
Different methods of separating substances
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
Types of methods Separations Materials used
Chromatography Separating two or more - Paper
dissolved solids in a solution chromatogram
(or) - Locating agents
Separating pigments (colored
substances) using filter paper
Simple distillation Separating a liquid from a - Condenser
solution
Fractional distillation Separating any solution - Fractionating
containing liquids with different column
boiling points - Condenser
(The lowest boiling point distils first)
Filtration Separating undissolved solids - Filter paper
from liquids - Filter funnel
Decanting & Separating liquid from an - Centrifuge
centrifugation insoluble solid
Crystallization To obtain a crystalline solid from - Evaporating
solution basin
Solvent extraction Separating two solutes dissolved - Separating
in a solvent funnel
I am a gifted student, and I can succeed in anything
You might also like
- ChemLab Synthesize An Ionic Compound Student EditableDocument5 pagesChemLab Synthesize An Ionic Compound Student EditableJonah Carlson50% (2)
- 1.1 The Components of MatterDocument33 pages1.1 The Components of MatterwisyahazmanNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Notes - 2018Document60 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Notes - 2018Giovani100% (1)
- Chemistry Let Review 2021Document209 pagesChemistry Let Review 2021Joel Stacruz100% (1)
- Chemistry IGCSE Rev PackDocument39 pagesChemistry IGCSE Rev Packرهام کاظمیNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - NotesDocument15 pagesChemistry - Notesdagakabbier1718No ratings yet
- Ros Unit 2 Matter and EnergyDocument18 pagesRos Unit 2 Matter and EnergyNina GanapaoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Properties and Structure of MatterDocument17 pagesModule 1 Properties and Structure of Matterisaheqq12No ratings yet
- MatterDocument12 pagesMattermathaimath2001No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 01 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - AQA Chemistry GCSEDocument137 pagesFlashcards - Topic 01 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - AQA Chemistry GCSEEva xuNo ratings yet
- HTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFDocument82 pagesHTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFayoubNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Polaris LectureDocument80 pagesChemistry Polaris LectureDonn SabalNo ratings yet
- Scientific Skills in Scientific InvestigationsDocument4 pagesScientific Skills in Scientific InvestigationsJeremieh Jan CorpuzNo ratings yet
- BrudaDocument6 pagesBrudaemmalin2025No ratings yet
- Gas Liquid Solid: Some Characteristics of Gases, Liquids and SolidsDocument8 pagesGas Liquid Solid: Some Characteristics of Gases, Liquids and SolidsDavidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes English Medium by Goswami SirDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes English Medium by Goswami SirManoj GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 01 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - AQA Chemistry GCSEDocument137 pagesFlashcards - Topic 01 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - AQA Chemistry GCSEgamer1842011No ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry - Modules 1-4Document60 pagesYear 11 Chemistry - Modules 1-4WarNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsDocument49 pagesTopic 1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsMohammad Andrew GhaniNo ratings yet
- Class 9th PDFDocument9 pagesClass 9th PDFHitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ODB - Chem (Matter)Document2 pagesODB - Chem (Matter)aloevera1994100% (1)
- Chemistry NotesDocument60 pagesChemistry Noteshcv7cptvs6No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterNicole VictorinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Stoichiometric RelationshipsDocument11 pagesChapter-1 Stoichiometric RelationshipstychrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument13 pagesLesson 1: Matter and Its Propertiesricky100% (1)
- Final ChemistryDocument84 pagesFinal ChemistryPupun SahooNo ratings yet
- Chemical Vocabulary ListDocument3 pagesChemical Vocabulary ListseptinurmalaNo ratings yet
- Chem ChecklistDocument21 pagesChem Checklist逸星吕No ratings yet
- 1b Glossary Particles and Bonding (2017)Document2 pages1b Glossary Particles and Bonding (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- Classificationofmatter 140910134732 Phpapp01Document4 pagesClassificationofmatter 140910134732 Phpapp01janneeshaaNo ratings yet
- Stages of AggregationDocument6 pagesStages of AggregationgrandayaizaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Chem A4 SizeDocument12 pagesWeek 5 Chem A4 SizeKrisha Mae PalomarNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry: Unit 1 - The Particle Nature of MatterDocument5 pagesIB Chemistry: Unit 1 - The Particle Nature of MattermjohnmccNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationDocument15 pagesGrade 9 Science Matter and Chemical Change Final Exam PreparationBekki VanderlendeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument70 pagesIGCSE Chemistry NotesKim Seng OnnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Definition ListDocument2 pagesChemistry Definition ListrandomvidsNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Bohr Model of AtomsDocument31 pagesAtoms and Bohr Model of Atomsogedengbed28No ratings yet
- What Is MatterDocument7 pagesWhat Is MatterpinieraaurapaulaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Vocabulary SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Vocabulary Sheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MatterDocument79 pagesChapter 1 MatterdwyquishNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsRusher SigueNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledWaggle The GreatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes by Vasumitra GajbhiyeDocument41 pagesChemistry Notes by Vasumitra GajbhiyeYash Asudani100% (2)
- Chem HandoutDocument11 pagesChem HandoutEllen Mae PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Delivery SystemsDocument28 pagesDelivery SystemscNo ratings yet
- Full Detailed Notes (All Syllabus) 2Document42 pagesFull Detailed Notes (All Syllabus) 2EveNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument13 pagesChemAngelica Marie DiegoNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument24 pagesClassification of MatterJuloura PastorNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument70 pagesCHEMISTRYF E R N A NNo ratings yet
- EOY RevisionDocument8 pagesEOY RevisionPaxton NyeoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Matter PHYSICAL SCIENCEDocument3 pagesClassification of Matter PHYSICAL SCIENCEYya Jalynna PenillaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry GlossaryDocument5 pagesChemistry Glossarytesk2No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaDocument75 pagesChemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaJESPHER GARCIANo ratings yet
- Substances: Copper CoinDocument4 pagesSubstances: Copper CoinDane BosevNo ratings yet
- 3 1Document90 pages3 1Joy MercadoNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesTopic 1 - Atomic StructureElle Na nagaraNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGrade 7 ReviewerHunger StealSMPNo ratings yet
- Important DefinitionsDocument6 pagesImportant DefinitionsicedgoblinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic ChemistryDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Basic ChemistryHannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Activities in Science 9 Quarter 2, Week 1Document6 pagesSupplemental Activities in Science 9 Quarter 2, Week 1Rose Ann ChavezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42ZubairHassanNo ratings yet
- Eastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Document3 pagesEastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Isaac PiaoNo ratings yet
- Selective Extraction of Copper, Mercury, Silver, and Palladium Ions From Water Using Hydrophobic Ionic LiquidsDocument7 pagesSelective Extraction of Copper, Mercury, Silver, and Palladium Ions From Water Using Hydrophobic Ionic Liquidsفایلجو پروژه و مقالهNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Group 2Document8 pagesChapter 10 Group 2Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Rural Dairy Technology PDFDocument123 pagesRural Dairy Technology PDFSajjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals and Catalytic Applications of CeO2 Based MaterialsDocument55 pagesFundamentals and Catalytic Applications of CeO2 Based Materialsjiawen dingNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Summative Test 2Document3 pagesScience 9 Summative Test 2Ma. Socorro Hilario50% (2)
- 2 2 - Naming Ionic Molecular CompoundsDocument31 pages2 2 - Naming Ionic Molecular Compoundsapi-263048875100% (1)
- Fully Ionised Resin Systems: 4 Necessary ComponentsDocument5 pagesFully Ionised Resin Systems: 4 Necessary ComponentsSantanu BiswasNo ratings yet
- Experiment n6Document2 pagesExperiment n6Javan Mamogay BrionesNo ratings yet
- Actual Repeat Paper 2013Document10 pagesActual Repeat Paper 2013Jasmeet Kaur SandhuNo ratings yet
- Core Notes by Dr. Maha FariedDocument122 pagesCore Notes by Dr. Maha Fariedmmkhst005No ratings yet
- DHS H1 CHEM P1 QP With Answer KeyDocument15 pagesDHS H1 CHEM P1 QP With Answer KeyLim EnningNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Solid State Gujcet PyqDocument19 pagesCh-1 Solid State Gujcet PyqWhoaretoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter and StoichiometryDocument223 pagesChapter 1 - Matter and StoichiometryJatjediNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Document10 pagesUnit-4 - Chapters (1,2,3,4)Farah AounNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSSC 1 Paper IDocument8 pagesChemistry HSSC 1 Paper IShahid Ur Rehman100% (1)
- Introduction To Materials PDFDocument96 pagesIntroduction To Materials PDFMircea Dubenco100% (1)
- Removal of Metal Ions From Aqueous Solutions by Extraction With Ionic LiquidsDocument4 pagesRemoval of Metal Ions From Aqueous Solutions by Extraction With Ionic LiquidsMohanad El-HarbawiNo ratings yet
- Colorants and Auxiliaries Vol 2Document455 pagesColorants and Auxiliaries Vol 2Putri Mayangsari100% (11)
- Index: Physical ChemistryDocument9 pagesIndex: Physical Chemistrypulkit asatiNo ratings yet
- GCI Topics PDFDocument4 pagesGCI Topics PDFMuhammad QaisarNo ratings yet
- The Art of Using Ionic Liquids in The Synthesis of Inorganic NanomaterialsDocument10 pagesThe Art of Using Ionic Liquids in The Synthesis of Inorganic NanomaterialsAhsan JalalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of WaterDocument6 pagesChemistry of Waterkeycynarra.bonatrainologyNo ratings yet
- Complied ABC PTest PDFDocument54 pagesComplied ABC PTest PDFanon_281694614100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument56 pagesChemistryJaxon Isack90% (10)
- CHEMISTRY-P2-Teacher Co KeDocument8 pagesCHEMISTRY-P2-Teacher Co KeASSIGNMENTS PRIORITYNo ratings yet