Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chromotography Background
Chromotography Background
Uploaded by
api-708477233Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ChromatographyDocument23 pagesChromatographysatish pradhanNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument56 pagesChromatographyapi-26998277100% (14)
- Instrumental Methods of Drug AnalysisFrom EverandInstrumental Methods of Drug AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Paper ChromatographyDocument6 pagesPaper ChromatographysamNo ratings yet
- Merits: Microliter Is The Only Sample RequiredDocument27 pagesMerits: Microliter Is The Only Sample RequiredNitin RathodNo ratings yet
- AlexDocument2 pagesAlexYasar Arafath SNo ratings yet
- Chromatography and Its TypesDocument8 pagesChromatography and Its TypesAyesha HameedNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument6 pagesChromatographyNaveen ShankarNo ratings yet
- Principle of ChromatographyDocument8 pagesPrinciple of ChromatographyMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Paper ChromatographyDocument5 pagesLiterature Review of Paper Chromatographydafobrrif100% (1)
- Chromatography SirkeDocument36 pagesChromatography SirkeAkash RoyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Chromatographic TechniquesDocument8 pagesClassification of Chromatographic TechniquesArfa AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chromatography and Microscopy (BIO - 204)Document8 pagesChromatography and Microscopy (BIO - 204)Karen AgbaegbuNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic Methods of SeparationDocument22 pagesChromatographic Methods of SeparationtsteadmanNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPaper ChromatographySai SridharNo ratings yet
- SBCC 1106-1Document30 pagesSBCC 1106-1opolla nianorNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPaper ChromatographyAsida Maronsing DelionNo ratings yet
- Instumental Methods of AnalysisDocument10 pagesInstumental Methods of AnalysissanjhinehrotraNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument6 pagesPaper ChromatographyAsida Maronsing DelionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 FYDocument68 pagesChapter 4 FYvrishtichauhan20No ratings yet
- CHROMATOGRAPHYDocument9 pagesCHROMATOGRAPHYmaggyebanksNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography PDFDocument13 pagesPaper Chromatography PDFGLADYS FERNANDESNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: BioanalyticalDocument17 pagesTerm Paper: BioanalyticalGyanendra GoshwamiNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh ChromatographyDocument17 pagesUtkarsh ChromatographyUtkarsh Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh ChromatographyDocument17 pagesUtkarsh ChromatographyUtkarsh Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Biochem LabDocument6 pagesBiochem LabSyed Sharique AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Chemical AnalysisDocument3 pagesChromatography: Chemical AnalysisafnaanqurreshiNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument40 pagesChromatographySAGAR POUDELNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument38 pagesChromatographyelizabeth merzyNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument3 pagesChromatographySadra AhmadiNo ratings yet
- ChromotographyDocument22 pagesChromotographyDeepak KarnaniNo ratings yet
- Chromatography EdexcelDocument4 pagesChromatography EdexcelKevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument68 pagesChromatographythamizh555No ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument17 pagesChromatographyMahima JyothiNo ratings yet
- Yulo, Dylan Francesca G.: ChromatographyDocument3 pagesYulo, Dylan Francesca G.: ChromatographyDylan Francesca G YuloNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistery: Muhammad Azhar 1056 Bs Chemistry 4 (M)Document5 pagesAnalytical Chemistery: Muhammad Azhar 1056 Bs Chemistry 4 (M)Open UserNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT Kundan DeoreDocument25 pagesASSIGNMENT Kundan DeoreKuNdAn DeOrENo ratings yet
- Basic ChromatographyDocument8 pagesBasic ChromatographyPrajyot SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chromatography 1Document5 pagesChromatography 1Tanuj VermaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6Document18 pagesTopic 6Worede A.No ratings yet
- Principle of Paper Chromatography: The Separation in Paper Chromatography Is AchievedDocument12 pagesPrinciple of Paper Chromatography: The Separation in Paper Chromatography Is AchievedSoumik MahapatroNo ratings yet
- 222 Chapter 4Document35 pages222 Chapter 4talha saleemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigative ProjectDocument27 pagesChemistry Investigative ProjectrekhanagarajanNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Paper Chromatography Is An Analytical Method Used To Separate Chemicals orDocument4 pagesPaper Chromatography Paper Chromatography Is An Analytical Method Used To Separate Chemicals orMooma fatimaNo ratings yet
- From WikipediaDocument4 pagesFrom WikipediazohaimranNo ratings yet
- Column ChromatographyDocument14 pagesColumn ChromatographyBalagopal OsNo ratings yet
- Subdivision of Chromatography InstrumentDocument6 pagesSubdivision of Chromatography Instrumentmigom7md1No ratings yet
- Chromatography: Analytical Chromatography Is Used To Determine The Existence and Possibly Also TheDocument5 pagesChromatography: Analytical Chromatography Is Used To Determine The Existence and Possibly Also Themaria ayubNo ratings yet
- Types of Chroma To Grap GyDocument75 pagesTypes of Chroma To Grap GyMohammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Terms: Pigments Chlorophyll Carotenes XanthophyllsDocument9 pagesChromatography Terms: Pigments Chlorophyll Carotenes XanthophyllsAnggun IcNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh ChromatographyDocument18 pagesUtkarsh Chromatographycute loverNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 05Document38 pagesLecture 04 05Munna IslamNo ratings yet
- A. Title: Paper Chromatography B. Date: 28 C. Purpose: Determine RF On Markers Using Opaque Paper and MineralDocument4 pagesA. Title: Paper Chromatography B. Date: 28 C. Purpose: Determine RF On Markers Using Opaque Paper and MineralLailatul BadriyahNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument13 pagesChromatographyswarnava.biswasNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Techniques for Detecting and Measuring Substances.From EverandAnalytical Chemistry Techniques for Detecting and Measuring Substances.No ratings yet
- Data Mining Algorithms in C++: Data Patterns and Algorithms for Modern ApplicationsFrom EverandData Mining Algorithms in C++: Data Patterns and Algorithms for Modern ApplicationsNo ratings yet
Chromotography Background
Chromotography Background
Uploaded by
api-708477233Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chromotography Background
Chromotography Background
Uploaded by
api-708477233Copyright:
Available Formats
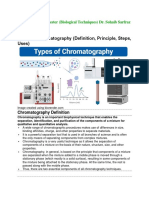
Chromatography in it’s most basic definition is the separation of mixtures.
The separation of
these mixtures have two states the mobile state and the stationary state. The mobile state are
materials that actively move while separating, while stationary are for materials that remain still.
Along with these states there are several methods with varying complexities. Paper, thin layer,
gas, and high performance liquid chromatography. All of these methods have their own uses
and advantages.
First is paper chromatography, the most common method and is oftened used to teach in school
do it’s relatively easy to understand process. One example of this method is to put dye spots
onto a piece of paper and hang it vertically into a solvent. As the solvent travels up the paper it
will meet the dye. After this process is done, remove the paper from the solvent to leave the
mobile phase.
Next is thin layer chromatography, this method uses a thin plate. Materials are placed into this
plate in a stationary state and a solvent is added. This solvent will cause the materials to enter a
mobile state, in which they will begin to move. As they move they will begin to separate out into
a more pure state closer to the original material.
Gas chromatography method is used to help identify materials that do not have a solid or liquid
state instead separating gasses. This method is unique compared to the previous two methods
as it uses a machine. First materials are added to a machine along with a neutral gas to help
things travel. As the machines activates it will move the materials helping them separate in a
mobile phase. The machine will record the data into a chart that has a series of peaks that
identifies the materials.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), it is the most mainstream method of
identification and separation of materials in a biological enviroment. Similar to gas
chromatography this method also uses a machine to help scientists process the information. It
can be used for identification, separation, and analysis. The stationary phase is a solid packed
into a metal column in which its then placed into a machine that will enter it into a mobile phase.
As the liquids are forced through a bond in a solvent, it will separate the material.
You might also like
- ChromatographyDocument23 pagesChromatographysatish pradhanNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument56 pagesChromatographyapi-26998277100% (14)
- Instrumental Methods of Drug AnalysisFrom EverandInstrumental Methods of Drug AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Paper ChromatographyDocument6 pagesPaper ChromatographysamNo ratings yet
- Merits: Microliter Is The Only Sample RequiredDocument27 pagesMerits: Microliter Is The Only Sample RequiredNitin RathodNo ratings yet
- AlexDocument2 pagesAlexYasar Arafath SNo ratings yet
- Chromatography and Its TypesDocument8 pagesChromatography and Its TypesAyesha HameedNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument6 pagesChromatographyNaveen ShankarNo ratings yet
- Principle of ChromatographyDocument8 pagesPrinciple of ChromatographyMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Paper ChromatographyDocument5 pagesLiterature Review of Paper Chromatographydafobrrif100% (1)
- Chromatography SirkeDocument36 pagesChromatography SirkeAkash RoyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Chromatographic TechniquesDocument8 pagesClassification of Chromatographic TechniquesArfa AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chromatography and Microscopy (BIO - 204)Document8 pagesChromatography and Microscopy (BIO - 204)Karen AgbaegbuNo ratings yet
- Chromatographic Methods of SeparationDocument22 pagesChromatographic Methods of SeparationtsteadmanNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPaper ChromatographySai SridharNo ratings yet
- SBCC 1106-1Document30 pagesSBCC 1106-1opolla nianorNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPaper ChromatographyAsida Maronsing DelionNo ratings yet
- Instumental Methods of AnalysisDocument10 pagesInstumental Methods of AnalysissanjhinehrotraNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument6 pagesPaper ChromatographyAsida Maronsing DelionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 FYDocument68 pagesChapter 4 FYvrishtichauhan20No ratings yet
- CHROMATOGRAPHYDocument9 pagesCHROMATOGRAPHYmaggyebanksNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography PDFDocument13 pagesPaper Chromatography PDFGLADYS FERNANDESNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: BioanalyticalDocument17 pagesTerm Paper: BioanalyticalGyanendra GoshwamiNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh ChromatographyDocument17 pagesUtkarsh ChromatographyUtkarsh Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh ChromatographyDocument17 pagesUtkarsh ChromatographyUtkarsh Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Biochem LabDocument6 pagesBiochem LabSyed Sharique AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Chemical AnalysisDocument3 pagesChromatography: Chemical AnalysisafnaanqurreshiNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument40 pagesChromatographySAGAR POUDELNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument38 pagesChromatographyelizabeth merzyNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument3 pagesChromatographySadra AhmadiNo ratings yet
- ChromotographyDocument22 pagesChromotographyDeepak KarnaniNo ratings yet
- Chromatography EdexcelDocument4 pagesChromatography EdexcelKevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument68 pagesChromatographythamizh555No ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument17 pagesChromatographyMahima JyothiNo ratings yet
- Yulo, Dylan Francesca G.: ChromatographyDocument3 pagesYulo, Dylan Francesca G.: ChromatographyDylan Francesca G YuloNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistery: Muhammad Azhar 1056 Bs Chemistry 4 (M)Document5 pagesAnalytical Chemistery: Muhammad Azhar 1056 Bs Chemistry 4 (M)Open UserNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT Kundan DeoreDocument25 pagesASSIGNMENT Kundan DeoreKuNdAn DeOrENo ratings yet
- Basic ChromatographyDocument8 pagesBasic ChromatographyPrajyot SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chromatography 1Document5 pagesChromatography 1Tanuj VermaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6Document18 pagesTopic 6Worede A.No ratings yet
- Principle of Paper Chromatography: The Separation in Paper Chromatography Is AchievedDocument12 pagesPrinciple of Paper Chromatography: The Separation in Paper Chromatography Is AchievedSoumik MahapatroNo ratings yet
- 222 Chapter 4Document35 pages222 Chapter 4talha saleemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigative ProjectDocument27 pagesChemistry Investigative ProjectrekhanagarajanNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Paper Chromatography Is An Analytical Method Used To Separate Chemicals orDocument4 pagesPaper Chromatography Paper Chromatography Is An Analytical Method Used To Separate Chemicals orMooma fatimaNo ratings yet
- From WikipediaDocument4 pagesFrom WikipediazohaimranNo ratings yet
- Column ChromatographyDocument14 pagesColumn ChromatographyBalagopal OsNo ratings yet
- Subdivision of Chromatography InstrumentDocument6 pagesSubdivision of Chromatography Instrumentmigom7md1No ratings yet
- Chromatography: Analytical Chromatography Is Used To Determine The Existence and Possibly Also TheDocument5 pagesChromatography: Analytical Chromatography Is Used To Determine The Existence and Possibly Also Themaria ayubNo ratings yet
- Types of Chroma To Grap GyDocument75 pagesTypes of Chroma To Grap GyMohammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Terms: Pigments Chlorophyll Carotenes XanthophyllsDocument9 pagesChromatography Terms: Pigments Chlorophyll Carotenes XanthophyllsAnggun IcNo ratings yet
- Utkarsh ChromatographyDocument18 pagesUtkarsh Chromatographycute loverNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 05Document38 pagesLecture 04 05Munna IslamNo ratings yet
- A. Title: Paper Chromatography B. Date: 28 C. Purpose: Determine RF On Markers Using Opaque Paper and MineralDocument4 pagesA. Title: Paper Chromatography B. Date: 28 C. Purpose: Determine RF On Markers Using Opaque Paper and MineralLailatul BadriyahNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument13 pagesChromatographyswarnava.biswasNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Techniques for Detecting and Measuring Substances.From EverandAnalytical Chemistry Techniques for Detecting and Measuring Substances.No ratings yet
- Data Mining Algorithms in C++: Data Patterns and Algorithms for Modern ApplicationsFrom EverandData Mining Algorithms in C++: Data Patterns and Algorithms for Modern ApplicationsNo ratings yet