Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2211CS010358-Structure of DBMS
2211CS010358-Structure of DBMS
Uploaded by
2211cs0103580 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesThe document discusses the key components and structure of a database management system (DBMS). It is divided into a storage manager and query processor. The storage manager handles interfacing with the low-level data storage and includes subcomponents like the file manager, buffer manager, and transaction manager. The query processor translates queries and updates into efficient data access operations and includes a DDL interpreter, DML compiler, and query evaluation engine.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the key components and structure of a database management system (DBMS). It is divided into a storage manager and query processor. The storage manager handles interfacing with the low-level data storage and includes subcomponents like the file manager, buffer manager, and transaction manager. The query processor translates queries and updates into efficient data access operations and includes a DDL interpreter, DML compiler, and query evaluation engine.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pages2211CS010358-Structure of DBMS
2211CS010358-Structure of DBMS
Uploaded by
2211cs010358The document discusses the key components and structure of a database management system (DBMS). It is divided into a storage manager and query processor. The storage manager handles interfacing with the low-level data storage and includes subcomponents like the file manager, buffer manager, and transaction manager. The query processor translates queries and updates into efficient data access operations and includes a DDL interpreter, DML compiler, and query evaluation engine.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
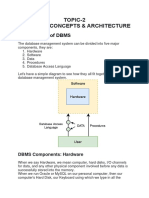
STRUCTURE OF DBMS
•A database system is partitioned into modules that deal with each of
the responsibilities of the overall system.
• The functional components of a database system can be broadly
divided into the storage manager and the query processor
components.
• The storage manager is important because databases typically
require a large amount of storage space.
• The query processor is important because it helps the database
system to simplify and facilitate access to data.
• It is the job of the database system to translate updates and queries
written in a nonprocedural language, at the logical level, into an
efficient sequence of operations at the physical level. 1.6.1 Query
Processor The query processor components include
• DDL interpreter, which interprets DDL statements and records the
definitions in the data dictionary.
• DML compiler, which translates DML statements in a query language
into an evaluation plan consisting of low-level instructions that the
query evaluation engine understands.
• A query can usually be translated into any of a number of alternative
evaluation plans that all give the same result. The DML compiler also
performs query optimization, that is, it picks the lowest cost evaluation
plan from among the alternatives.
• Query evaluation engine, which executes low- level instructions
generated by the DML compiler.
Storage Manager: A storage manager is a program module that
provides the interface between the low-level data stored in the
database and the application programs and queries submitted to the
system. The storage manager is responsible for the interaction with
the file manager. The raw data are stored on the disk using the file
system, which is usually provided by a conventional operating system.
The storage manager translates the various DML statements into low-
level file-system commands. Thus, the storage manager is responsible
for storing, retrieving, and updating data in the database. The storage
manager components include Authorization and integrity manager It
tests for the satisfaction of integrity constraints and checks the
authority of users to access data
Transaction manager: It’s a component of DBMS which ensures
that the database remains in a consistent (correct) state despite
system failures, and that concurrent transaction executions proceed
without conflicting.
File manager: which manages the allocation of space on disk storage
and the data structures used to represent information stored on disk.
Buffer manager: is responsible for fetching data from disk storage
into main memory, and deciding what data to cache in main memory.
The buffer manager is a critical part of the database system, since it
enables the database to handle data sizes that are much larger than
the size of main memory.
Transaction Manager: A transaction is a collection of operations
that performs a single logical function in a database application. Each
transaction is a unit of both atomicity and consistency. Thus, we
require that transactions do not violate any database-consistency
constraints. That is, if the database was consistent when a transaction
started, the database must be consistent when the transaction
successfully terminates. Transaction manager ensures that the
database remains in a consistent (correct) state despite system failures
You might also like
- Database System Architecture: Unit 1Document11 pagesDatabase System Architecture: Unit 1Kathan DhebarNo ratings yet
- Database System StructureDocument6 pagesDatabase System StructureNAJIYA KVNo ratings yet
- Structure of A DBMSDocument26 pagesStructure of A DBMSmaneesh sNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems ComponentsDocument11 pagesDatabase Management Systems ComponentsCarlos WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Data Storage and QueryingDocument3 pagesData Storage and Queryingrambabu mahatoNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems: Course: Credits: 3Document22 pagesDatabase Management Systems: Course: Credits: 3phuongltbkNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1, Pages 50-69Document20 pagesChapter-1, Pages 50-69Kajal KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Concepts and Architecture PDFDocument20 pagesTopic 2 Concepts and Architecture PDFvibhav thakurNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit IDocument3 pagesDBMS Unit IVds KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Ch. Keerthi IT-A - 18951A1239 Adavanced DatabasesDocument10 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Ch. Keerthi IT-A - 18951A1239 Adavanced DatabasesKeerthi ChukkaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Week2-Text LearningDocument14 pagesUnit 1 - Week2-Text LearningaaquibcaptainamericaNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: Contains Information About A Particular EnterpriseDocument5 pagesDatabase Management System: Contains Information About A Particular EnterpriseIzzy AnocheNo ratings yet
- Structure of Database Management SystemDocument5 pagesStructure of Database Management SystemReeya RamudamuNo ratings yet
- Complete Architecture of DbmsDocument19 pagesComplete Architecture of DbmsArin AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Database System Architecture L2 2023Document7 pagesDatabase System Architecture L2 2023Pra SanthNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument68 pagesDBMSkanojiyanikhil034No ratings yet
- What Is Database?Document3 pagesWhat Is Database?Apna MianwaliNo ratings yet
- Presentation DBMS 1Document10 pagesPresentation DBMS 1Mamta BajgotraNo ratings yet
- DBMS Implementation and Administration: by Liyakathunisa, SJCE, MysoreDocument43 pagesDBMS Implementation and Administration: by Liyakathunisa, SJCE, MysoreKrishna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Structure of DBMS PDFDocument2 pagesStructure of DBMS PDFAnup Kumar50% (4)
- Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology School of Computer EngineeringDocument10 pagesKalinga Institute of Industrial Technology School of Computer Engineering089ASHUTOSH PATINo ratings yet
- What Are The Components of DBMSDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Components of DBMSGeethavaniTalupulaNo ratings yet
- Structure of A DBMSDocument3 pagesStructure of A DBMSMazen HNo ratings yet
- Suresh Gyan Vihar University: Department of CEITDocument5 pagesSuresh Gyan Vihar University: Department of CEITDARSHNIK DEEPNo ratings yet
- Structure of DbmsDocument1 pageStructure of DbmsRitu Jain100% (1)
- Notes 2Document8 pagesNotes 2Roob HoodNo ratings yet
- A DBMS Is A Complex Software System The Figure Showed in Previous Slide Is Divide Into Two HalvesDocument2 pagesA DBMS Is A Complex Software System The Figure Showed in Previous Slide Is Divide Into Two Halvesstudy materialNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument86 pagesDatabase Management SystemG.K.HarishNo ratings yet
- Database 064644Document10 pagesDatabase 064644Q JawedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0 PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 0 PDFDen ThanhNo ratings yet
- ADBMGKDocument22 pagesADBMGKguestmodeplmNo ratings yet
- Components of DBMSDocument13 pagesComponents of DBMSDinesh PitaleNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1NotesDocument43 pagesDBMS Unit-1Noteskanikasolanki2003No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 - Part3 - DBMS ArchitectureDocument4 pagesUnit - 1 - Part3 - DBMS ArchitectureAnmol MogalaiNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: A S S I G N M E N T OFDocument6 pagesDatabase Management System: A S S I G N M E N T OFAnshul SaxenaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Asignment 1Document6 pagesDBMS Asignment 1tinashe tagariraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Database Management SystemDocument104 pagesUnit 4: Database Management SystemPoojitha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Distributed DBMS Reliability Unit IVDocument27 pagesDistributed DBMS Reliability Unit IVRahilNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1 NotesDocument34 pagesDBMS Unit-1 NotesakkiketchumNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Distributed DBMS Architecture) : Architecture: The Architecture of A System Defines Its StructureDocument11 pagesUnit 3 (Distributed DBMS Architecture) : Architecture: The Architecture of A System Defines Its StructureParth HirparaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Question 2Document2 pagesDBMS Question 2Syeda Wahida SabrinaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Database Management System (Or DBMS) ?: SoftwareDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Database Management System (Or DBMS) ?: SoftwareMerad HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 IS099Document36 pagesLecture 2 IS099kimarodamian123No ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1 PPT 1.2 (Advantages & Disadvantages of DBMS, Components, Overall System Tructure)Document5 pagesDBMS Unit-1 PPT 1.2 (Advantages & Disadvantages of DBMS, Components, Overall System Tructure)lightNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Understanding Database System - Part 09 - Database Manager or EngineDocument8 pagesUnit 1 Understanding Database System - Part 09 - Database Manager or EngineAsmatullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Dbms UNIT 1Document13 pagesDbms UNIT 1chowdary 123No ratings yet
- Dbms Def AdvDocument13 pagesDbms Def AdvMuhammad Jawad AbidNo ratings yet
- ADBMSDocument13 pagesADBMStudurajanikantaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - BCSE302L - DBMS ArchitectureDocument17 pagesLecture 3 - BCSE302L - DBMS Architecturebojon27556No ratings yet
- Dbms Unit-1 - Important PointsDocument58 pagesDbms Unit-1 - Important PointsSathwika DoddarapuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 DBMSDocument22 pagesLecture 1 DBMSAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document34 pagesChap 2TalalNo ratings yet
- Role of DBADocument3 pagesRole of DBAEiqaa ˘˛˘No ratings yet
- DBMS SlidesDocument127 pagesDBMS SlidesAmit KushwahaNo ratings yet
- DBMS ReviewerDocument12 pagesDBMS ReviewerAebreme Mae ColladoNo ratings yet
- 25 HoangTrungHoaDocument3 pages25 HoangTrungHoavannhucuma03No ratings yet
- DBMS Final Part2 UIDocument30 pagesDBMS Final Part2 UITanmoy GhoshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Database Management SystemDharshanNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 1Document47 pagesDBMS Unit 1Faisal Nazir (ANDY)No ratings yet
- Overview:: Factors Affecting Demand of Cadbury Products in IndiaDocument7 pagesOverview:: Factors Affecting Demand of Cadbury Products in IndiaNajish FarhanNo ratings yet
- Nora Esd ProfileDocument4 pagesNora Esd ProfileProjectinsightNo ratings yet
- Identification and Prediction of Piping System NoiseDocument7 pagesIdentification and Prediction of Piping System NoisejjirwinNo ratings yet
- T7 B12 Flight 93 Calls - Jeremy Glick FDR - FBI 302 Transcript - Joanne Makely 911 Call 412Document48 pagesT7 B12 Flight 93 Calls - Jeremy Glick FDR - FBI 302 Transcript - Joanne Makely 911 Call 4129/11 Document ArchiveNo ratings yet
- Technical Proposal CAREDocument9 pagesTechnical Proposal CAREfeyera100% (1)
- 2021 Nissan Kicks Owner ManualDocument556 pages2021 Nissan Kicks Owner ManualNoel HermidaNo ratings yet
- Intro - Slides Systemc SCVDocument28 pagesIntro - Slides Systemc SCVShaikAzharNo ratings yet
- 275 River Ave Carramar Qmf-Os-080-Application-Tree-Work-Permit-Updated-Annually-For-Website-And-Customer-Service-Centre2Document1 page275 River Ave Carramar Qmf-Os-080-Application-Tree-Work-Permit-Updated-Annually-For-Website-And-Customer-Service-Centre2dsfeir123No ratings yet
- GBP Statement: Account SummaryDocument16 pagesGBP Statement: Account SummaryKris TheVillainNo ratings yet
- 5.3. 402020-01391-08-PI-SPC-0002 Rev0 PDFDocument136 pages5.3. 402020-01391-08-PI-SPC-0002 Rev0 PDFsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- XNXDocument5 pagesXNXHaythem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Burj DubaiDocument27 pagesBurj DubaiInche Helmi Dori DoriNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting I - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesIntermediate Accounting I - Cash and Cash EquivalentsJoovs JoovhoNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide To Ensemble Learning (With Python Codes)Document21 pagesA Comprehensive Guide To Ensemble Learning (With Python Codes)omegapoint077609100% (1)
- LG 5 Year Promotion Terms and Conditions 2016Document4 pagesLG 5 Year Promotion Terms and Conditions 2016sadlkasdNo ratings yet
- Splash25 Winner InstructionsDocument8 pagesSplash25 Winner InstructionsRamkrishna PaulNo ratings yet
- Form 7-No Dues Certificate.Document3 pagesForm 7-No Dues Certificate.naveen1712jNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1: (Vibration Measurement) : Vibration Measurement, From The Word Itself Measures Vibration. "Vibration MeasurementDocument5 pagesTOPIC 1: (Vibration Measurement) : Vibration Measurement, From The Word Itself Measures Vibration. "Vibration MeasurementShanks XDNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Students Satisfaction On Online LearningDocument8 pagesQuestionnaire Students Satisfaction On Online Learningapi-563923766No ratings yet
- JP Programme Officer PAK-OxfamNDocument2 pagesJP Programme Officer PAK-OxfamNxtremist2001No ratings yet
- Triple Compliant, Lightweight, Flexible ArmorDocument1 pageTriple Compliant, Lightweight, Flexible ArmorvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Flower BlindDocument16 pagesFlower BlindEle Jay AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- School Bus AgreementDocument2 pagesSchool Bus AgreementtinduganmdNo ratings yet
- Sabar Group: Three Phase Cooling Tower MotorsDocument2 pagesSabar Group: Three Phase Cooling Tower MotorsHrithik Sai TummalaNo ratings yet
- SAN Troubleshooting PDFDocument510 pagesSAN Troubleshooting PDFSanjay DeyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Air CompressorDocument15 pagesUnit 5 Air Compressormadhume01No ratings yet
- Products For Leisure TourismDocument32 pagesProducts For Leisure TourismMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- License Surrendered: Detail of Registered Travel Agents in Jalandhar DistrictDocument90 pagesLicense Surrendered: Detail of Registered Travel Agents in Jalandhar DistrictRodhraksh RajputNo ratings yet
- Mapper User ManualDocument66 pagesMapper User ManualHarsha KodaliNo ratings yet
- Adp PDFDocument22 pagesAdp PDFSkill IndiaNo ratings yet