Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mannitol Salt Agar
Mannitol Salt Agar
Uploaded by
Joelle DwekOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mannitol Salt Agar
Mannitol Salt Agar
Uploaded by
Joelle DwekCopyright:
Available Formats
All O SAL AGAR
- differential media ⇒ used to visually distinguish microorganisms from one another
- selective media ⇒ used to grow/isolate specific types of microorganisms suppressing the growth of other microorganisms
- mannitol salt agar (USA) contains the carbohydrates mannitol, 7.5% sodium chloride (NaCl), and the pH indicator phenol red
- components
↳ phenol red indicate ⇒ yellow below pH = 6.8
⇒ red at pH = 7.4 - 8.4
⇒ pink at pH = 8.4 and above
↳ mannitol ⇒ gives substrate for fermentation and makes medium differential
↳ sodium chloride ⇒ makes medium selective since its concentration is high enough to dehydrate/kill most bacteria
• bacteria
↳ staphylococci thrive on this medium due to its adaptation to salty habitats such as human skin
↳ phenol red ⇒ indicates whether fermentation with an acid has taken place by changing color as the pH changes
↳ most staphylococci are able to grow on MSA, but do NOT ferment mannitol, showing growth as pink or red and the medium stays unchanged
↳ Staphylococcus aureus ferments mannitol, producing acids and lowers medium pH ⇒ bright yellow colonies form
• application ⇒ mannitol salt aga.r used for isolation and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus from other StaphylococcuS species
BLOOD AGAR
• blood agar separates Gram + cocci that produces exotoxins called hemolysins
- hemolysins ⇒ lipids/proteins that break down red blood cells
• blood agar is made of 5% of blood (sheep blood) in a tryptic soy agar base
blood agar allows differentiation of bacteria based on their ability to hemolyze red blood cells
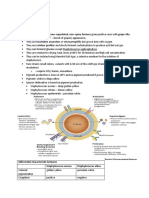
3 types of hemolysis
↳ beta-hemolysis ⇒ complete destruction of red blood cells and hemoglobin, resulting in a clearing of the medium around the colonies
↳ alpha-hemolysis ⇒ partial destruction of red blood cells and produces an olive-greenish discoloration of the agar around the colonies
in reflected light → converting heme in hemoglobin to methelglobin that cannot bind oxygen, appearing as green
↳ gamma-hemolysis ⇒ nonhemolysis, appearing as simple growth with no change to the medium
- hemolysins produced by streptococci ⇒ streptolysins
. 2 forms ⇒ Type O and Type S
↳ streptolysin 0 ⇒ oxygen sensitive, grows best under anaerobic conditions (in agar)
↳ streptolysin S ⇒ oxygen stable, grows in aerobic conditions surface of agar plate)
- streak stab technique ⇒ method to provide environment favorable for streptolySins
↳ blood agar plate streaked for isolation and then stabbed with a loop
↳ alpha-hemolysis on the surface but beta-hemolysis in the stab
BAA RACH SUSCEPT/BHi T St
. bacitracin ⇒ made by Bacillus licheniformis is a powerful peptide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by
interfering with peptidoglycan transport across the cytoplasmic membrane → effective only to bacteria with cell walls
that are in the process of growing
• novobiocin ⇒ antibiotic produced by Streptomyces nivens →
interferes with ATPase activity associated with DNA gyrase
(enzyme needed for DNA replication)
- optochin ⇒ antibiotic derived from quinine that disrupts ATP synthase activity - reduced ATP production in susceptible bacteria
- bacitracin test is used to differentiate and identify ⇒ beta-hemolytic group A streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes - bacitracin susceptible)
from other beta-hemolytic streptococci (bacitracin resistant)
You might also like
- Student Exploration: Natural Selection GizmoDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Natural Selection Gizmothanossssss56% (27)
- ANIMAL CELLS AND TISSUES Lecture Notes PDFDocument17 pagesANIMAL CELLS AND TISSUES Lecture Notes PDFAnonymous HXLczq383% (6)
- Lesson-09 MODUL PDFDocument9 pagesLesson-09 MODUL PDFanggaririn100% (1)
- Stability Testing of PhytopharmaceuticalsDocument30 pagesStability Testing of PhytopharmaceuticalsPoornaBasuri88% (32)
- Anaphy 10Document5 pagesAnaphy 10fio.maglaya13No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - SCI 8007SEF Medical Microbiology & Virology-Introduction To Medical Microbiology I - 24 Sep 2023Document62 pagesLecture 4 - SCI 8007SEF Medical Microbiology & Virology-Introduction To Medical Microbiology I - 24 Sep 2023Ada ChanNo ratings yet
- Blood Agar - Composition, Preparation, Uses and Types of HemolysisDocument4 pagesBlood Agar - Composition, Preparation, Uses and Types of HemolysisHYATT PATH LAB & RESEARCH CENTRENo ratings yet
- The Culturing MicroorganismsDocument10 pagesThe Culturing MicroorganismsEbruAkharmanNo ratings yet
- AnaerobesDocument39 pagesAnaerobesnasarcedaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Media Tests PicturesDocument26 pagesMicrobiology Media Tests Picturesthu_vu_29No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Hema and IsbbDocument53 pagesDiagnostic Exam Hema and IsbbAlliah Jessa PascuaNo ratings yet
- Pneumoniae and Neisseria Species. It Is Also: Preparation of Blood Agar PlateDocument4 pagesPneumoniae and Neisseria Species. It Is Also: Preparation of Blood Agar PlateKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Giemsa StainDocument5 pagesGiemsa StainBarnali RoyNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Blood Agar PlateDocument4 pagesActivity 6 Blood Agar PlateNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Bacteriology FinalsDocument6 pagesMtap - Bacteriology FinalsMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- MTAP - 1.1 - BacteriologyDocument14 pagesMTAP - 1.1 - BacteriologyKassandra CordetaNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - Biochemical ID of GN BacteriaDocument8 pagesWeek 13 - Biochemical ID of GN BacteriaDax Liwell SalesNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology 3Document17 pagesBacteriology 3JulanHalimuyakNo ratings yet
- Blood AgarDocument4 pagesBlood Agarsyafa latifahNo ratings yet
- Blood-Composition & FunctionsDocument11 pagesBlood-Composition & FunctionsAmirAmeer AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Selective and Differential MediaDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Selective and Differential MediaJoshua ZeelanderNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Part I - BloodDocument123 pagesCirculatory System Part I - BloodAngelyn DomingoNo ratings yet
- DR Katek BalapalaDocument73 pagesDR Katek BalapalaNathan LupiyaNo ratings yet
- Nitika SankhyanDocument31 pagesNitika SankhyanNitika sharmaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument27 pagesGram Positive Coccishekhar JhaNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Identification of StaphylococciDocument5 pagesIsolation and Identification of Staphylococciangelinarod33445No ratings yet
- Microbial DiagnosticsDocument17 pagesMicrobial DiagnosticsDr Preeti SolankiNo ratings yet
- Microbio (Bacte)Document22 pagesMicrobio (Bacte)Carl PinedaNo ratings yet
- C. Blood Agar: B. Campy Blood Agar C. Cefsulodin-Irgasan-Novobiocin Agar D. Thioglycollate BrothDocument4 pagesC. Blood Agar: B. Campy Blood Agar C. Cefsulodin-Irgasan-Novobiocin Agar D. Thioglycollate BrothMaria Micaela CabarlesNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument22 pagesHematologyytmdrayushdubeyNo ratings yet
- Preparation of BAP and CHOCDocument5 pagesPreparation of BAP and CHOCKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Hematology Ii Lectures Introduction To HemostasisDocument28 pagesHematology Ii Lectures Introduction To HemostasisJoshua Trinidad100% (1)
- Micrococcaceae and Streptococcaceae TransesDocument9 pagesMicrococcaceae and Streptococcaceae TransesaguirreangNo ratings yet
- Somatic HybridizationDocument23 pagesSomatic HybridizationJan VivienelNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci Reviewer 1Document6 pagesGram Positive Cocci Reviewer 1alianaNo ratings yet
- PC W7 Pharmaceutcial Chemistry of Antibacterial DrugsDocument32 pagesPC W7 Pharmaceutcial Chemistry of Antibacterial Drugszainab ElsayedNo ratings yet
- StaphylococciDocument7 pagesStaphylococciAlexander PanodNo ratings yet
- Blood: "Classified As A Liquid Connective Tissue"Document8 pagesBlood: "Classified As A Liquid Connective Tissue"Ma. Pia Lorein JacintoNo ratings yet
- Blood HandoutsDocument14 pagesBlood HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Cardiovascular System Blood HeartDocument98 pages8.1 Cardiovascular System Blood HeartElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- DISSCUSSION Microb Practical 4Document4 pagesDISSCUSSION Microb Practical 4domo- kunNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY BloodDocument4 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY BloodJonski JamNo ratings yet
- Practice 6 - Colonial Morphology PDFDocument30 pagesPractice 6 - Colonial Morphology PDFScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesGram Positive Cocci The Staphylococci CharacteristicsKyle PicocNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Morphology Growth Requirements 1Document7 pagesBacteria Morphology Growth Requirements 121-54405No ratings yet
- Romanowky StainsDocument45 pagesRomanowky StainsFinu FarisaNo ratings yet
- Gen Micro Micro D&R AgamDocument157 pagesGen Micro Micro D&R AgamNirosha Arul100% (3)
- Mtap MicrobioDocument6 pagesMtap Microbioreginarosesalazar0127No ratings yet
- 4 - Rumen Microbiology PDFDocument31 pages4 - Rumen Microbiology PDFImbasat YousafNo ratings yet
- Specific Granules (Phagocytins) GranulesDocument3 pagesSpecific Granules (Phagocytins) GranulesMay MiNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument175 pagesBLOODJohn JimsNo ratings yet
- Week+4+Lineage+Specific+Hematopoiesis Revised+ +Document7 pagesWeek+4+Lineage+Specific+Hematopoiesis Revised+ +tinemagsino.05No ratings yet
- Gram Positive & Gram NegativeDocument15 pagesGram Positive & Gram NegativeMohamed NourNo ratings yet
- HEMA-1-LEC-LESSON-1Document3 pagesHEMA-1-LEC-LESSON-1aldegamoNo ratings yet
- PMLS - Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesPMLS - Midterm ReviewerIan IglesiaNo ratings yet
- Blood Agar Base (Infusion Agar) : Intended Use Summary and ExplanationDocument2 pagesBlood Agar Base (Infusion Agar) : Intended Use Summary and ExplanationSarehElizabetNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument4 pagesBLOODariansofia1031No ratings yet
- Micro 1Document5 pagesMicro 1naazaninrahat76No ratings yet
- Important Media and Biochemical Tests For Diagnostic Microbiology 2023Document3 pagesImportant Media and Biochemical Tests For Diagnostic Microbiology 2023yn6q5fc5pzNo ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyFrom EverandMicrobial PhysiologyAlbert G. MoatNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- 2009 HSC Exam BiologyDocument34 pages2009 HSC Exam Biologyeducator56100% (1)
- Plus One BIOLOGY Answer Key Annual Exam March 2020 by Sunil Sir PDFDocument4 pagesPlus One BIOLOGY Answer Key Annual Exam March 2020 by Sunil Sir PDFNissar v aNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument21 pagesPPTaqsamazin100% (1)
- Prospectus BotanyDocument28 pagesProspectus BotanyCutepieNo ratings yet
- Blotting Assignment by MPhil 5,12Document31 pagesBlotting Assignment by MPhil 5,12Amina ChNo ratings yet
- Ebook Marks Basic Medical Biochemistry A Clinical Approach 6Th Edition Michael A Lieberman Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesEbook Marks Basic Medical Biochemistry A Clinical Approach 6Th Edition Michael A Lieberman Online PDF All Chapterfrederick.mcintyre148100% (10)
- Profil Hematologi Dan Gambaran Morfologi Darah Sapi Bali (Bos Sundaicus) Yang Dipelihara Di Tempat Pembuangan Akhir Alak Kota KupangDocument13 pagesProfil Hematologi Dan Gambaran Morfologi Darah Sapi Bali (Bos Sundaicus) Yang Dipelihara Di Tempat Pembuangan Akhir Alak Kota KupangKeju Mozarella ChizzuNo ratings yet
- Helicobacter Pylori. One Bacterium and A Broad Spectrum of Human Disease! An OverviewDocument14 pagesHelicobacter Pylori. One Bacterium and A Broad Spectrum of Human Disease! An OverviewAlexandru CozmaNo ratings yet
- TRP E ColiDocument35 pagesTRP E Coli張若凡No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesLesson 3 - Digestive Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- 5090 w05 QP 1Document20 pages5090 w05 QP 1mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Science6 2ndquarter Test NewDocument9 pagesScience6 2ndquarter Test NewSonny Matias0% (1)
- Past Paper Questions and AnswersDocument61 pagesPast Paper Questions and AnswerssophiaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal HidroponikDocument6 pagesJurnal HidroponiknurfadillahmzNo ratings yet
- Blood CellsLymphatic SystemDocument2 pagesBlood CellsLymphatic SystemrizkaNo ratings yet
- Celltox Green Cytotoxicity Assay ProtocolDocument22 pagesCelltox Green Cytotoxicity Assay Protocolnaveenmi2No ratings yet
- Wu Et Al. - 2013 - Science (New York, N.Y.)Document6 pagesWu Et Al. - 2013 - Science (New York, N.Y.)Mariana NannettiNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Simplified Melc-Based Budget of Lessons in General Biology 2Document3 pagesDepartment of Education Simplified Melc-Based Budget of Lessons in General Biology 2Aurea BodoNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 - F4 - 2016 PDFDocument4 pagesBiology 1 - F4 - 2016 PDFOMARY MWAKAJENo ratings yet
- Activity Xi Serum and Plasma Prepartion PDFDocument3 pagesActivity Xi Serum and Plasma Prepartion PDFReinzoCardenasNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Glycolysis (From Glycose, An Older TermDocument3 pagesGlycolysis: Glycolysis (From Glycose, An Older TermProff AhengNo ratings yet
- SBI3U - Genetics Processes-Meiosis and MitosisDocument3 pagesSBI3U - Genetics Processes-Meiosis and Mitosisapi-280363197No ratings yet
- Internet Resource Guide For BiologyDocument13 pagesInternet Resource Guide For BiologyLawrence KlompsNo ratings yet
- 1.mofologi Dan Sitologi Bakteri MikrobioDocument38 pages1.mofologi Dan Sitologi Bakteri MikrobiomerlindikaNo ratings yet
- 2010 A Level H2 Biology P2 AnsDocument8 pages2010 A Level H2 Biology P2 AnsImagreenbucklegirl SGNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Composition and Functions of Cell MembraneDocument42 pagesBiochemical Composition and Functions of Cell MembraneAmir NangyalNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Aspects in Ultra-Endurance Exercise: Edith M. PetersDocument8 pagesNutritional Aspects in Ultra-Endurance Exercise: Edith M. PetersTBC TBCNo ratings yet